Liver Function Test
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
Chief metabolic organ in the body
Liver
Liver
receives _ mL of blood per minute
15 mL
Liver
composed of 2 cell types:
hepatocytes
kupffer cells
Liver
cells are arranged into the _ > the anatomic unit of the liover
lobule
Liver
has a unique capacity to generate by _
cell division
Liver
_ % of the liver must be destroyed to abolish its functions
80%
Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver (5)
Synthetic Function
Conjugation Function
Detoxification and Drug Metabolism
Excretory and Secretory Function
Storage Function
Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver
Synthetic Function
Plasma proteins > 12 g albumin, globulins
Carbohydrates
Cholesterol
Triglycerides and Lipoproteins
Ketone bodies
Enzymes
Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver
Conjugation Function
-
involves bilirubin metabolism > 200 to 300 mg produced daily
Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver
Detoxification and Drug Metabolism
protects the body from potentially injurious substances absorbed fro the intestinal tract and toxic by-products of metabolism
ammonia →urea
Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver
Excretory and Secretory Function
Bile excretion
Bile acids are conjugated with amino acids glycine and taurine to form bile salts
Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver
Storage Function
Vitamins A, D, E, K and B12
Glycogen
Some Examples of Liver Dysfunction (8)
Hepatocellular disease
Cholestasis > obstruction of bile flow
Cirrhosis
Hepatitis
Jaundice
Liver cancer
Steatosis > fatty liver
Genetic disorders > hemochromatosis, iron storage
Liver Function Tests (4)
Noninvasive methods for screening liver dysfunction
Help in identifying general types of disorder
Assess severity and allow prediction of outcome
Disease and treatment follow-up
Liver Function Tests
Broadly classified as: (2)
Tests to detect hepatic injury
Tests to assess hepatic function
Liver Function Tests
Tests to detect hepatic injury (2)
Mild or severe; acute or chronic
Nature of liver injury > hepatocellular or cholestasis
Classification of Liver Function Tests
3 GROUPS
Group I: Markers of Liver Dysfunction or Synthetic Function Tests
Group II: Markers of Hepatocellular Injury
Group III: Markers of Cholestasis
Classification of Liver Function Tests
Group I: Markers of Liver Dysfunction or Synthetic Function Tests (4)
Serum Bilirubin > total and conjugated
Urine > bile salts and urobilinogen
Total protein, serum albumin, and albumin/globulin ratio
Prothrombin time
Classification of Liver Function Tests
Group II: Markers of Hepatocellular Injury (2)
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Classification of Liver Function Tests
Group III: Markers of Cholestasis (2)
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
g-glutamyltransferase (GGT)
Limitations of Liver Function Tests (2)
Normal LFT values do not always indicate absence of liver disease > liver has very large reserve capacity
Asymptomatic people may have abnormal Liver Function Tests results > diagnosis should be based on clinical examination
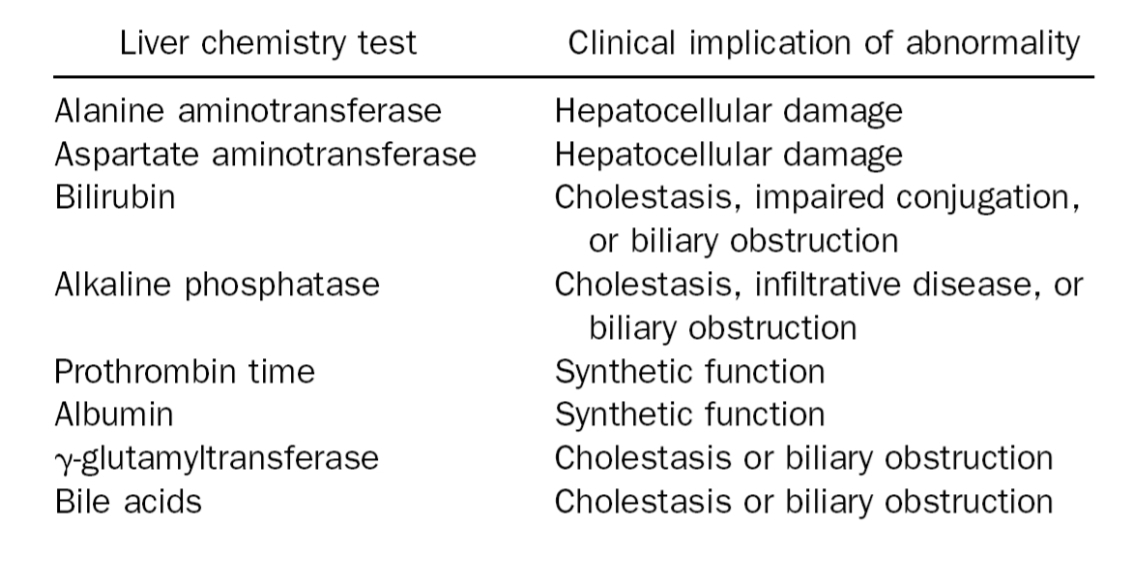
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test (8)
Alanine aminotransferase
Aspartate aminotransferase
Bilirubin
Alkaline phosphatase
Prothrombin time
Albumin
g-glutamyltransferase
Bile acids
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Alanine aminotransferase
hepatocellular damage
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Aspartate aminotransferase
Hepatocellular damage
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Bilirubin
Cholestasis
Impaired conjugation
Biliary obstruction
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Alkaline phosphatase
cholestasis
infiltrative disease
biliary obstruction
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Prothrombin time
synthetic function
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Albumin
Synthetic function
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
g-glutamyltransferase
cholestasis
biliary obstruction
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Test
Bile acids
cholestasis
biliary obstruction
Common Serum Liver Chemistry Tests
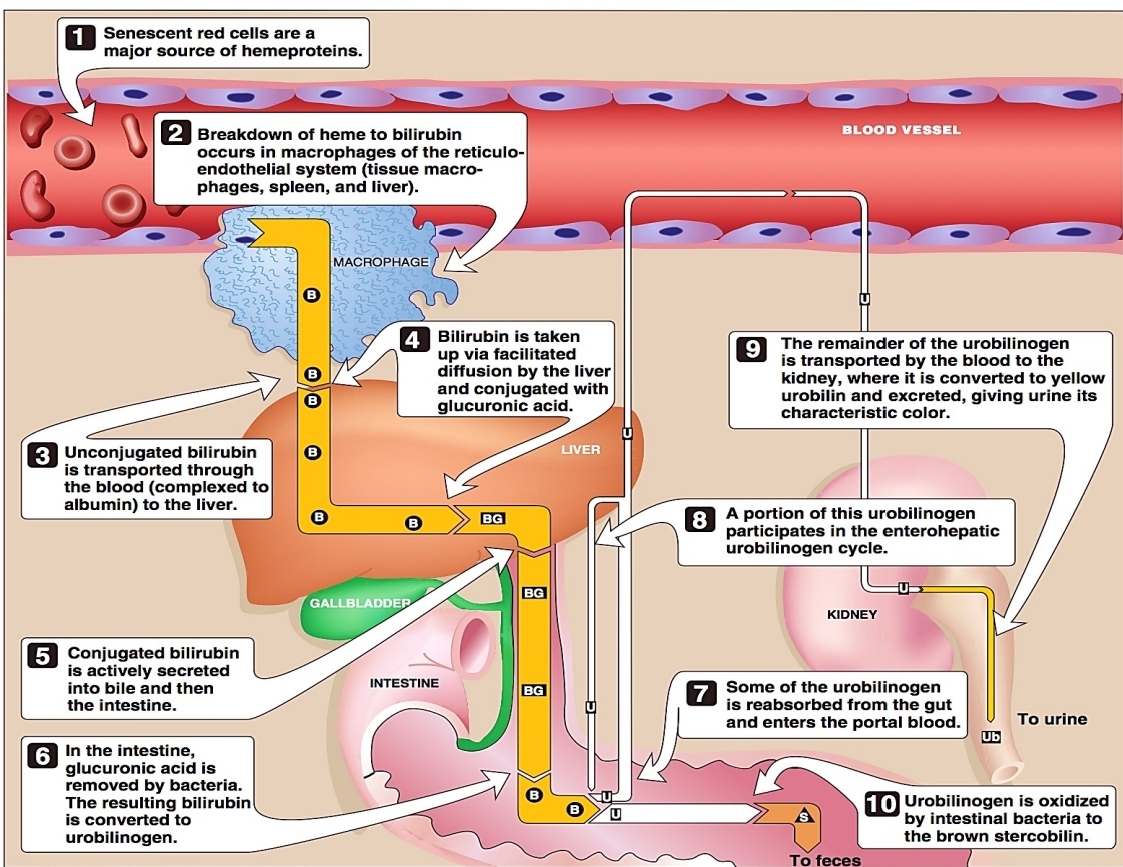
A by-product of RBC breakdown
Major metabolite of heme
Bilirubin
Bilirubin
approximately - to - mg is produced in healthy adults daily
- % is derived from turnover of senescent RBCs
approximately 250 to 350 mg is produced in healthy adults daily
85 % is derived from turnover of senescent RBCs
Bilirubin
yellowish pigment observed in -
jaundice
Bilirubin
high bilirubin levels are observed in (3)
gallstones
acute hepatitis
chronic hepatitis
Breakdown of RBCs
Jaundice
comes from the French “_” = _
yellow discoloration of skin, mucous, membrane and sclera of the eyes
jaune = yellow
Jaundice
visible indication of _
hyperbilirubinemia
Jaundice
yellow discoloration of serum
icterus
Jaundice
evident when bilirubin levels exceed _
2 to 3 mg/dL
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
diazotization of bilirubin to produce azobilirubin
Van Den Bergh Reaction
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
Van Den Bergh Reaction (3)
Evelyn and Malloy Method
Jendrassik and Grof Method
Modified Jendrassik and Grof Method
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
Van Den Bergh Reaction
→Evelyn and Malloy Method
Coupling accelerator:
Diazo Reagents:
Final Reaction:
Coupling accelerator:
50% methanol
Diazo Reagents:
A - 0.1% sulfanilic acid + HCl
B - 0.5% sodium nitrite
BLANK - 1.5% HCl
Final Reaction:
Positive > pink to purple azobilirubin (560 nm)
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
Van Den Bergh Reaction
→most sensitive and most widely used
→more sensitive than Evelyn Malloy
Jendrassik and Grof Method
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
Van Den Bergh Reaction
→Jendrassik and Grof Method
Popular technique for _
Not falsely elevated by _
Coupling accelerator:
Buffer:
Final reaction:
Popular technique for DISCRETE ANALYZERS
Not falsely elevated by HEMOLYSIS
Coupling accelerator: CAFFEINE SODIUM BENZOATE
Buffer: SODIUM ACETATE > less sensitive to pH change
Final reaction: POSITIVE > pink to blue azobilirubin (600 nm)
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
Van Den Bergh Reaction
→candidate reference method for total bilirubin
Modified Jendrassik and Grof Method
Principle of Bilirubin Assays
Van Den Bergh Reaction
→Modified Jendrassik and Grof Method
Coupling accelerator:
Coupling accelerator: caffeine-benzoate
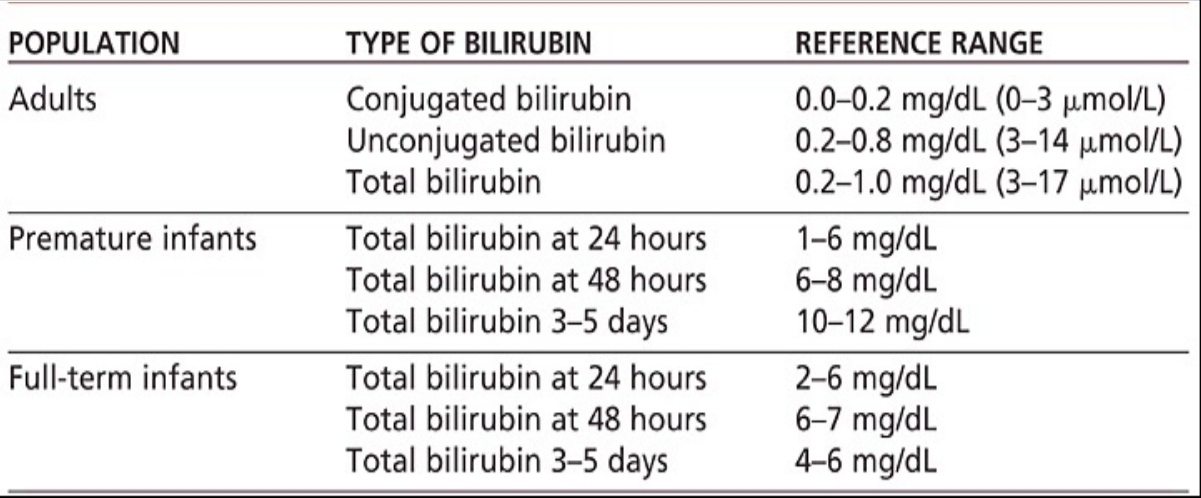
Serum Bilirubin Levels - Normal Values
Class of Jaundice (3)
Pre-hepatic or Hemolytic (Unconjugated)
Hepatic or Hepatocellular
Post-hepatic
Class of Jaundice
Pre-hepatic or hemolytic (Unconjugated)
→LAB FINDINGS (5)
increased amount of bilirubin being presented to the liver
B1 markedly increased, B2 normal
negative urine bilirubin
increased urobilinogen
dark stool
Class of Jaundice
Pre-hepatic or hemolytic (Unconjugated)
→CAUSES (7)
abnormal red cells
antibodies
drugs and toxins
thalassemia
hemoglobinopathies
Gilbert's
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Class of Jaundice
Hepatic or Hepatocellular
→LAB FINDINGS (4)
intrinsic liver defect
increased B1 and B2
increased urobilinogen
positive urine bilirubin
Class of Jaundice
Hepatic or Hepatocellular
→Causes (3)
viral hepatitis
toxic hepatitis
intrahepatic cholestasis
Class of Jaundice
Post-hepatic
→LAB FINDINGS (6)
Obstruction in the bile duct
B2 markedly increased
B1 normal
positive urine bilirubin
decreased urobilinogen
pale-colored stool
Class of Jaundice
Post-hepatic
→Causes (4)
Extrahepatic cholestasis
Gallstones
Tumors of the bile duct
Carcinoma of pancreas
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia (5)
Gilbert Syndrome
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
Rotor Syndrome
Lucey-Driscoll Syndrome
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia
bilirubin transport deficit
Gilbert Syndrome
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia
bilirubin conjugation deficit
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia
2 types of Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
Type 1: Complete deficiency of enzyme UDPGT
Type 2: Partial deficiency of enzyme UDPGT
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia
bilirubin excretion deficit
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia
defective excretion of bilirubin WITHOUT liver pigmentation
Rotor Syndrome
Congenital Hyperbilirubinemia
caused by a circulating inhibitor to bilirubin conjugation
Lucey-Driscoll Syndrome
severe unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia characterized by deposition of bilirubin in the brain, particularly affecting the basal ganglia, mainly the lenticular nucleus
causes motor dysfunction, retardation, death
Kernicterus
Kernicterus
the danger of kernicterus is a certainty at levels _
exceeding 20 mg/dL
yellowish discoloration of the skin but not the sclera due to increases ingestion of carotenoids
Carotenemia
Liver Diseases (5)
Biliary Obstruction
Cirrhosis
Tumors
Reye's Syndrome
Drug- and Alcohol-Related Disorders
Liver Diseases
Biliary Obstruction
→In adults, _ or presence of bile stones is the most common cause of hyperbilirubinemia
→_ is bile stones in the common bile duct
→cholelithiasis
→choledocholithiasis
Liver Diseases
Cirrhosis
→_ replaces normal healthy liver
→most common cause:
→signs and symptoms:
→SCAR TISSUE replaces normal healthy liver
→most common cause: CHRONIC ALCOHOLISM
→signs and symptoms: OCCUR IN LATE STAGES
Liver Diseases
Tumors
→Primary:
→Metastatic/Secondary:
→Tumors of the liver may also be classified as benign or malignant:
→Primary: BEGINS IN THE LIVER CELLS
→Metastatic/Secondary: Tumors from other parts of the body spread to the liver, accounts for 90% to 95% of all hepatic malignancies
→Tumors of the liver may also be classified as benign or malignant:
BENIGN: hepatocellular adenoma
MALIGNANT: hepatocellular carcinoma, bile duct carcinoma
Liver Diseases
Reye's Syndrome
→precise cause is unknown but studies found strong epidemiological association between _ and subsequent development of Reye's syndrome
→an acute illness, characterized by - and - of the liver
→precise cause is unknown but studies found strong epidemiological association between INGESTION OF ASPIRIN DURING A VIRAL SYNDROME and subsequent development of Reye's syndrome
→an acute illness, characterized by NON-INFLAMMATORY ENCEPHALOPATHY and FATTY DEGENERATION of the liver
Liver Diseases
Drug- and Alcohol-Related Disorders
→Drug-induced liver disease accounts for _ to _ of all reported cases of acute liver failures
→most important drug-associated with hepatoxicity
→one of the most common drugs associated with serious hepatic injury
→Drug-induced liver disease accounts for 1/3 to ½ of all reported cases of acute liver failures
→most important drug-associated with hepatoxicity = ETHANOL
→one of the most common drugs associated with serious hepatic injury = ACETAMINOPHEN / PARACETAMOL
colorless end-product of bilirubin metabolism that is oxidized by intestinal bacteria
Urobilinogen
Urobilinogen
is oxidized into (3)
urobilin
stercobilin
mesobilin
Urobilinogen
After formation in the intestines: (2)
most urobilinogen are reabsorbed and re-excreted by the liver; a minor fraction may be excreted in the urine
some urobilinogen in the stool are converted into stercobilin
Urobilinogen
absence in the urine or stool denotes _
complete biliary obstruction
Urobilinogen
Specimen for testing:
_ sample is preferred because of alkaline tide
avoid exposure to _
Specimen for testing: 2-HOUR URINE SAMPLE
2 to 4 PM sample is preferred because of alkaline tide
avoid exposure to LIGHT
Urobilinogen
Method for testing:
Principle:
_ to form RED color which is read spectrophotometrically
Method for testing: EHRLICH'S REACTION
Principle: REACTION OF EHRLICH'S REAGENT
PDAB or PARA-DIMETHYL-AMINO-BENZALDEHYDE to form RED color which is read spectrophotometrically
Urobilinogen
Reference Range:
→Urine
→Feces
→Urine > 0.1 to 1.0 Ehrlich unit/ 2 hours
→Feces > 75 to 275 Ehrlich units/ 100 g
Urobilinogen
Clinical Significance
→In post-hepatic obstruction, urobilinogen formation is - because of impaired bilirubin excretion into the intestine
→This is evidenced by a (2)
→increased urine urobilinogen is associated with (2)
→In post-hepatic obstruction, urobilinogen formation is DECREASED because of impaired bilirubin excretion into the intestine
→This is evidenced by:
CLAY-COLORED > partial biliary obstruction
CHALKY WHITE STOOL > complete biliary obstruction
→increased urine urobilinogen is associated with (2)
hemolytic disease
hepatocellular disease like hepatitis
Total Protein
important in assessing: (2)
nutritional status
severe diseases involving liver, kidney, and bone marrow
Total Protein
about _% higher in ambulatory persons
10%
Total Protein
Plasma total protein is _ higher than serum total protein (fibrinogen)
0.2 to 0.4 g/dL
Total Protein
Transudates have a TP of _
Exudates have a TP of _
Transudates have a TP of <3.0 g/dL
Exudates have a TP of >3.0 g/dL
Total Protein
Reference Value:
6 to 8 g/dL
Total Protein
INCREASED (3)
malignancy
multiple myeloma
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Total Protein
DECREASED (4)
hepatic cirrhosis
glomerulonephritis
nephrotic syndrome
starvation
Total Protein
Specimen Requirements and Result Variations
→ Use _ rather than plasma
→_ is not needed
→ _ may affect results
→_ falsely elevates total protein
→as person ages, there is a slight decrease in _
→lower total protein are also seen in _
→ Use SERUM rather than plasma
→FASTING is not needed
→ LIPEMIA may affect results
→HEMOLYSIS falsely elevates total protein
→as person ages, there is a slight decrease in ALBUMIN
→lower total protein are also seen in PREGNANCY
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods (8)
Kjeldahl Method (Indirect Method)
Biuret Method (Direct Method)
Folin-Ciocalteau (Lowry) Method
Ultraviolet Absorption Method
Salt Fractionation
Refractometry
Turbidimetric and Nephelometric Methods
Serum Protein
Others (2)
Coomassie Brilliant Blue Dye
Ninhydrin
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→standard reference method
→quantifies protein by nitrogen content
→uses serum with tungstic acid, forming protein free-filtrate
Kjeldahl Method (Indirect Method)
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→Kjeldahl Method (Indirect Method)
REAGENT:
END-PRODUCT:
REAGENT: sulfuric acid > digesting agent
END-PRODUCT: ammonia
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→most widely used method
→requires 2 peptide bonds and alkaline medium
Biuret Method (Direct Method)
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→Biuret Method (Direct Method)
PRINCIPLE:
PRINCIPLE: cupric ions react with peptide bonds in alkaline medium producing violet colored complex at 545 nm
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→Reagents (4)
Copper sulfate > main reagent
Potassium sodium tartrate > keeps copper in solution
Potassium iodide > stabilizer
Sodium hydroxide < alkalinizes solution
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→highest analytical sensitivity
Folin-Ciocalteau (Lowry) Method
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→Folin-Ciocalteau (Lowry) Method
PRINCIPLE:
REAGENT:
COLOR ENHANCER:
PRINCIPLE: oxidation of tyrosine, tryptophan, and histidine to give a deep blue color
REAGENT: phenol/ phosphotungstic-molybdic acid
COLOR ENHANCER: Biuret reagent
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→proteins absorb light at 210 nm due to peptide bonds
Ultraviolet Absorption Method
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→globulins can be separated from albumin by salting out procedures using sodium salts
Sal Fractionation
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→Salt Fractionation
SALT USED FOR ANALYSIS
Sodium sulfate
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
-.based on the measuremnt of refractive index due to solutes in serum
Refractometry
Total Protein
Laboratory Methods
→Turbidimetric and Nephelometric Methods
Reagents:
Scatter incident light:
Block light:
Reagents:
sulfosalicylic acid (SSA),
trichloroacetic acid (TCA
Scatter incident light:
Nephelometry
Block light:
Turbidimetry