AP Human Geo Final
1/219
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
Reference maps
Maps designed for general information about places.
Thematic maps
Maps used to communicate how human activities are distributed.
Cartogram
A map that distorts the size of countries based on a specific variable.
Choropleth
A thematic map that uses different colors or patterns to represent data.
Dot Density
A thematic map that uses dots to represent data.
Isoline
A map that uses lines to connect points of equal value.
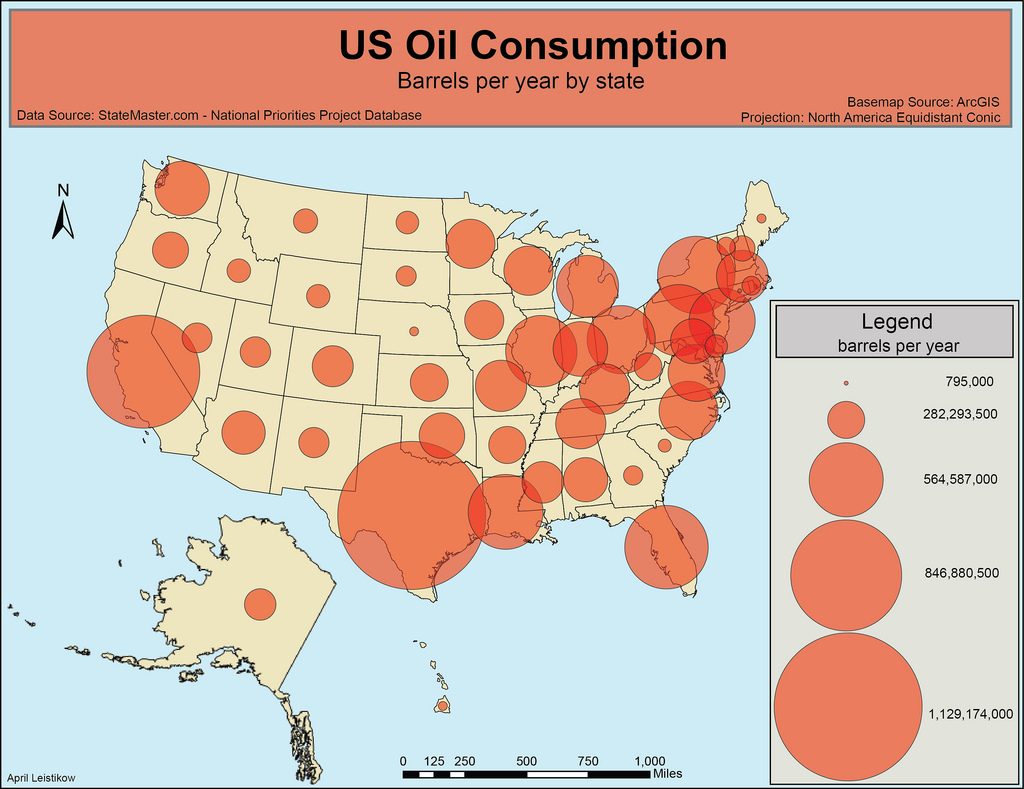
Proportional Symbol
A thematic map that uses symbols of different sizes to represent data.
Spatial Patterns
Patterns of absolute and relative distance and direction on a map.
Clustering
Spatial pattern where objects are grouped or bunched together.
Dispersal
Spatial pattern where objects are distributed over a wide area.
Elevation
Spatial pattern that represents the levels of height or depth on the land.
Map Projections
Methods used to represent the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map.
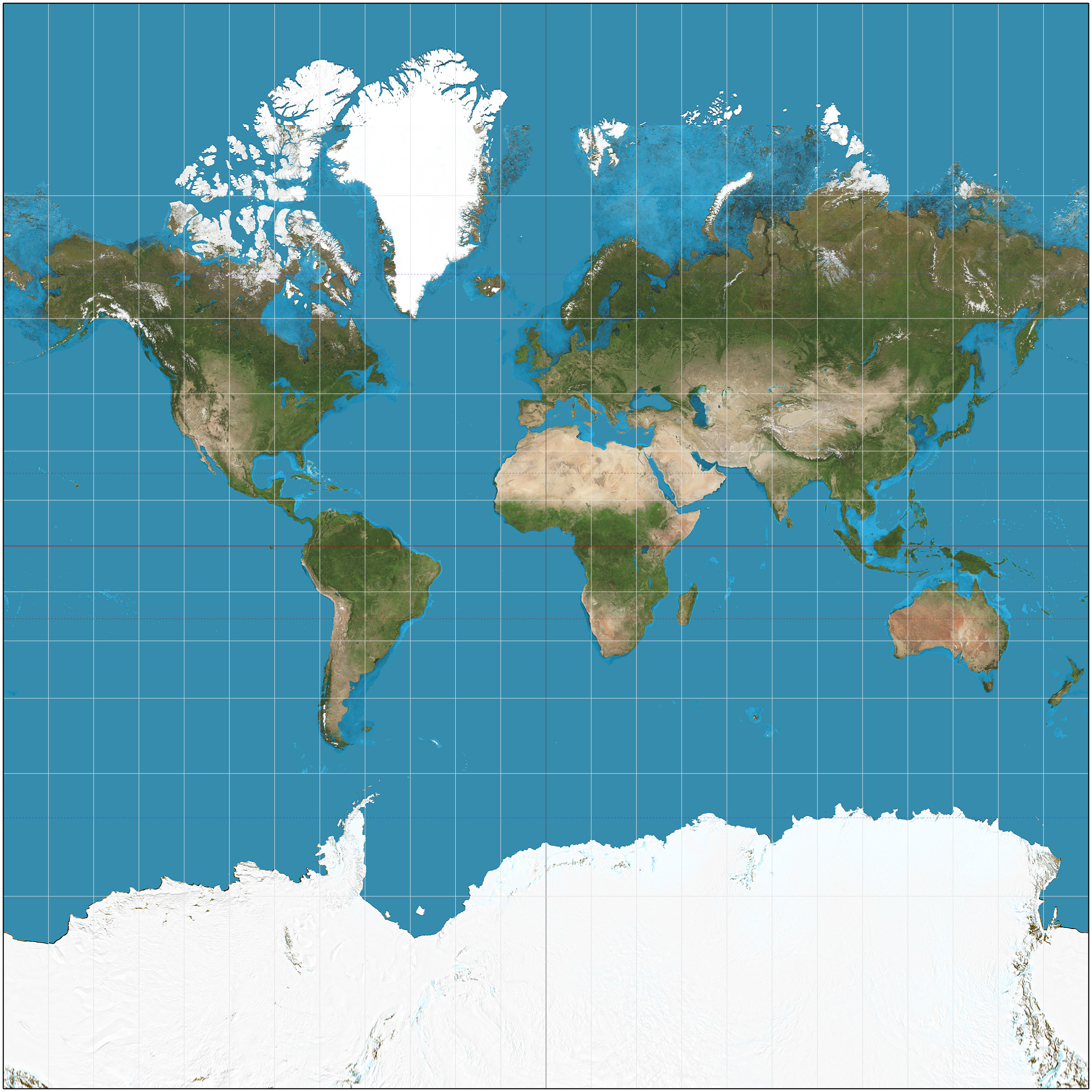
Mercator Map
A map projection that accurately represents shape and direction but distorts size.
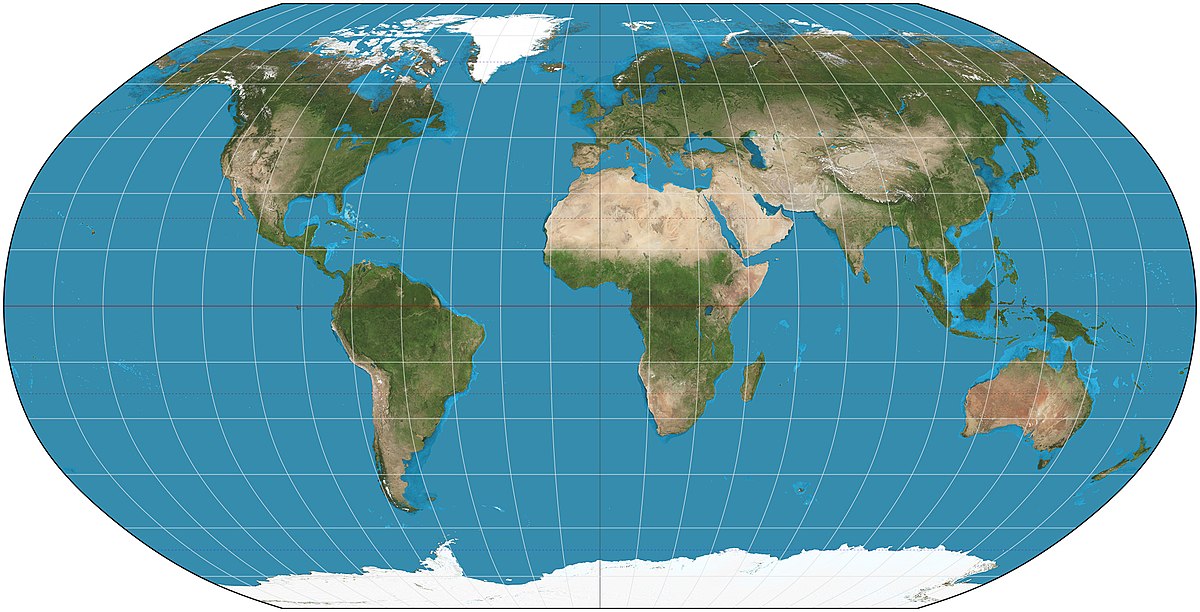
Robinson Map
A map projection that distorts everything in small amounts.
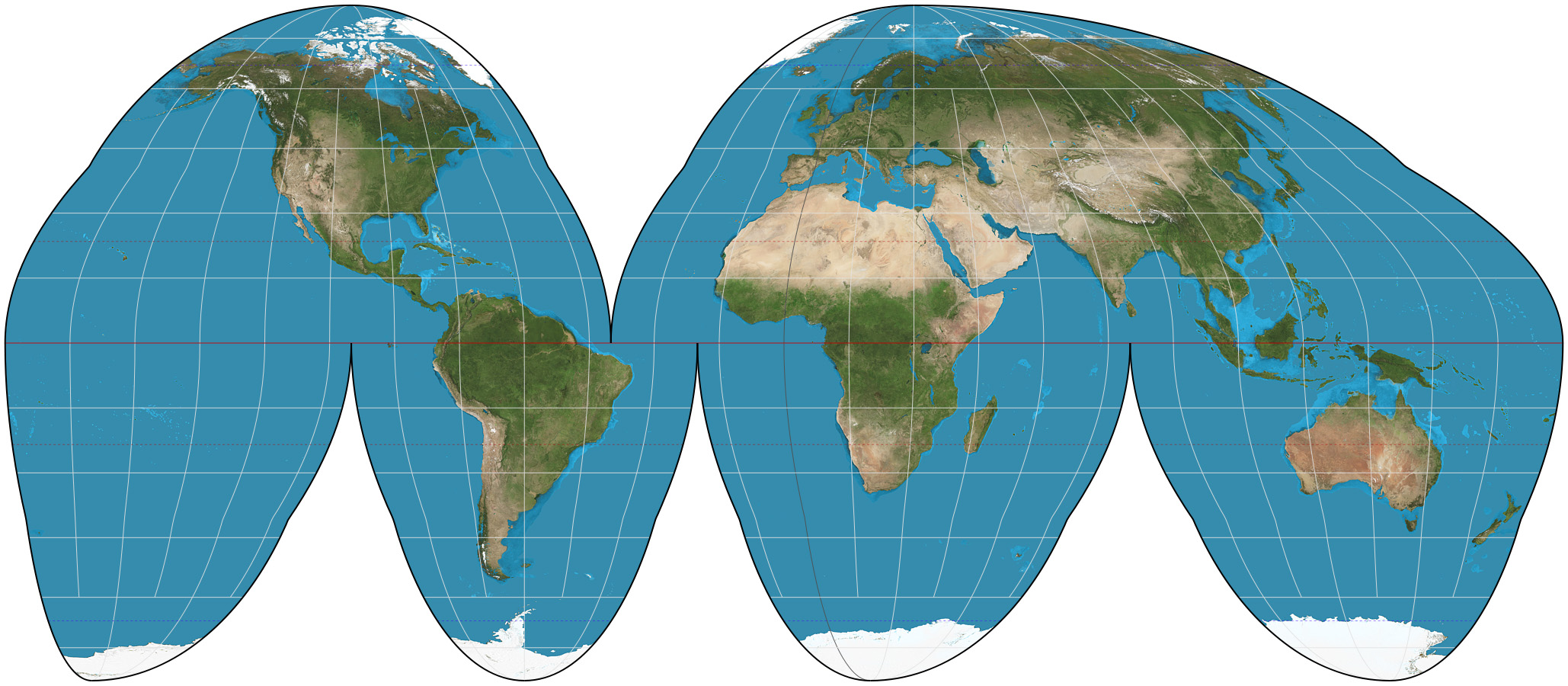
Goode Map
A map projection that accurately portrays continent sizes but distorts directions and distances.
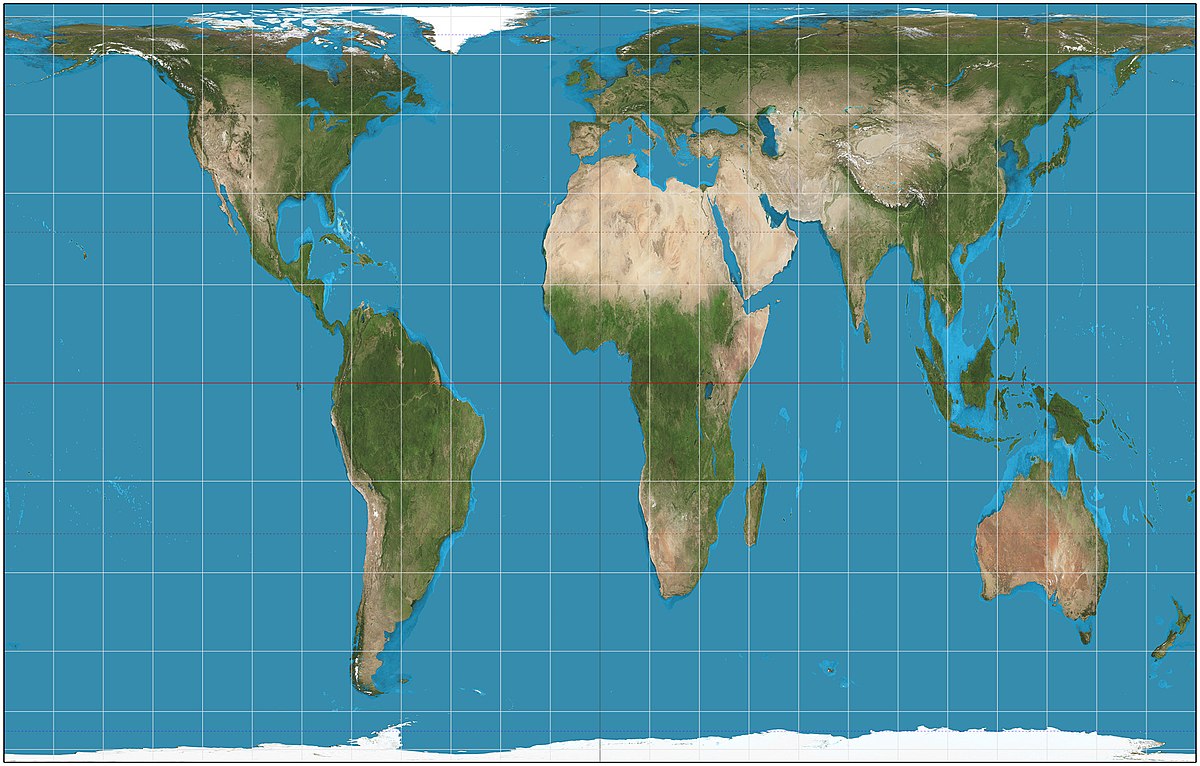
Gall Peters Map
A map projection that distorts the shape of countries, especially near the equator.
Geospatial Data
All information, including physical features and human activities, related to positions on Earth's surface.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying geospatial data.
GPS (Geographic Positioning System)
A system that uses satellite data to pinpoint locations on Earth's surface.
Remote Sensing
The process of taking pictures of Earth's surface from satellites or airplanes to understand its geography.
Spatial Information
Information about the Earth's surface obtained from various sources such as field observations, media reports, and photographic interpretation.
Census Data
Official count of individuals in a population, usually conducted every 10 years.
Absolute Location
The precise spot where something is located.
Relative Location
The position of something in relation to other things.
Space
The extent of an area, both in a relative and absolute sense.
Place
The specific human and physical characteristics of a location.
Distance Decay
The decrease in interaction or cultural/spatial connections as distance increases.
Time-Space Compression
The increasing sense of connectivity that brings people closer together despite physical distances.
Pattern
The geometric or regular arrangement of something in an area.
Sustainability
The goal of reaching equilibrium with the environment and meeting present needs without compromising resources for future generations.
Natural Resources
Physical materials on Earth that are valuable and necessary for human needs.
Environmental Determinism
The belief that the physical environment determines or shapes social development.
Possibilism
The belief that while the physical environment may limit human actions, people have the ability to adapt and adjust to their environment.
Scale
The relationship between the distance on the ground and the corresponding distance on a specific map.
Scale of Analysis
The level of detail or zoomed-in/out perspective when studying geographic data.
Region
A place that is larger than a point and smaller than a planet, grouped together based on a common feature.
Formal Region
A region based on quantitative data that can be measured or documented.
Functional Region
A region based around a node or focal point.
Vernacular (Perceptual) Region
A region that is perceived to have a common qualitative characteristic.
Ecumene
Areas where people are settled on the Earth, often along rivers, fertile land, or coasts.
Physical Factors
Factors that influence population distribution, such as climate, topography, and natural resources.
Cultural Factors
Factors that influence population distribution, such as access to education, healthcare, and entertainment opportunities.
Historical Factors
Factors that influence population distribution based on areas where human life could be sustained and flourished.
Arithmetic Density
The total number of objects in an area.
Physiological Density
The number of people supported by a unit area of arable land.
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land.
Political, Economic, and Social Power
The influence and control that areas with larger populations and greater population density have in these aspects.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum population size that the environment can sustain.
Overpopulation
When there are not enough resources in an area to support the population.
Age/Sex Ratio
The comparison of the numbers of males and females of different ages in a population.
Population
Brain drain
When educated or skilled workers leave an area for better opportunities elsewhere.
Loss of culture
The cultural impact of migration where the culture of a place is diminished or diluted.
Material culture
The physical manifestations of culture, such as tools, housing, and clothing.
Nonmaterial culture
The beliefs, traditions, and values of a group, including religion and morals.
Cultural relativism
The idea that a culture should be judged based on its own standards, not compared to another culture.
Ethnocentrism
Judging other cultures based on the rules and values of one's own culture.
Taboo
Something that is forbidden by a culture or religion and is often not discussed.
Cultural landscapes
The forms created by human activities on the physical environment, such as street lights and churches.
Ethnic neighborhoods
Distinct neighborhoods or districts that retain cultural distinctions from the surrounding area.
Indigenous people
The original inhabitants of a territory, distinct from the dominant national culture.
Sense of place
A strong feeling of identity and connection to a specific location.
Language
A set of sounds and symbols used for communication.
Religion
The belief in and worship of a higher power or powers.
Ethnicity
Belonging to a social group with a common cultural tradition.
Gender
Cultural differences in the treatment of men and women.
Relocation diffusion
The spread of ideas through migration to new areas.
Expansion diffusion
The spread of ideas through a population, continuously reaching more people.
Contagious diffusion
The spread of a phenomenon through close contact with nearby places.
Hierarchical diffusion
The spread of ideas from large connected cities to other cities, often following a hierarchy.
Stimulus diffusion
The spreading of an underlying principle of an idea when the idea as a whole cannot spread to a particular culture.
Creole language
A language that originated from the combination of two other languages.
Lingua franca
A commonly understood language used by people with different native languages.
Colonialism
The establishment of settlements in a territory and the imposition of political, economic, and cultural principles.
Imperialism
Extending a country's influence through political or military force in already developed areas.
Globalization
World interaction and integration driven by international trade, investment, and technology.
Media
Exposure to Western television, movies, and other forms of media.
Technological changes
The impact of cell phones, the internet, and other technological advancements on culture.
Politics
The spread of democratic ideals and political equality through globalization.
Economics
The influence of trade and globalization on culture, including the introduction of new industries and outside investment.
Social relationships
The push for equal rights for women and changes in traditional gender roles through globalization.
Time-Space Convergence
The decrease in travel time between locations due to transportation and communication advancements.
Cultural Convergence
Different cultures becoming more similar through the acquisition of common ideas and traits.
Cultural Divergence
Different parts of a cultural region becoming dissimilar due to exposure to different influences.
Indigenous language
A language native to a region and spoken by indigenous people.
Language extinction
A language that is no longer spoken by anyone as their native language.
Dialect
Different forms of the same language used by groups with some vocabulary and pronunciation differences.
Language family
A collection of languages descended from a common, original language.
Ethnic religion
A religion focused on a single ethnic group and not attempting to appeal to all people.
Universalizing religion
A religion that attempts to appeal to all people and has a worldwide focus.
Pilgrimage
A journey for religious purposes to a sacred place.
Acculturation
The adoption of cultural traits, such as language, by one group under the influence of another.
Assimilation
The process of a person or group losing cultural traits that made them distinct from others.
Multiculturalism
The coexistence of various ethnic groups without sacrificing their particular identities.
Syncretism
The blending of traits from two different cultures to form a new trait.
State
A political unit with a permanent population and recognized boundaries.
Nation
A group of people who share a sense of culture and history and desire political autonomy.
Nation-state
A state with a single nation.
Stateless nation
A nation without its own independent state.
Multinational state
A state with two or more nations.