Main Frame JCL | Screen and Commands Cheat Sheet
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards created for reviewing key concepts and parameters in mainframe Job Control Language (JCL).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
In JCL, JOB can also be referred to as __.
Job card or Batch Job
JCL statements are coded as records with of those bytes available for JCL code.
80-byte; 72
The __ identifies the statement in JCL so that other statements and system can refer to it.
NAME
In JCL, the OPERATION for a statement is a valid operation code such as __, __, or __.
JOB; EXEC; DD.
The __ parameter specifies the name of the data set(s) to be handled in the JCL statement.
DSNAME
In JCL, SEQ refers to __ numbers in columns 73-80.
Sequence.
The syntax of the DD statement would be defined as: //ddname DD DSN=__, DISP=(status,normal-disp,abnormal-disp).
data-set-name
In JCL, __ is used to request space for a new data set.
SPACEparameter.
When allocating space, the primary space value is the initial amount of space allocated, and the __ is the additional space that will be allocated if needed.
secondary space.
The __ parameter allows you to specify the maximum CPU time a job or job step can consume.
TIME.
In JCL, the __ parameter is used to define job classes, which dictate the characteristics assigned to a job.
CLASS.
The __ parameter is used to specify the messaging and logging destination for the job's output and messages.
MSGCLASS.
In JCL, when you use DD DSN=NAME, __ parameter specifies the disposition, or status of the data set.
DISP.
In JCL, the __ parameter, when coded, ensures that any unused space is released once the dataset is closed.
RLSE.
The __ parameter in a JOB statement is often used to inform the user when the job is finished.
NOTIFY.
In Job Control Language (JCL), a __ is a collection of related datasets, each distinguished by a generation number.
Generation Data Group (GDG).
The __ parameter allows for detailed messages to be processed based on specific conditions or events during job execution.
WHEN.
In JCL, the __ parameter can be used to define a scheduling environment that a batch job can run upon.
SCHENV.
The __ code in JCL defines the allowable conditions for job continuation or termination based on the results of previous steps.
COND.
In JCL, the __ statement is a shorthand way to define common JCL steps that can be reused across different jobs.
Procedure.
A __ DD statement allows you to append data to an existing dataset rather than overwriting it.
DISP=MOD.
The __ symbol in JCL can refer back to a previous step's outputs to establish data dependencies between job steps.
Asterisk (*) or referback.
In the output and logging within JCL, avoiding using the __ class can be critical as it often indicates that the output will not be stored for retrieval.
MSGCLASS=Z.
The __ DD statement is designed to identify output datasets to which the job's results will be directed during execution.
SYSOUT.
In JCL, how do you specify in-line source data? You use the format for the data in the DD statement.
DD *.
What does SYSUT1 statement mean?
The SYSUT1 statement is for input file or dataset
What does SYSUT2 statement mean?
The SYSUT2 statement is for output file, which will be a copy of the file identified in SYSUT1.
When you see this with in your data set (+0), What is this?
Generation Data Group. A Generation Data Group (GDG) is a collection of historically related non-VSAM data sets organized in chronological order, where each data set (or "generation") is related to the others in the group. For eample, (+0) or (0) would call the latest or current, generation of that dataset.
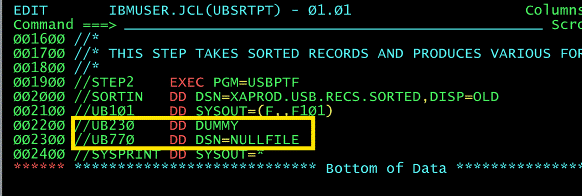
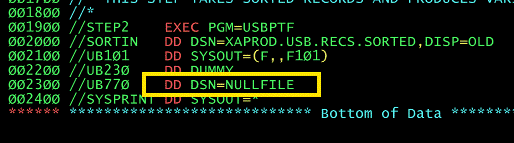
What does DD DUMMY mean?
Dummy Data Set. This is no input data set is provided to the program through SYSIN. This is used for testing purposes when the program does not require any data input.In this scenario, you will need to define the DD statement so that any data set reference is ignored. This is achieved using a DSN=NULLFILE or just specifying DUMMY for the DD statement.
What does MOD perform within the DISP parameter? For example, DISP=MOD
This will append the information at the end of an existing dataset, rather than overwrite it This is another method of sending data to an existing data set without overring the previous content.
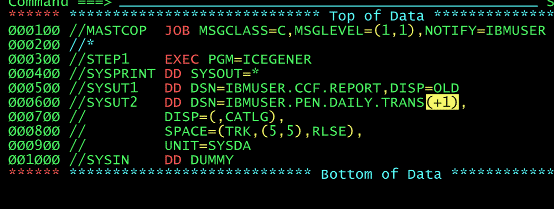
When you see DSN+IBSMUSER.PEN.DAILY.TRANS(+1)
(+1) is telling to create a new generation of a dataset.For example, if the latest generation is G0005V00, specifying (+1) will create G0006V00. (-1) refers to the previous generation.
What does TRANS mean in JCL code?
What does UNIT=SYSDA mean?
What does DCB= mean?
TRK mean in JCL code?
SPACE= (TRK,(5,5),RLSE),
// UNIT= SYSDA mean?
DISP= ( , CATLG)
DISP=PASS
What does SORTIN mean and do?
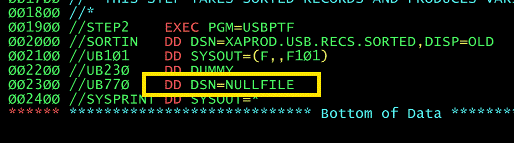
What does this Dummy, DSN=NULLFILE does?
DD statement so that any data set reference is ignored.
DISP= NEW
he DISP=NEW parameter is crucial for creating new data sets in a controlled manner within a job, ensuring that the system handles the allocation and creation of the data set correctly. the default is NEW, you can signify using the default by coding a comma.
For example, DISP=(,CATLG,DELETE). The new is the comma.

DISP= normal-disp
DISP= abnormal-disp
What do you sub parameters like for DISP?
DISP= (NEW,normal-disp,abnormal-disp)
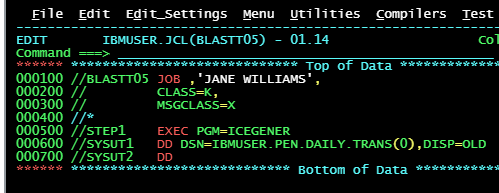
You must back-up a dataset and the SYSTI DD statement ( input dataset has been coded. How you code the backup dataset?
It is a new sequential data set
The name of the data set is: BACKUP.PENTRANS
If the step is successful then cataloged it.
Also if the step is unsuccessfully then deleted it.
How would you code this in the SYSUT2 DD statement?
//SYSU2 DD DSN=BACKUP.PENTRANS,DISP=(NEW,CATLG,DELETE)
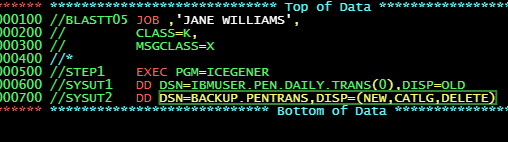
What is the purpose if this PGM=ICEGENER program?
You need to create a generation of a data set and stored in the GENREPS DD statement. This producer data is named PROD.DAILY.RLSREP and the data set is be kept complete successfully, or unsuccessfully. The environment is SMS-managed.
A new generation is specified by coding (+1) at the end of the data set name. DISP=(NEW,CATLG,CATLG)
Select True or False for each statement as it relates to an output DD statement.
An output data set with a DISP=OLD parameter indicates that data will be added to the end of the existing data set content.
False. DISP=OLD indicates that the existing content will be written over.
Select True or False for each statement as it relates to an output DD statement.
A generation data set with a name ending with (+0) indicates a new data set.
False.A generation data set with (+0) indicates the current generation.
Select True or False for each statement as it relates to an output DD statement.
A step will fail if you attempt to create and catalog a data set with a name of an existing cataloged data set.
True. The system will not allow you to create and catalog a data set using a name that belongs to an existing cataloged data set.
Select True or False for each statement as it relates to an output DD statement.
A maximum of 80 characters can be specified for a data set name.
False. A maximum of 44 characters can be specified for a regular data set name, and for generation data sets, 35 characters.
Which two DD statements contain the correct syntax for coding a new data set?
DISP=(NEW,CATLG,DELETE),DSN=XPROD.TRANS
DSN=XPROD.TRANS DISP=(,CATALOG)
DISP=(KEEP,KEEP),DSN=XPROD.TRANS
DDNAME=XPROD.TRANS,DISP=NEW
DISP=(NEW,KEEP,KEEP),DDNAME=XPROD.TRANS
DSNAME=XPROD.TRANS,DISP=(,CATLG)
DSNAME=XPROD.TRANS,DISP=(,CATLG)
DISP=(NEW,CATLG,DELETE),DSN=XPROD.TRANS
The z/OS UNIX file creation parameter to its correct description.
This parameter is used to assign file access attributes to the file being created.
PATHMODE
The z/OS UNIX file creation parameter to its correct description.
This parameter instructs the system on the action to be taken with the specified z/OS UNIX file on successful completion, and on failure.
PATHDISP
The z/OS UNIX file creation parameter to its correct description.
This parameter is used to define the access type, and processing status.
PATHOPTS
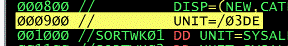
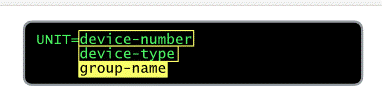
When creating a data set, the system will need to know what type of device it is to be stored on.
For example: UNIT=device-number
// UNIT=/03DE
This specific three or four characters device number, in hexadecimal. When coding a four character number, a slash, such as the one shown here, must precede it. Be aware that if the device you specify is unavailable, then your job will most likely be delayed, or may need to be canceled.

When creating a data set, the system will need to know what type of device it is to be stored on.
For example: UNIT=device-type
This is a storage device. For example, a value of 3390 is common for a system DASD device, while 3400-5 related to a tape drive device.

When creating a data set, the system will need to know what type of device it is to be stored on.
For example: UNIT=group-name
What is this group-name devices refer to?
// UNIT=SYSALLDA Devices may be grouped together and referenced using a symblic name. For eaxmple, SYSALLDA is an IBM-defined group name pertaining to all DASD devices.
Z14 is short for______
Mainframe - Z14ZR1-3907 E02 (scaled to D02)
Physical tape library is referred to as
TS3500
The Virtual tape library is referred as______
TS7770 Virtual tape library
The Hitachi VSP 5100 is used for_____
Disk array
What is the current operating system on?
z/OS v2.4 and is upgrading to z/OS v3.1
What is a DASD device?
(Direct Access Storage Device) s used for fast, random access to data, unlike sequential storage devices like tape drives.
When it comes to UNIT parameter, what are three ways you store dataset information?
UNIT= device-number , device-type, group-name.
What does this JCL code represent? VOL=SER=(v1,v2)
VOL=SER=(v1,v2)
Where v1, v2 are volume serial numbers. You can use the following syntax as well.VOL (or VOLUME) parameter: Identifies the physical storage volume(s) on which a data set is located or will be created.
SER (Serial): Indicates the serial number(s) of the volume(s).
(v1,v2): Lists one or more volume serial numbers (each up to 6 characters). For example,
VOL=SER=(123456,654321)specifies two volumes.
How do you refer back to a volume in JCL Code?
VOL=REF=*.DDNAME
Where REF is the backward reference to the volume serial number of a dataset in any of the preceding job steps in the JCL.

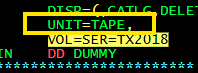
If UNIT=TAPE is coded in the UNIT parameter and there is no VOL parameter, then an available tape cartridge will be requested to store your data. True or False ?
True.
The UNIT parameter can be used to define general or specific devices to be used for your data set. True or False?
True.
Can the VOL parameter be used for DASD devices, but is more commonly used for tape cartridges . True or False
True. For example, the VOL parameter may reference a specific tape cartridge that is used to store data that will later be sent to another organization for their use.

How do you create a new dataset sent it to there department of organization to processing it. Using the JCL code UNIT and Volume?
UNIT=TAPE,VOL=SER=H11256 (The organization)

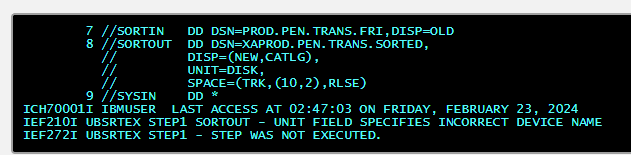
The SDSF job log shown here indicates what problem Error?
The DISP on the SORTOUT statement should specify an existing data set.
A VOL parameter is required to define the correct device.
The XAPROD.PEN.TRANS.SORTED data set already exists.
DISK is an incorrect value when specifying the UNIT parameter.
DISK is an incorrect value when specifying the UNIT parameter. The UNIT says DISK instead of TAPE.
Volume Question. you need to create and store a data set on a specific disk storage volume. What will happen if the job is submitted and it cannot locate volume VPMVSI?
An alternate volume will be automatically selected by the system
The job will not even begin processing as initial syntax checking will identify the problem
The job will fail as it requires that specific volume
The operator will receive a message on the action to be taken
The operator will receive a message on the action to be taken. The system will identify that a disk storage volume is required and will issue an operator message, prompting for an alternate volume, or to cancel the job.
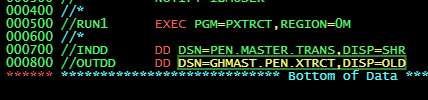
What is //OUTDD used for?
//OUTDD is a DD statement used to define output data sets for jobs in JCL.
You are required to create an Output DD statement and you must name the data set name is GHMAST.PEN.XTRCT
This is an existing data set.
Any data in this data set should be overwritten
How do you code it in the JCL?
//OUTDD DD DSN=GHMAST.PEN.XTRCT,DISP=(OLD)