CV2 EKG - Junct + Vent Rhythms, 12 Lead Acquistion, Axis Dev
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
arrhythmias sustained or originating in the AV junction (4)
*Premature Junctional Contractions
*Junctional Escape Complexes and Rhythm
*Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
*Paroxysmal Junctional Tachycardia
characteristics of arrhythmias sustained or originating in the AV junction
*Inverted or absent P Waves in Lead II
*PRI of < 0.12 Seconds
Normal QRS Complex Duration
junctional rhythms originate from
electrically active tissue with automaticity in the junction between the atria and the ventricles, typically near the AV node
intrinsic rate of AV node
40-60 bpm
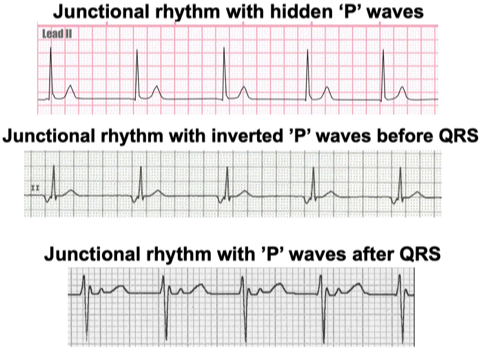
p waves morphologies in junctional rhythms
premature junctional contractions
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = depends
rhythm = depends
pacemaker site = ectopic focus in AV junction
p waves = inverted; may occur after QRS
PRI = normal except for early beat
QRS = usually normal
PJC
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
junctional rhythm
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = 40-60
rhythm = regular
pacemaker site = AV junction
p waves = absent, inverted or after QRS
PRI = often can’t measure
QRS = usually normal

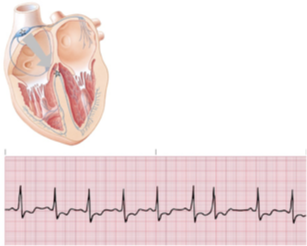
junctional rhythm
junctional escape rhythms
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = </= 40
rhythm = regular
pacemaker site = AV junction
p waves = absent, inverted, may occur after QRS
PRI = often cannot measure
QRS = usually normal
junctional escape rhythm
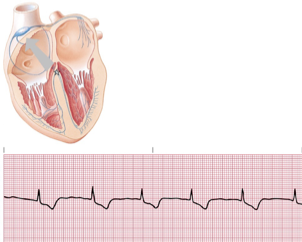
accelerate junctional rhythm
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = 60-100
rhythm = regular
pacemaker site = AV junction
p waves = inverted, may occur after QRS
PRI = often cannot measure
QRS = normal
accelerated junctional rhythm
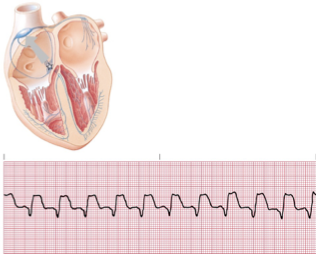
junctional tachycardia
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = 100-180
rhythm = regular
pacemaker site = AV junction
p waves = inverted, may be after QRS
PRI = often cannot measure
QRS = normal
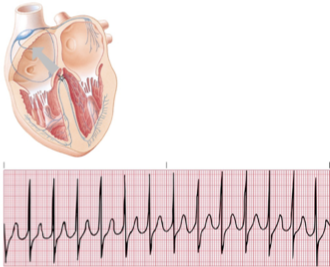
junctional tachy
AV node reentrant tachycardia occurs due to
an electrical “short circuit” contained within the AV node
AVNRT is characterized by
*Very rapid rates (usually 150-250)
*Regular with no beat-to-beat variability
*P waves difficult to discern. If present, may be buried in QRS complex (arrows).
*PR interval usually prolonged
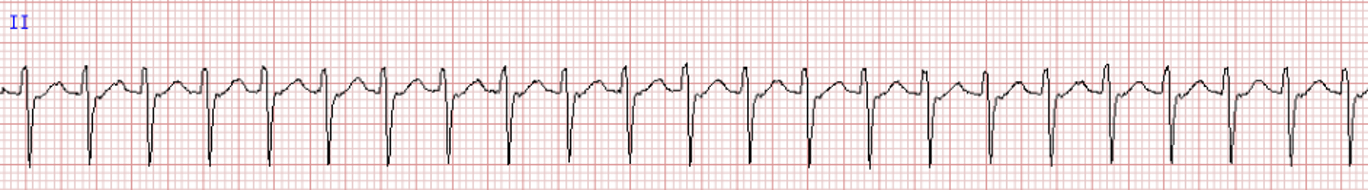
AVNRT
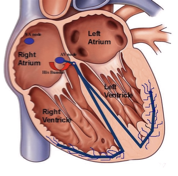
AVNRT
AV reentrant tachycardia is different than AVNRT because
it occurs due to an electrical “short circuit”, but in AVRT the short circuit is not contained to the ventricle.
In patients with AVRT, communication between the atria and ventricles may happen either via the
AV node or via a pathological accessory pathway
In AVRT, conduction may be
orthodromic or antidromic
orthodromic AVRT is
*Antegrade conduction (normal) via AV node and His bundle
*Retrograde conduction via accessory pathway
orthodromic AVRT is the most
common form of AVRT (90%)
orthodromic AVRT may be initiated by
PVCs; ECG features are nearly identical to an AVNRT
antidromic AVRT is
*Antegrade conduction via accessory pathway
*Retrograde conduction via AV node and His bundle
antidromic AVRT can also be initiated by ___ and is ___
PVCs; rare (~10%)
**on ECG = if present, P waves are inverted. PR interval will be prolonged
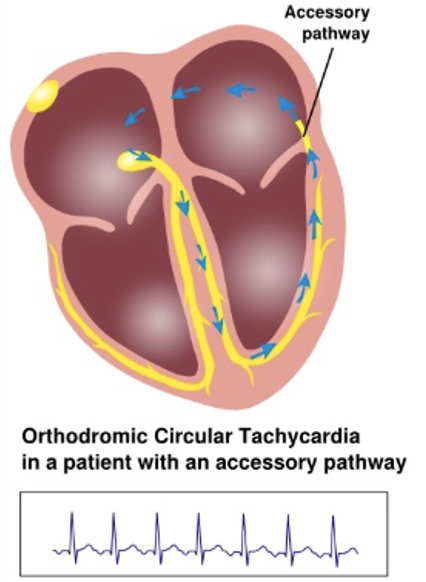
orthodromic AVRT

antidromic AVRT
Patients who have pathological accessory conduction pathways between atrium and ventricle tend to have
abnormal baseline features on their ECG, even when not experiencing an arrhythmia.
These conditions are called preexcitation syndromes, named because the ventricle is
depolarized earlier than usual by antegrade conduction through the accessory pathway
There are two commonly recognized preexcitation syndromes:
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
*Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome
WPW syndrome involves
*Accessory pathway via the Bundle of Kent
*Bridges fibrous tissue between atrium and ventricle, providing an electrical connection
*Usually remote from the AV node
*Can be on either left or right side of heart
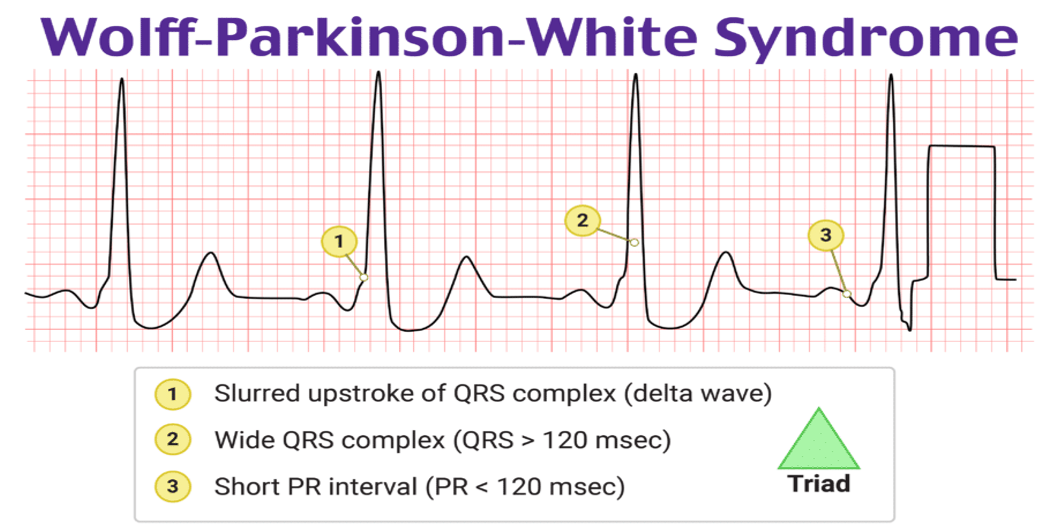
criteria for WPW syndrome
wolff-parkinson-white syndrome
lown-ganong-levine syndrome consists of
*Accessory pathway historically thought to be James bundle (James fibers)
*Connect atria to distal AV node or proximal His bundle
caveat with LGL syndrome is
*electrophysiology data casts some doubt on this mechanistic hypothesis and has had difficulty identifying a consistent accessory pathway in LGL patients
The ECG findings of Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome are
more subtle than those of WPW
The only characteristic baseline finding of LGL syndrome
is a short PR interval <120 ms
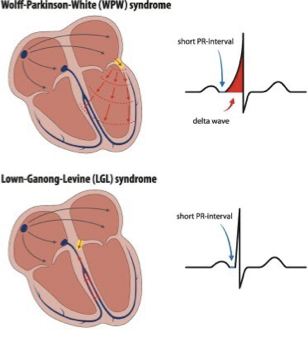
WPW vs LGL syndromes
Arrhythmias Originating Within the AV Junction (AV blocks)
located = at the AV Node, at the Bundle of His, or below the Bundle of His
*First-Degree AV Block
*Type I Second-Degree AV Block
*Type II Second-Degree AV Block
*Third-Degree AV Block
first degree AV block
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = depends on underlying rhythm
rhythm = usually regular
pacemaker site = SA node or atrial
p waves = normal
PRI = > 0.20 seconds
QRS = usually <0.12 seconds
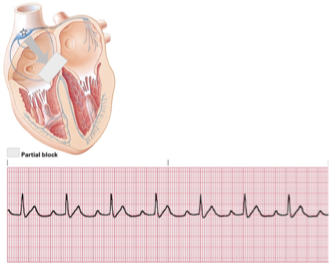
first degree AV block
first degree AV block
etio
clinical significance
treatment
*Etiology
Delay in the conjunction of an impulse through the AV node.
May occur in healthy hearts, but often indicative of ischemia at the AV junction.
*Clinical Significance
Usually not significant, but new onset may precede a more advanced block.
*Treatment
Generally, none required other than observation.
Avoid drugs that may further slow AV conduction.
type I second degree AV block
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = atrial, normal; ventricular, normal to slow
rhythm = atrial, regular; ventricular, irregular
pacemaker site = SA node or atrial
p waves = normal, some P waves; not followed by QRS
PRI = increase until QRS is dropped, then repeats
QRS = usually, <0.12 seconds
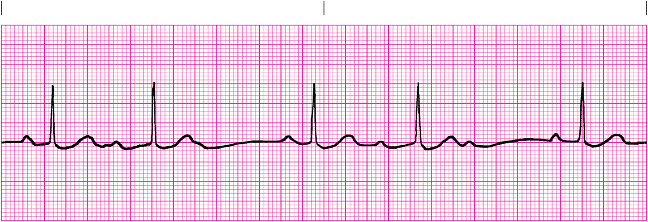
type I second degree AV block
Conduction Pattern in Type I Second Degree
type I second degree AV block
etio
clinical significance
treatment
*Etiology
Also called Mobitz I, or Wenckebach.
Delay increases until an impulse is blocked.
Indicative of ischemia at the AV junction.
*Clinical Significance
Frequently dropped beats can result in cardiac compromise.
*Treatment
Generally, none required other than observation.
Avoid drugs that may further slow AV conduction.
Treat symptomatic bradycardia.
Mobitz 1 or Wenkebach is
type I second degree AV block
type II second degree AV block
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = arial, normal; ventricular, slow
rhythm = may be regular or irregular
pacemaker site = SA node or atrial
p waves = normal, some p waves not followed by QRS
PRI = constant for conducted beats, may be > 0.21 seconds
QRS = normal or > 0.12 seconds
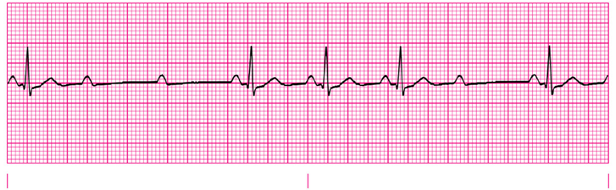
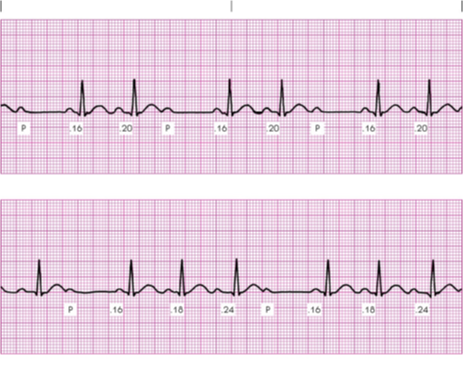
type II second degree AV block
2:1 AV block
narrow vs wide QRS in second degree AV blocks
Narrow QRS favors final diagnosis of 2nd degree type I
Wider QRS favors final diagnosis of 2nd degree type II

conduction Ratios in Type II Second Degree Heart Block
type II second degree AV block
etio
clinical significance
treatment
*Etiology
Also called Mobitz II or Classic.
Intermittent block of impulses.
Usually associated with MI or septal necrosis.
*Clinical Significance
May compromise cardiac output and is indicative of MI.
Often develops into full AV blocks.
*Treatment
Avoid drugs that may further slow AV conduction.
Treat symptomatic bradycardia.
Consider transcutaneous pacing.
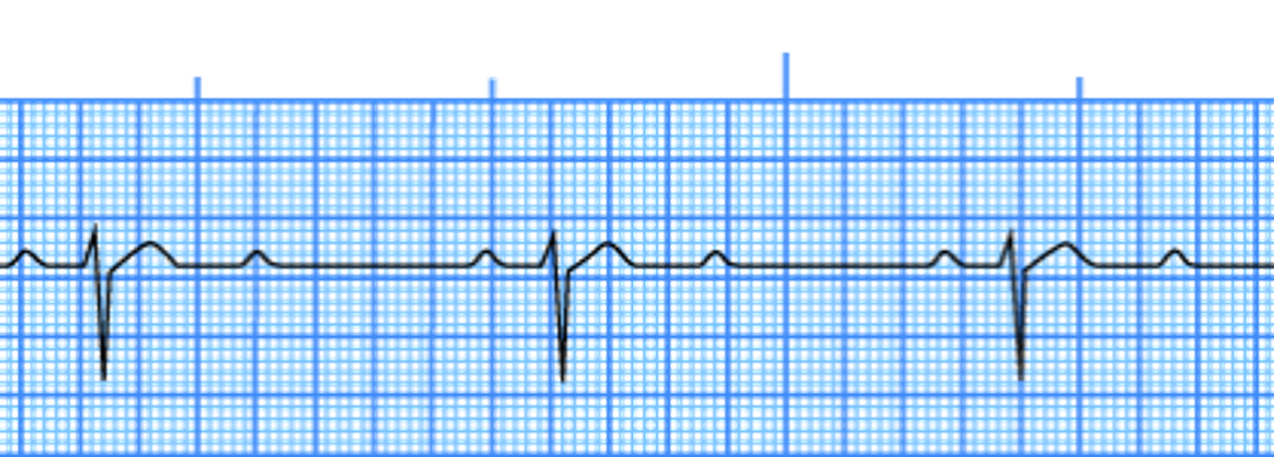
third degree AV block
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = atrial, normal; ventricular, 40-60
rhythm = both atrial and ventricular regular
pacemaker site = SA node and AV junction or ventricle
p waves = normal, with no correlation to QRS
PRI = no relationship to QRS
QRS = 0.12 seconds or >
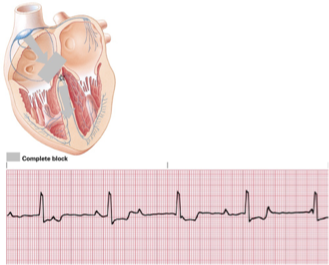
third degree AV block
third degree AV block
etio
clinical significance
treatment
*Etiology
Absence of conduction between the atria and the ventricles
Results from AMI, digitalis toxicity, or degeneration of the conductive system.
*Clinical Significance
Severely compromised cardiac output.
*Treatment
Transcutaneous pacing for acutely symptomatic patients.
Treat symptomatic bradycardia.
Avoid drugs that may further slow AV conduction.
arrhythmias Originating in the Ventricles
*Ventricular Escape Complexes and Rhythms
*Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
*Premature Ventricular Contractions
*Ventricular Tachycardia
*Related Dysrhythmia
*Ventricular Fibrillation
*Asystole
Artificial Pacemaker Rhythm
ventricular escape rhythm/idioventricular escape complex
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = 25-40
rhythm = escape complex, irregular; escape rhythm, regular
pacemaker site = ventricle
p waves = non
PRI = none
QRS = > 0.12 seconds, bizarre
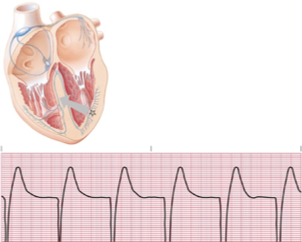
ventricular escape rhythm/idioventricular escape complex
ventricular escape rhythm/idioventricular escape complex
etio
clinical significance
tx
*Etiology
A subtype of ventricular escape rhythm that frequently occurs with MI.
Ventricular escape rhythm with a rate of 60–110.
*Clinical Significance
May cause decreased cardiac output if the rate slows.
*Treatment
Does not usually require treatment unless the patient becomes hemodynamically unstable.
Primary goal is to treat the underlying MI.
premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = underlying rhythm
rhythm = interrupts regular underlying rhythm
pacemaker site = ventricle
p waves = none
PRI = none
QRS = >0.12, bizarre
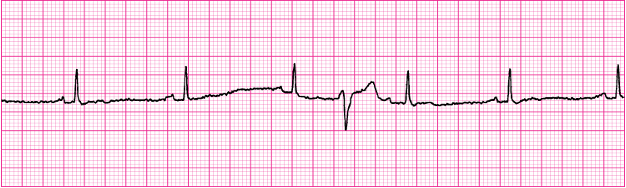
PVCs
PVCs etio
*Single ectopic impulse resulting from an irritable focus in either ventricle.
*Causes may include myocardial ischemia, increased sympathetic tone, hypoxia, idiopathic causes, acid–base disturbances, electrolyte imbalances, or as a normal variation of the ECG.
*May occur in patterns
*Bigeminy, trigeminy, or quadrigeminy.
*Couplets and triplets.
bigeminy
every other
trigeminy
every third (2 normal QRS, 1 PVC)
quadrigeminy
every fourth (3 normal QRS, 1 PVC)
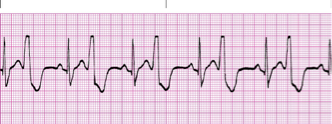
bigeminy PVCs
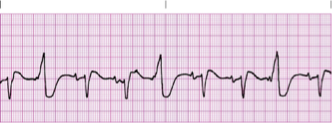
trigeminy PVCs
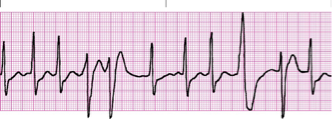
PVC couplets
PVCs clinical significance
*Malignant PVCs
More than 6/minute, R on T phenomenon, couplets or runs of ventricular tachycardia, multifocal PVCs, or PVCs associated with chest pain.
*Ventricles do not adequately fill, causing decreased cardiac output.
ventricular tachycardia
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = 100-250
rhythm = usually regular
pacemaker site = ventricle
p waves = if present, not associated with QRS
PRI = none
QRS = >0.12 seconds, bizarre
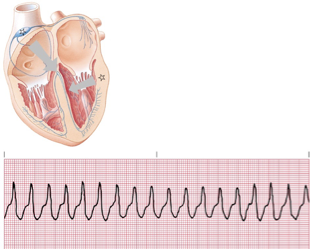
ventricular tachycardia
vtach etio and clincial significance
*Etiology
3 or more ventricular complexes in succession at a rate of >100.
Causes include myocardial ischemia, increased sympathetic tone, hypoxia, idiopathic causes, acid–base disturbances, or electrolyte imbalances.
VT may appear monomorphic or polymorphic
*Clinical Significance
Decreased cardiac output, possibly to life-threatening levels.
May deteriorate into ventricular fibrillation.
torsades de pointes is
polymorphic VT
torsades de pointes typically occurs in
*nonsustained bursts.
Prolonged Q–T interval during “breaks.”
QRS rates from 166–300.
RR interval highly variable.
torsades de pointes can be exacerbated by
by administration of antihistamines, azole antifungal agents and macrolide antibiotics, erythromycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin
vfib
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = no organized rhythm
rhythm = no organized rhythm
pacemaker site = numerous ventricular foci
p waves = usually absent
PRI = none
QRS = none
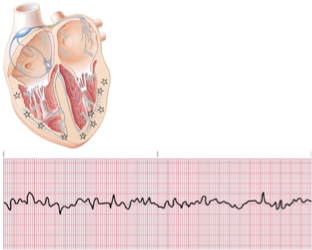
vfib
vfib etio and clinical significance
*Etiology
Wide variety of causes, often resulting from advanced coronary artery disease.
*Clinical Significance
Lethal dysrhythmia with no cardiac output and no organized electrical pattern.
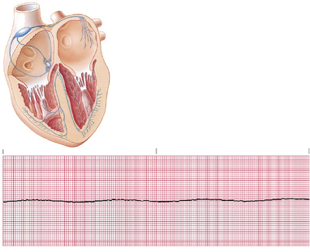
asystole
asystole etio and clinical significance
*Etiology
Primary event in cardiac arrest, resulting from massive myocardial infarction, ischemia, and necrosis.
Final outcome of ventricular fibrillation.
*Clinical Significance
Asystole results in cardiac arrest.
Poor prognosis for resuscitation.
artifical pacemaker rhythm
rate
rhythm
pacemaker site
p waves
PRI
QRS
rate = varies with pacemaker
rhythm = may be regular or irregular
pacemaker site = depends upon electrode placement
p waves = none produced by vent pacemakers, pacemakers spike
PRI = if present, varies
QRS = > 0.12 seconds, bizarre
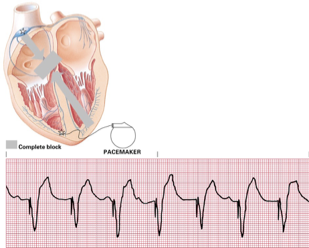
artificial pacemaker rhythm
causes of artifact
patient movement
cable movement
electrical interference
an accurate ECG should have
*Negative aVR
aVR should be negative
If aVR is upright, check for reversed limb leads
*One complete cardiac cycle in each lead
*Proper calibration
*Appropriate speed
the hexaxial system is represented by
a circle
each lead has a positive (+) half and a negative (–) half
the hexaxial system has an
Isoelectric lead: 90°angle from the dividing line between the positive and negative halves of the lead.
–This lead is neither positive nor negative.
–Each lead has a corresponding isoelectric lead.
On the ECG..
The positive vector will be taller or more positive.
The negative vector will appear deeper or more negative.
If the vector is exactly isoelectric, it will fall
directly on the isoelectric lead.
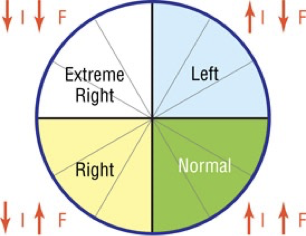
Four quadrants of the hexaxial system:
–Normal
–Left
–Right
–Extreme right
Causes of right axis deviation
*Normal in adolescents and children
*Right ventricular hypertrophy
*Left posterior hemiblock
*Dextrocardia
*Ectopic ventricular beats and rhythm
Causes of left axis deviation
*Left axis deviation (LAD):
Left anterior hemiblock (LAH)
Ectopic ventricular beats and rhythms
*Most frequent cause of LAD is LAH.
You tell axis deviation using
lead I and aVF
lead I +
aVF +
normal
lead I +
aVF -
left axis deviation
lead I -
aVF +
right axis deviation
lead I -
aVF -
extreme right axis deviation
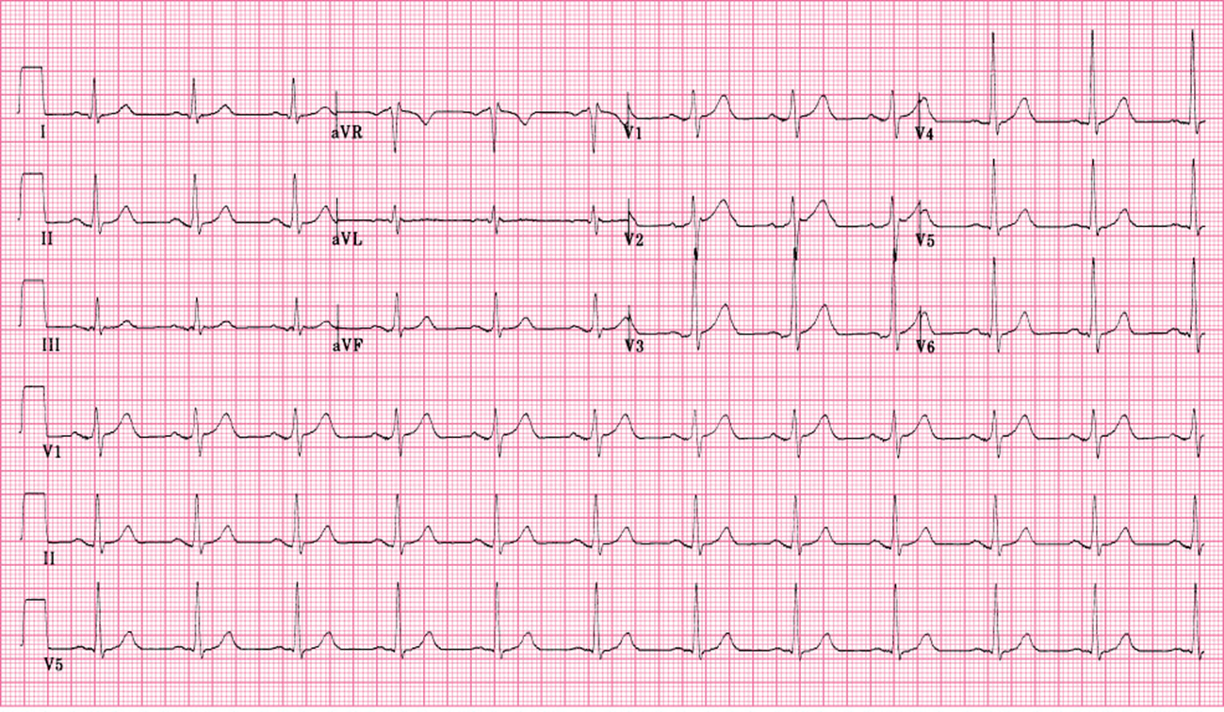
identify axis
lead I +
avf +
normal