AQA Computer Science (Paper 2) - Computer System, Computer Networks, Cyber Security
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What is computer hardware?
Physical components of a computer system
What are the 2 main types of hardware
internal & external (aka. peripheral devices)
What is internal hardware? + examples
Physical components IN a computer system which help it process info.
Examples: CPU, RAM, motherboard, graphics card, HDD
What is external hardware? + examples
Physical components OUTSIDE or connected to a computer system.
Examples: keyboard, monitor, mouse, USB port, microphone
What is computer software?
Collection of programs, data and instructions that run on a computer
What are the two main types of software?
Systems & application software
What are system softwares & the two types of systems software?
= software that manages hardware & provides platform for application software
2 main types are: operating systems & utility software
What are operating systems & what are their functions?
= collection of programs that manage and control the computer.
Functions: MUMPS - memory management, user interface, multitasking, peripheral management, security!
List some examples of operating systems
iOS, android, windows
What is utility software? (+examples)
= software that helps maintain the computer system
eg. antivirus , encryption, data compression softwares
What is application software (aka. apps)? (+examples)
= software that performs end-user tasks
eg. word processors, web browsers, media players, CAD software
What is a device driver?
= a type of software which enables communication between the operating system and a hardware device
What are the 4 types of logic gates & how do they work?
1. AND Gate: Outputs 1 only if both inputs are 1; otherwise, it outputs 0.
2. OR Gate: Outputs 1 if at least one input is 1; outputs 0 only when all inputs are 0.
3. NOT Gate: Inverts the input; if the input is 1, the output is 0, and vice versa.
4. XOR (Exclusive OR) Gate: Outputs 1 if the inputs are different; outputs 0 if the inputs are the same.
What Boolean operators are used for each logic gate?
. → AND gate
+ → OR gate
⊕ → XOR gate
Overbar [line above letter] → NOT gate
What are the main difference between low-level and high-level programming languages? (2 points for each + examples)
Low-level (eg: machine code, assembly):
Closer to machine code
Less readable and more complex
High-level (eg: Python, Java):
Closer to human language
Easier to debug and maintain
What are the differences between machine code and assembly language?
Machine code:
Consists of binary that the CPU directly executes (doesn’t need to be translated)
Specific to a type of processor
Assembly code:
Consists of mnemonics
Needs an assembler to translate code to machine code (to be processed by CPU)
Often used to make software for embedded systems
PS: Each assembly language instruction matches a machine code instruction exactly
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of low-level programming languages?
Pros:
Faster execution
More detailed control over hardware
Cons:
Hard to read and write
Less portable - specific to one processor
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of high-level programming languages?
Pros:
Easier to read and write
Have convenient features/libraries to improve development
Cons:
Less control over hardware (compared to low-level)
Slower code → abstraction & longer processing time
What is a translator?
Program that translates source code into machine code
What are the 3 types of program translators? (+outline how they work)
Interpreters - translates code line-by-line
Compiler - translates all the code in one go
Assembler - translates assembly code to machine code
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of an interpreter?
Pros:
Stops when it reaches an error- good for debugging
Can run on many types of CPU
Cons:
Slower than compilers
Doesn’t produce a compiled file - re translates each time program runs
What are 2 pros and a con of a compiler?
Pros:
Produces an executable program - don’t need to repeat process more than once
Hides source code from end user - protects intellectual property
Cons:
Compilation process is quite slow
What are 2 pros and a con of using assemblers?
Pros:
Exact control over hardware
Quick & efficient
Con:
Less portable across different CPUs
What is the CPU + what does it do?
Component that processes data/ instructions and controls the computer system
What are the 5 main components of a central processing unit (CPU)?
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Control Unit
Clock
Register
Bus
What does the Arithmetic Logic Unit do?
= CPU component that performs the operations on the data
What does the Control Unit do?
= CPU component that control and manages the execution of instructions
What are registers?
= quick & small stores of data within the CPU
What is a bus + what does it do?
= Collection of wires that data/signals are transmitted through from one component to another
What is the clock + what does it do?
= CPU component that provides timing signals to keep the CPU in sync
What happens at each stage of the Fetch-Execute cycle?
Fetch:
Instruction retrieved by CPU from main memory
Decode:
Instruction broken down into main components
What is does is determined as well as data used
Execute:
Control unit performs necessary circuitry/data transfers
Output stored in register
Data may be read/written to/from main memory.
What is main memory?
= any form of memory that is directly accessible by the CPU
What are 2 examples of main memory?
RAM (random access memory) & ROM (read only memory)
What are the 2 types of memory? (Outline + examples)
Volatile memory = loses its data when power is lost - eg. RAM, cache
Non-volatile memory = retains its data when power is lost - eg. ROM, hard disk
What does the RAM do & why is it needed?
Random access memory (named as it can access/store data from any location within memory)
= volatile main memory that holds data and programs currently in use
Why it’s needed: quick read/write times so it responds to tasks quickly
What does the ROM do & why is it needed?
Read Only Memory
= non-volatile main memory that stores essential programs & can only be read (not edited)
Fairly small
What is a cache & why is it needed?
= a type of memory that stores copies of frequently used data
Faster + lower capacity than RAM
Why it’s useful: Closer to processor + checked before RAM in ‘fetch’ stage
What is secondary storage?
= any non-volatile storage device not directly connected to the CPU
Why is secondary storage needed?
So that there is non-volatile storage available
What 6 factors should be considered when evaluating types of secondary storage devices? (Name at least 3)
Capacity
Cost
Durability
Portability
Reliability
Speed
What are the 3 main types of secondary storage?
Solid state
Optical
Magnetic
How does optical storage work?
A laser burns pits into the disc surface to write binary data (lands = 1s and pits = 0s).
The laser shines on the disc & light reflects differently for pits or lands.
The drive reads these reflections, converting them into digital data
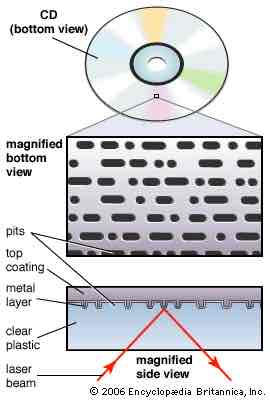
Give an example of an optical storage device
CD (compact disk)
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of optical storage?
Pros:
Very portable (easy to transport + compatible)
Durability (resistant to water/dust)
Cons:
Small capacity (less than SSDs)
Fragile (easily scratched/damaged)
How does magnetic storage work?
Small areas of the disk’s surface are magnetised (1s) or demagnetised (0s)
Read/write head contains electromagnets that can read or alter the magnetic state, for data to be stored/recieved
Data stored in tracks on the disk
Give an example of a magnetic storage device
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of magnetic storage?
Pros:
Large capacity
Cheap to buy
Cons:
Not very portable
Generates lots of noise & heat
How does solid state storage work?
Consists of digital circuits that retain data and can be changed
Non-mechanical
Give an example of a solid state device
SSD (solid state drive)
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of solid state storage?
Pros:
Very fast
Very reliable
Cons:
Smaller capacity than magnetic
Expensive
What is cloud storage?
= where data is stored on multiple servers in a remote location
servers use magnetic or solid-state storage
What s an embedded system?
= a special purpose computer encapsulated by a larger system
Give 2 examples of embedded & non-embedded systems
Embedded system: microwave, autopilot of a plane
Non-embedded system: laptop, phone
What are 3 characteristics of an embedded system?
Tend to:
Have memory & CPU on same chip (easier to manufacture)
Has more ROM than RAM (as data doesn’t need to be changed + is cheaper)
Work in real-time (no delays after taking input, unlike a laptop)
What is a network?
= 2+ devices connected together for communication purposes
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of cloud storage, compared to local storage?
Pros:
Portable - files accessed from anywhere on internet
Cost effective for large companies (instead of large local storage software)
Cons:
Dependence on internet connection
Slower than local storage
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of having a network?
Pros:
File sharing across devices
Centralised management of security and updates across devices
Cons:
More vulnerable to viruses and hacking
Specialists needed for maintenance
What are the 3 types of computer network?
Personal Area Network (PAN)
Local Area Network (LAN)
Wide Area Network (WAN)
What are the characteristics of a PAN?
For close proximity devices (<10 metres)
Bluetooth = most commonly used PAN
What are the characteristics of a LAN?
Has small geographical area (under 1 mile)
Managed by single person/company
What are the characteristics of a WAN?
For wide geographical area (over 1 mile)
Collection of LANs joined together, under collective ownership
Internet = biggest WAN
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of wireless networks, compared to wired ones?
Pros:
More portable as location is only limited by range
Less expensive to setup & add devices
Cons:
Slower data transfer than wired
Less secure/safe than wired
What are the 2 main LAN topologies?
Star
Bus
What is a bus topology + how does it work?
= All devices are connected on a single ‘bus’ cable, terminated at each end (stops signal bouncing back)
At each device: 1) Listens to electrical signals. 2) checking data packets for specific address. 3) Ignoring data packets it doesn’t recognise
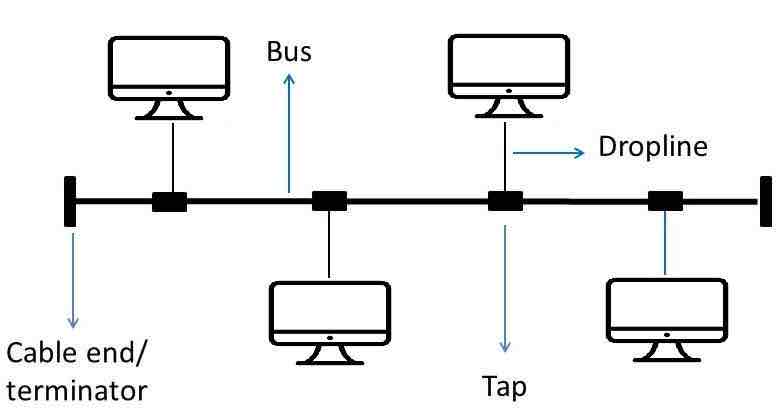
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of a bus topology?
Pros:
Easy and cheap to set up (only 1 cable is required)
Doesn’t rely on any other network hardware (eg. Central hub)
Cons:
Prone to data collisions
If cable breaks, whole network is affected
What is a star topology?
= all devices are connected to a central switch/hub
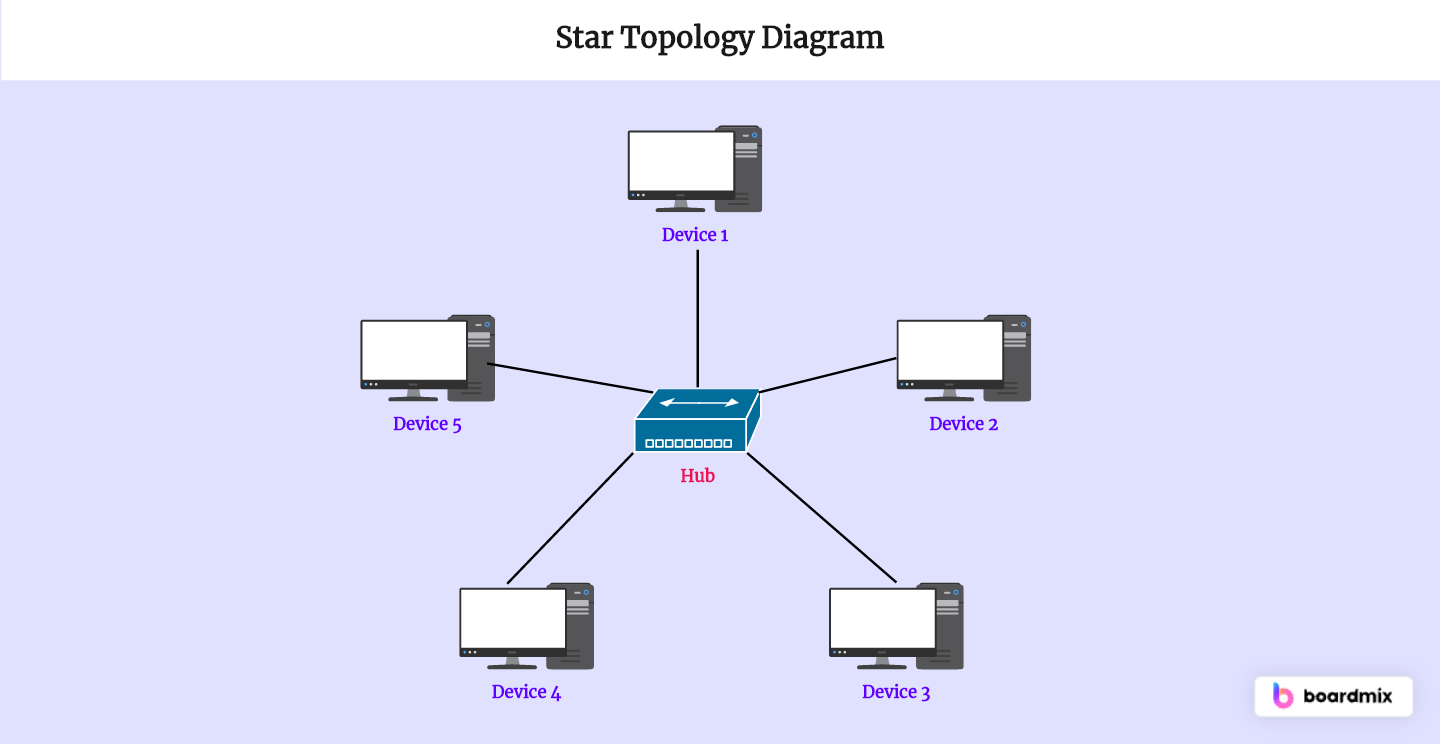
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of a star topology?
Pros:
Network can still work even if single cable stops working
High speed + most efficient topology
Cons:
If central switch stops working, entire topology fails
High maintenance costs
What is cyber security?
= involves safeguarding systems and data from attacks, damage, and unauthorized access
What is social engineering?
= manipulating people into sharing confidential information or performing actions that compromise security
What are the 3 main types of social engineering?
Phishing
Shouldering
Blagging
What is phishing?
= fraudulently obtaining private info, often via email or SMS
What is shouldering?
= observing someone’s private info over their shoulder
eg. at an ATM
What is blagging?
= tricking someone into giving private information by pretending to be someone trustworthy
What is pharming?
= a cyber attack intended to redirect a website’s traffic to another, fake site
What is malware?
(Malicious code) = code intended to cause undesired effects, security breaches or damage to a system
What are the 4 main types of malware?
Computer virus
Trojan horse
Adware
Spyware
What is a computer virus?
= piece of code able to copy itself and have a detrimental effect
What is a trojan horse?
= malware that hides within seemingly harmless programs
What is adware?
= malware that presents unwanted ads on a computer (pop up ads)
What is spyware?
= malware installed onto a computer to collect personal information or monitor internet browsing
What are 3 ways to reduce risk of malware?
Read software license agreements before installing
Update anti virus software regularly
Don’t open email attachments from people you don‘t know
What is penetration testing + what is it used for?
= security assessment where professionals simulate cyber attacks to identify vulnerabilities
What are the 2 main types of penetration testing?
Malicious insider: tester simulates attack from inside and has knowledge of basic system credentials
External attack: tester simulates attack from outside with no knowledge of system credentials
What are 4 security risks?
Weak passwords
Misconfigured access rights (incorrectly set permissions)
Removable media (physical storage devices)
Outdated software (not updated to fix security flaws)
What are some security measures to prevent cyber security threats?
Biometric measures
Passwords
CAPTCHA
Email confirmations (to confirm identity)
Automatic software updates
What is a database?
= A structured, persistent collection of data
What are the 2 types of databases?
Flat file databases & relational databases
What are the benefits of using relational databases over flat file databases? (give 2 benefits)
Reduce data redundancy (as records can be linked & redundant data easily identified)
Eliminates data inconsistency (as all related data can be updated at once)
What is a relational database?
= a database that organises data into multiple related tables
What is a primary key?
= a field that uniquely identifies a record in a table
What is a foreign key?
= a primary key in another table that makes a link between tables
What SQL command(s) is used to select a data item?
SELECT field
FROM table
WHERE primary key = …
ps - if field value is a string, don’t forget quotation marks “”
What SQL operator do you use to select all columns in a table?
* ← aka a “wildcard”
Eg: SELECT * FROM table_name
What SQL command is used to sort data into ascending or descending order?
ORDER BY ASC field
ORDER BY DESC field
What SQL command(s) is used to insert data into a database?
INSERT INTO table_name (field1, field2,…)
VALUES (value1, value2,…)
ps - if field value is a string, don’t forget quotation marks “”
What SQL command(s) is used to update data in a database?
UPDATE table_name
SET field = …, field = …
WHERE field = condition
ps - if field value is a string, don’t forget quotation marks “”
What SQL command(s) is used to delete data in a database?
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE field = condition