Chemistry - Topic 6 Alkenes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is meant by the term electrophile?
electron-deficient species that accepts electrons
Hydrogenation - conditions
as Hydrogen is a poor electrophile this reaction only occurs using a nickel catalyst and high temperatures + pressures
Hydrogenation
alkene reacts via electrophilic addition with hydrogen in presence of nickel catalyst to form alkane - e.g. catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated vegetable oils to manufacture margerine
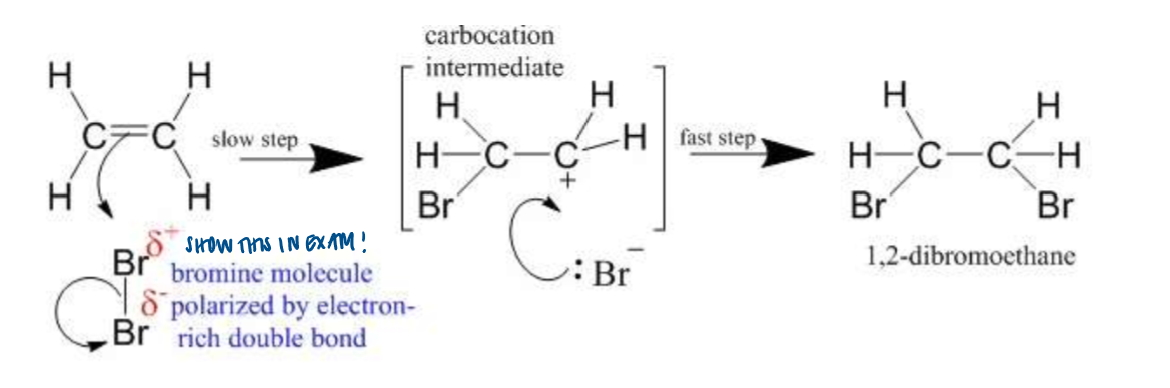
Electrophilic Addition - halogens
react to form dihalogenoalkanes
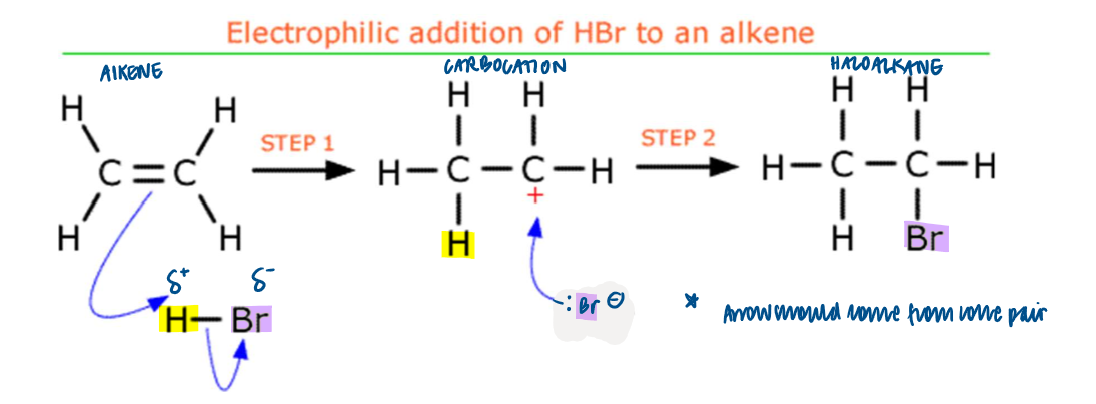
Electrophilic Addition - hydrogen halides
react to form halogenoalkanes
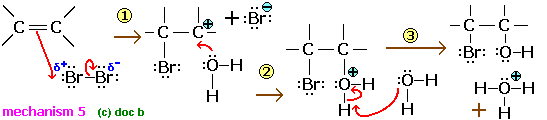
Electrophilic Addition - steam
react to form alcohols, in presence of an acid catalyst (e.g. H2SO4)
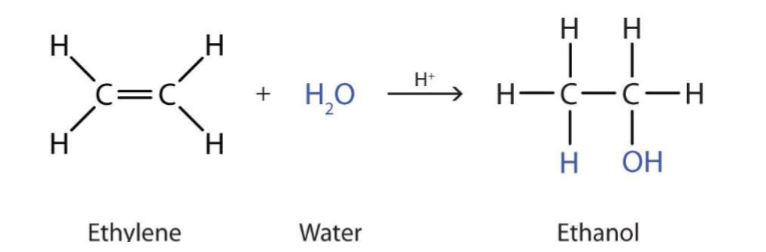
Why can water not just be added to form an alcohol?
Water is not a very good electrophile - therefore an acid must be added as a catalyst - this forms H3O+ which can then act as an electrophile as it is positively charged)
When bromine is added to trans-but-2-enal, the aldehyde group is oxidised and the carbon-carbon double bond reacts. The product is 2,3-dibromobutanoic acid. When trans-but-2-enal reacts with bromine mixed with a little sodium chloride, a mixture of 2,3-dibromobutanoic acid and 2-bromo-3-chlorobutanoic acid is produced. No 2,3-dichlorobutanoic acid is formed. Explain these observations.
Br delta plus is the only electrophile
Cl is only present as Cl- and it must add to the carbocation
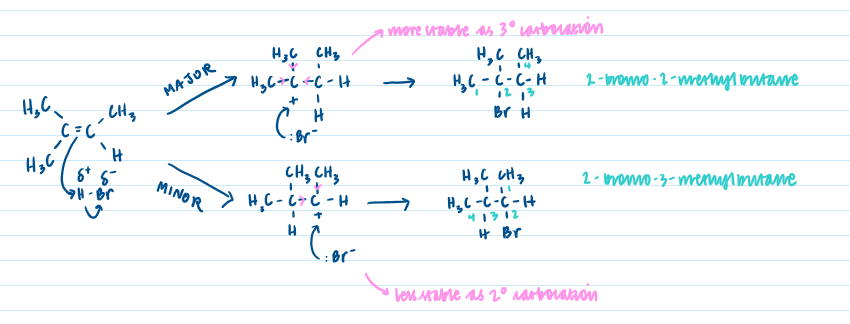
Relative stability of primary, secondary and tertiary carbocation intermediates:
Tertiary>Secondary>Primary - alkyl groups are electron-donating and push the electrons in their bond towards the (+)ve charge to stabilise it - use ‘That which as gets’ (in terms of hydrogens) + Markovnikov’s rule to determine which reaction pathway will give major product
Qualitative Test for C=C double bond
decolourises bromine water as dibromoalkane is formed - however note that if using bromine water then bromoalcohol is formed + water
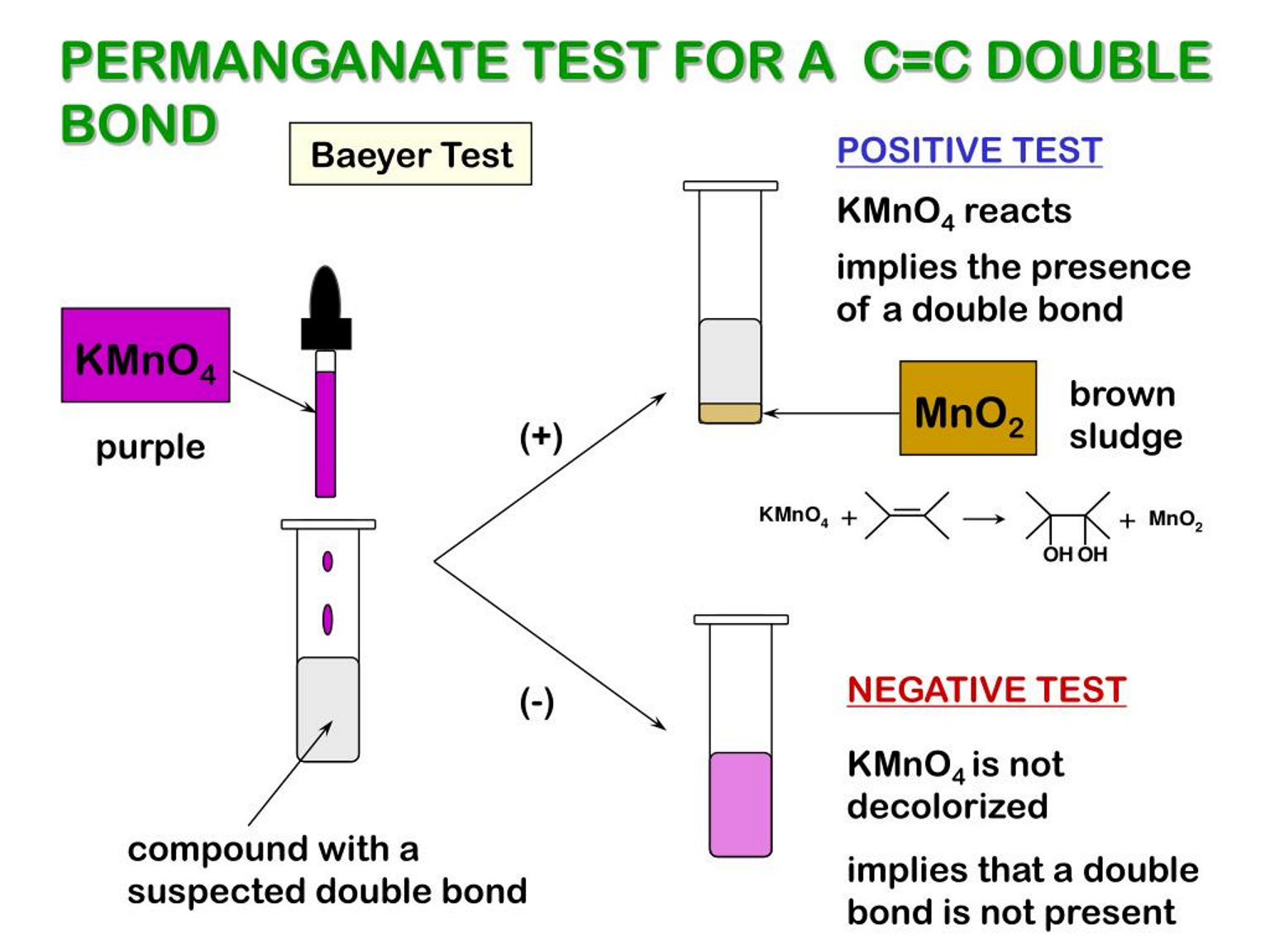
Other potential tests that can be used to test for C=C double bond
burn with sooty flame (not clean)
add potassium permanganate (VII) in acidic conditions - KMnO4 oxidises double bond and decolourises from purple solution to form alco-diol and MnO2 brown sludge
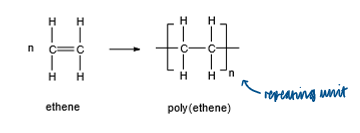
How can alkenes from polymers?
addition polymerisation
Why are the waste polymers separated into specific types:
for;
recycling
incineration to release energy
use as a feedstock for cracking
What does heterolytic bond fission result in?
The formation of ions
Advantages and Disadvantages of disposing polymers in landfill
Advantages:
quick/ easy/ convenient
Disadvantages:
polymers are non-biodegradable so will persist for a long time in landfill.
can form microplastics/ release harmful gases if they do break down
Advantages and Disadvantages of recycling polymers to make new plastics
Advantages:
reduces need for use of resources such as crude oil to make plastics
Disadvantages:
not all polymers can be recycled
requires sorting + washing etc
Advantages and Disadvantages of Incineration of polymers
Advantages:
quickly disposes waste
heat energy released can be used to heat homes/ power other industrial processes
Disadvantages:
releases toxic gases
Advantages and Disadvantages of using polymers as feedstock for cracking:
Advantages:
reduces demand for alkanes from crude oil for cracking
Disadvantages:
can produce a lower % yield / lower quality of reactants
How can chemists limit the problems caused by polymer disposal?
developing biodegradable polymers
removing toxic waste gases by incineration of plastics
Polymer Definition
a long chain of repeating monomers joined together
monomer definition
a small molecule (unit) from which a long polymer can be produced
addition polymerisation - definition
a type of polymerisation in which one product (the polymer) is formed, by adding together many monomers