Exam 2 + Final Review Content (PDFs)
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Clinically Significant Enzymes, Non-Protein Nitrogens [NPN], Liver, Vitamins and Minerals, Tumor Biomarkers, **NO Endocrinology .. 17 pgs**
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Enzymes - Influences
temperature
pH
substrate concentration
coenzymes
cofactors
Clinically Significant Enzymes
AST
ALT
ALP
GGT
LD
CK
Amylase
Lipase
ACP
AST Purpose/Source
NON-specific → skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and parenchymal hepatic cells - pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) is a coenzyme of transaminases
AST Test
Kinetics method using aspartate as substrate and converting NADH to NAD causing a decrease in Absorbance
ALT Purpose/Source
sensitive and specific indicator of liver damage, even before hyperbilirubinemia. Hepatocellular damage may elevate ALT levels in serum > 10- 100 times normal levels
ALT Test
Alanine + a-ketoglutarate <-> (ALT) pyruvate + glutamate
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ <-> (LD) lactate + NAD+
Decrease in NADH is measured at absorbance 340 nm
ALP Purpose/Source:
Sensitive indicator of cholestasis & extrahepatic obstruction. Also increases in bone disorders
ALP Test:
p-Nitrophenylphosphate <-> (ALP, pH 10.2) p-Nitrophenol + phosphate ion measures p-nitrophenol
GGT - Purpose/Source:
Found in many tissues but serum levels arise from hepatic biliary damage/chronic alcohol use
GGT - Test
y-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide + glycylglycin ➔ y-glutamyl-glycylglycine ➔ (GGT, pH 8.2) p-Nitroaniline
LD - Purpose/Source:
LD1>LD2 cardiac disease
LD 4 & 5 hepatic disease
LD - Test:
Pyruvic acid + NADH ➔ lactate + NAD Immunoassay & electrophoresis
CK - Purpose/Source
CK MB - cardiac [~5% of total]
CK BB - brain
CK MM - skeletal
CK - Test
Creatine + ATP ➔CK ➔ creatine phosphate + ADP + PPP ➔ pyruvate + ATP + NADH ➔ lactate + NAD Immunoassay & electrophoresis
Amylase - Purpose/Source
Pancreas
Amylase - Test
Starch (substrate) + iodine (indicator) in absence of amylase ➔ loss of blue color
Kinetic methods employ malto-tetraose as a substrate producing maltose; the method is coupled with enzymatic reactions using NAD ➔ NADH
Lipase: Purpose/Source
oil substrate: measure loss of turbidity (UV absorption) due to hydrolysis of oil by lipase
Enzymatic method couples hydrolysis production of fatty acids with color production
ACP: Purpose/Source
Prostate
ACP: Test
p-nitrophenolphosphate <-> (ACP, pH5) p-nitrophenol + phosphate ion
Non-Protein Nitrogens [NPN]
are important for assessing kidney function and nitrogen balance in the body.
Urea
Creatinine
Uric Acid
Ammonia
Urea
produced in the liver from the breakdown of amino acids; used to assess the function of the kidney
Pre-renal uremia: dehydration, shock, blood loss, cardiac failure, high protein diet
Renal uremia: glomerular, tubular and renal vascular dysfunction
Post-renal uremia: obstruction to renal flow
Renal uremia:
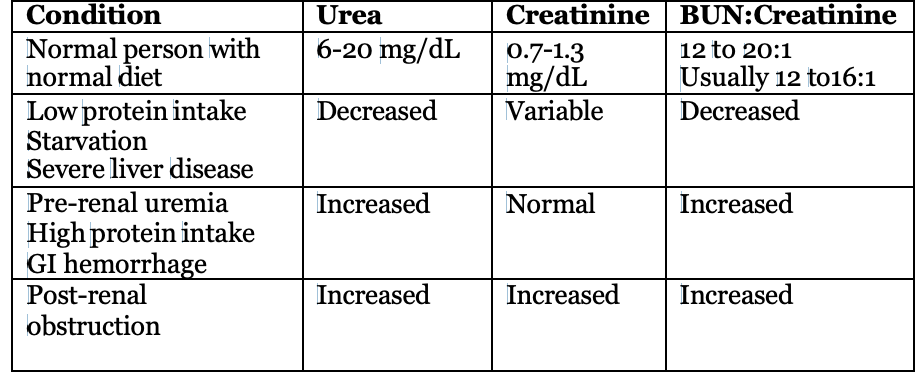
Condition + Urea + Creatinine + BUN:Creatinine
Normal person with normal diet + 6-20 mg/dL + 0.7-1.3 mg/dL + 12 to 20:1 + Usually 12 to16:1
Low protein intake Starvation: Severe liver disease + ↓ + V + ↓
Pre-renal uremia: High protein intake GI hemorrhage ↑ + N + ↑
Post-renal obstruction: ↑ + ↑ + ↑
Creatinine:
produced from muscle creatine by CK [so related to muscle mass]; filtered through renal glomerulus but not reabsorbed significantly [so is a good estimate of glomerular filtration function]
Estimates glomular function but also increased in muscle wasting diseases
Uric acid:
breakdown product of purines; increased body fluid uric acid may form crystals in joints, with pain and inflammation, in urine, forming calculi
Gout, kidney stones
Ammonia:
breakdown of amino acids in liver; normally converted to urea and excreted through kidney; increased in
Hepatic coma:
Terminal stages of cirrhosis: Reyes Syndrome
Urea Lab Tests:
Urease method
Urea + H2O –> (urease) 2NH4+ + CO -2
NH 3+ + pH indicator ➔ color change
NH4 ++2-oxoglutarate + NADH ➔ (GLDH) NAD+ + glutamate + H2O
Monoxime method: Dicetyl monoxime + H2O ➔ (H+) diacetyl + HONH2 Urea + diacetyle ➔ (H+) diazine (yellow) + 2H2O
Conductimetric
Berthelot
Creatinine Lab Tests: Jaffe reaction
Creatine + picrate ➔ (OH-) red-orange complex
Reacted with alkaline picrate to form colored complex [can be timed to lower interference by non-creatinine chromogens]
Creatinine Lab Tests: Creatininase method
Creatinine + H2O ➔ (creatininase) creatine
Creatine + ATP ➔ (CK) creatine phosphate + ADP
ADP + PEP ➔ (PK) pyruvate + ATP
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ ➔ (LD) lactate + NAD+
Creatinine Lab Tests: Creatinine clearance
small number means creatinine is not filtered through the glomerulus
Urine Creat x 24 hour urine volume x 1.73 m² in units of ml per minute Plasma Creat x 1440 min x patient SA in m²
OR
Urine Creat x 24 hour urine volume. in units of ml per minute Plasma Creat x 1440 min
Uric Acid Lab Tests: Phosphotungstic acid method
Uric acid + H3PW12O40 + O2 ➔ (Na2CO3/OH-) allantoin + tungsten blue + CO2
Uric Acid Lab Tests: Enzyme method
Uric acid + O2 + 2H2O ➔ (uricase) allantoin + CO2 + H2O2
Coupled I: H2O2 + CH3OH ➔ (catalse) H2CO + 2H2O
CH2O + 3C5H8O2 + NH3 ➔ 3H2O + colored compound
Coupled II: H2O2 + indicator ➔ (peroxidase) colored compound + 2H2O
Ammonia Lab Tests:
sensitive to temperature changes [levels increase]; must be placed on ice after collection
Enzymatic method
Glutamate dehydrogenase consumes NADPH with ammonia
Decrease in absorbance at 340 nm
ISE
Ammonia diffuses across a semipermeable membrane
Change in pH of ammonium chloride solution
Ammonia Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) Purpose
Sensor for measuring ammonium ion (NH4+) concentration.
Operates on potentiometry principle.
Generates voltage proportional to ammonium ion activity.
Valuable for assessing metabolic disorders, monitoring kidney function, detecting ammonia toxicity.
Provides rapid, accurate measurements with minimal sample volume.
Bilirubin Metabolism Diagram
The process by which bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of hemoglobin, processed in the liver, and excreted in bile. It involves conjugation to glucuronic acid, making it water-soluble for elimination from the body through urine
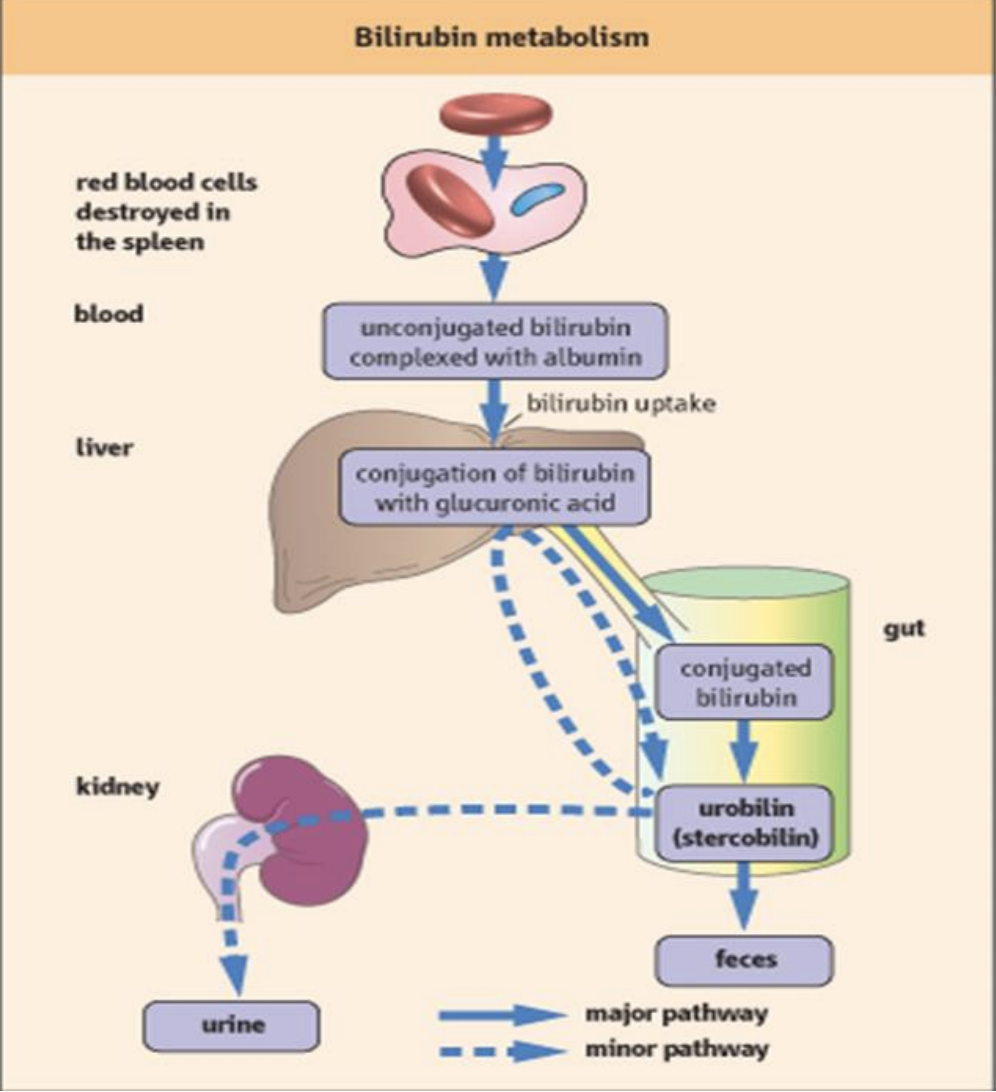
Bilirubin Metabolism Significance
significance includes its role in diagnosing liver diseases and jaundice, as elevated levels indicate liver dysfunction or hemolysis.
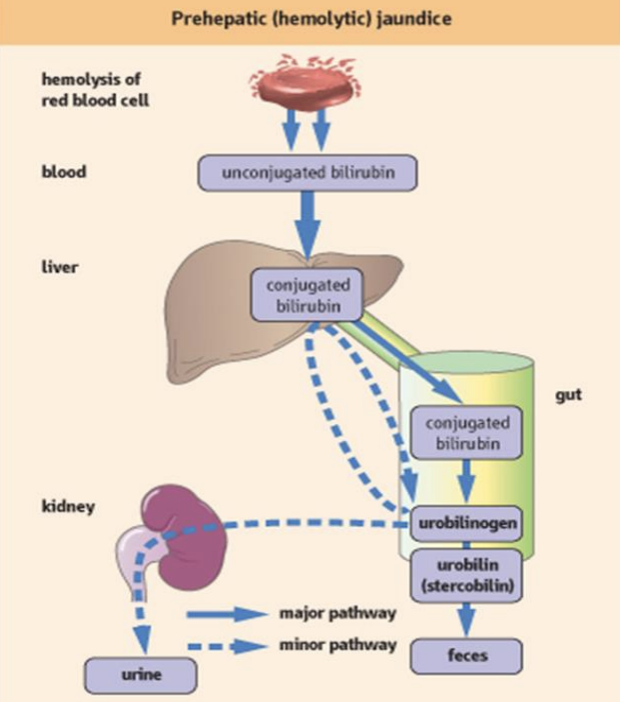
Prehepatic (hemolytic) jaundice Diagram
A type of jaundice caused by excessive breakdown of red blood cells, leading to increased bilirubin production before it reaches the liver. This results in elevated unconjugated bilirubin levels in the blood.
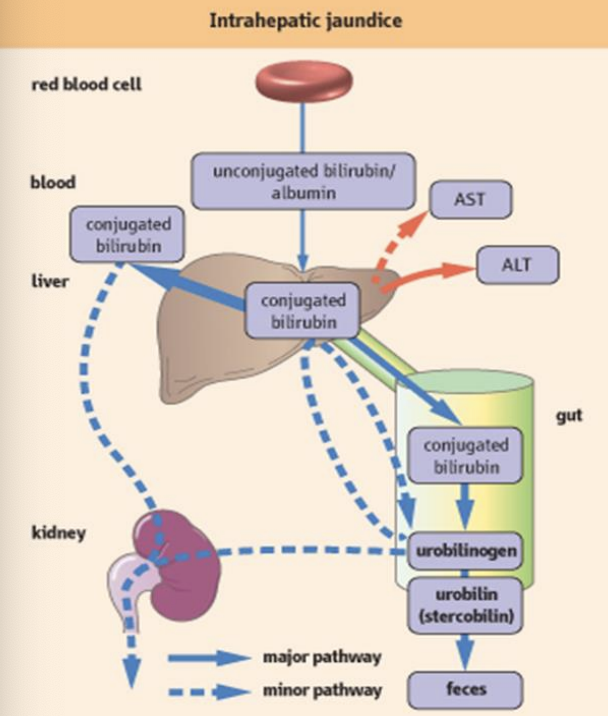
Intrahepatic Jaundice Diagram
A type of jaundice that occurs due to liver disease or damage, affecting the liver's ability to conjugate and excrete bilirubin, resulting in elevated conjugated bilirubin levels in the blood.
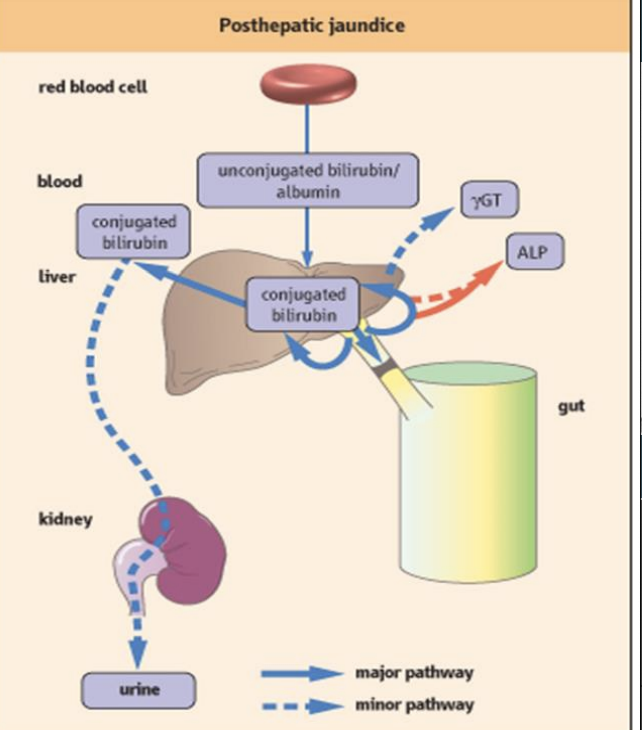
Posthepatic Jaundice Diagram
A type of jaundice caused by obstruction of bile flow after bilirubin has been processed by the liver, leading to elevated conjugated bilirubin levels in the blood.
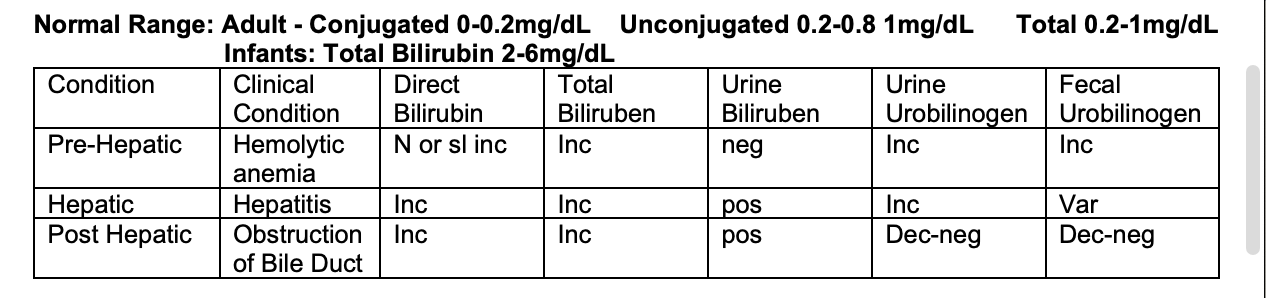
Bilirubin Ranges
Normal Range:
Adult:
Conjugated 0-0.2mg/dL
Unconjugated 0.2-0.8 1mg/dL
Total 0.2-1mg/dL
Infants: Total Bilirubin 2-6mg/dL
Pre-Hepatic Conditions:
Hemolytic Anemia
Direct Bilirubin: Increase
Total Bilirubin: Increase
Urine Bilirubin: Negative
Urine Urobilinogen: Increased
Fecal Urobilinogen: Increased
Hepatic Conditions:
Hepatitis
Direct Bilirubin: Increase
Total Bilirubin: Increase
Urine Bilirubin: Positive
Urine Urobilinogen: Increased
Fecal Urobilinogen: Variable
Post-Hepatic Conditions:
Obstruction of bile duct
Direct Bilirubin: Increased
Total Bilirubin: Increased
Urine Bilirubin: Positive
Urine Urobilinogen: Decreased/Negative
Fecal Urobilinogen: Decreased/Negative
Types of Jaundice
Pre-Hepatic
Hepatic
Post Hepatic
Prehepatic Jaundice: Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemias
Hemolytic Anemia (any cause)
Ineffective erythropoiesis (ex. Pernicious anemia)
Produces more bilirubin than Liver can remove
Serum bilirubin levels rarely exceed 5 mg/dL
Bilirubin does not appear in the urine
Prehepatic Jaundice
Neonatal physiological jaundice
Enzymes necessary for metabolism and conjugation of bilirubin are not present or newborn with Rh or ABO incompatibility
Bili >15 mg/dL→ Kernicterus (Unconjugated Bili in CNS causing severe neurologic damage) or Bili >10 mg/dL for more than 2 weeks
HDN Treatment is phototherapy
Hepatic Jaundice
Impaired cellular uptake
Defective conjugation
Lack of UDP-glucuronyl transferase (any cause)
Abnormal secretion of bilirubin from hepatocytes
Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemias
Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemias
Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia
high levels of unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin in the bloodstream (decreased hepatic uptake and conjugation)
Gilbert’s syndrome
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Gilbert’s syndrome
Inherited condition (least serious)
Impaired cellular uptake of bilirubin
↑ bilirubin < 3 mg/dL (unconjugated)
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
rare, inherited condition
Absence of enzyme (UDP-glucuronosyltransferase) or decreased enzyme activity
Patients die within the first year of life due to severe jaundice and kernicterus
Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemias - Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
An inherited condition
Lack of transport molecule into bile canal causing defective excretion by liver cells
Produces an obstructive liver disease that reduces biliary excretion of conjugated bilirubin
Posthepatic Jaundice
Obstructive (Posthepatic) jaundice
Blockage (mechanical obstruction) of the flow of bile from the liver into the intestine
Significantly Increased in Conjugated bilirubin in serum, stool appears pale.
Biliary artesia
Lack of development of bile canal (posthepatic)
Acquired defect
Other Disorders of Liver
Cirrhosis
Tumors
Reye Syndrome
Cirrhosis
Scarring of the liver is permanently damaged→ End stage of a number of diseases such as hepatitis
Caused by alcohol abuse, hemochromatosis (iron toxicity), post necrotic hepatitis,
primary biliary cirrhosis (an autoimmune disorder) and Hepatitis
Reye Syndrome
A rare condition causing liver and brain swelling, mainly in children post-viral infections like influenza or chickenpox, often linked to aspirin use. Symptoms include vomiting, confusion, and seizures
Liver enzymes used in diagnosis
Found within Hepatocytes → highly active → high enzyme activity
Most common enzymes
AST (SGOT) -- aspartate aminotransferase
ALT (SGPT) -- alanine aminotransferase
LD -- lactate dehydrogenase
Common Liver Enzymes Source:
AST: in heart , liver, muscle and RBC (non-specific)
ALT (more liver specific) also in heart, kidney, skeletal muscle and rbc
LD also in muscle, heart and rbcSource of liver enzymes used in diagnosis includes hepatocytes, where they are highly active and released into the bloodstream during liver damage.
Liver Enzyme Changes in Biliary Obstruction and Hepatic Disease
If bile duct is obstructed or bile canals inflamed, then hepatocytes become inflamed too → ↑ AST, ↑ ALT, ↑ LD
If true hepatic disease, then ↑↑↑ AST, ↑↑↑ ALT, ↑↑↑ LD in serum and ALT > AST
In obstruction, then only mild increases in serum AST, ALT, LD
Liver Enzyme Summary
Most intense increase in ALP is seen in extra hepatic biliary obstruction.
GGT is most sensitive for liver damage due to alcohol abuse.
LD (specifically LD-5) is present in liver
Bilirubin Lab Measurement
Evelyn- Malloy Principle
Bilirubin + Diazo Rgt → Azobilirubin
Diazo Reagent = Sulfanilic acid + HCl + Sodium nitrite (NaNO3)
Conjugated (direct) bilirubin gives an immediate reaction
Unconjugated bilirubin must have albumin bond broken with methanol
Jandrasik-Grof Principle
Bilirubin + Na acetate (buffer) + diazo
Add ascorbic acid to stop reaction + Alkaline tartrate (changes pH)
Read in spectrophotometer
Add caffeine-Na benzoate (accelerator) to measure indirect [unconjugated]
DMSO [dimethyl sulfoxide] solubilizes the indirect (unconjugated) form of bilirubin
Porphyrin
Normal ALA ↑ urorphyrinogen → Porphyria Cutanea Tarda ( PCT) → Most common
↑ ALA ↑ porphobilinogen in urine → Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP)
↑ ALA ↑ uroporphyrinogen and copro→ Cogenital Erythropoetic Porohyria( Gunther’sdisease)
Protophyrin accumulates in the bone marrows,rbc, no excess porphyrins in urine → Erythropoetic Protoporphyri(EPP)
Laboratory - Watson- Schwartz Urobilinogen Erhlich’s test
P-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (Erhlich’s Reagent) + Na acetate
Forms a red color with urobilinogen
assessing liver function and detecting hemolytic diseases.
Plasma Protein Indicators of Nutritional Status
Albumin
Transferrin
Transthyretin
(thyroxinebinding pre-albumin,
pre-albumin)
Retinol-binding Protein
Insulin-like Growth factor, somatomedin
Albumin Half Life & Function:
Half-Life: 18-20 days
Maintains osmotic pressure and is carrier of
hydrophobic molecules in plasma
Transferrin Half Life & Function:
Half-Life: 2-3 days
Function: Carrier protein for thyroid hormones in plasma,
carrier for retinol-binding protein
Transthyretin Half Life & Function:
Half-Life: 2-3 days
Function: Carrier protein for thyroid hormones in plasma,
carrier for retinol-binding protein
Retinol-binding Protein Half Life & Function:
Half-Life: 12 hrs
Function: Transports vitamin A in plasma; binds noncovalently to pre-albumin
Insulin-like Growth factor, somatomedin
Half-Life: 2-6 hrs
Function: Have similar metabolic effects to insulin; sensitive to nutritional variation while free from the effects of inflammation
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin A: Retinol, Retinal, Retinoic acid
Vitamin D: Ergocalciferol, Cholecalciferol
Vitamin E: Tocopherols, Tocotrienols
Vitamin K: Phylloquinone, Menaquinones
Vitamin A:
Function: Required for normal vision and immune function
Disease:
Deficiency: degeneration of eyes and skin
Toxicity: abdominal pain, headaches, skin roughness
Laboratory Assessment: Fluorospectrophotometry,
immunoassay, HPLC
Vitamin D
Function:
Calcium and phosphorous metabolism
Maintains bone structure
Disease:
Deficiency: rickets, osteomalacia
Toxicity: hypercalcemia
Laboratory Assessment: Immunoassay, HPLC
Vitamin E
Function:
Antioxidant of unsaturated fatty acyl groups of membrane phospholipids
Protects membranes
Disease:
Deficiency: hemolytic anemia due to fragility of RBC membranes
Toxicity: antagonistic to vitamin K, may enhance the effect of coumarin therapy, resulting in hemorrhage
Laboratory Assessment: Erythrocyte hemolysis
functional test, GC, HPLC
Vitamin K
Function:
Required for synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX and X
Coumarins act by interfering with the activation of
Vitamin K
Disease: hemorrhagic disease, increased clotting time
Laboratory Assessment: Immunoassay, HPLC,
Prothrombin time functional test
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin B1: Thiamine
Vitamin B2: Riboflavin
Vitamin B6: Pyridoxine
Niacin: Nicotinic acid
Folate
Vitamin B12: cyanocobalamin
Biotin
Pantothenic acid
Vitamin C: Ascorbic acid
Vitamin B1
Function: Co-enzyme of metabolic reactions
Disease: Deficiency - Beriberi
Laboratory Assessment: Fluorospectrophotometry, HPLC, transketolase functional test
Vitamin B2
Function: Component of coenzymes, FMN and
FAD, for redox reactions
Disease: Deficiency → General metabolic defect
Laboratory Assessment: Fluorospectrophotometry, HPLC, glutathione reductase functional test
Vitamin B6
Function: co-enzyme of metabolic reactions
Disease: Deficiency → General metabolic defect
Laboratory Assessment: HPLC, tyrosine decarboxylase functional test
Niacin
Function: Component of coenzymes, NAD and
NADP, for redox rxns
Disease: Deficiency → Pellagra
Laboratory Assessment: Fluorospectrophotometry
Folate
Function: Carrier of one carbon groups for metabolic reactions
Disease: Deficiency → Megaloblastic
anemia
Laboratory Assessment: Competitive Binding
Protein, HPLC
Vitamin B12
Function:
Complexes with intrinsic factor to
pass through the
intestinal mucosa
Involved in the
synthesis of
methionine and
conversion of
methylmalonate to
succinate
Disease: Deficiency → Megaloblastic anemia, Pernicious anemia
Laboratory Assessment: Competitive Binding
Protein, Immunoassay
Biotin
Function: Prosthetic group for carboxylation reactions
Disease: Deficiency → vomiting, anorexia, dermatitis
Laboratory Assessment: Microbiological
functional assay
Pantothenic acid
Function: Component of carrier molecules such co-enzyme A and acyl protein carrier
Disease: general metabolic defect
Laboratory Assessment: Microbiological
functional assay, immunoassay, GC, HPLC
Vitamin C
Function:
Cofactor of protocollagen Aid the synthesis of cartilage, dentin, and bone
Reducing agent for hydroxylation
reactions
Disease: Scurvy, inability to form connective tissue
Laboratory Assessment: Fluorospectrophotometry,
photometry
Trace Element
Indicator of Nutritional Status
Chromium
Copper
Selenium
Zinc
Chromium
Function: Promotes insulin action
Disease: Glucose intolerance
Laboratory Assessment: AAS
Copper
Function: Component of redox reactions and cytochrome reactions
Disease:
Menkes’ syndrome
Wilson’s disease
Indicated in inflammatory
rxns
Laboratory assessment:
AAS
Functional assay of superoxide dismutase and cytochrome c oxidase
Selenium
Function: protects against oxidative stress constituent of enzymes
Disease: Associated with increased instance of
cancer and cardiopathy
Laboratory Assessment: AAS
Zinc
Function: Constituent and co-factor of enzymes
Disease: General metabolic defect, including growth retardation and poor wound healing
Laboratory Assessment: AAS
Enzyme Tumor Markers
Prostate-specific antigen
Lactate dehydrogenase
Alkaline phosphatase
Neuron-specific enolase
Tumor Marker: Tumor Types
Prostate-specific antigen: Prostate Cancer
Lactate dehydrogenase: Hematologic malignancies
Alkaline phosphatase: Metastatic carcinoma of bone, hepatocellular carcinoma, osteosarcoma, lymphoma, leukemia
Neuron-specific enolase: Neuroendocrine tumors
Tumor Marker: Method
Prostate-specific antigen: IA
Lactate dehydrogenase: EA
Alkaline phosphatase: EA
Neuron-specific enolase: RIA, IHC
Specimen for Enzyme Tumor Markers
Serum
Prostate-specific antigen: Clinical Utility
Prostate cancer screening, therapy monitoring, and recurrence
Lactate Dehydrogenase: Clinical Utility
Prognostic indicator; elevated nonspecifically in numerous cancers
Alkaline phosphatase: Clinical Utility
Determination of liver and bone involvement; nonspecific elevation in many bone-related and liver cancers
Neuron-specific enolase: Clinical Utility
Prognostic indicator and monitoring disease progression for neuroendocrine tumors
Carbohydrate and Cancer Antigen Tumor Markers
CA 19-9, CA 15-3, CA 27-29, CA-125 are biomarkers used to monitor certain cancers, including pancreatic, breast, and ovarian cancers.
CA 19-9, CA 15-3, CA 27-29, CA-125 Methods and Specimen
Immunoassay and Serum
CA 19-9, CA 15-3, CA 27-29, CA-125 Tumor Types
CA 19-9: Gastrointestinal cancer and adenocarcinoma
CA 15-3: Metastatic breast caner
CA 27-29: Metastatic breast carcinoma
CA-125: Ovarian Cancer
CA 19-9 Clinical Utility
Monitoring pancreatic cancer