BIOL& 241 Human Anatomy & Physiology: Chapter 13&14 Peripheral & Autonomic Nervous System Overview
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Neural structures outside the Central Nervous System. Afferent (sensory) receptors, Peripheral nerves, Efferent (motor) endings, and their associated ganglia.
Nerve
A bundle of axons encased in connective tissue.
Endoneurium
Connective tissue covering individual axons.
Perineurium
Connective tissue covering a fascicle of axons.
Epineurium
Connective tissue covering an entire nerve.
Cranial Nerves + Spinal Nerves
12 pairs of nerves exiting directly from the brain + Nerves exiting from the spinal cord.
Cranial Nerve I
Olfactory Nerve, smell. Tiny. Not the olfactory bulb or the tract. Pure Sensory.
Cranial Nerve II
Optic Nerve, vision. Brain tract; part that starts in eye and reaches optic chiasm = nerve, part of the axon that continues on to the thalamus is the tract. Pure Sensory.
Cranial Nerve III
Oculomotor Nerve; controls eye movement. Somatic Motor Fibers control 4 of 6 extrinsic eye muscles & muscle for eyelid. "Pure" motor.
Medial Rectus Muscle (CN III)
Turns the eye medially.
Superior Rectus Muscle (CN III)
Muscle that turns the eye upward.
Inferior Rectus Muscle (CN III)
Muscle that turns the eye downward.
Inferior Oblique Muscle (CN III)
Muscle that turns the eye upward and laterally.
Levator Palpebrae Superioris (CN III)
Muscle that lifts the upper eyelid.
Cranial Nerve IV
Trochlear Nerve; controls Superior Oblique Muscle --> turns the eye downward and laterally. "Pure" motor.
Cranial Nerve VI
Abducens Nerve; controls Lateral Rectus Muscle --> turns the eye laterally. "Pure" Motor.
Proprioception
Awareness of body position and movement.
Cranial Nerve V
Largest cranial nerve with three branches. Mixed. Proprioceptor fibers from muscles of mastication.
V1 - Ophthalmic Division (CN V)
Sensory to anterior scalp, upper eyelid, lacrimal gland, cornea, nose & nasal cavity mucosa.
V2 - Maxillary Division (CN V)
Sensory to lower eyelid, nasal cavity mucosa, palate, palate, upper lip, cheek.
V3 - Mandibular Division (CN V) (1)
Sensory to anterior tongue, lower teeth, chin, lateral (temporal) scalp.
V3 - Mandibular Division (CN V) (2)
Motor to Muscles of mastication (Masseter, Temporalis, Medial Pterygoid, Lateral Pterygoid).
Masseter
Prime mover of jaw closure; elevates mandible.
Temporalis
Closes jaw; elevates and retracts mandible.
Medial Pterygoid
Helps protract (pull anteriorly) mandible; grinding movements.
Lateral Pterygoid
Protracts mandible; forward sliding & grinding jaw movements.
Cranial Nerve VII
Large facial nerve controlling facial expression muscles. 5 branches. Sensory: Taste. Mixed.
Facial Nerve Branches
Includes temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical.
Cranial Nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear nerve (AKA Auditory Nerve) for hearing and balance (vestibular nerve: balance & equilibrium, cochlear nerve: hearing). Pure Sensory.
Cranial Nerve IX (1)
Glossopharyngeal nerve for taste and pharynx. Mixed. Innervates / senosry to posterior tongue & pharynx.
Cranial Nerve IX (2)
Motor to Stylopharyngeus Muscle & Parotid Salivary gland.
Cranial Nerve X
Vagus nerve extending beyond head and neck, to thorax and abdomen.
Cranial Nerve XI
Accessory nerve that joins Vagus with motor function to neck. "Pure" Motor.
Cranial Division (CN XI)
Motor to larynx, pharynx, and soft palate.
Spinal Root (CN XI)
Motor to trapezius and sternocleidomastoid.
Cranial Nerve XII
Hypoglossal nerve supplying the tongue. "Pure" Motor.
Spinal Nerves
Cervical (C1 - C8), Thoracic (T1 - T12), Lumbar (L1 - L5), Sacral (S1 - S5), Coccygeal (C0).
Facts about Cervical Nerves (1)
C1 starts between skull and Atlas (above the first cervical vertebra).
Facts about Cervical Nerves (2)
C8 is the last nerve below C7 (last cervical vertebra) --> 8 nerves but 7 cervical vertebrae.
Cauda Equina
Bundle of nerves resembling a horse's tail. The part where it extend beyond the spinal cord length, reaching the intervertebral foramina between the lumber and sacral vertebrae.
Dorsal Roots
Afferent sensory fibers from sensory receptors. Its ganglia relay info form sensory receptors.
Ventral Roots
Efferent motor fibers to muscles and glands. Somatic fiber for Sk. muscles. ANS efferent fibers exist.
Spinal nerves
Mixed. Neurons enter or exit it at levels appropriate to the organ they serve.
Meningeal Branch (Spinal Nerves)
Supplies meninges and spinal cord blood vessels.
Rami Communicantes (Spinal Nerves)
Connects thoracic and lumbar axons of preganglionic sympathetic neurons.
Dorsal Ramus (Spinal Nerves)
Supplies posterior body regions.
Ventral Ramus (Spinal Nerves)
Supplies anterior body (becomes intercostal nerves in the thoracic region) and forms plexuses.
Cervical Plexus
C1 - C5 supplying deep muscles of neck and shoulder, upper body skin (around ear and anterior neck).
Phrenic Nerve (Cervical Plexus)
Supplies diaphragm for breathing.
Brachial Plexus
C5 - T1. Supplies upper extremities.
Axillary/Circumflex Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
Supplies shoulder and deltoid muscle.
Musculocutaneous Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
Upper arm muscles (biceps & brachialis), sensory of forearm skin.
Median Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
Controls hand flexors & forearm (Flexor carpi radialis); responsible for Carpal Tunnel.
Ulnar Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
Supplies lower arm and hand flexors (Flexor carpi ulnaris).
Radial (Brachial Plexus)
Extensors of the back of arm (Triceps brachii).
Lumbar Plexus
T12 - L4.
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous (Lumbar Plexus)
Skin of lateral, anterior, and posterior thigh.
Femoral Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
Largest lumbar nerve; innervates thigh flexors and knee extensors (Quadriceps, Sartorius). Skin of thigh, hip, and medial lower leg & foot.
Genitofemoral Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
Scrotum and skin of thigh.
Obturator Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
Thigh adductor muscles (Adductors, Gracilis).
Sacral Plexus
L4 - S4.
Pudendal Nerve (Sacral Plexus)
Skin & muscles of the perineum (pelvic cavity floor), oenis, scrotum, part of vagina.
Sciatic Nerve (Sacral Plexus)
Largest nerve; innervates hamstrings of thigh and splits into Peroneal nerve and TIbial nerve.
Peroneal Nerve (Sciatic Nerve)
Tibialis anterior & Peroneus longus.
Tibial Nerve (Sciatic Nerve)
Innervates gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.
Dermatomes
Skin areas supplied by specific spinal nerves.
Intercostal Muscles
Muscles between ribs, innervated by T2 - T11.
Referred Pain
Pain resulting from noxious stimuli of visceral organs of thorax & abdomen
Referred Pain Cause
Visceral sensory info converges with 2nd order somatic sensory neurons at same level.
Referred Pain Sensation
Dull aching, gnawing, burning.
Important Referred Pain Stimuli
Extrem stretching of tissue, ischemia (low blood flow), irritating chemicals, muscle spasms.
Reflex Arc Components
Sensory receptor, Sensory neuron, Integration center (w/o an interneuron), Motor neuron, Effector organ.
Loss of Reflex
Interruption in basic reflex arc.
Hyporeflexia
Decreased intensity; pressures on nerve root.
Hyperreflexia
Hyperactivity; interruption of upper motor neuron.
Flaccid Paralysis
Total loss of muscle tone & atrophy of muscle. Due to lower motor neuron damage (anterior horns - gray matter).
Spastic Paralysis
Increased muscle tone (reduced inhibition / no voluntary control over skeletal muscle) from upper motor neuron damage (corticospinal tract).
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary functions, subdivision of PNS.
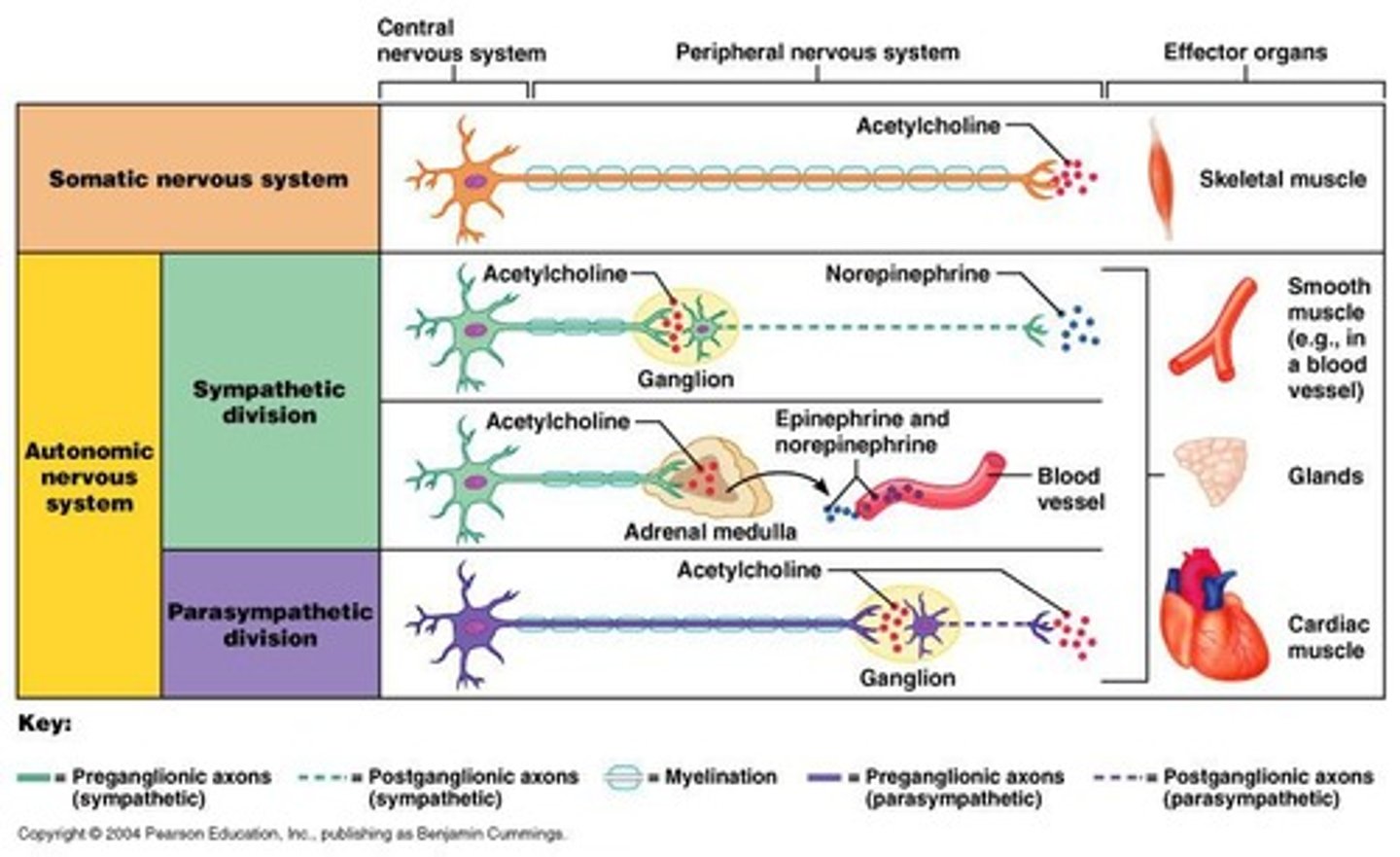
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary muscles.
ANS Controls....
Involuntary muscles (cardiac, smooth - walls of visceral organs and blood vessels), and glandular epithelial tissue.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Resting state, conserves energy, promotes digestion. Takes care of daily conditions. Gives slower response.
Signs of Parasympathetic Nervous System
Low blood pressure/heart rate/respiratory rate, GI tract actively digesting food, skin is warm, eye pupils constricted, lenses of eye are accommodated for close vision.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Prepares body for fight or flight response. For emergency., gives instantaneous response.
Signs of Sympathetic Nervous System
Pounding heart, rapid deep breathing, cold sweaty skin, dilated eye pupils.
CN that serve PNS
Head: 3 (Oculomotor), 7 (Facial), 9 (Glossopharyngeal).
Neck & Trunk (Throax, Abdomen): 10 (Vagus).
Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves
Serve distal half colon, bladder, ureters, reproductive organs. In Sacral region (S2 - S4)
Sympathetic Nervous System Distribution
T1 to L2 (middle of spinal cord).
Preganglionic fibers
Myelinated fibers in the autonomic nervous system. White Rami.
Synapses.... (1)
At same, higher, or lower level in the sympathetic trunk. Or at collateral region after passing through the trunk.
Synapses.... (2)
Most preganglionic fibers pass through sympathetic trunk w/o synapsing, forming the splanchnic nerves.
Collateral ganglion
Ganglia located anterior to the vertebral column.
Splanchnic nerves
Nerves formed by preganglionic fibers passing through the trunk.
Postganglionic axons
Unmyelinated fibers that extend to target organs. Gray Rami.
Rami Communicantes
Associated only with sympathetic division. Never carry parasympathetic fibers.
Visceral sensory neurons
Sense chemical changes, stretch, temp, viscera irritation.
Brain interprets visceral senses as....
Hunger, fullness, pain, nausea.
Effector organs
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
Somatic Nervous System Neurotransmitters
All somatic neurons: Acetylcholine (Ach). Always excitatory, stimulation causes postsynaptic potential reach threshold & muscle contracts.
Autonomic Postganglionic Neurons Neurotransmitters
Parasympathetic: Ach
Sympathetic: Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline (usually). Ach - eccrine sweat glands, arrector pili muscles of skin, sm. muscles in vessels walls for sk. muscles.
1st Order Motor Neuron
Motor neurons exiting the CNS. Somatic: Lower motor, Autonomic: Preganglionic.