Clin Med 1 Infectious Disease 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Staphylococcus aureus
The most common staphylococcal infections
Normally on the skin, Break in skin or mucous membrane, Suppurative - form abscesses/ pus-filled
What can staphylococcus aureus cause?
Cellulitis, folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles in skin
How does staphylococcus aureus spread?
Through hematogenous spreading (blood)
Bone, joint, and heart valves
How to control staphylococcus aureus?
Proper handwashing
What does MRSA stand for?
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
How is hospital vs community acquired MRSA different?
Hospital MRSA is severe and hard to treat
Community acquired is mild and needs an antibiotic to treat
Why is MRSA more prevalent?
Misuse of antibiotics, Resistant to more antibiotics
Where is MRSA colonized?
Nasal Mucosa
How to treat MRSA?
Clindamycin, sulfa, and possibly quinolones if skin infection
Need aggressive IV antibiotics if more severe
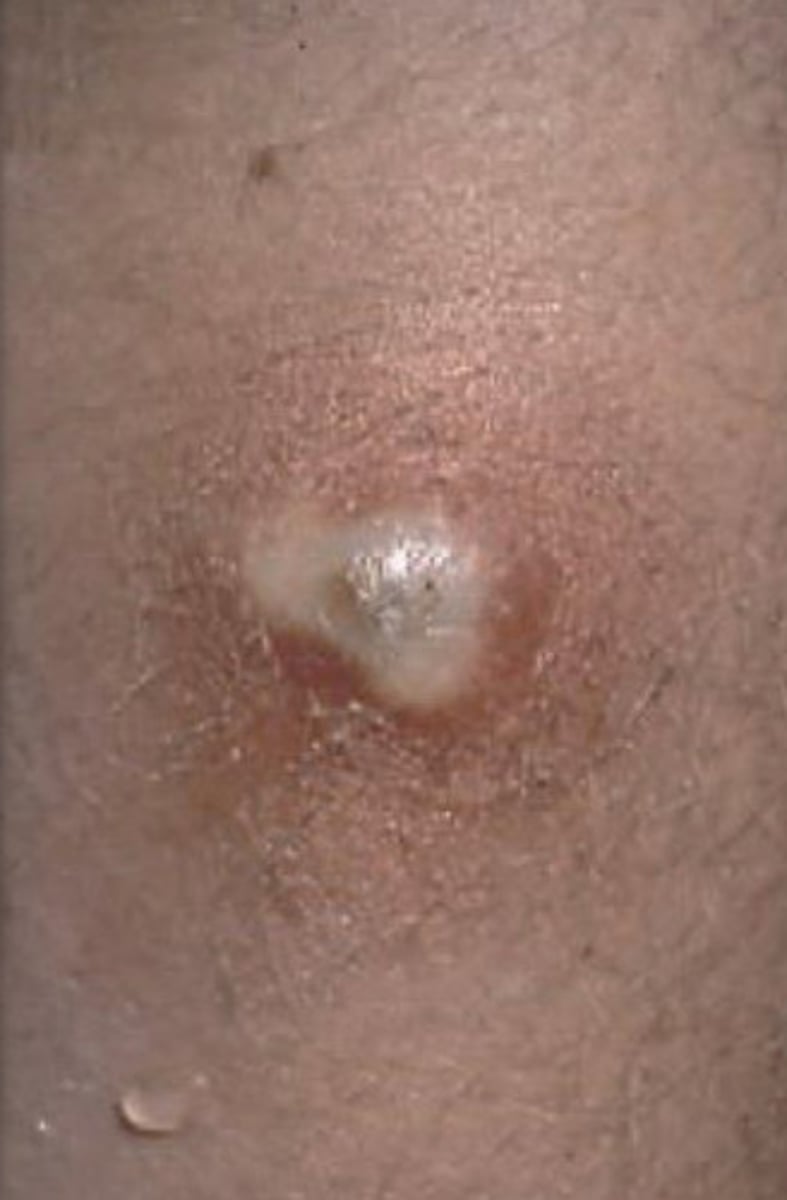
How does MRSA present?
Infection of open wound, pimple-like lesion, spider bite, infected mosquito bite
Progresses quick
Forms abscesses
MRSA
What is streptococcus pyogenes?
group A strep
True of False: Streptococcus pyogenes is the most common bacterial cause of pharyngitis.
True
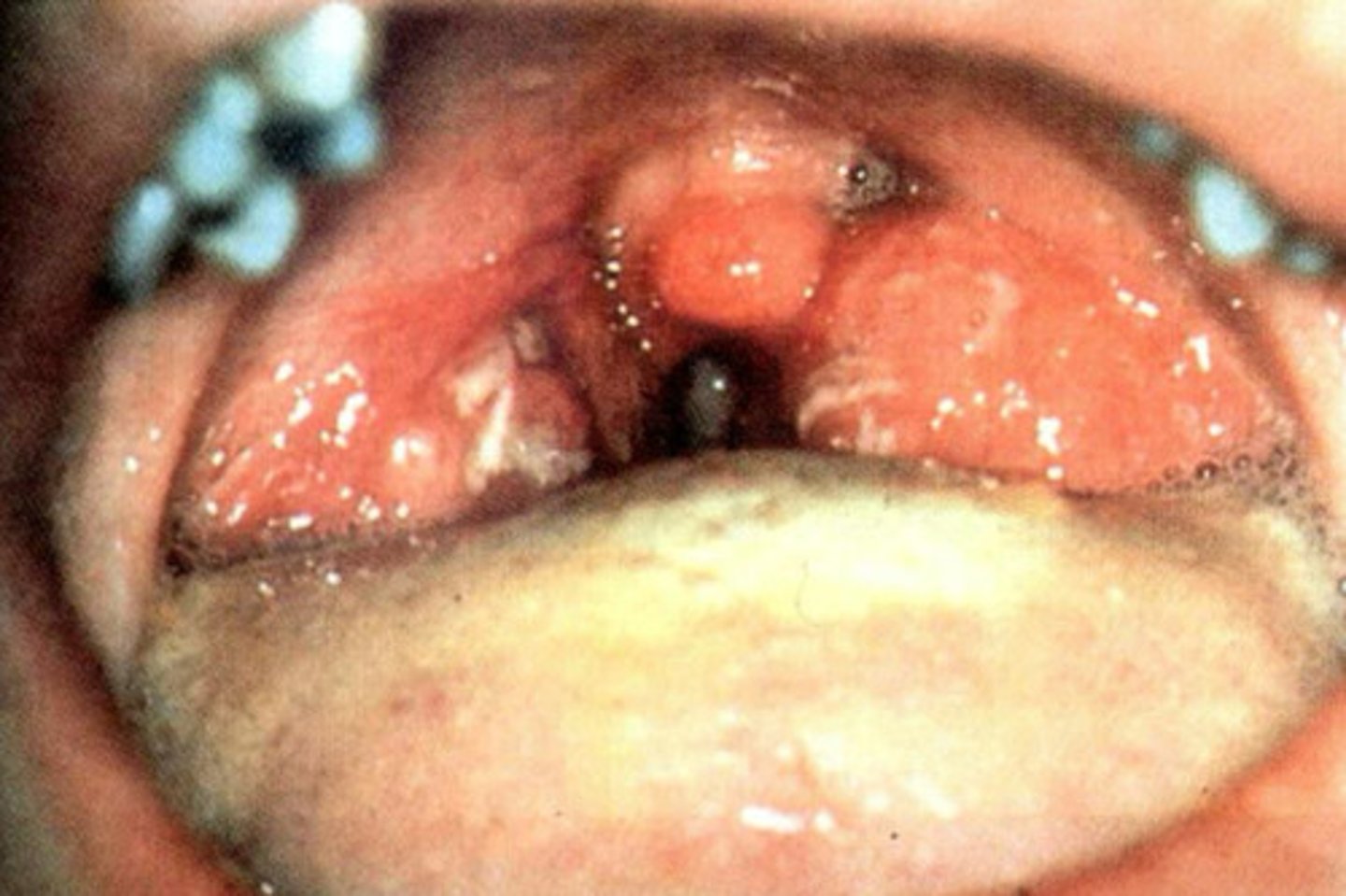
What are the symptoms for streptococcus pyogenes?
Sore throat w/o runny nose or cough, Fever, Headache, Nausea, Exudate, Lymphadenopathy
Strep throat
What are the ways of evaluating strep throat?
Culture, Rapid strep test
Why is a culture not as good at evaluating strep throat?
Duration of time to find is not as reliable
Why is rapid strep test a good test?
Antigen test and quick
Treatments for strep throat
Self-limited, Penicillin to avoid complications
Complication of strep throat
Rheumatic Fever
What does rheumatic fever do?
Diffuses the inflammation process
What type of hypersensitivity is Rheumatic Fever?
Type 2 hypersensitivity, Cross-reactive antibodies
What are the signs and symptoms for rheumatic fever?
Migratory arthralgias (spreading joint pain), Subcutaneous nodules, Chorea (abnormal moves - dancing or smooth moves), Flat skin rash, Valvular destruction, Weakness, Malaise (feeling ill), weight loss, anorexia
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
A complication of strep throat
Hypersensitivity of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Type 3 hypersensitivity, Affects the glomerulus of kidneys
What is Streptococcus pneumoniae also known as?
pneumococcus
Can streptococcus pneumoniae be seen on a gram stain? If so, how does it present?
Yes, it does present on a Gram stain. Presents as a diplococcus
What is the most common cause of pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
What can Streptococcus pneumoniae cause?
Otitis media (ear infection), Meningitis, Sepsis
What are vaccines for children for streptococcus pneumonia?
Prevnar
What are the vaccines for adults for streptococcus pneumoniae?
Pneumovax
Where is c. difficile found?
Normal flora in the intestines
True or False: C. diff is not resistant to antibiotics
False
Wha happens if antibiotics kill off other normal flora?
C. diff can overgrow
What is the inflammatory infection of c. diff?
Pseudomembranous colitis
How to get rid of c. diff?
Soap and water, Alcohol sanitizer does not work
What is pseudomonas?
A common nosocomial infection (health care environment infection)
What are the risk factors of pseudomonas
Burns, urinary catheters, cystic fibrosis, chronic lung disease, swimming pools, whirlpools
What does pseudomonas result in?
Pneumonia, UTI, and wound infections
What is the rate of resistance for pseudomonas?
High