AP World History Unit 0 - Vocabulary and Definitions - VHS
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
paleolithic
(Old Stone Age) a long period of human development before the development of agriculture. People lived in small kinship based, nomadic societies. They relied on hunting and gathering.
pastoral
nomadic animal-herding societies often known for spreading religion, culture, and technology across trade routes throughout history
metallurgy
the science of working with metals
agrarian
relating to land; relating to the management or farming of land
egalitarian
believing in the social and economic equality of all people - existing before settled societies in hunter-gatherer groups
patriarchy
a form of social organization in which men are dominant- the supreme authority in the family, society, and political realm
Neolithic Revolution (Agricultural Revolution)
(10,000 - 8,000 BCE) The development of agriculture and the domestication of animals as a food source. This led to the development of permanent settlements and the start of civilization.
specialization
Occurred as a consequence of the neo-lithic revolution. People became highly skilled at one job. The concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and firms on a limited number of activities; increases efficiency
social hierarchy
The division of society by rank or class.
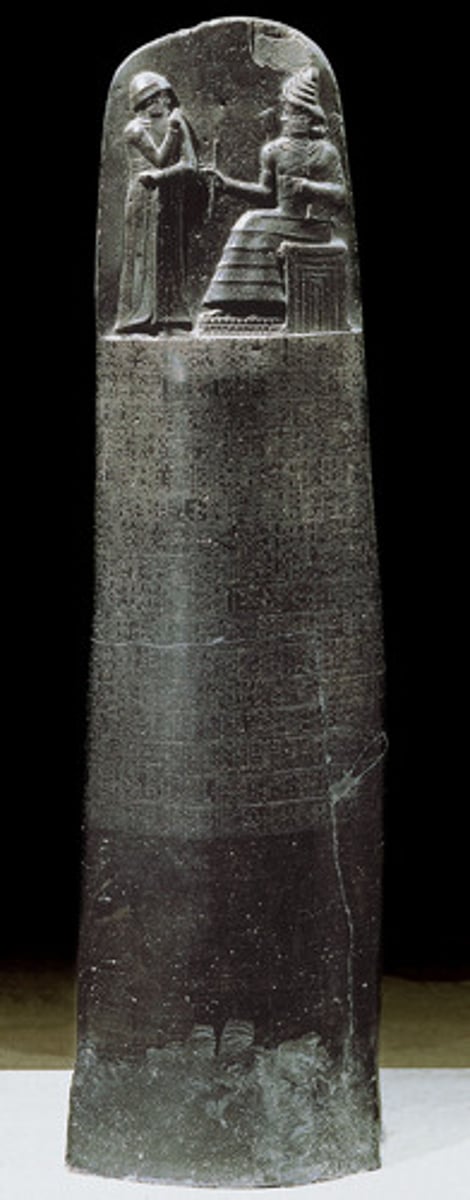
Code of Hammurabi
credited as the first written law code; written by a Babylonian king and established the basis for law codes

Zoroastrianism
One of the first monotheistic religions, particularly one with a wide following. It was central to the political and religious culture of ancient Persia.

Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. They preserved their early history in the Old Testament.

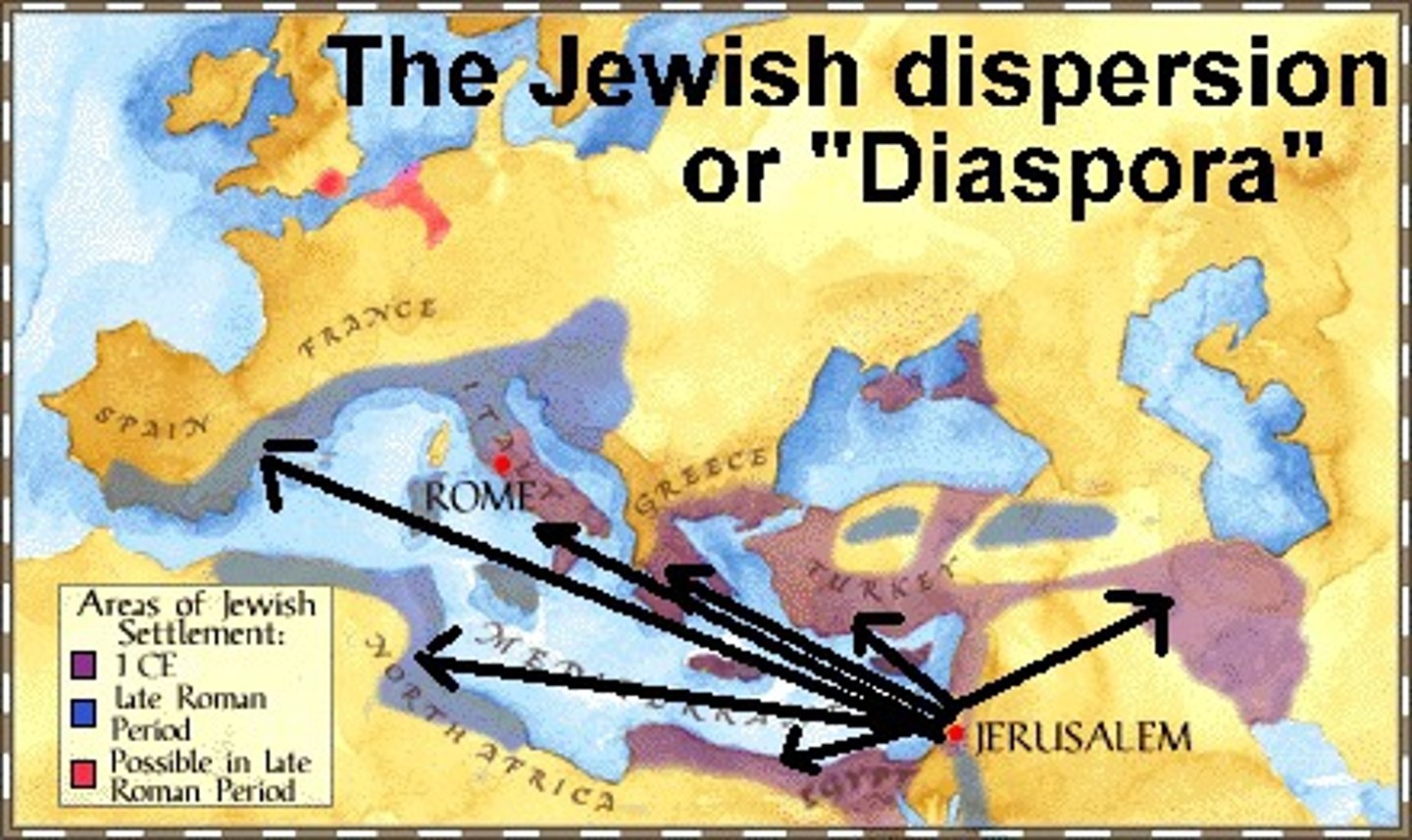
diaspora
any group migration or flight from a country or region; dispersion. Particularly used in relation to Jews scattered by Romans in 70 CE or to Africans spread to new places during the Atlantic Slave Trade.
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation, karma, the caste system, and a supreme being who takes many forms

Buddhism
A religion with origins Southern Nepal/Northern India. Taught that life is permeated with suffering caused by desire and suffering ceases when desire ceases. Enlightenment (Nirvana) obtained through right conduct, wisdom, and meditation releases one from desire, suffering, and rebirth (reincarnation).

Confucianism
A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society in the present world and stresses a moral code of conduct.

filial piety
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.
Mandate of Heaven
A political theory developed during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China in which those in power were believed to have the right to rule from divine authority.
Christianity
An Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in the New Testament. Drew on Judaism and initially rejected Roman and Hellenistic influences. Spread through the efforts of missionaries and merchants. Eventually gained support by the time of Emperor Constantine.

Hellenistic
The spread of Greek culture, Greek history, language from the death of Alexander the Great
centralized government
A government in which power is concentrated in a central authority to which local governments are subject (ex: China, Rome, Byzantines, etc)
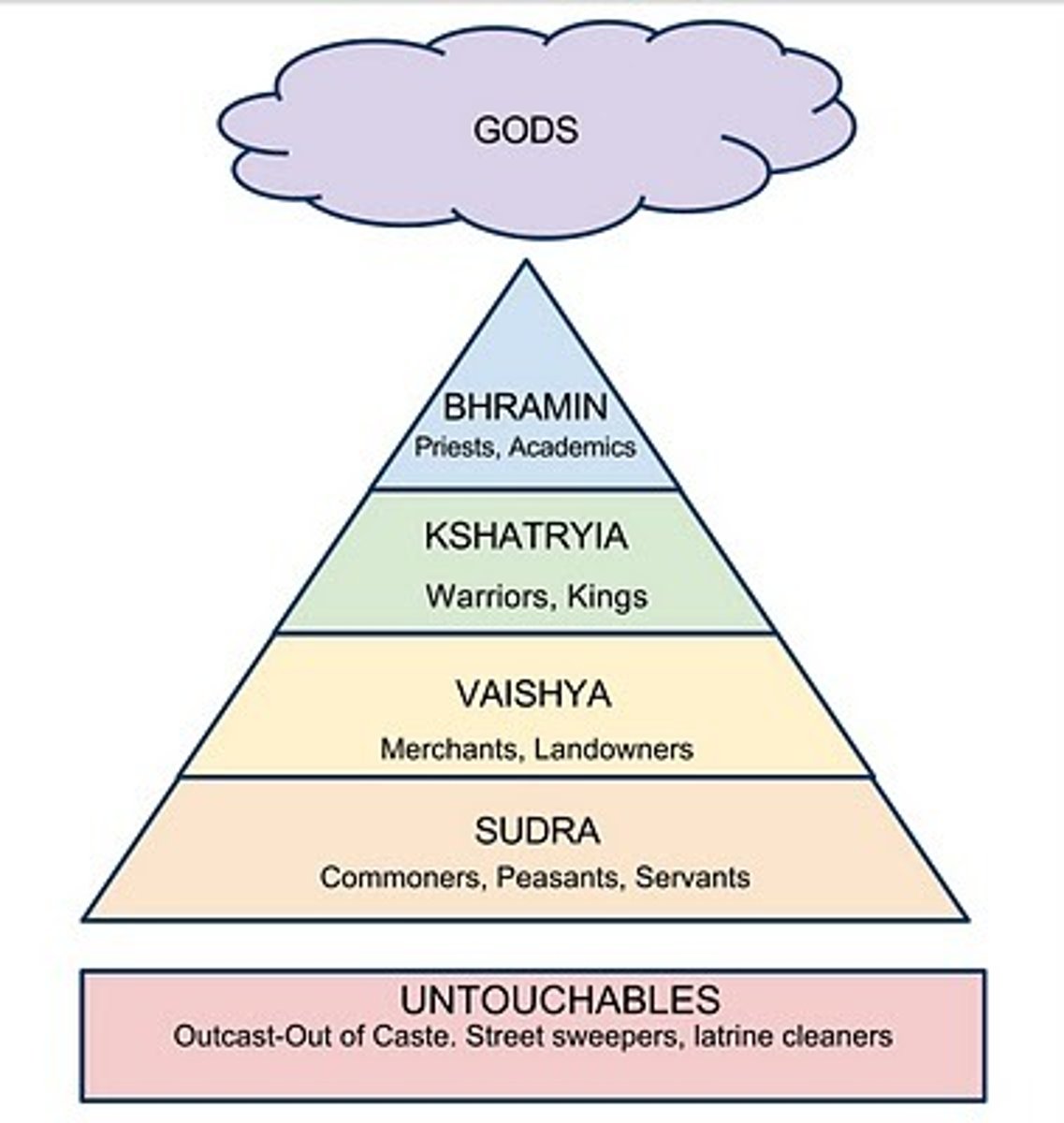
caste system
(n.) any of the social or subclasses of traditional Hindu society, such as the Brahman or Sudra castes; a social class distinct from others and characterized by hereditary rank, profession or wealth; (n.) a social position conferred on someone based on a system of castes
Daoism
Chinese religion that believes the world is always changing and is devoid of absolute morality or meaning. They accept the world as they find it, avoid futile struggles, and deviate as little as possible from "the Tao/Dao" also known as "the way" or "path" of nature; emphasized living in harmony with nature; ying and yang
Bureaucracy
A large, complex organization composed of appointed officials
city-state
a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state.
Civil-Service Exam (CSE)
An institution originating in Han China. A test based on Confucian teachings- that was given to staff the bureaucracy. Produced a government of well-educated individual and allowed for some social mobility.
civilization
A society with cities, a central government, job specialization, and social classes
Cultural Diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another
Democracy
A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them
Empire
An extensive group of territory under a centralized, supreme government. The population is typically diverse- containing many different nations, religions, languages etc.
Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah) and equality of people. The holy text is known as the Quran. Followers are called Muslims.
Mesopotamia
A region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers that developed the first urban societies/civilization. Many city-states emerged here, including Sumer.
Migration
movement of people from one place to another
Monotheism
Belief in one God
monsoon winds
Major winds in the Indian Ocean that blew into India for half the year, and blew away from India for the other half. Helped facilitate trade in the Indian Ocean.
nomadic
wandering, moving about from place to place, rather than settling down and living in one area.
Polytheism
the belief in or worship of more than one god.
society
a community, nation, or broad grouping of people having common traditions, institutions, and collective activities.