PSYCH 1/2 - EXAM SEM 1
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Psychological Development
The way a person grows and changes over time.
Nature (Hereditary Factors)
Inborn or inherited factors genetically passed from biological parents. EG - genes
Nurture (Environmental Factors)
Experiences, objects, and events to which we are exposed to across our lifetime.
EG - learning environment
Interaction
A person's genes give them potential, but whether this potential is reached depends on their environment.
The Biopsychosocial Model
Examines how biological, psychological, and social aspects all play roles in health and disease.
Biological Factors
Physical health, disabilities, and genetics
Psychological Factors
Behaviour, beliefs, personality, and mental health
Social Factors
Education, peers, childhood trauma, and work
Sensitive Periods
A time when a person is more receptive to learning skills. Eg. Ideal time that something happens in - learning instrument as a child is easier than an adult
Critical Periods
A short, specific time when a skill or ability must be developed; if not learned, it may never be developed. Eg if a child isn't exposed to language during their first few days of life then they may struggle to develop the skill later
Emotional Development
How an individual experiences different feelings and how those feelings are expressed. Eg. The way anger is expressed by a 10-year-old compared to a 60-year-old.
- ainsworths attachment theory
Harlows experiment on attachment in monkeys
Cognitive Development
Changes in a person's mental abilities over time.
Eg. Reasoning, learning
Assimilation
Adding new info to existing ideas.
EG - seeing a Dalmatian and thinking "this is a dog"
Accommodation
Adjusting existing ideas after new experiences.
EG - "whales aren't fish but they just live in the ocean"
Social Development
Changes in a person's relationships and interaction skills.
EG - Msingsining relationships
Typical Behaviour
Behaviour you expect; occurs at expected stages.
EG - Eg. Meeting milestones, sleeping at night
Atypical Behaviour
Unusual or unexpected behaviour.
EG - Staying up for days without sleep
Normality
Patterns of behaviour that are typical and expected.
Abnormality
Behaviour that is unusual or strange.
Neurotypicality
People with typical brain development and cognitive functioning.
Neurodiversity
Refers to neurological differences (e.g., ADHD, autism) being normal variations of human functioning, not deficits.
Adaptive
Any behaviour that allows someone to adjust to the environment.
EG. Studying consistently for a good grade - "I can learn from mistakes"
Maladaptive
Behaviour that stops a person from adjusting to the environment.
EG - Extreme anxiety before social interactions - "I will never be good at this
Cultural Perspectives
Different cultures have different views of normal/abnormal behaviour.
EG - making slurping sounds with noodles in Japan is appropriate but not in Western countries
Social Norms
Behaviour that goes against what most people in society see as normal.
EG - don't push in line, go to the back
Statistical Rarity
Behaviour that is unusual compared to what most people do.
EG - having a super high IQ like 160 is rare
Personal Distress
Behaviour that causes the person to feel upset or stressed.
EG - feeling extreme sadness for weeks may show a mental health issue
Maladaptive Behaviour
Behaviour that makes it hard for someone to live their daily life.
EG - not going to school because of anxiety - stops normal functioning.
Autism
Differences in communication, behaviour, and social interaction.
EG - difficulty understanding sarcasm
ADHD (Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
Affects attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
EG - people get easily distracted fidget and squirm
Dyslexia
Affects reading and spelling.
EG - mixing of letters, struggle matching letters to sounds
Psychologists
Study for 6 years (no medical degree) and focus on mental and emotional issues.
Psychiatrists
Study for 12 years (with medical degree), can prescribe medication, and treat serious mental illnesses
Monozygotic Twins (Identical Twins)
They have 100% the same DNA, are always the same sex, and look very similar.
Dizygotic Twins (Fraternal Twins)
They share about 50% of their DNA (like any siblings), can be same or different sex, and may not look alike.
Independent Variable (IV)
The thing that you change in the experiment; it's what you're testing to see if it has an effect.
Think: "I" change this.
Dependent Variable (DV)
The thing that you measure in the experiment; it's what changes because of the independent variable.
Think: "Depends" on the IV.
Control Group
The group that isn't exposed to the IV.
EG - If you're testing if music helps with studying, the control group studies with no music.
Brain vs heart debate
Egyptians believed the heart was the most central for mental processes while the Greeks thought it was the brain.
Mind-body problem
French philosopher didn't know whether the mind controlled the body or if the body controlled the mind.
Phrenology
Technique used to predict your behaviour and characteristics based on weather lumps and bumps with sitting on the surface of the skull.
Brain ablation and lesioning
Brain ablation is the surgical removal of tissue and brain lesioning damaging specific brain areas; this was used to observe behavioural changes.
Split brain research
In the experiment, information is sent to one side of the visual field only; it examines patients whose corpus callosum has been severed.
- Info from the right visual feild is seen by the left side of each eye and sent to the left hemisphere
CT scan
Patient receives an injection of iodine dye into the blood vessels to act as a contrast to the features of the brain.
MRI
Harmless magnetic field that is used to produce a more clear and detailed image than a CT scan.
PET
Produces a computer generated image involves using radioactive glucose which is harmless and is injected into the body.
FMRI
Measures brain activity by detecting red blood cells that contain iron (has magnetic properties).
Cerebellum
( hind brain)
Helps co-ordinate voluntary movement, core balance and repetitive tasks.
Medulla
( hind brain)
Vital functions such as breathing, heart rate.
Pons
( hind brain)
Sleep + breathing.
Reticular formation
(midbrain)
Regulates flow of information to the brain and modulates incoming sensory stimuli.
Hypothalamus
(forebrain)
Homeostasis, hormones, hunger + thirst.
Thalamus
(forebrain)
Transmits sensory info except for smell.
Cerebrum
(forebrain)
Responsible for cognitive functions + voluntary movement.
Cerebral Cortex
Outermost layer of the brain responsible for complex mental functions (language, memory + reasoning).
Left hemisphere
Language, writing, logic, maths.
Right hemisphere
Spatial/visual tasks, music, art, face recognition.
Frontal lobe
Higher mental functioning such as thinking planning and organising.

Primary motor cortex
Controls voluntary movement and fine motor skills.
Prefrontal cortex
Responsible for executive functions like planning and decision making.
Broca's area
Responsible for language production.
Parietal Lobe
Receives sensory information within the lobe and controls spatial reasoning and attention
Primary somatosensory cortex
Receives and processes sensory information responsible for touch temperature pain and body movements.
Occipital lobe
Processing of visual data and interprets visual data to form visual perceptions.
Primary visual cortex
Processes visual information (line colours and textures).
Temporal lobe
Functions: memory, face recognition.
Primary auditory cortex
Receives and processes sound.
Wernicke's area
Language comprehension (left hemisphere).
Neuroplasticity
The brain's ability to change and adapt its structure and function in response to experience, learning or injury.
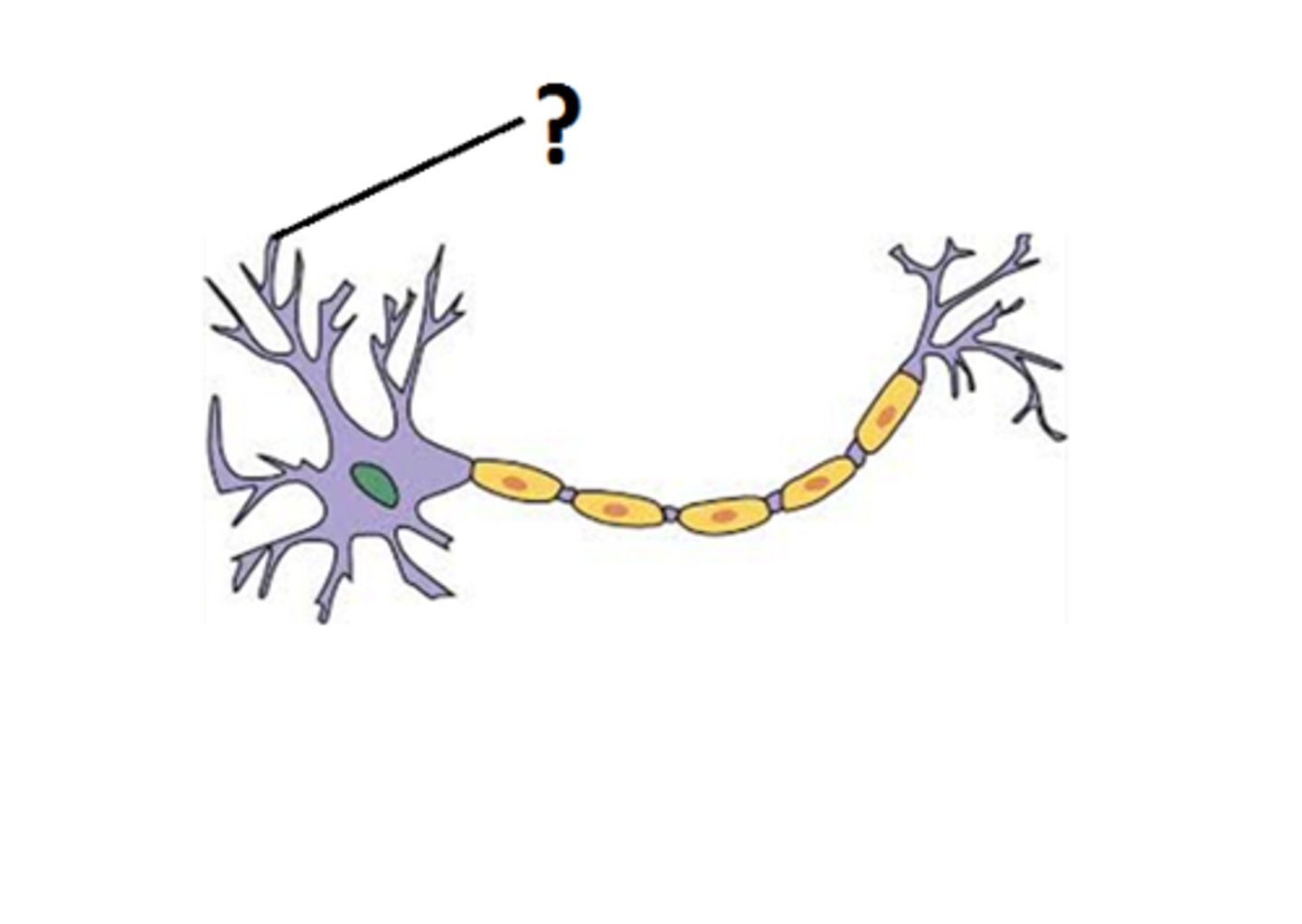
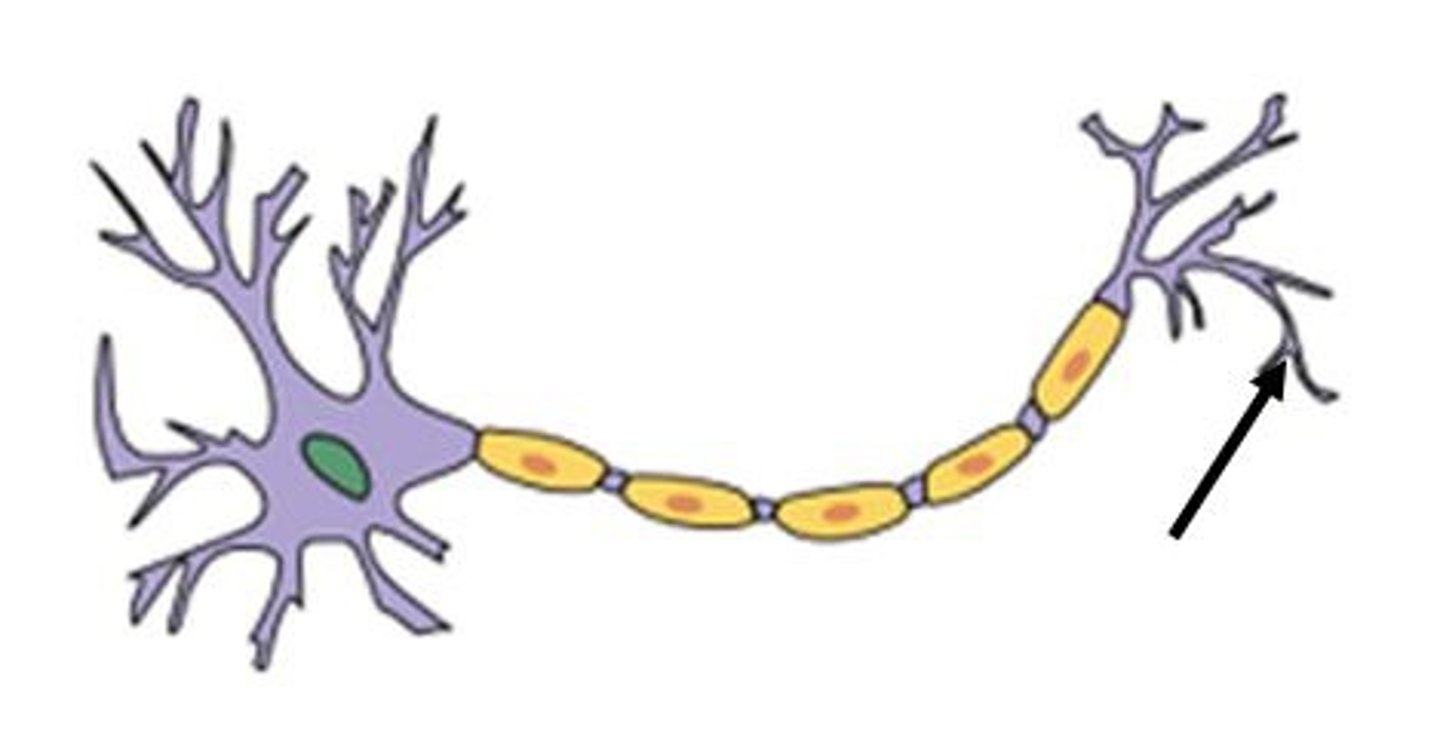
Dendrites
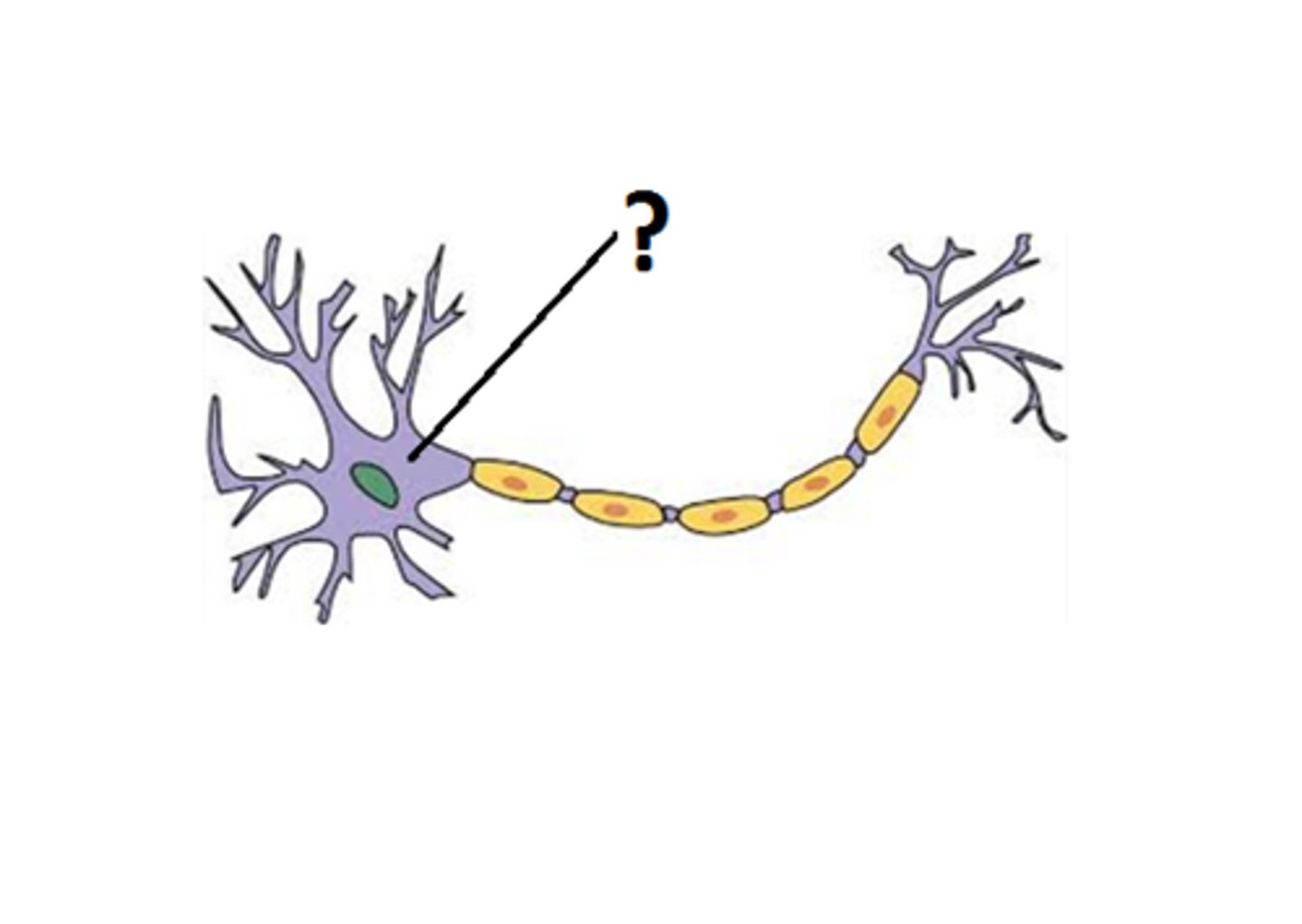
Soma
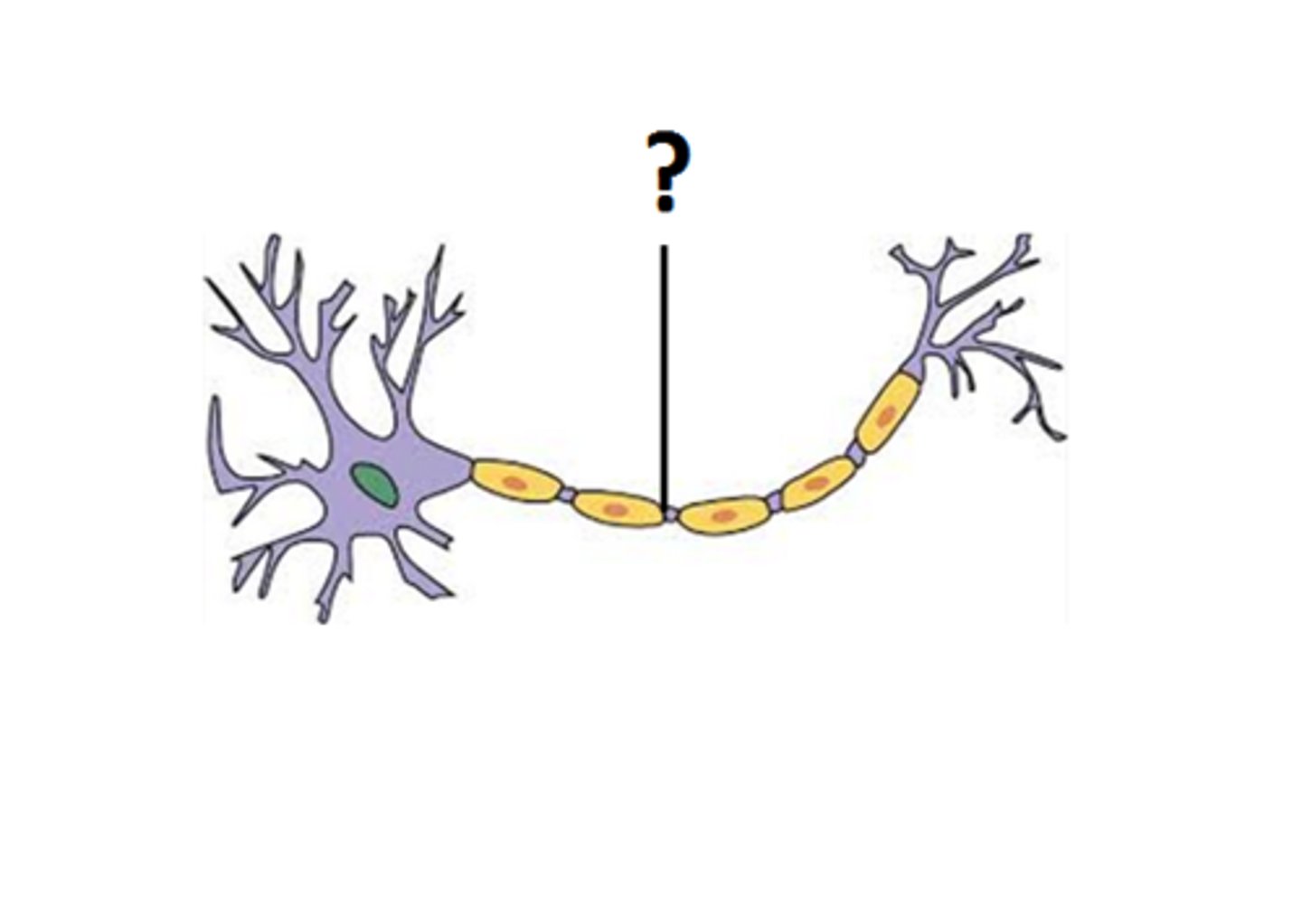
Nucleus
Axon
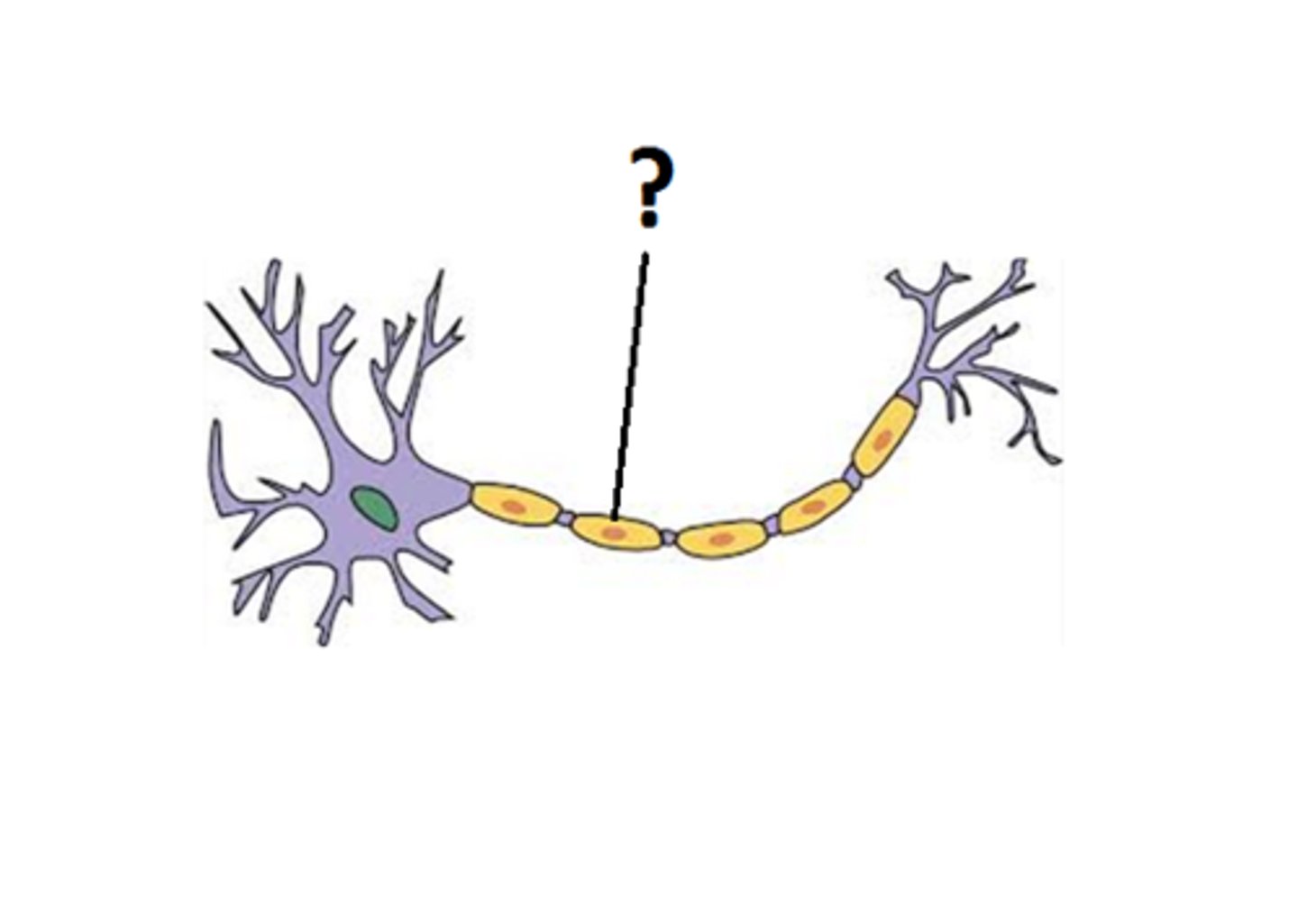
Myelin sheath
Axon terminal
Experience-expectant plasticity
Refers to the brain's ability to adapt and change in response to the environmental experiences during development (EG- sound, language and exposure to light).
Experience-dependent plasticity
Refers to the ability of the brain to change and adapt its neural connections based on specific individual experiences (EG- learning new skills, adapting to a new environment).
LTP
Strengthening of synaptic connections.
LTD
Weakening of unused synapses.
Synaptogenesis
Creation of new synapses.
Synaptic pruning
Removal of unused synapses.
Myelination
Coating axons with myelin for faster communication.
Sprouting
Growth of new dendrites to connect with axons.
Rerouting
Creating new neural pathways around damage.
Acquired brain injury
Brain damage that occurs after birth.
Sudden onset
Happens quickly (e.g. trauma, stroke, infection, alcohol/drug overdose).
Insidious onset
Develops slowly (e.g. tumour, degenerative disease, prolonged alcohol use).
Concussion
A type of acquired brain injury caused by a blow to the head.
Neurological disorders
A condition that affects the brain or spinal cord, often long lasting, impacting language, movement, vision, cognition.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
Progressive brain disease caused by repeated head trauma. Tau protein cannot breakdown because of the trauma so it kills cells
Symptoms of CTE
Memory loss, confusion, depression, anxiety.
Diagnosis of CTE
Only diagnosable after death using autopsy (look for abnormal tau protein buildup).
Treatment of CTE
No cure, but medications can help manage mood symptoms, anxiety, seizures, etc.
Epilepsy
Neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures.
Parkinson's disease
Progressive neurodegenerative disorder that mainly affects movement and coordination.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
Tremors, slowed movement, balance issues, speech changes.
Neuroimaging
Non-invasive scans (EEG, CT, MRI, fMRI, PET) that help study the brain.
Animal studies
Used to explore causes, treatments, and effects of neurological disorders.