reproductive hormones 15
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the pituitary gland
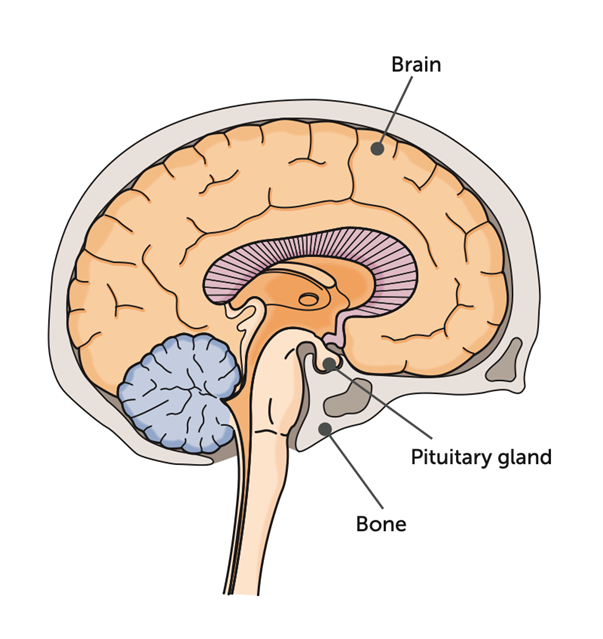
Small organ located below the brain
What is the anterior pituitary gland
•The anterior pituitary gland releases gonadotropins (these hormones affect the gonads). The gonadotropins are:
oFollicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
oLuteinising hormone (LH)
Also releases other hormones:
oProlactin
oOxytocin
FSH in a male
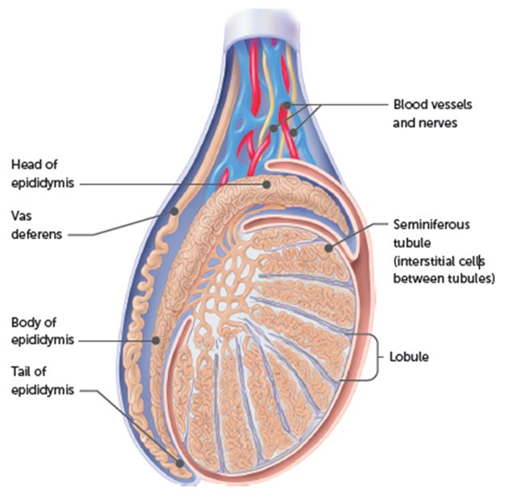
stimulates epithelial tissue of the seminiferous tubules to produce sperm via spermatogenesis
LH male
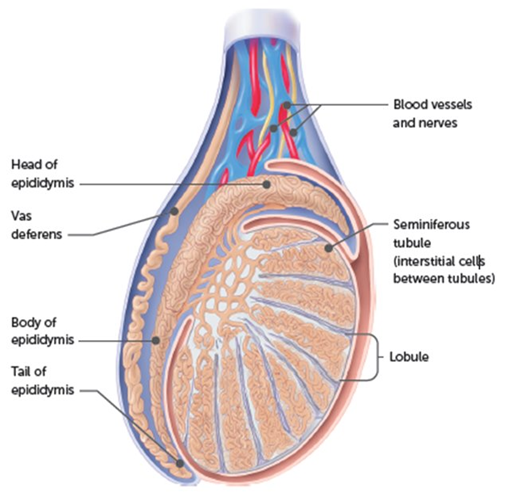
Stimulates cells in the testes to produce testosterone
Testosterone male
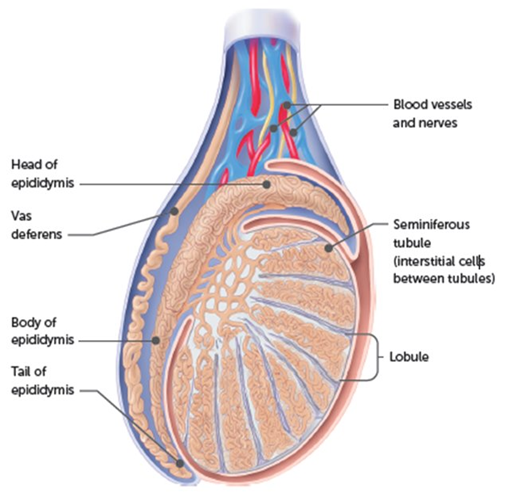
develops the immature spermatids into mature spermatozoa, maintains the male reproductive organs and sex drive, testosterone at puberty influences the body to develop into sexual maturity
Oxytocin male
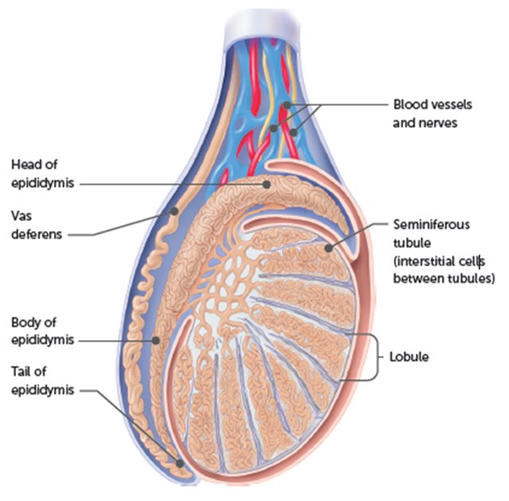
pushing the sperm and semen down the reproductive tract and the production of testosterone
Prolactin
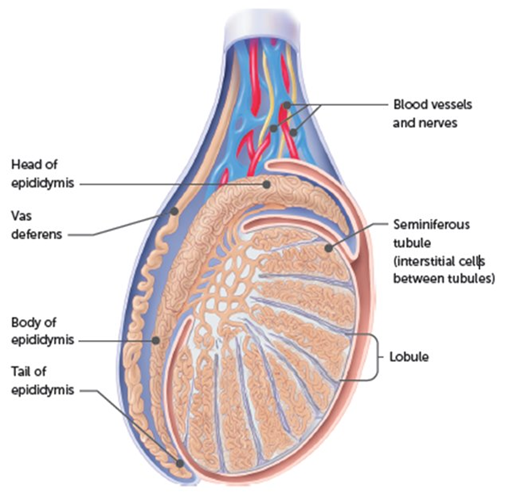
encourages the sperm formation and testosterone
Are progesterone and oestrogen produced in males
At low levels and assist in spermatogenesis
What is FSH connected to? male
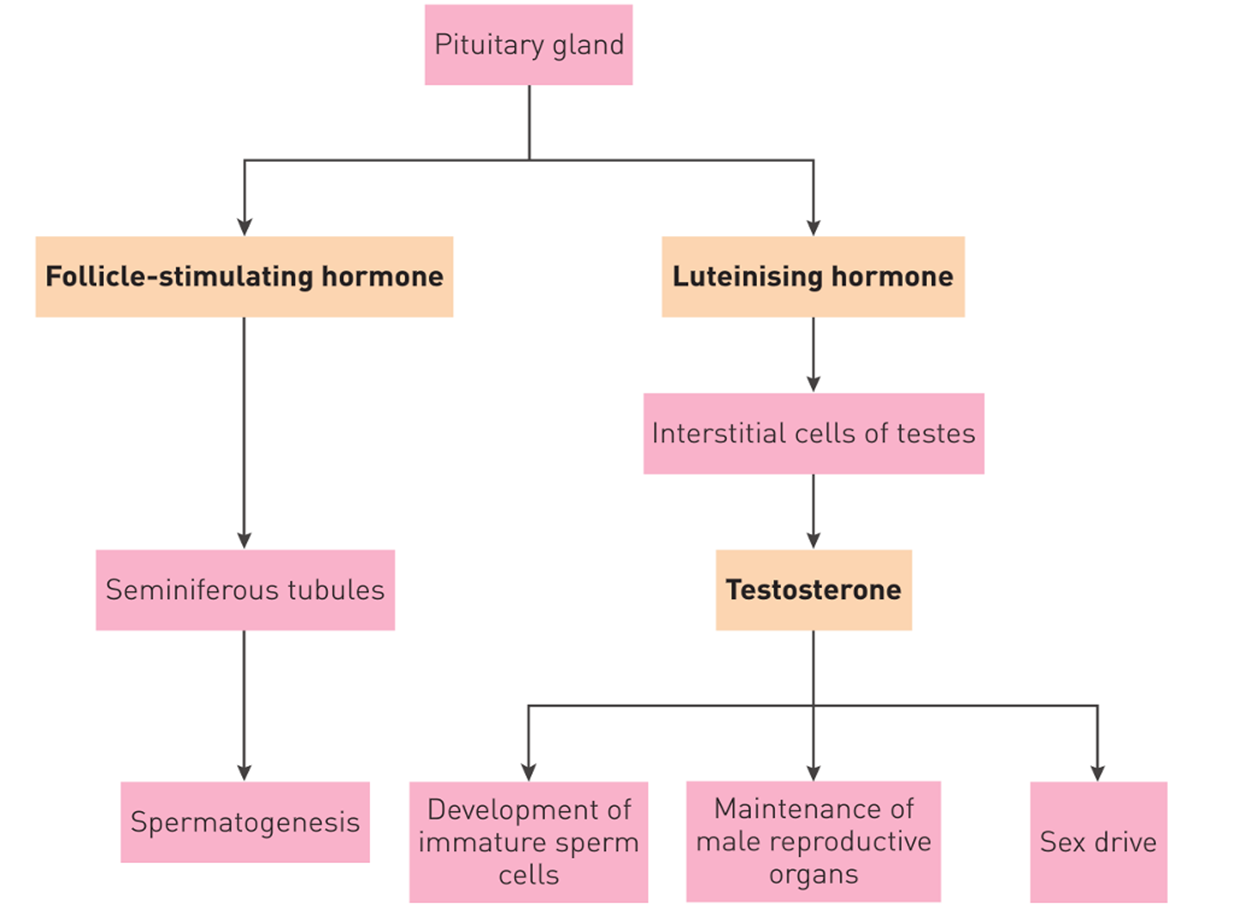
Seminiferous tubules → spermatogenesis
What is the luteinising Hormone connected to? male
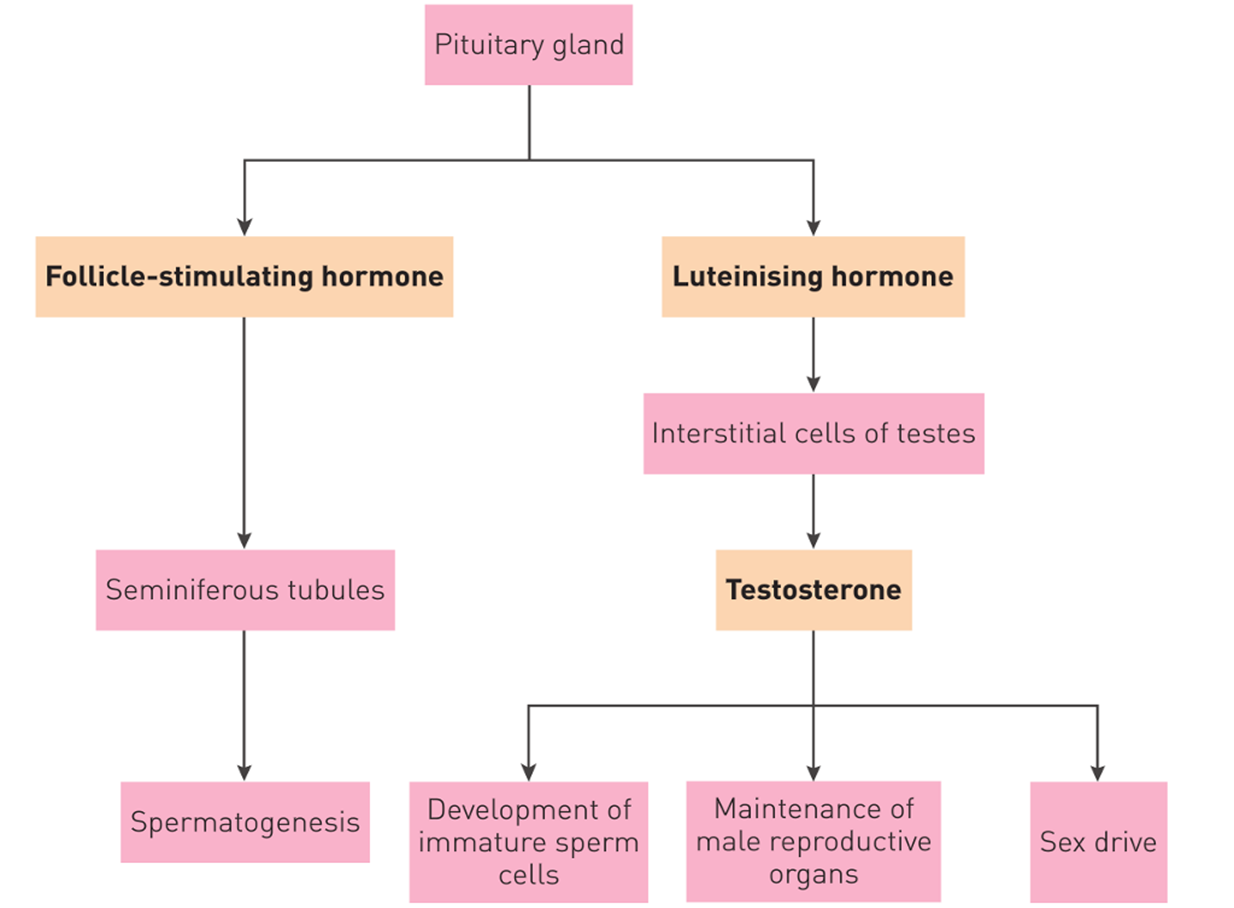
Interstitial cells of testes → testosterone → development of immature sperm cells, maintenance of male reproductive organs, sex drive
FSH female
Stimulates the growth and development of the ovarian follicle in the ovaries
LH female
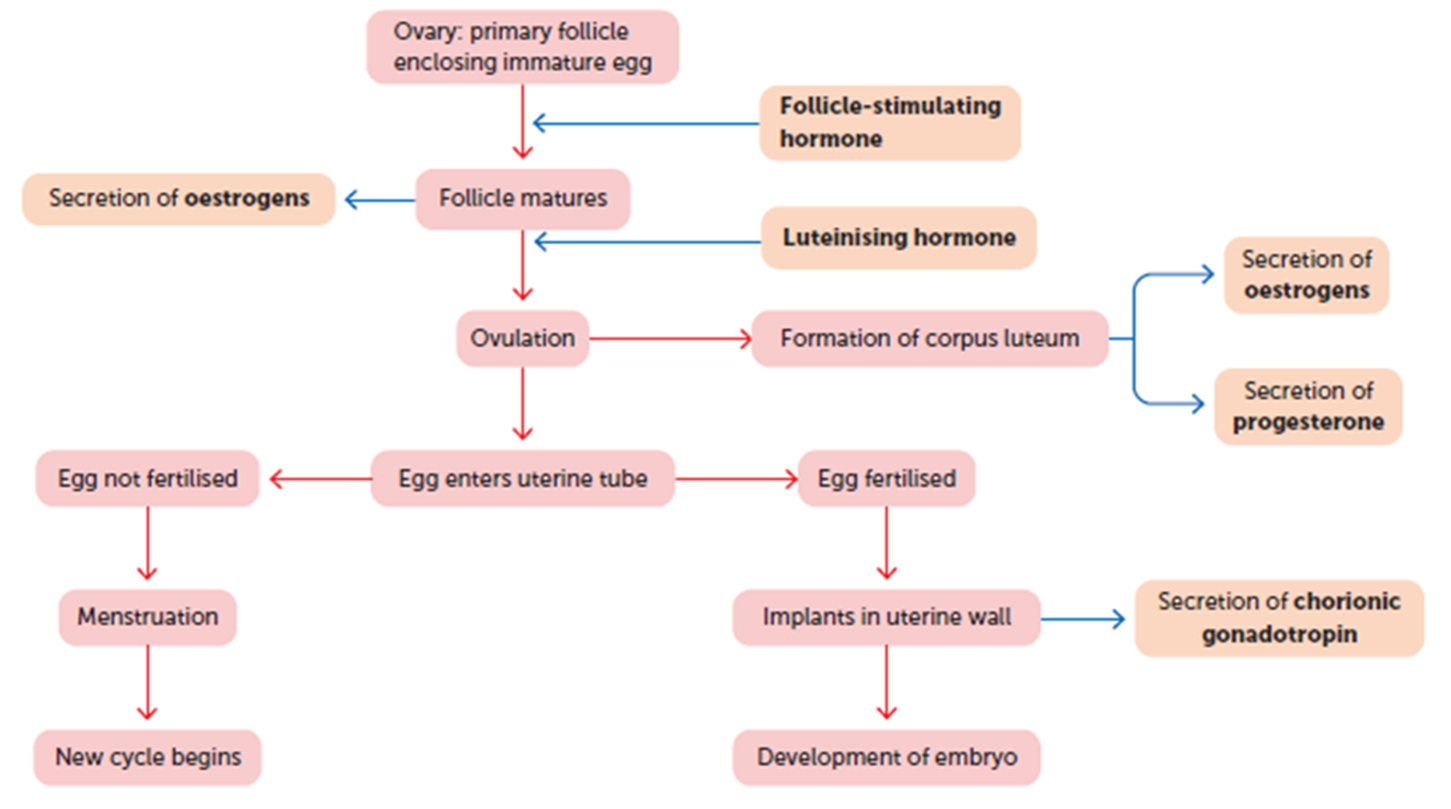
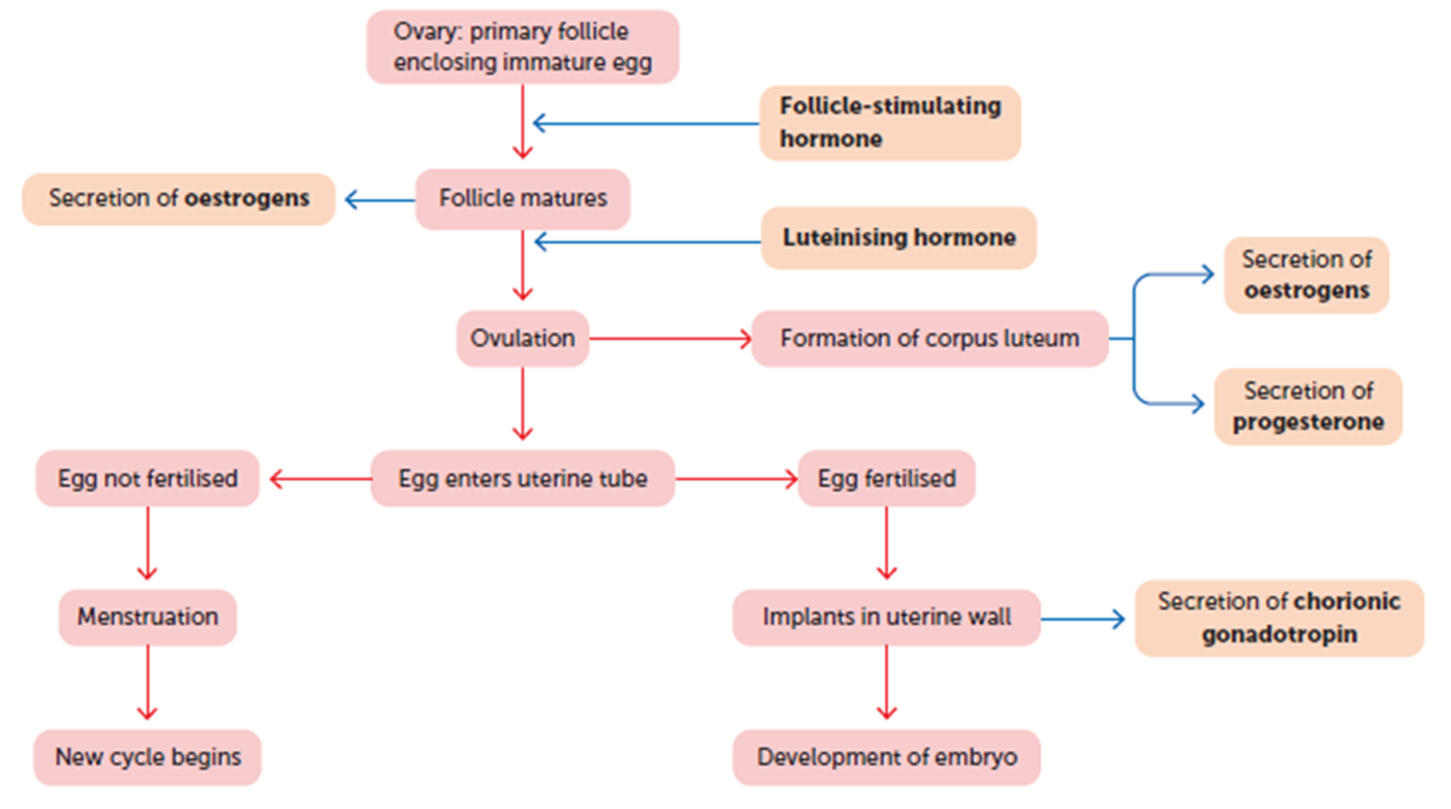
Promotes maturation of the ovarian follicle, ovulation, and formation of the corpus luteum
Oestrogen female
Secreted by the follicle in the ovaries, increased oestrogen decreases the release of FSH, it develops the secondary sex characteristics
Progesterone female
Secreted by the corpus luteum, as progesterone increases LH decreases
Prolactin female
Affects the breasts of a woman and prepare/maintains milk production
Oxytocin female
Causes uterine contractions and promotes milk movement
Human chronic gonadotropin (HCG) women
is produced by the placenta in a pregnant woman, it maintains the corpus luteum until the placenta itself can secrete oestrogens and progesterone
What is corpus luteum?
A post ovulation temporary endocrine (hormone producing) structure that maintains, repairs and allows for the growth of the endometrium to allow for implantation and pregnancy
Where does the menstrual cycle start
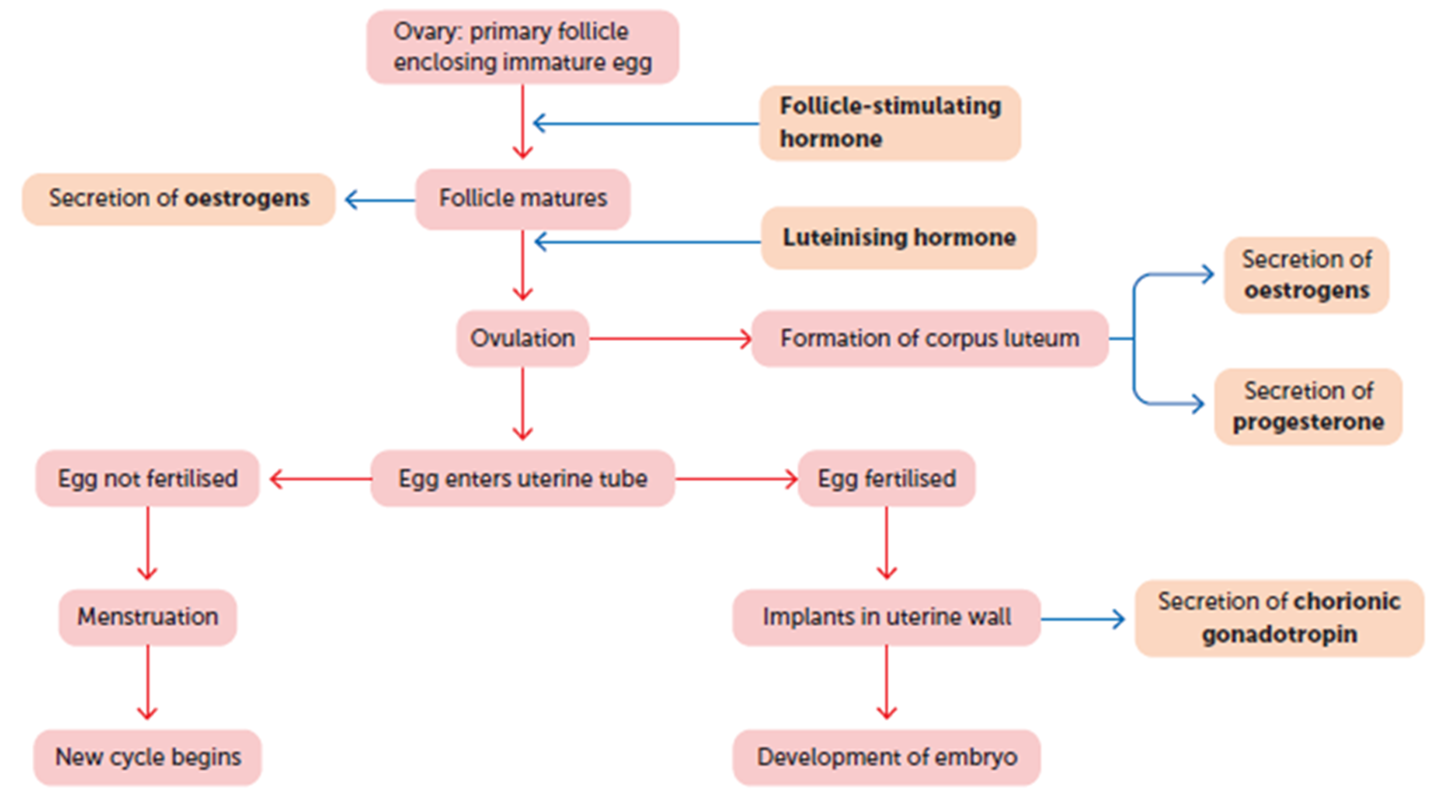
Ovary: primary follicle enclosing immature egg, each month a group of primary follicles each containing an immature egg begins to develop
What does FSH do in menstrual cycle and how?
the pituitary gland in the brain releases FSH. This hormone is a starter signal, telling the ovaries to begin maturing those follicles.
What happens after FSH is released during menstrual cycle
Secretion of oestrogens
As the follicles develop, they start secreting the hormone oestrogen. Oestrogen has two main jobs:
It causes the uterine lining (endometrium) to thicken in preparation for a potential pregnancy.
Once oestrogen levels get high enough, it triggers the next step.
What comes after the secretion of oestrogens in menstruation cycle
Follicle matures Usually, only one follicle becomes the "dominant" follicle and fully matures. The others fade away. This mature follicle is now a fluid-filled sac containing a nearly-ready egg.