Unit 4: Linear Momentum
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
motion in which the center of mass of an object or system changes position
linear momentum
motion where c.o.m changes position is ________ or ___________ motion
linear / tranlational
t/f: momentum is a vector
t
t/f: momentum + velocity are SOMETIMES in the same direction
f; they are ALWAYS
momentum equation
p = mv
units for momentum
kg⋅m/s
A 15,000.0 kg rocket launcher holds a 5000.0kg rocket. The rocket exits the launcher at +450.0m/s. What is the momentum of the rocket?
+2250000 kg m/s
law of conservation of momentum
if there is no outside force, a system/object’s momentum remains constant
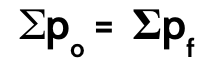
law of conservation of momentum
t/f: external force exerted on an object or system can change the momentum of that object/system
t
the direction of force is _____________ as the direction of change in momentum
the same
F equation in terms of momentum
(change in momentum)/t
change in momentum is called
impulse
impulse equation
change in p = m(v2-v1)
t/f: impulse and momentum have the same units
t
_________ is an interaction in which forces are exerted for a finite period of time
collision
elastic collisions have conservation of _______________
KE and p
inelastic collisions have conservation of _______________
momentum
t/f: If the momentum before an interaction is zero, then (assuming no interfering force, such as friction or gravitational force) the momentum afterward is equal to a positive number
f; it should be equal to 0 because no outside forces act upon it
A cart with mass 1.5 kg moving at 4.0 m/s to the right collides head-on with a cart with mass 3.0 kg moving at 4.0 m/s to the left. After the collision, the 1.5 kg cart is moving to the left at 2.0 m/s. What is the 3.0 kg cart doing after the collision?
-1.0 m/s
total inelastic collision
the objects stick together during the collision and move as one object after the collision.This means they have the same velocity after collision.
darts or arrows or embedding into objects, sticky clay, train cars locking/latching together indicate what type of collision?
totally inelastic
A cart with mass 1.5 kg moving at 2.0 m/s to the right collides head-on with a cart with mass 3.0 kg moving at 3.0 m/s to the left. Their bumpers lock. What are they doing after the collision?
-1.3 m/s; they are moving as one object to the left
A cart with mass 1.5 kg moving at 4.0 m/s to the right collides head-on and elastically with a cart with mass 3.0 kg moving at 4.0 m/s to the left. After the collision, what are the carts doing?
1.3 m/s
where does lost KE go during inelastic collisions
the “lost” kinetic energy is transferred to thermal energy of molecules and to the sound you hear from the collision (which is actually also a form of thermal energy of molecules)
which type of inelastic collision is most common in real life?
partial/incomplete inelastic
the area under the curve for a F v. t graph
impulse
What is the impulse of the cart of mass 2.0 kg moving at 3.0 m/s if the cart is moving at -2.5 m/s after hitting the block?
-11 kg⋅m/s
What is the impulse of the block if a cart of mass 2.0 kg moving at 3.0 m/s if the cart is moving at -2.5 m/s after hitting the block?
+11 kg⋅m/s
F equation in terms of impulse
I/t
What is the force exerted on a cart of mass 2.0 kg moving at 3.0 m/s if the cart is moving at -2.5 m/s after hitting the block and being in contact with it for 1.0 ms? What is the force exerted by the cart on the block?
(1) -11,000 N
(2) +11,000 N
the point in any object around which the mass of the object is evenly distributed
center of mass
Translational motion is a change in position of the _____ of an object
center of mass
t/f: for small macroscopic objects (the majority of our studies in this class), the center of mass is the same location as the object’s center of gravity
t
You are given an object of mass 3 kg, a second object of mass 1 kg located 4 cm away from it, and a third object of mass 2 kg located 2 cm toward the second object and 3 cm perpendicular to a line between the first two. What is the center of mass of the system?
(1.33, 1)
non-head-on collision definition
velocity vector of each object do not point at each others’ center of mass
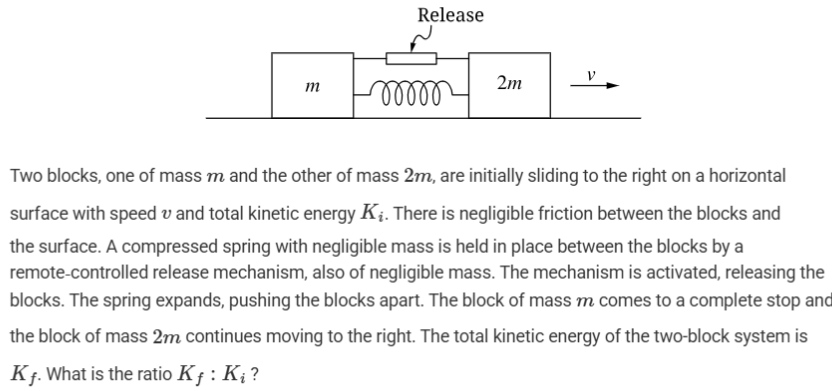
3:2
center of mass equation
(∑mx)/(∑m)