Exam 2 - Anatomy & Physiology
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 5, (skin), 6 (bone ), 7 (axial bone)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Integumentary System
Largest system of the body (skin)
Two Major Parts
Cutaneous membrane (skin)
Accessory structures
made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis
Cutaneous Membrane
(Skin)
Components include:
Epidermis (Outer Dermis) - superficial (On the surface) epithelium (tissue that line internal and external body surfaces; made up of cells)
Dermis (Inner Dermis) - Connective Issues
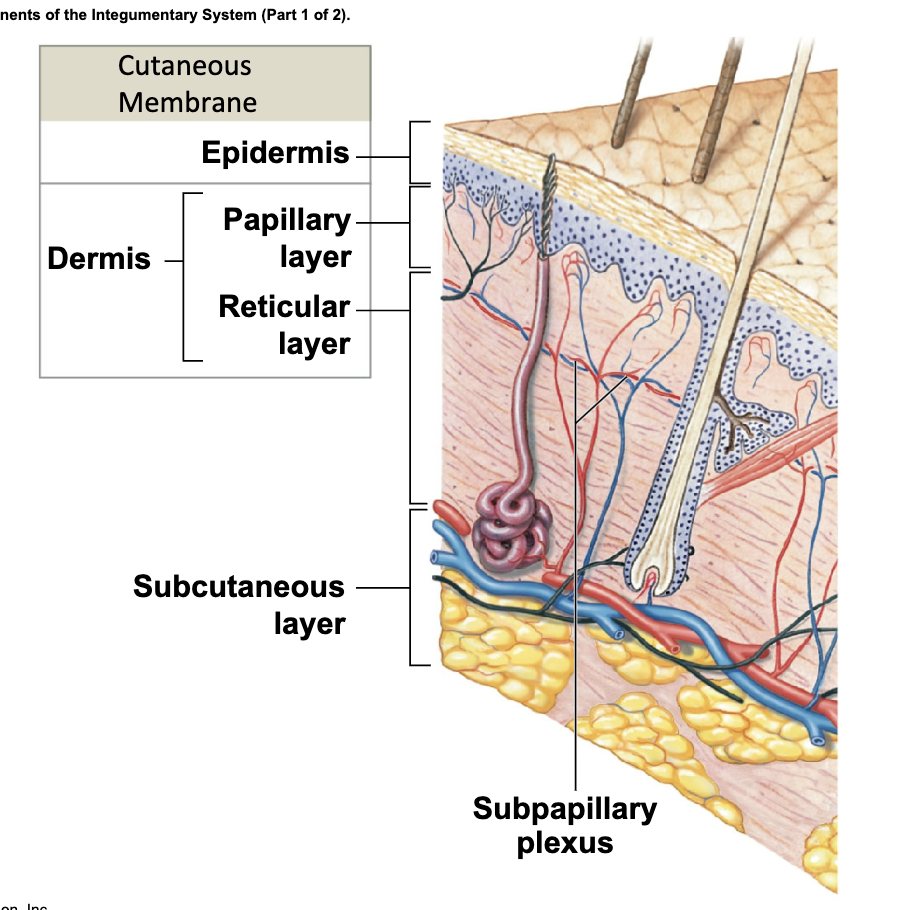
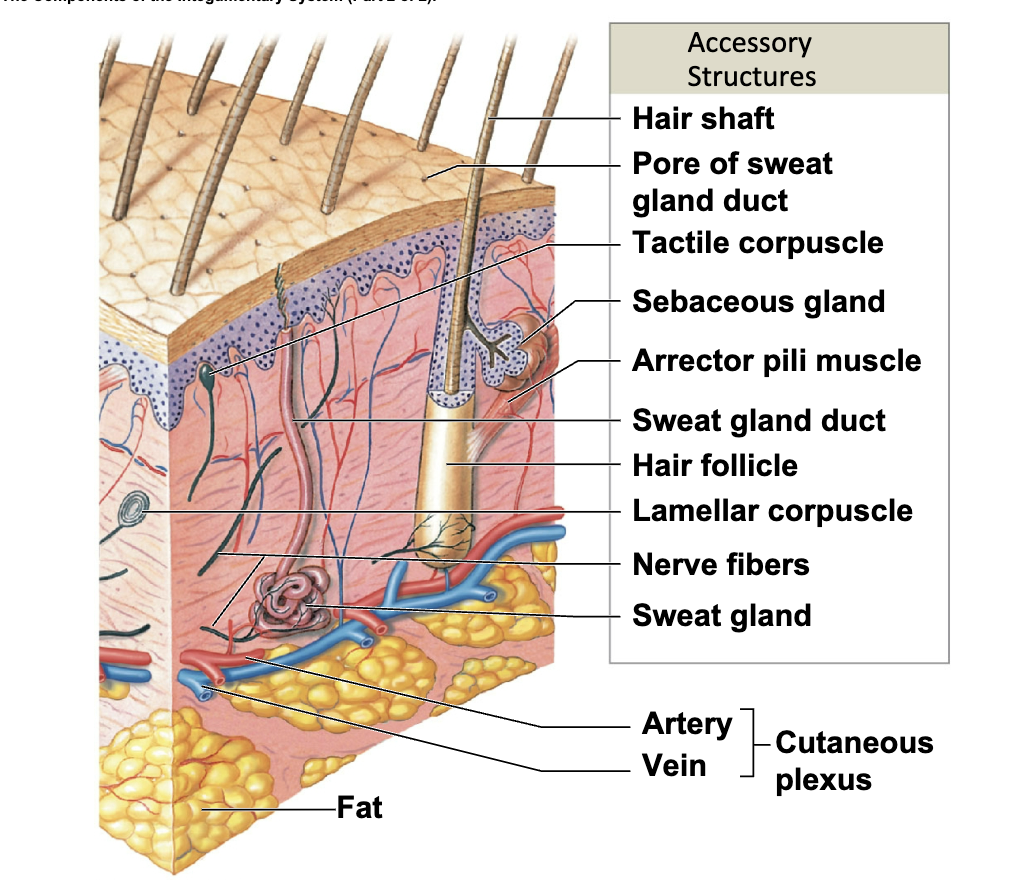
Accessory structures
Originate in the dermis
Extend through the epidermis to skin surface
• Hair and hair follicles
• Exocrine glands
• Nails
Integumentary Functions
Protection of underlying tissues and organs
Excretion of salts, water, and organic wastes
Maintenance of normal body temperature
Production of melanin: protection against uv light
Production of keratin
Synthesis of vitamin D3
Storage of lipids
Detection of touch, pressure, pain, etc.
Coordination of the immune response
Skin Regeneration
takes 7-10 days for it to go from the lowest level to the top
Epidermis
Stratified squamous epithelium
Avascular, like all epithelia
Contains Keratin
Nutrients and oxygen diffuse from capillaries in the dermis
Dermis
Located between epidermis and subcutaneous
layer (middle layer of the skin)
-Anchors epidermal accessory structures (e.g., hair follicles and sweat glands)
Two components
• Outer papillary layer
• Deeper reticular layer
Subcutaneous Layer
(Hypodermis)
Lies deep to dermis
Connected to reticular layer by connective tissue
stabilizes position of the skin
Primarily adipose tissue
Large arteries and veins are in superficial region
Distribution of subcutaneous fat determined by sex hormones
site of subcutaneous injections using hypodermic needles
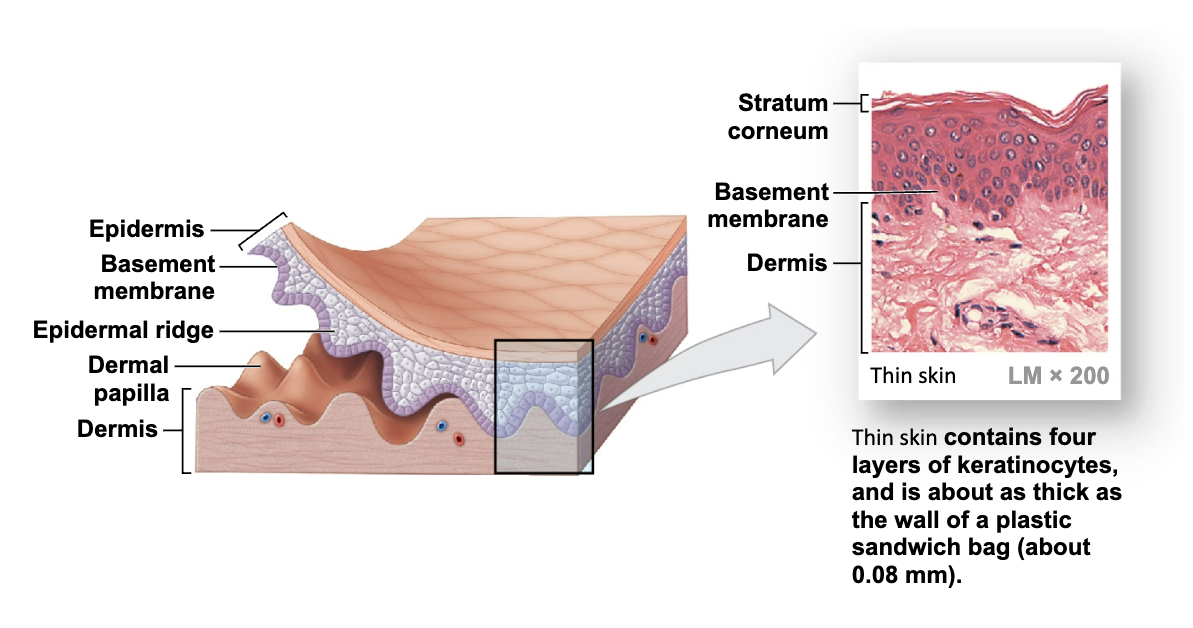
Thick Skin
Covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
Has five layers of keratinocytes
Five Strata Layers
(of keratinocytes in thick skin): found in palms and soles
-From basement membrane to free surface
• Stratum basale
• Stratum spinosum
• Stratum granulosum
• Stratum lucidum
• Stratum corneum
Thin Skin
Covers most of the body
Has four layers of keratinocytes
Keratinocytes
(Cells of the Epidermis)
•The body’s most abundant epithelial cells
• Contain large amounts of keratin
Keratin
tissue found in hair, nails, and the skin outers layer. Can also be found in glands and organs
Four Layers of Thin Skin
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum corneum.
Sinuses
Air-filled chambers in the skull
Decrease weight of the skull
Lined with mucous membranes, which
produce mucus to moisten and clean the air
Serve as resonating chambers in speech production
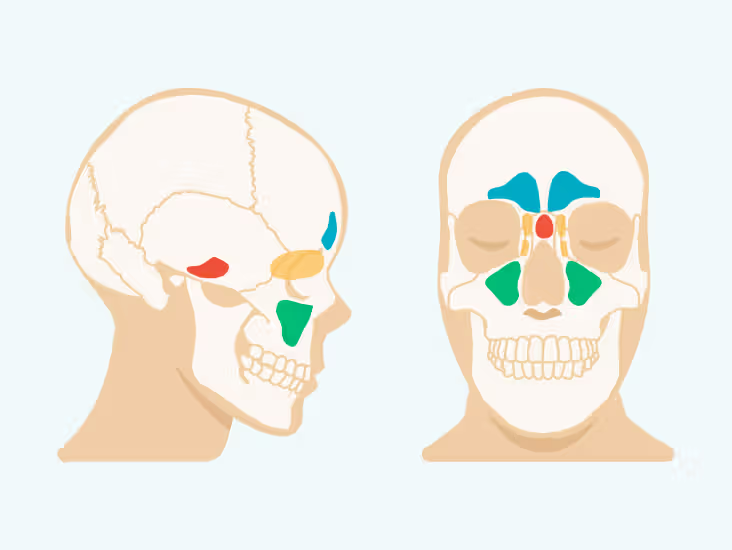
Paranasal sinuses
Air-filled chambers connected to nasal cavities
Lighten skull bones
Contain mucous epithelium
Releases mucus into nasal cavities
Neck has how many cervical vertebrae?
7 cervical vertebrae
How many thoracic vertebrae does the upper back have?
12 thoracic vertebrae
• Each articulates with one or more pairs of
ribs
How many lumbar vertebrae does the lower back have?
Five lumbar vertebrae
How are vertebrae numbered?
By region, from top (superior) to bottom (inferior)
C1 articulates with skull, L5 with sacrum
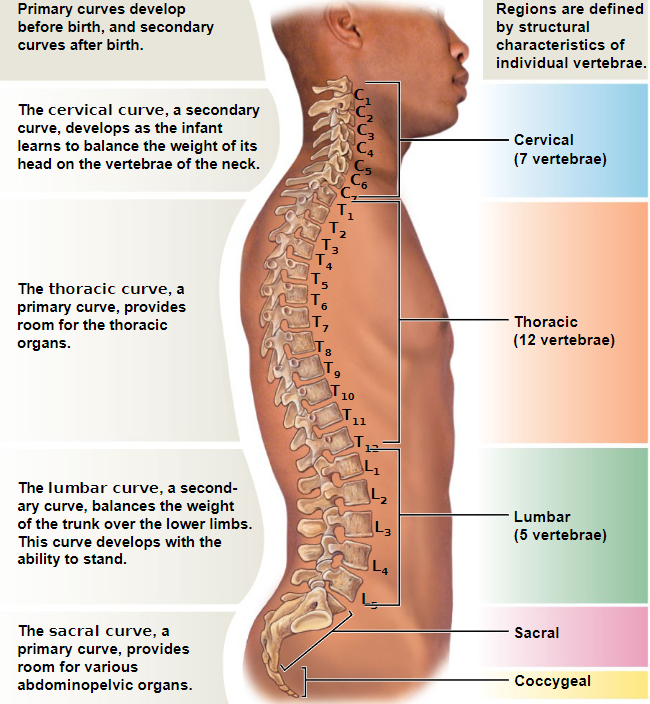
Regions of the vertebral column
Cervical (C)
Thoracic (T)
Lumbar (L)
Sacral (S)
Coccygeal (Co)
C1 to C7
Small body (support only head)
Large vertebral foramen (largest part of spinal cord)
Concave superior surface
Anterior edge is inferior to posterior edge
All except C1 have spinous processes
Thoracic vertebrae (T1–T12)
Have heart-shaped bodies
Larger bodies and relatively smaller vertebral foramina than those in cervical vertebrae
Long, slender spinous process
Dorsolateral surfaces of body have costal facets
• Articulate with heads of ribs
Lumbar vertebrae (L1–L5)
Largest vertebrae
Thick, oval-shaped bodies
No costal facets or transverse costal facets
Triangular vertebral foramen
Superior articular processes face medially
Inferior articular processes face laterally
Slender transverse processes project dorsolaterally
Massive spinous processes
• For attachment of lower back muscles
Thoracic cage
The skeleton of the chest
• Thoracic vertebrae
• Ribs
• Costal cartilages
• Sternum
Functions of thoracic cage
Protects organs of the thoracic cavity
Including heart, lungs, and thymus
Provides attachment for muscles involved in:
Breathing
Maintaining position of vertebral column
Moving pectoral girdles
Ribs and sternum form rib cage
Ribs
12 pairs of long, curved, flat bones
Extending from thoracic vertebrae
Ribs are divided into two type which are
• True ribs
• False ribs
What ribs are true ribs?
Ribs 1–7 are true ribs (Vertebrosternal ribs)
True ribs (vertebrosternal ribs) are connected to
the sternum by costal cartilages
What are false ribs?
Ribs 8–12 are false ribs and they do not attach directly to sternum
Vertebrochondral ribs (ribs 8–10)
• Costal cartilages fuse together
• Merge with cartilages of rib pair 7 before reaching sternum
Floating or vertebral ribs (ribs 11–12)
• Have no connection with the sternum
• Connect only to vertebrae and muscles of body wall
Sternum (breastbone)
A flat bone in anterior midline of thoracic wall
What are the three parts of the sternum?
• Manubrium
• Body
• Xiphoid process
Bone shapes
Sutural, Irregular, short, flat, long, sesamoid
Irregular Bones
Have complex shapes
ex: spinal vertebrae, pelvic bones
Flat bones
Thin with parallel surfaces
ex: bones of skull roof, sternum, ribs, and scapulae
Consists of spongy bone between 2 layers of compact bone (cortex)
within the cranium, the layer of spongy bone is called diploe
Long bones
Long and slender
Found in arms, legs, palms, soles, fingers, toes
Structures of the long bone
Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Metaphysis
Diaphysis
wall of compact bone
central space called the medullary cavity (marrow cavity)
(bone marrow)
Epiphysis
mostly spongy bone (trabecular bone)
Metaphysis
where the diaphysis and epiphysis meet
osteocytes
osteocytes (bone cells ) within lacunae organized around blood vessels
Bone cells
Make up only 2% of bone mass
4 types- osteogenic cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
Osteogenic cells
Mesenchymal cells that divide to produce osteoblasts
–Located in inner cellular layer of periosteum and in endosteum
–Assist in fracture repair
Osteoblast
Immature cells that produce new bone matrix during osteogenesis
Osteoblast surrounded by bone matrix Become osteocytes
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that do not divide
Live in lacunae between layers of matrix
Have cytoplasmic extension that pass through canaliculi
Maintain protein and mineral content of matrix
Help repair damaged bone
Osteoid
Matrix produced by osteoblast that has not yet become calcified
Osteoclasts
Absorb and remove bone matrix
Large, multinucleate cells
Secrete acids and protein-digesting enzymes (dissolve bone matrix and release stored minerals, this osteolysis is important in homeostasis)
Derived from the same stem cells that produce monocytes and macrophages
Ossification(osteogenesis)
Bone formation
Two forms of ossification
Endochondral ossification - How bones form
Intramembrous ossification - Occurs in dermis
Produces dermal bones suck as mandible(lower jaw) and clavicles(collarbones)
Calcification
Deposition of calcium salts
Occurs during ossification
Bone remodeling
Occurs throughout life
Functions in bone maintenance (recycling and renewing bone matrix)
Involves osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts
Normally activities are balanced
Effects of exercise on bone
Mineral recycling allows bone to adapt to stress
Heavily stressed bones become thicker and stronger
Excercise particularly weight bearing exercise, stimulates osteoblasts
Bone degeneration
Bone degenerates quickly
Up to one third of bone mass can be lost in a few weeks of inactivity
hormonal effect on bone
Growth hormone and thyroxine stimulate bone growth
Sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone stimulate osteoblasts
Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin maintain calcium ion homeostasis
Nutritional effects on bone
Vitamin C is required for collagen synthesis and stimulates osteoblast differentiation
Vitamin A stimulates osteoblast activity
Vitamin K and B12 are required for synthesis of bone proteins
Minerals needed
Minerals calcium and phosphorus are required in the diet
Skeleton as a calcium reserve
Bone store 99% of the body’s calcium in addition to other minerals
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body
Calcium ions are vital to many physiological processes
Hormones and calcium ion balance
Calcium ion concentrations in body fluids must be closely regulated (8-11: normal range)
Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin affect storage absorption, and excretion of calcium ions in bones, digestive tract, kidneys
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Produced by parathyroid glands in neck
PTH increases blood calcium ion levels by
Stimulating osteoclast activity (indirectly)
Increasing intestinal absorption of calcium by enhancing Calcitirol secretion by kidneys
Decreasing calcium excretion by kidneys
Calcitonin
Secreted by C cells in thyroid
Calcitonin decreases blood calcium ion levels by
Inhibiting osteoclast activity
Increasing calcium excretion and reducing Calcitirol secretion by kidneys decreasing intestinal absorption of calcium
With age bone becomes
Thinner and weaker
Fractures
Cracks o breaks in bones due to physical stress
Open(compound) or closed (simple)
Major types of fractures
Transverse, displaced, compression, spiral, epiphyseal, comminuted,greenstick, colls,Potts
Osteopenia
Inadequate ossification (reduction of bone mass)
Begins ages 30 and 40
Women lose 8% bone mass per decade men lose 3%
Results in fragile limbs, reduced height, and tooth loss
Osteoperosis
Severe loss of bone mass
Over age 45 occurs in 29% of women 18% of me.
Hormones and bone loss
Sex hormones help maintain bone mass
In women osteoporosis accelerates after menopause
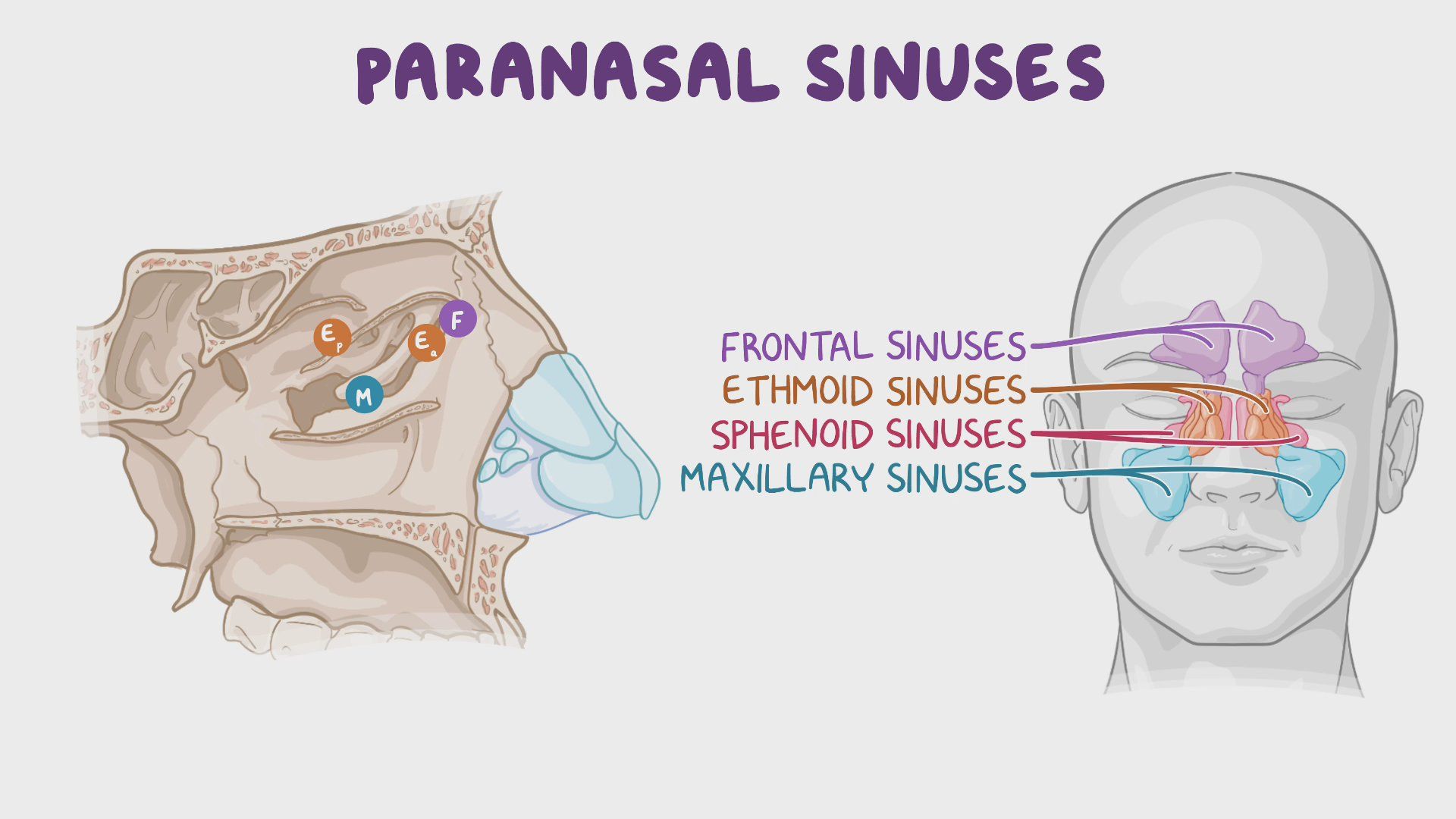
transverse fracture
Break is in a straight line across the bone.
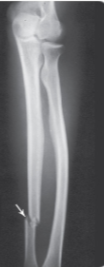
Displaced fracture
The ends of the bone have come out of alignment
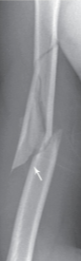
Compression fracture
Bone is crushed, causing it to look wider or flatter
Spiral fracture
Break spirals around the bone (twisting injury)
call cps
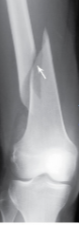
Epiphyseal fracture
affects the growing part of a child’s bone
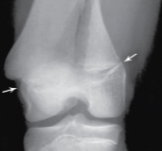
Comminuted fracture
Bone has broken into 3 or more pieces and fragments are present at fracture site.
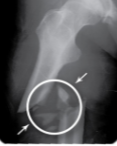
Greenstick fracture
Incomplete fracture, a portion of the bone is broken causing the other side to bend.
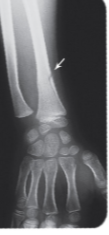
Coll’s fracture
Break in the radius close to the wrist.
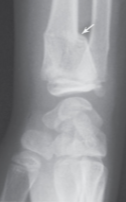
Potts fracture
Fractures around the ankle
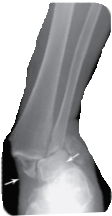
Where cant CPR be done and why?
low on sternum, because it will rupture
spinal/vertebral column
Clavicle(collarbones)
S-shape
Articulate with scapulae(acromial end)
Scapulae(shoulder blades)
Broad, flat triangles
Articulate with humerus and clavicle
Where to find elastic cartilage in the body?
External ears, Eustachian tubes, Larnyx