Robotics All
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
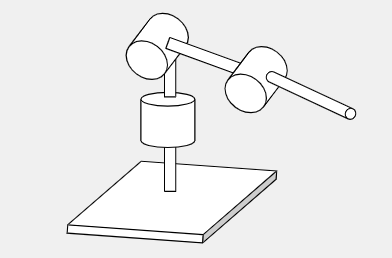
Spherical Workspace
Used for dexterous activities, i.e., welding or spray painting
Anthropomorphic Robot Arm (RRR)
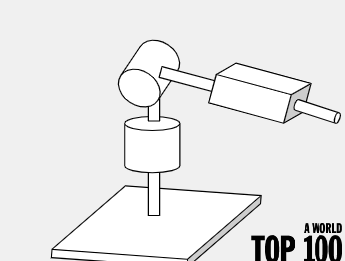
Spherical Workspace
Used for simple tasks that don’t require complex motion
Trades heavy loads for higher accuracy
Spherical Robot Arm (RRT)
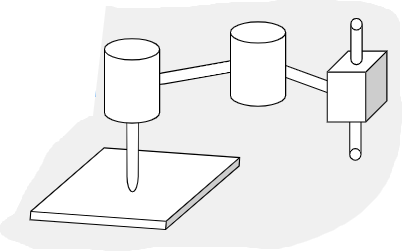
Cylindrical Workspace
Used for factory assembly in single planes
SCARA (Selective Compliant Articulated Robot for Assembly) (RRT)
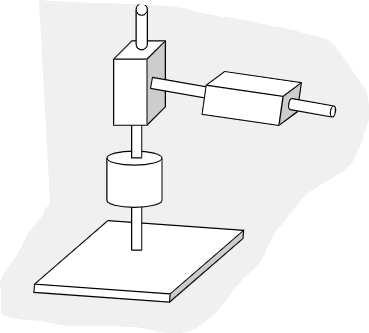
Cylindrical Workspace
Used for basic jobs
Cylindrical Robot Arm (RTT)
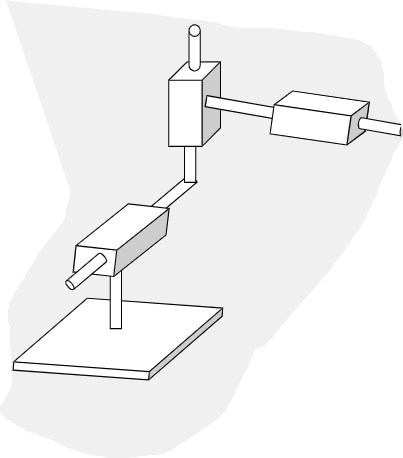
Prism Workspace
Known for high accuracy with less capacity for high loads
Cartesian Robot Arm (TTT)
Kinematics Definition
The study of motion without considering the forces and moments which are responsible for the motion.
The motion is described by trajectories, velocities and accelerations - in robotics the main interest is in trajectories and velocities.
Forward/Direct Kinematics
Given joint variables calculated the pose of end-effector
Forward/Direct Kinematics Additional Information
The solution is unique
Represents the simpler problemI
Inverse Kinematics
Given the pose of the end-effector calculate joint variables
Inverse Kinematics Additional Information
The equations are generally nonlinear
No closed form solution
No / Multiple / Infinite solutions may exist
Differential/Instantaneous Kinematics
Given joint velocities determine the end-effector linear and angular velocities
Inverse Differential Kinematics
Given end-effector velocities determine the joint velocities
Reachable Workspace
Set of points that can be reached by end-effector
Dexterous Workspace
Set of points that can be reached by end-effector with arbitrary orientation
Mechanical Structure of Robot Manipulator
Consists of a sequence of rigid bodies (links) interconnected by means of articulations (joints)
Characterisation of Robot Manipulator
An arm that ensures mobility, a wrist that grants dexterity, and an end-effector (gripper) that performs the task required
Task of Manipulator
Place an object grasped by the gripper to an arbitrary position and orientation in 3D
Path
Locusts of points required for travel of the manipulator
Trajectory
The path plus the timings involved for those point
Kinematic Redundancy
Number of DOF > number of variables needed to describe task
Can be obvious (7 DOF) or less obvious (task makes it redundant)
Adds dexterity and versatility
Accuracy
Actual and computed kinematics not the same
Varies across the workspace
Error typically <1mm
Repeatability
Ability to return to same position
Depends on mechanical structure, sensors and controllers
Difference typically < 0.1mm
Singularities
Arise when Jacobian is rank deficient as the inverse is ill defined
Close to singular configurations small velocities in end-effector may cause large joint velocities
There may be infintie solutions to inverse kinematics, configurations where mobility is reduced
Sense-Plan-Act Architecture
Measurements translated into an internal world model
Generate set of actions to achieve goal
Generate motion commands
Shakey’s architecture
Sense-Plan-Act Disadvantages
Planning in real world takes a long time (Delays in reaction time)
Sensing not involved in planning (not good in dynamic environments)
Rely directly on sensed information
Sub Sumption Architecture
Behaviour based architecture, built from layers of interacting behaviours
Behaviours connect sensors to actuators
Multiple behaviours can be active
Higher level behaviours override lower level ones (subsume)
Higher level behaviours only active when needed
Sub Sumption Advantages
Led to faster, more reactive robots
Sense and react in dynamic worlds
Sub Sumption Disadvantages
Difficult to achieve long term goals
Difficult to optimise robot behaviours
Hybrid Layer Control Architecture
Reactive Layer (Controller) - Behaviour control
Stateless, sensor based, short time scale actions
Glue Layer (Sequencer) - Executive control
Has a memory of the past, selects primitive behaviours for controller
Planning Layer (Deliberator) - Planning
Plans for the future, time consuming operations
Behavioural Control
Directly connecting sensors and actuators
Concerned with here and now
Executive Control
Interface between (numerical) behavioural control and (symbolic) planning layers
Translation of high level plans to low level behaviours
Invoking low level behaviours at appropriate times
Monitoring execution
Concerned with what has just happened and what should happen next
Planning Control
Determining long range activities of the robot based on high level goals
Fully Autonomous
Autonomy level 10
Co operative mission supervision
Autonomy level 9
Mission supervision
Autonomy level 8
Goal supervision
Autonomy level 7
Real time multi robot co operation (work together)
Autonomy level 6
Real time multi robot coordination (swarm robots)
Autonomy level 5
Adapts to faults/events (Compensate for uncertainties)
Autonomy level 4
Robust response to real time faults/events
Autonomy level 3
Changeable mission
Autonomy level 2
Execute preplanned missions
Autonomy level 1
Remotely operated
Autonomy level 0
Sensor Definition
Device that measures some attribute of the world
Transducer Definition
Mechanism that transforms the energy associated with what is being measured into another form of energy
Passive Sensor
Environment provides medium/energy for observation
Active Sensor
Puts out energy into the environment to either change energy or enhance it (sonar)
Active Sensing
Using an end-effector to dynamically position a sensor for a “better look”
Proprioceptive Sensors
Internal Sensors
Position
Velocity
Acceleration
Motor Torque
Exteroceptive Sensors
External Sensors
Tactile
Force + Torque
Proximity
Range Finders
Vision
Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)
Position/velocity/acceleration
Typically contain 3 orthogonal rate-gyroscopes and 3 orthogonal accelerometers
Measure angular velocity and linear ac eleration
Estimates position, orientation and usually velocities and accelerations using integration
Typically include 3 magnetometers to give heading and remove errors
Micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS Gyros)
Vibrating elements, no rotating parts
Measures angular velocity by measuring Coriolis force acting on the vibrating mass
Low power consumption
Small and low cost
Gyro Drift
The bias of a rate gyro is the average output from the gyroscope when it is not undergoing any rotation.
When integrated, this cause an angular error which grows linearly with time
To correct fuse IMU signals with additional sensors
Kalman and particle filters
Absolute positioning systems (GPS)
Magnetometers
Global Positioning System
Provides 3D position estimate, based on received radio signals from ensemble of satellites
Compare time delays to triangulate position
Signal may be unreliable
Require unobstructed line-of-sight to satellites
Depends on atmospheric conditions
Can pass through glass and plastic
Accuracy 20-25m horizontal, 43m vertical
Sonar / Ultrasonic
Measures time between acoustic pulse and echo
Low cost, light weight, low power consumption, low computational effort
Distance = speed of sound /(2 * time of interval)
Receiver disabled during pulse transmission and after first echo to avoid interference and false readings
Max detectable distance ~ 6.5m
Poor directional resolution
Low sensing rate
Oblique walls do not produce detectable echos
Artefacts from multiple reflections
Collaborative Robots
A robot that can be used in a collaborative operation
Defined by the operation that they are doing not by the type of robot itself
Collaborative Operation
A state in which a robot works in direct cooperation with a human within a defined collaborative workspace
Collaborative Workspace
A workspace within the safeguarded space where the robot and human can perform tasks simultaneously during production operation
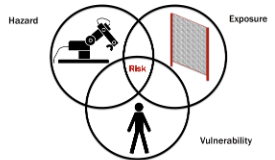
The Robot Risk Model
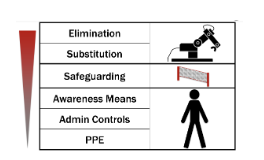
Robot Risk Reduction
ISO 10218 Part 1
Outlines the six steps to be considered as part of a risk assessment
The intended operations of the robot, including teaching, maintenance, setting and cleaning
Unexpected startup
Access by personal from all directions
Reasonably foreseeable misuse of the robot
The effect of failure in the control system
Where necessary, the hazards associated with the specific robot application
ISO 10218 Part 2
Requires a risk assessment for collaborative applications to evaluate task/hazard combinations and set appropriate limits
Means of anticipating tasks and hazards with the goal of applying suitable risk reduction measures
Uses iterative process to determine the desired effect is achieved
Avoids “one size fits all”
ISO TS 15066
Technical Specification about collaborative operations, which may include one or more of the following methods:
Safety rated monitored stop
Hand guiding
Speed and separation monitoring
Power and force limiting
Safety Rated Monitored Stop
What the collaborative robot does in the presence of an operator or obstruction
Stop motion condition ensured
Drive power remains on
Motion resumes after obstruction clears
Robot motion resumes without additional action
Protective stop delivered if stop condition is violated
Hand Guiding
Where an operator leads robot movement through direct interface
Robot stops when operateor arrives
Operator grasps enabling device, activating motion
Robot motion responds to operator commands
Non-collaborative operation resumes when operator leaves collaborative workspace
Speed and Separation Monitoring
Where the robot speed reduces when an obstruction is detected
Separation distances are monitored
Robot speed directly correlates to sparation distance
Stop given if direct contact proximity is attained
Power and Force Limiting
Where incidental contact initiated by robot are limited in energy to not cause the operator harm
Forces robot can exert are limited
Robot system design eliminates pinch points, sharp edges, to prevent the robot trapping operators
Robot complies and reacts when contact is made
Reduce robot velocity or inertia
Modify robot posture, to increase possible exposure surface area (reduce pressure)
Avoid sensitive body areas
ISO TS 15066 Onset of Pain Study
Guidance for power and force limits based on study examining these conditions and the onset of pain in 29 body regions.
Robot (ISO 8373)
Actuated mechanism programmable in two or more axes with a degree of autonomy, moving within its environment, to perform intended tasks
Autonomy (ISO 8373)
Ability to perform intended tasks based on current state and sensing, without human intervention
Industrial Robot (ISO 8373)
Automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator, programmable in three or more axes, which can be either fixed in place or mobile for use in industrial automation applications
Service Robot (ISO 8373)
A robot that performs useful tasks for humans or equipment excluding industrial automation applications (Personal/Professional)
Artificial Intelligence (ISO 8373)
Software systems designed by humans that, given a complex goal, act in the physical or digital dimension to achieve the given goal
Europe Robotics Culture
Trustability, explainable AI
Strong competencies in hardware engineering
High ethical standards
Very concerned, critical, fearful society
America Robotics Culture
Data driven service robotics startups, strong venture capital support
Advantages in data collection and AI
Deregulated, liberal society
Asia Robotics Culture
Financial support, technology enthusiasts
Strong competencies in computer engineering and hardware engineering
Embracing new technology
Ethical, legal, social and economic issues not a concern