TOPIC 1: biological molecules
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What’s some evidence for evolution
All living things share the same biological molecules. All have a similar biochemical basis.
What’s a monomer?
Smaller unites which can create larger molecules (polymers) e.g. glucose, amino acid, nucleotide, monosaccharides
What’s a polymer?
Molecules made from larger numbers of monomers joined together e.g. starch, cellulose, glycogen, polypeptide (protein), DNA+RNA
Condensation def
Joins two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water
Hydrolysis def
breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of a water molecule
what are carbohydrates made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
monomers of carbohydrates
carbohydrates are made up of monomers. The basic monomer unit is a sugar- saccharide. Thus, called a monosaccharide.
Pair= disaccharide
(much) larger numbers= polysaccharide
Monosaccharide general formula + examples
(CH2O)n (n= any number 1-7)
glucose, galactose, fructose
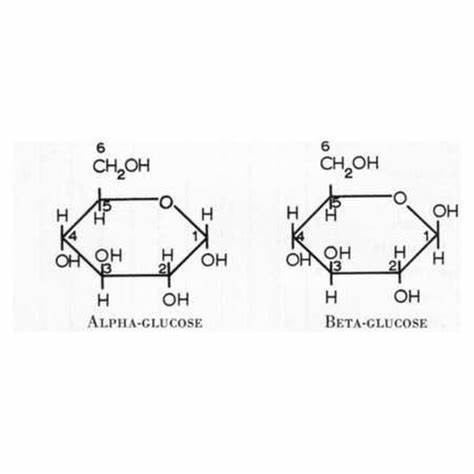
Alpha and beta glucose
glucose is a hexose (6 carbon sugar). It has 2 isomers: alpha and beta glucose.
Alpha Below Beta Above (whether OH is above or below)
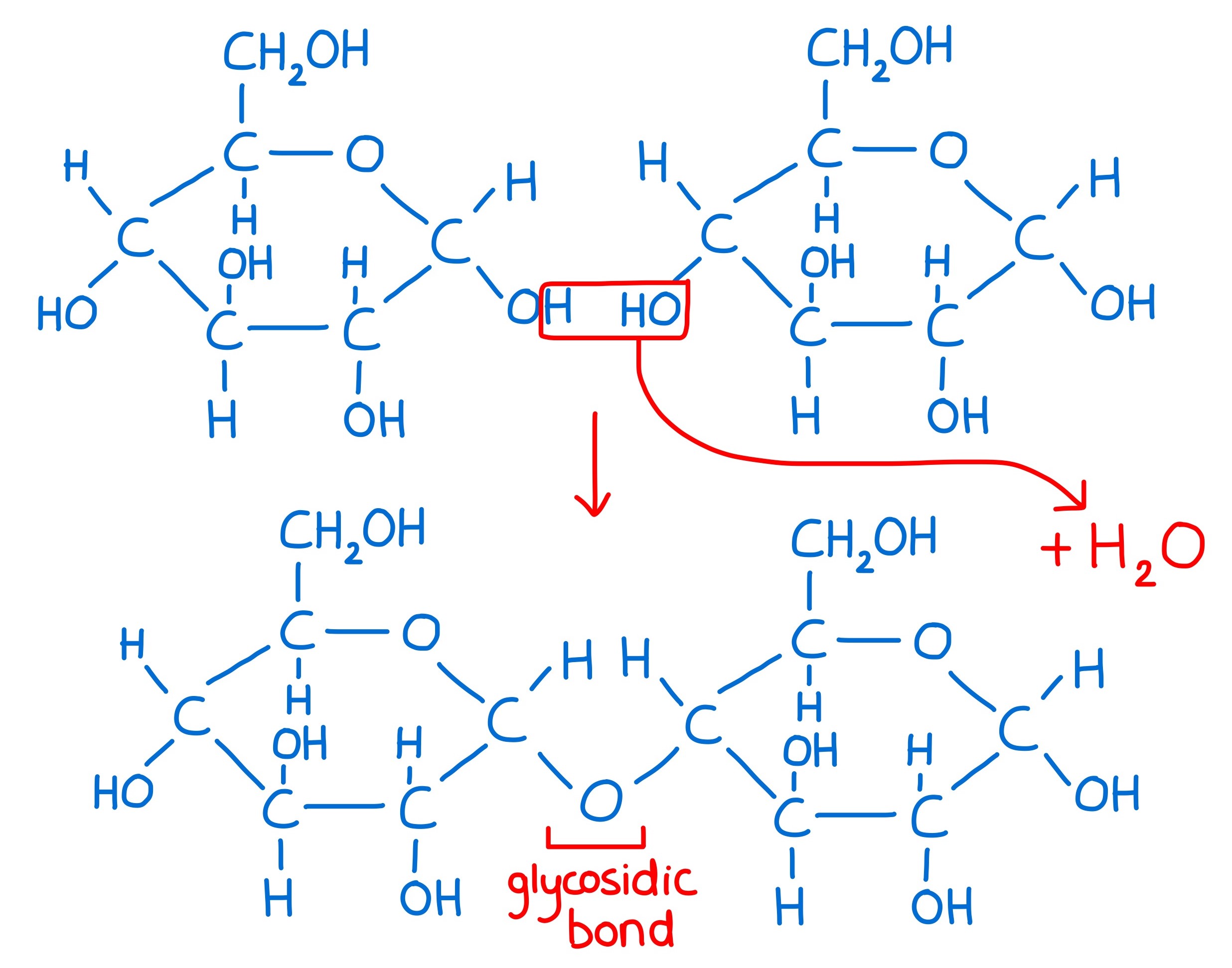
How are disaccharides formed?
Two monosaccharides join through a condensation reaction. The bond formed is called a glycosidic bond. The breaking of a disaccharide is called a hydrolysis reaction.
what monosaccharides are maltose, sucrose and lactose made from
maltose= glucose + glucose
sucrose=glucose + fructose
lactose= glucose + galactose
formula= C12H22O11
disaccharide diagram
Polysaccharides
Formed by many monosaccharides by condensation reactions. Very large molecules → insoluble → suitable for storage.
Reducing sugars
All monosaccharides and some disaccharides (maltose) are reducing sugars.
Reducing sugar= a sugar that can donate electrons to (reduce) another chemical. E.g. benedicts reagent
What’s benedict’s reagent
alkaline solution of copper (II) sulfate. When a reducing sugar is heated the solution forms an insoluble red precipitate of copper(II) oxide.
Benedicts test
Add 2cm3 of the sample to a test tube. Grind up in water if it’s not in liq form.
Add an equal volume of benedicts reagent.
Heat mixture in a gently boiling water bath for 5 minuets
reducing sugars present= orange-brown colour
Test for non-reducing sugars
(e.g. sucrose).
Do a benedicts test, if it doesn’t change colour→ reducing sugars not present
add another 2cm3 of the sample to 2cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid in a test tube and place it in a gently boiling water bath for 5 minuets. It will hydrolyse any disaccharide present into its constituent monosaccharides
Slowly add some sodium hydrogen carbonate solution to test tube→ to neutralise the acid (benedicts reagent doesn’t work on acidic solutions). Test with pH paper to check it’s alkaline
Re-test the resulting solution and if non-reducing sugar was present it should turn orange-brown. Due to reducing sugars produced from the hydrolysis of the non-reducing sugar
Test for starch
Starch changes the colour of the iodine in potassium iodine solution from yellow to blue-black. Test at room temp.
2cm3 of the sample into a test tube. (or two drops of the sample into a depression on a spotting tile)
2 drops of iodine solution and shake/stir
starch present= blue-black colour
where is starch found
plant cells in the form of small grains (e.g. inside chloroplasts). Cells get energy from glucose→ plants access glucose as starch (when needing energy → breaks down starch)
starch structure
polysaccharide formed from two polymers of alpha-glucose- amylose and amylopectin.
starch role and properties
main role: energy storage=
insoluble= doesn’t affect water potential→ water not drawn into cells by osmosis.
large and insoluble= doesn’t diffuse out of cells
compact= a lot can be stored in a small space
when hydrolysed it forms alpha-glucose, which is easily transported→ to be used in respiration
branched form has many ends→ each can be acted on by enzymes→ glucose monomers are released rapidly.
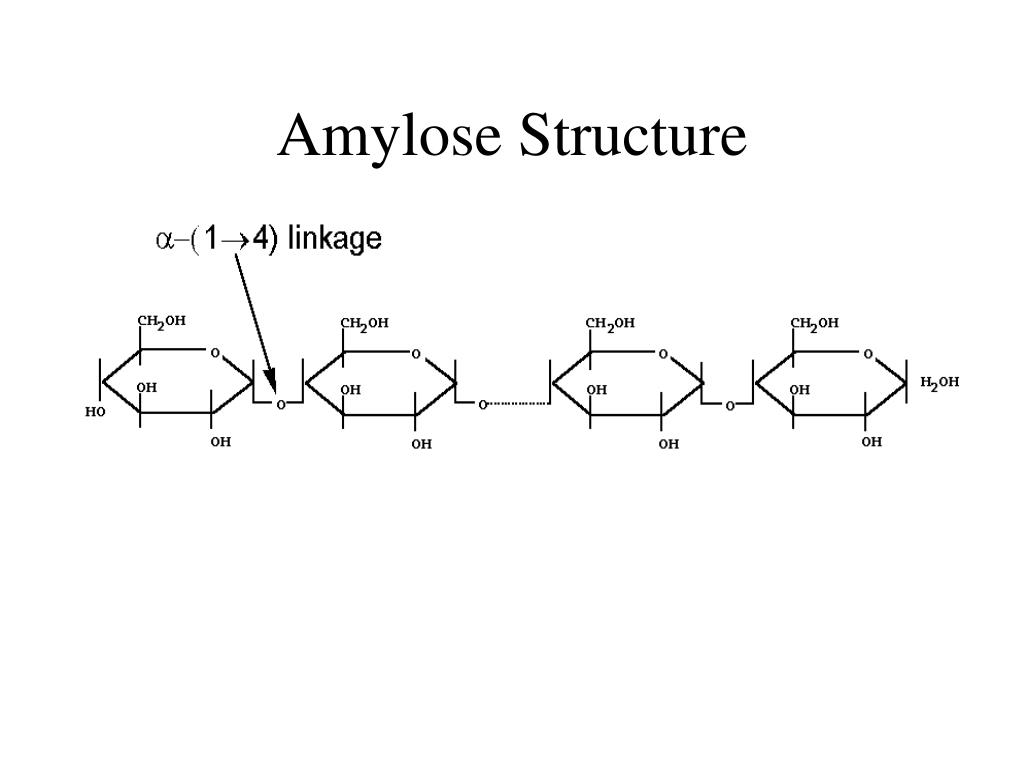
Amylose
Long, unbranched chain of alpha-glucose. Forms a 1-4 glycosidic bond through condensation reactions. Coiled structure= good storage, can fit more into a small space. Hydrogen bonds help hold it in its helical structure
Amylopectin
long, branched chain of alpha-glucose. 1-6 glycosidic bonds create a branch. Its side branches allow enzymes that break down the molecule to get at glycosidic bonds easily= glucose released quickly
Where is glycogen found
animal and bacteria cells. In animals it’s stored as small granules mainly in the muscles and the liver. Mass of carbohydrate stored in animals is relatively small because fat is the main storage molecule.
glycogen structure
apha-glucose. similar to starch- has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. However, it has shorter chains and is more highly branched
glycogen role and propeties
main role= energy storage:
Insoluble: doesn’t draw water into the cells by osmosis and doesn’t diffuse out of cells
Compact: a lot can be stored in a small space
More highly branched: more ends that can be acted on by enzymes. More rapidly broken down to form glucose monomers, used in respiration. Important for animals to have a higher metabolic rate + respiratory rate than plants bc they are more active.
where is cellulose found
plant cell walls
cellulose structure
Made of monomers of beta-glucose. Straight, unbranched chains that run parallel to each other, allowing hydrogen bonds to form cross-linkages between adjacent chains- adds little to the strength, but overall number makes contribution. Cellulose molecules grouped together to form microfibrils- arranged in parallel groups called fibres.
Cellulose main role and properties
Main role= providing support + rigidity:
made of beta-glucose= form long, straight, unbranched chains
they run parallel to each other + crossed linked by hydrogen bonds → add to collective strength
molecules grouped to form microfibrils → grouped to form fibres which provides more strength