FUND IMAGING: EXAM #2 (SKEL III W/PICS)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
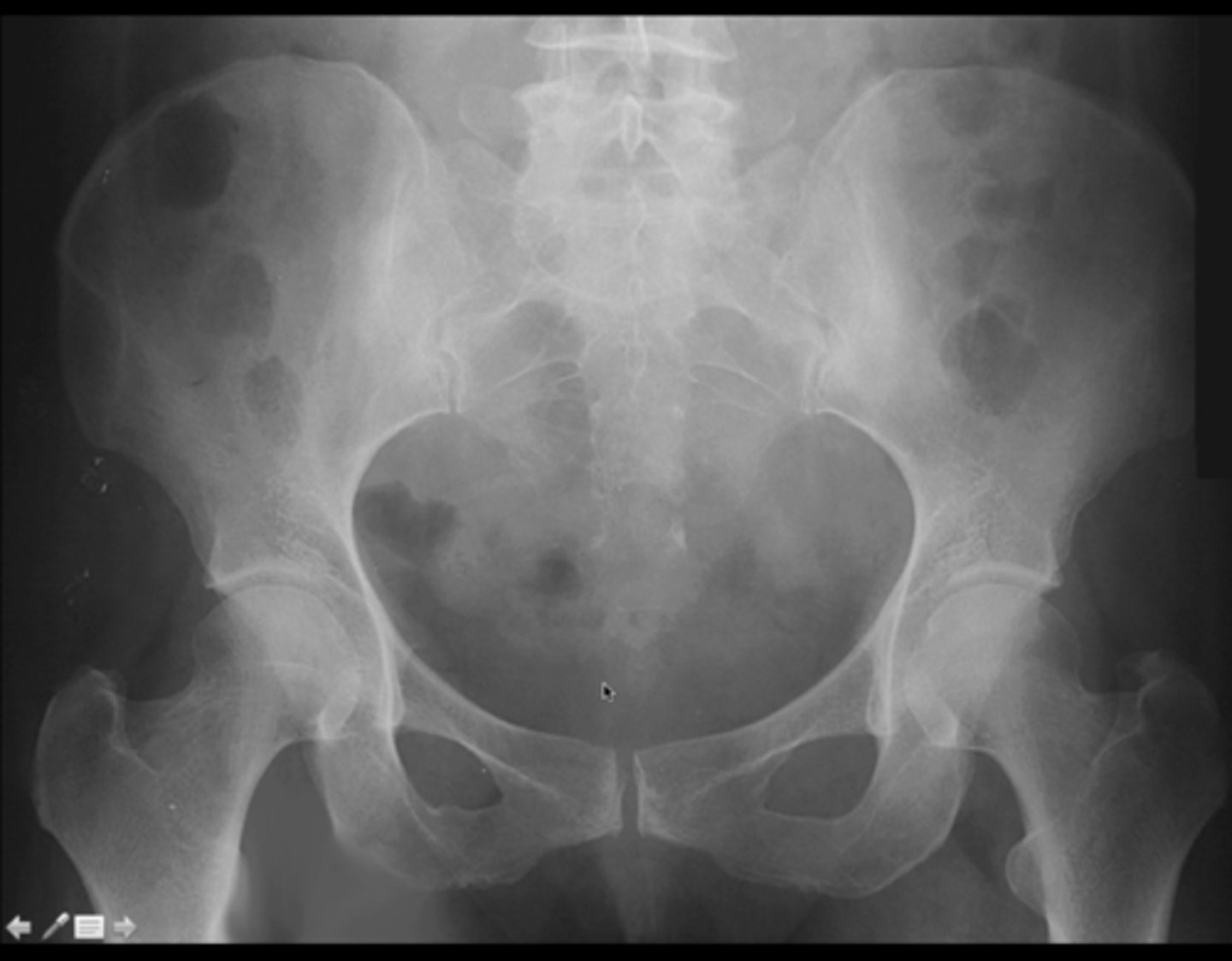
Female pelvis X-ray
(Female pelvis has a rounded (ovoid) shape)
What sex is this patient? How do you know?
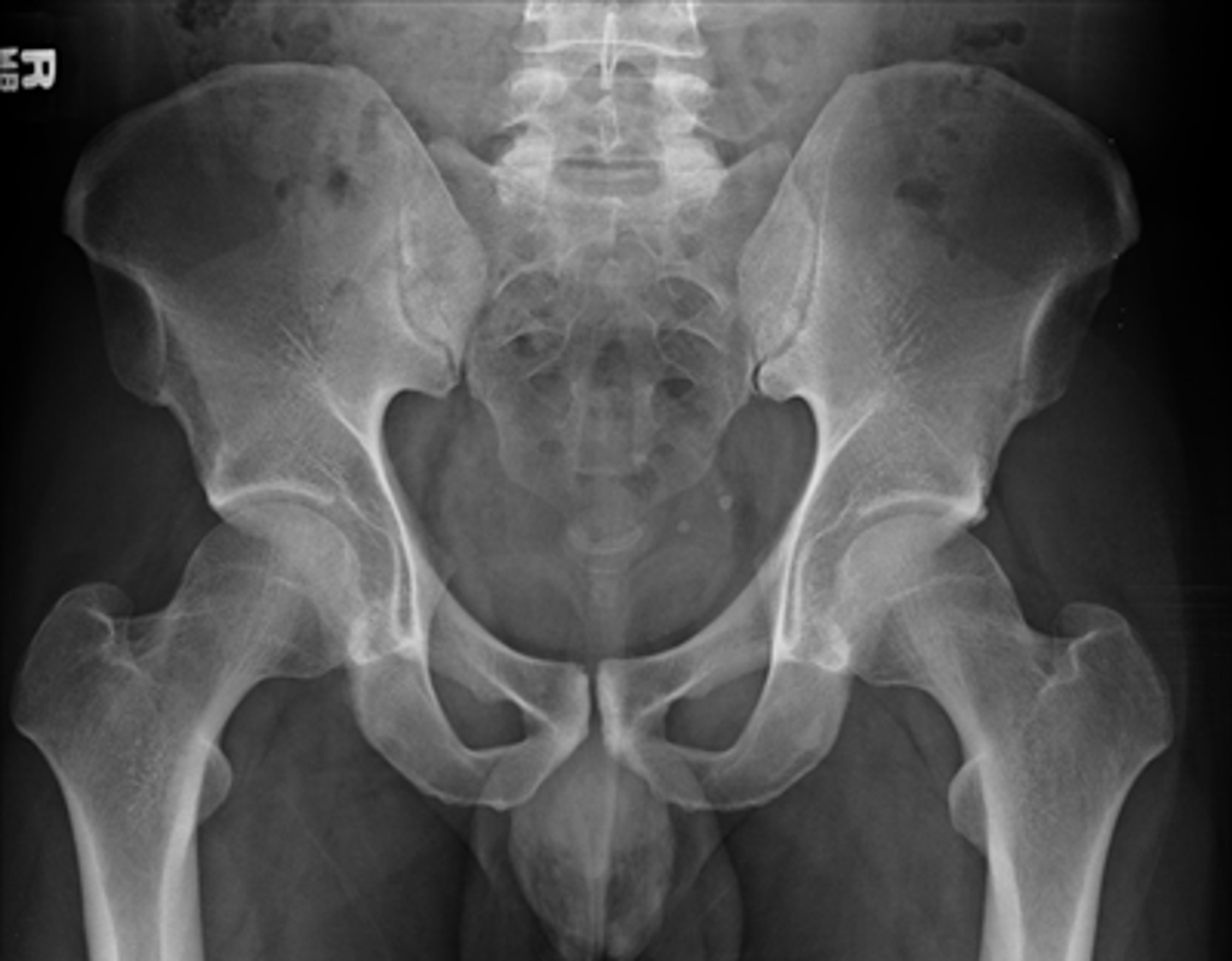
Male pelvic x-ray
(Male pelvis has a triangular (android) shape)
What sex is this patient? How do you know?
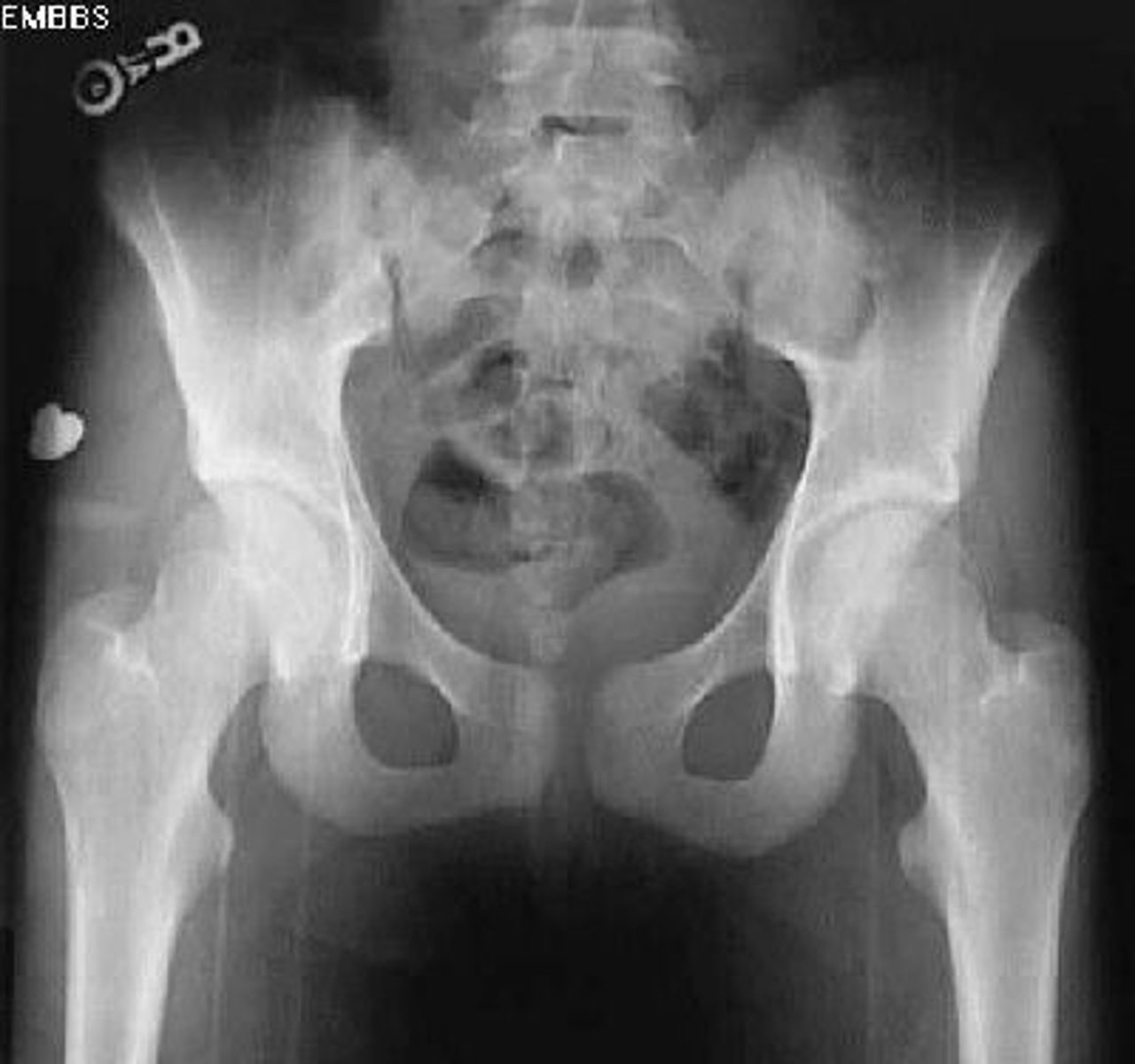
Pelvic trauma
____________ – AP view is usually sufficient CT scan is second line study
> 1 cm
Widening of the symphysis pubis ________ is abnormal = considered a fracture/pelvic instability
(**Observe for SI joint widening also!)
Widened symphysis pubis and SI joint
What's going on here?
Left inferior pubic rami fx
What's going on here?
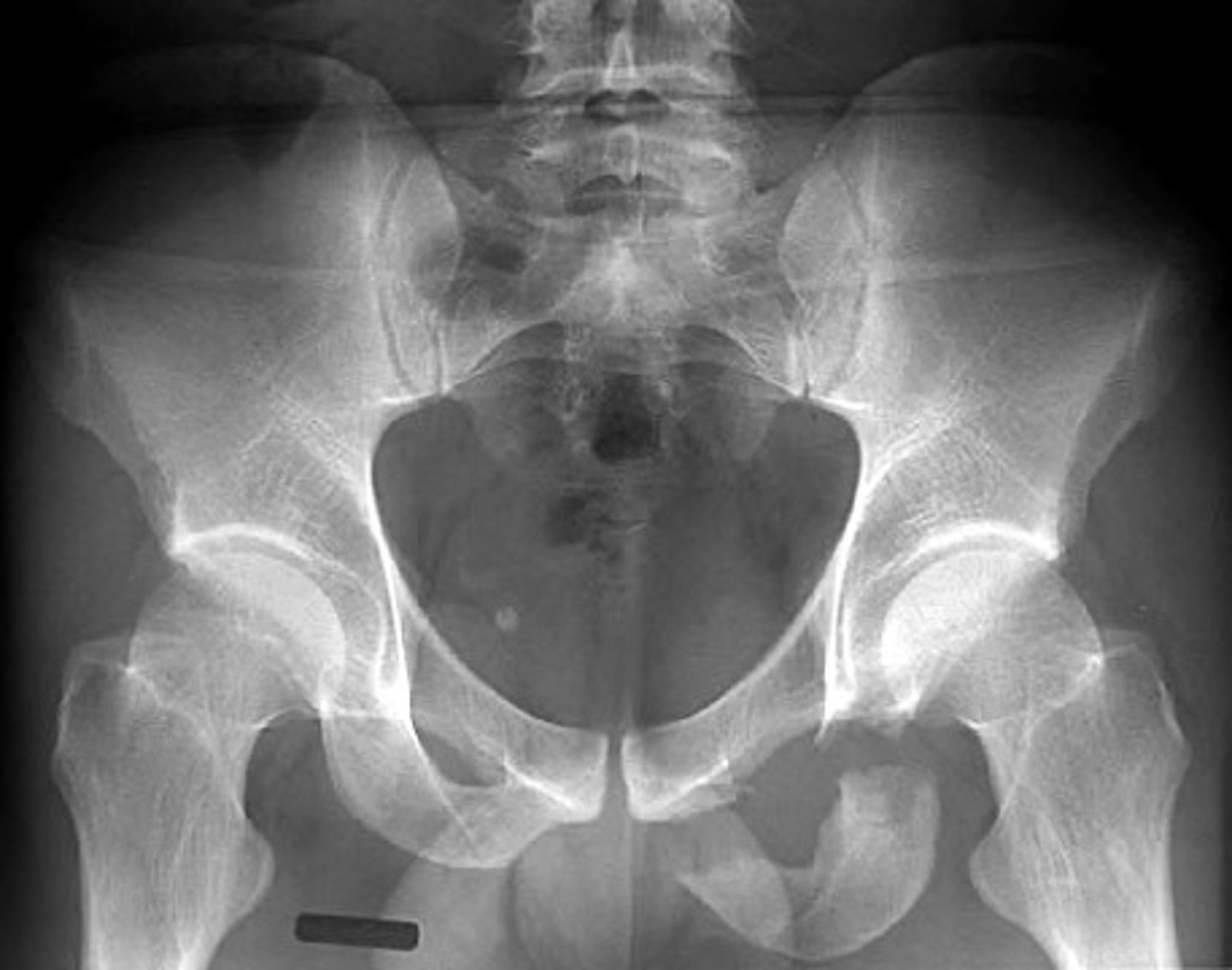
Avulsion fracture of anterior superior iliac crest
What's going on here?
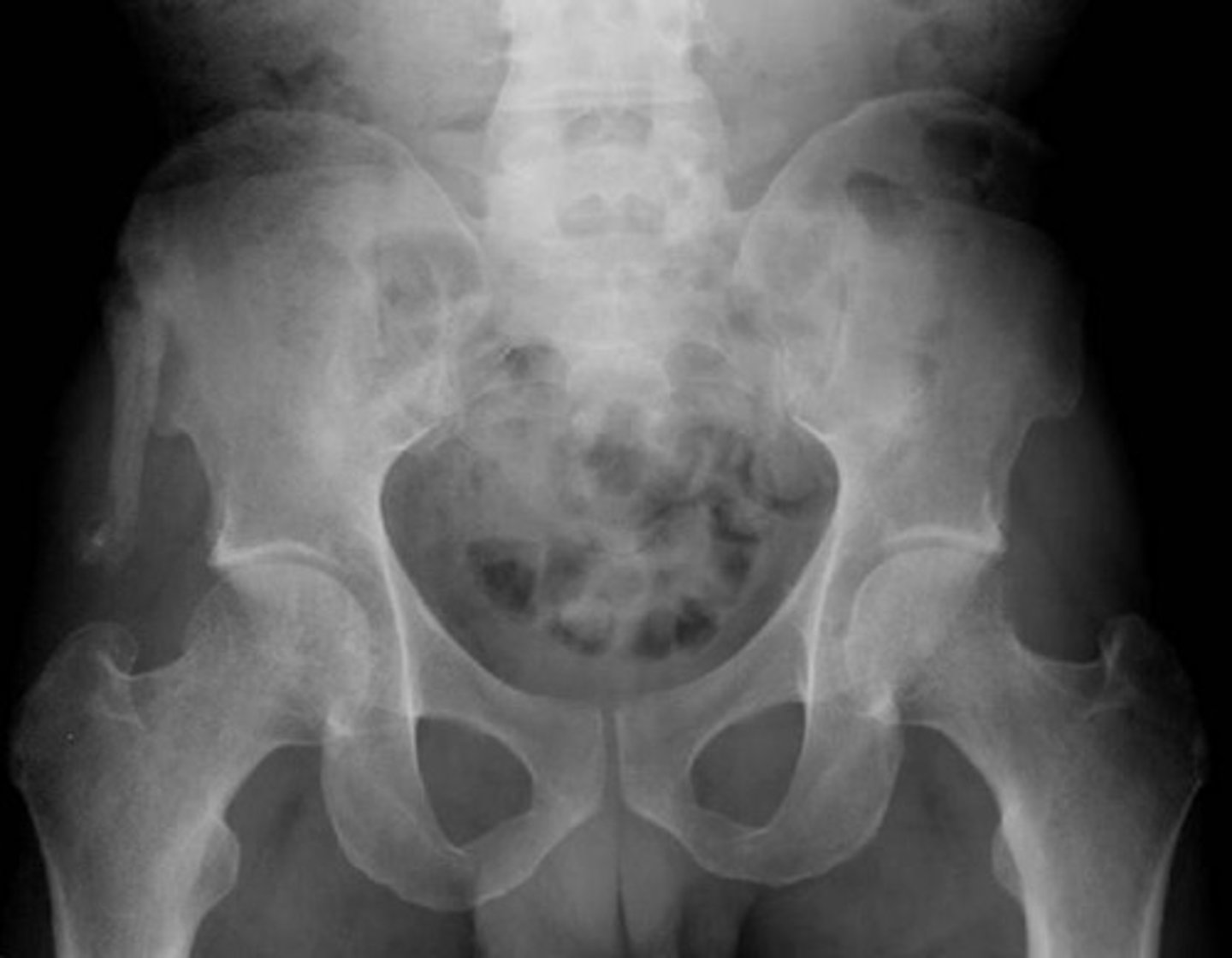
Pelvic fx with posterior dislocation of hip
What's going on here?
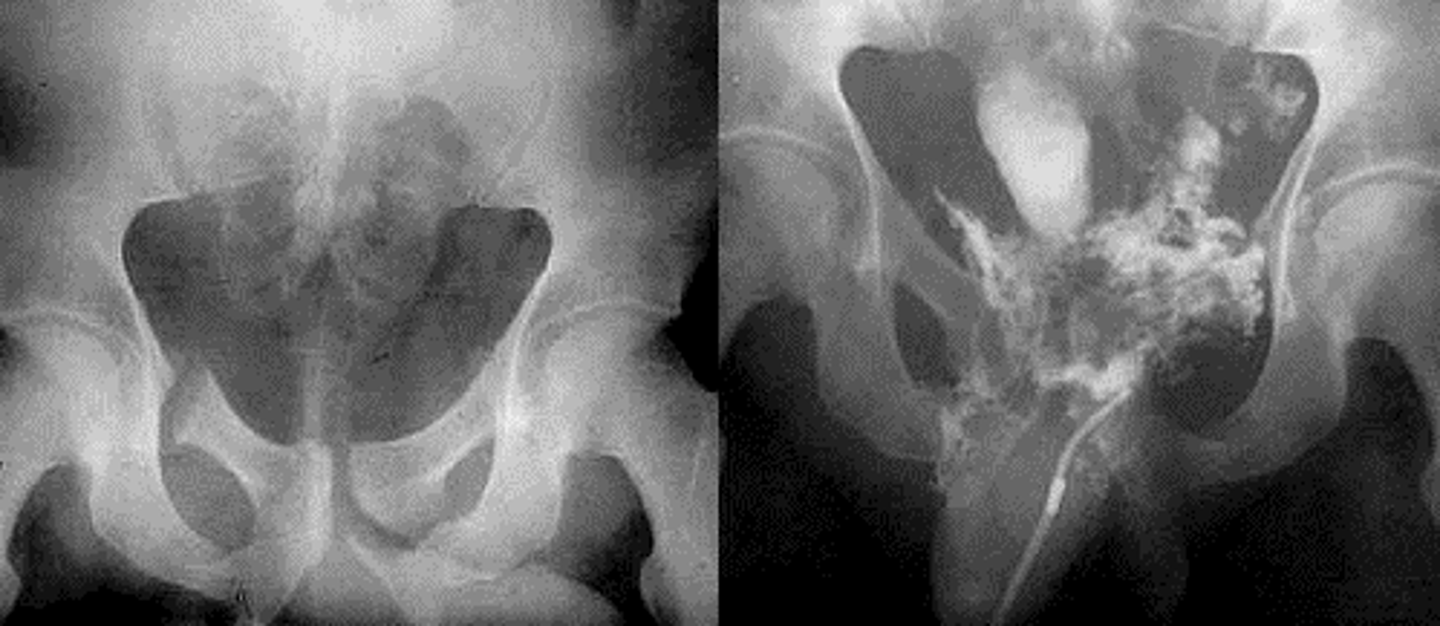
Severely fractured pelvis with ruptured bladder
What's going on here?
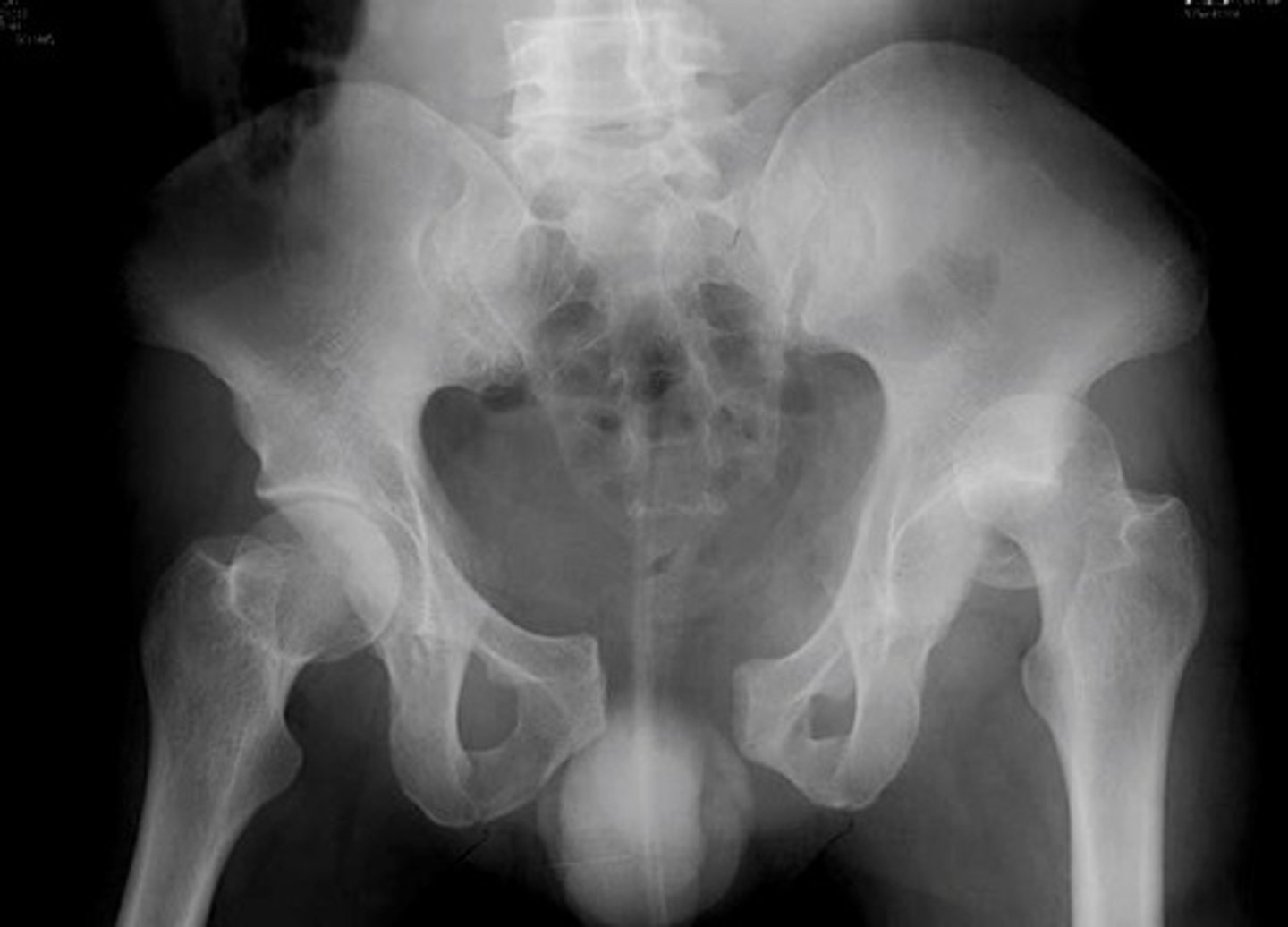
Fx superior pubic rami
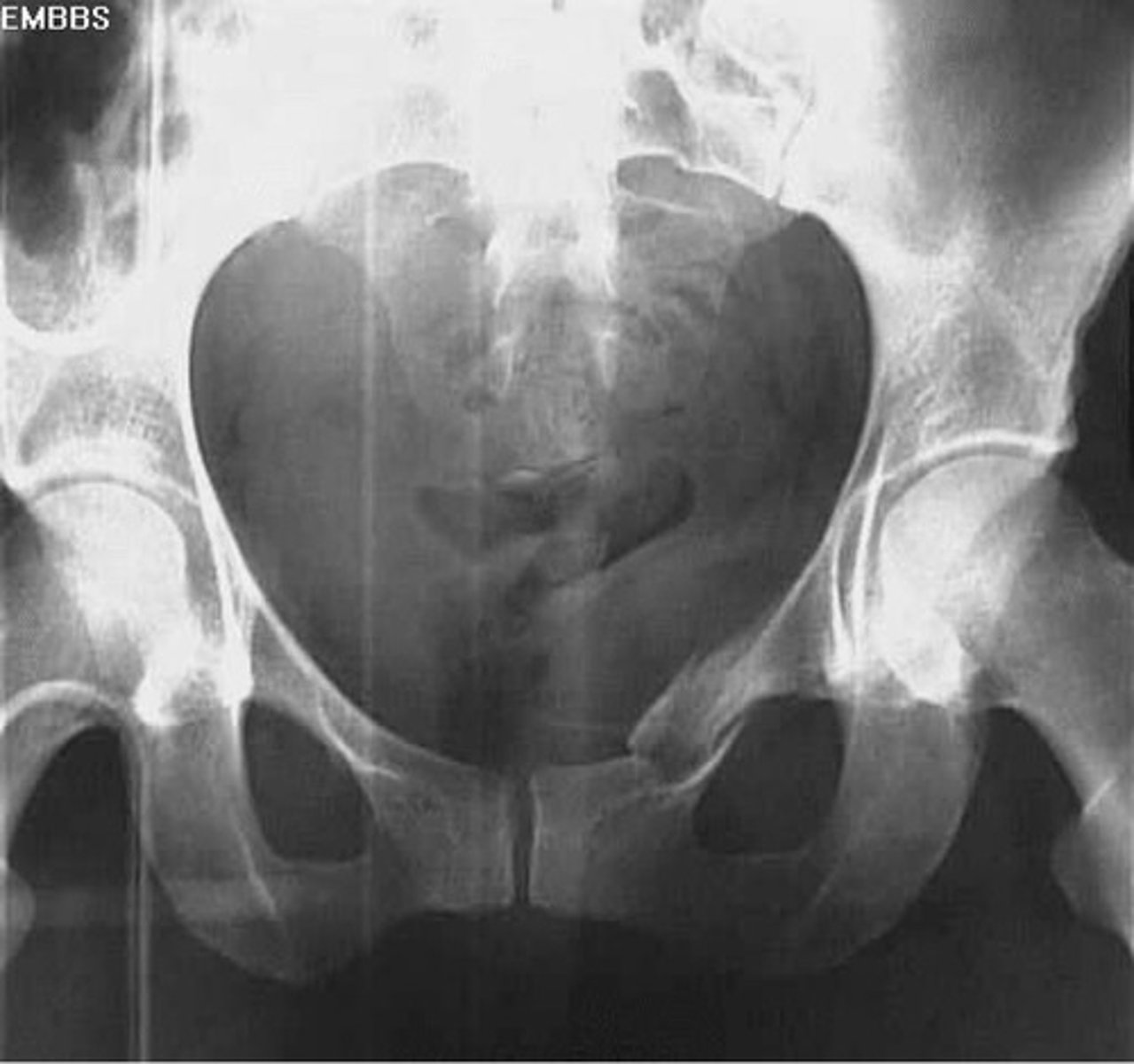
Flamingo view
Other Pelvic Views: ______________
o Look for instability of the pelvic ring
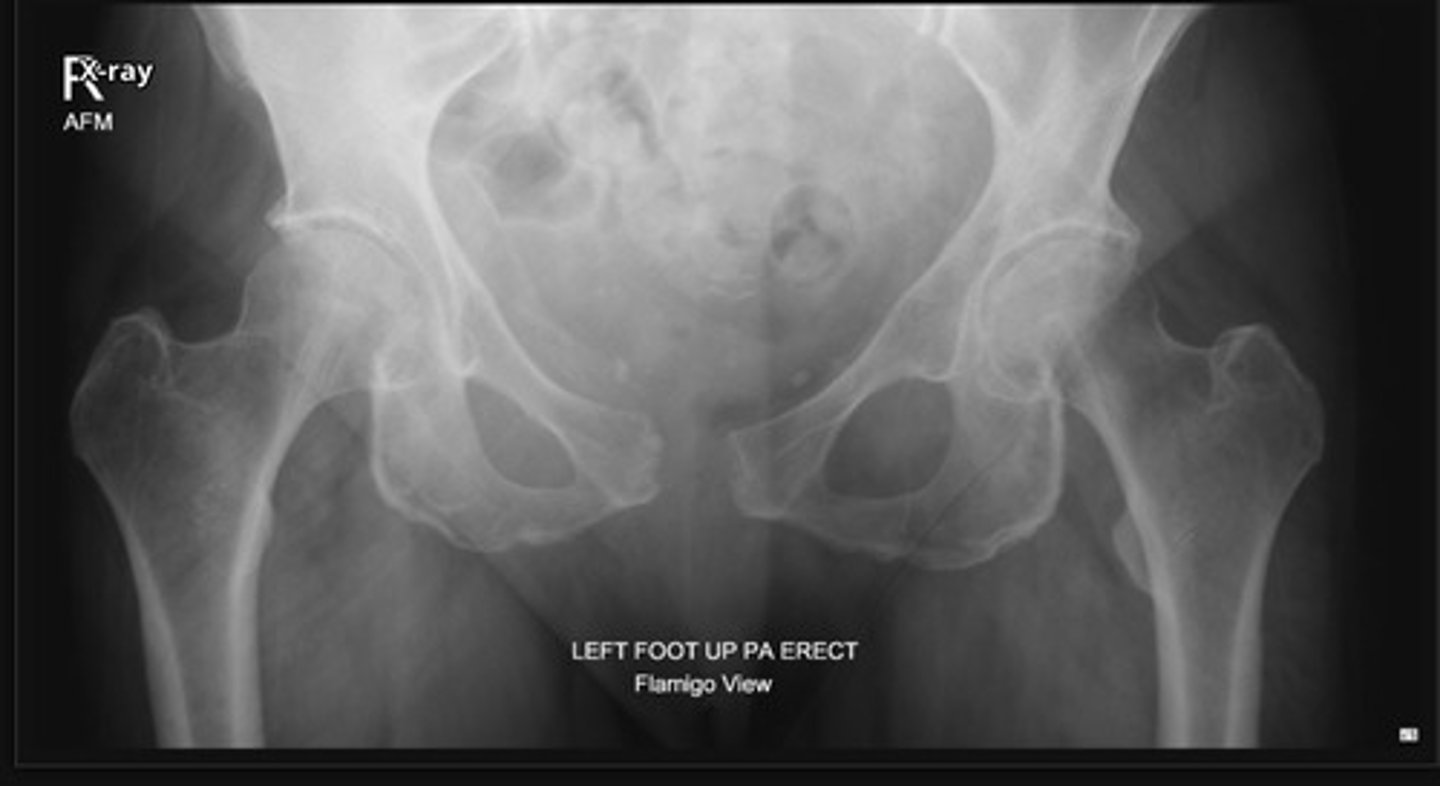
Judet View
Other Pelvic Views: ______________
o Evaluate posterior wall of acetabulum
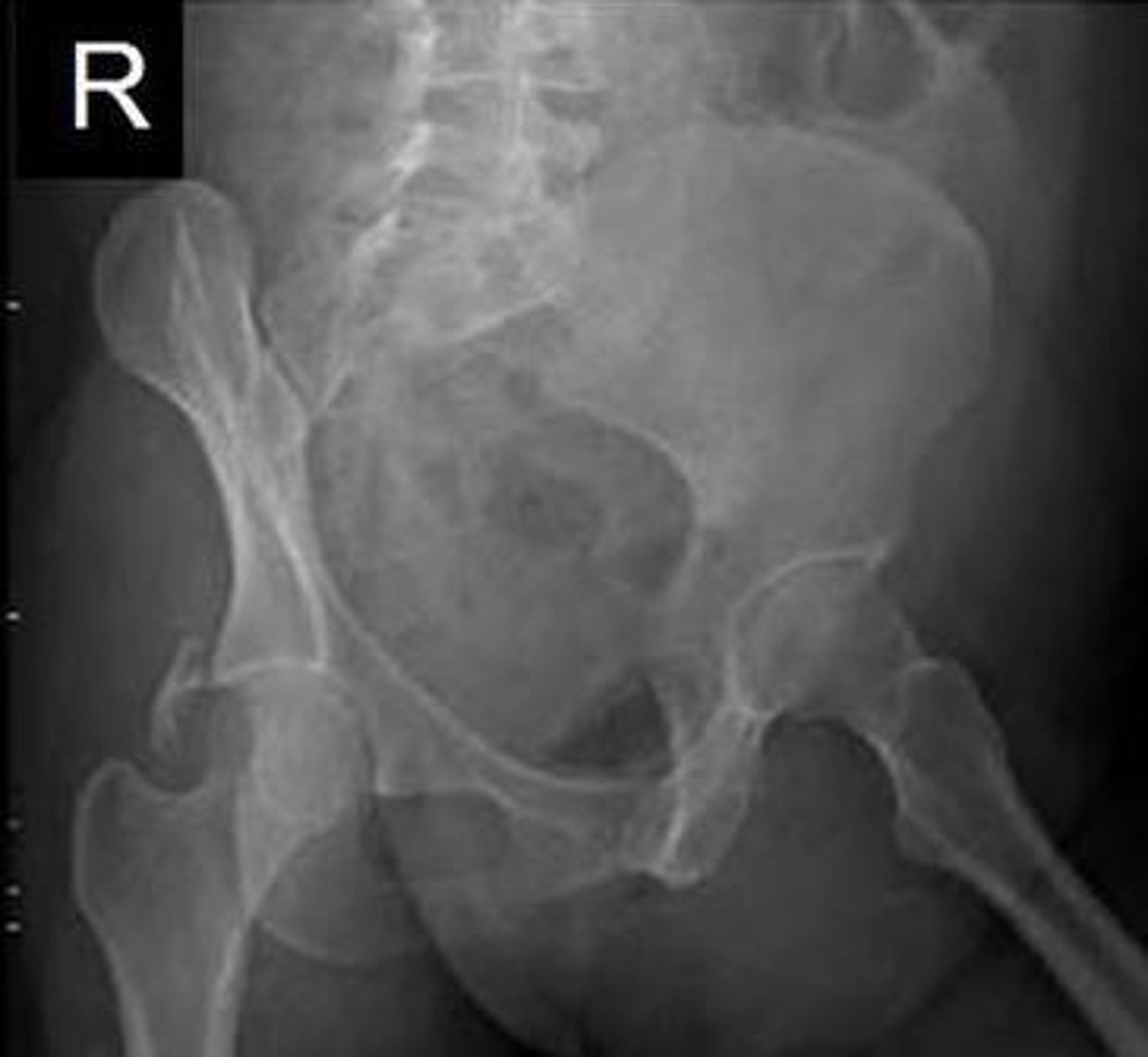
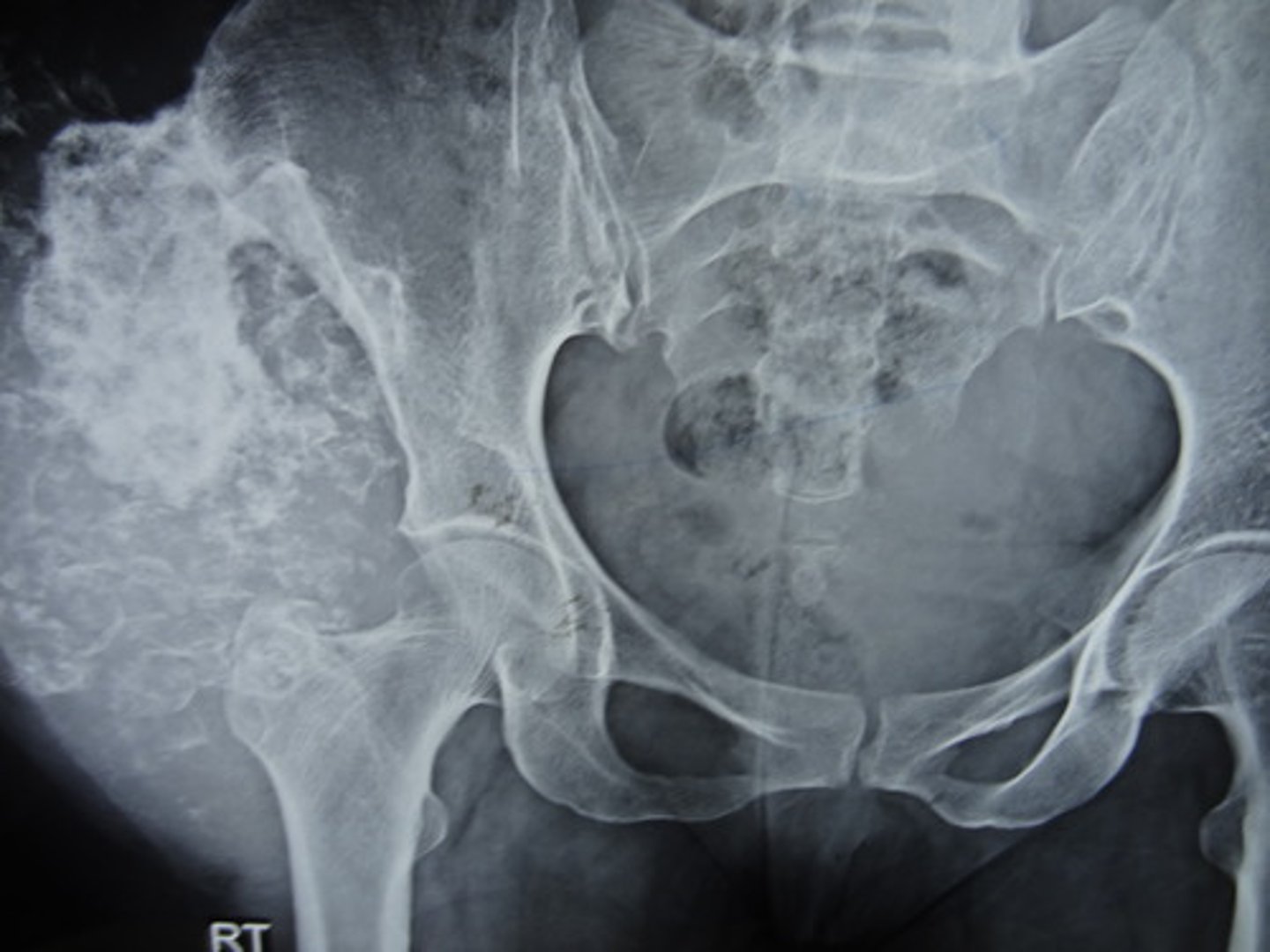
Paget's disease
______________ – benign lesion of the pelvis
o Increased sclerosis and enlargement of the left hemi-pelvis and right hip
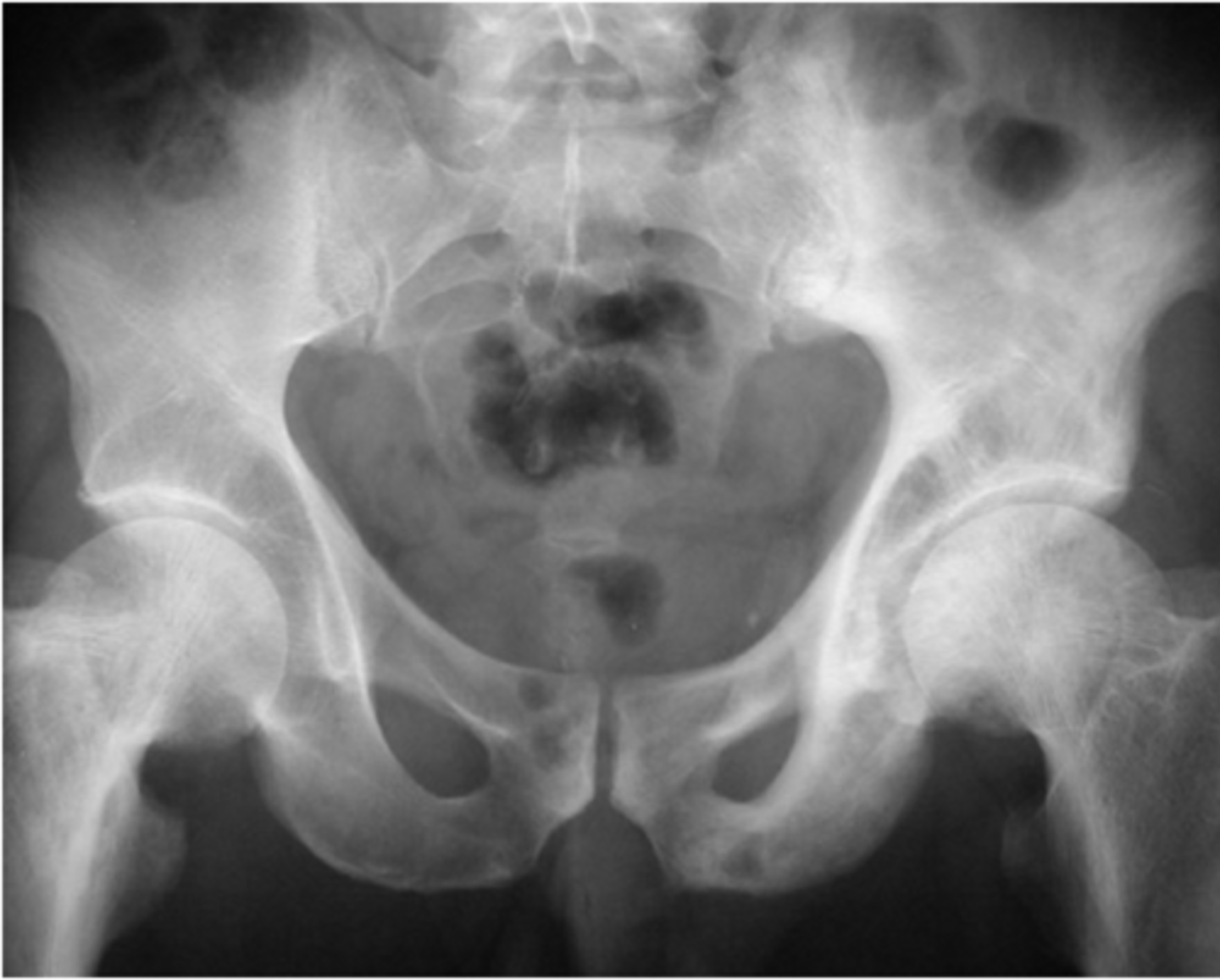
chondrosarcomas
Malignant tumors
Adult – ________________
- Metastases are also common
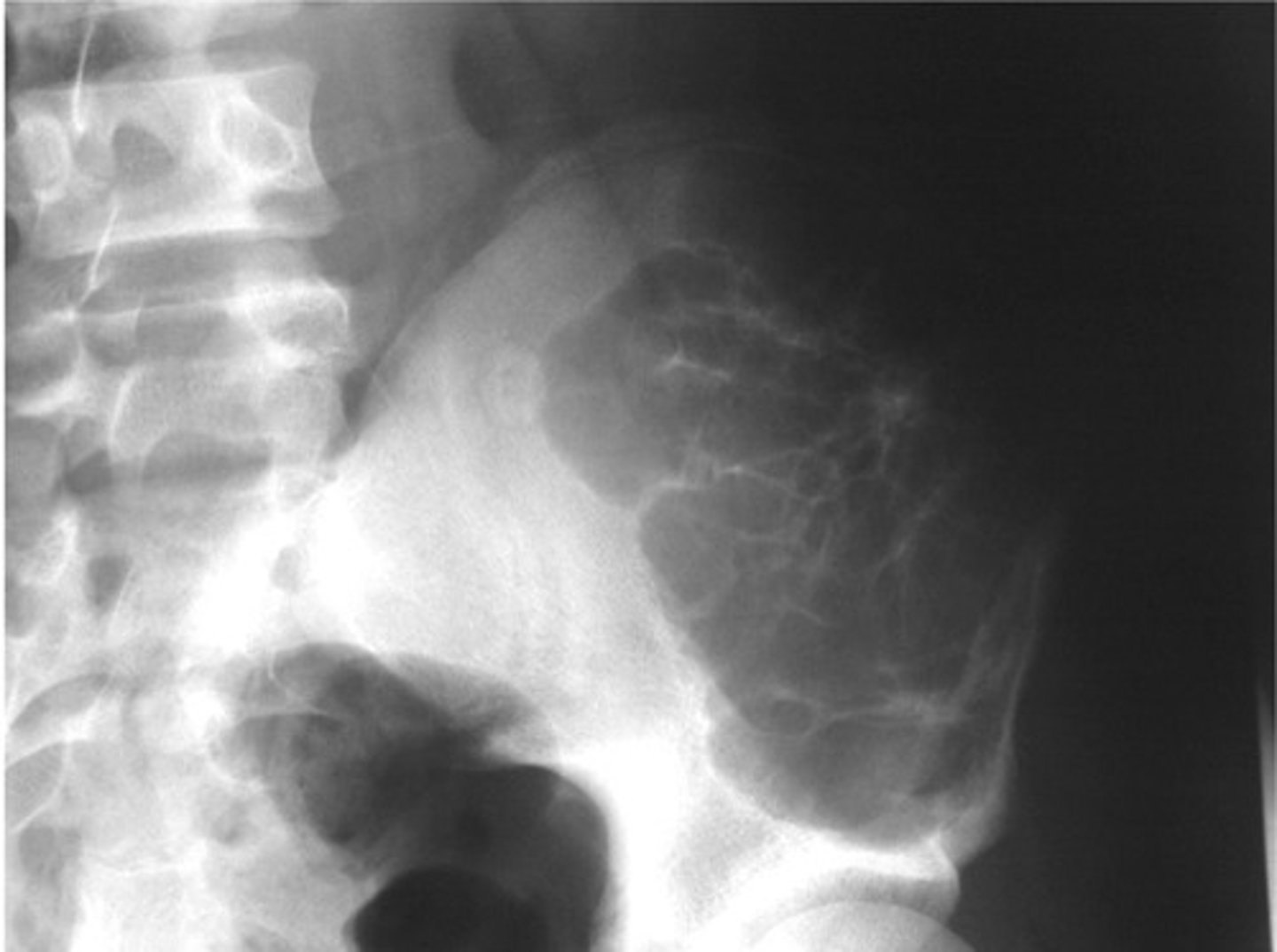
Ewing's sarcoma
Malignant tumors
Child – _______________
- Metastases are also common
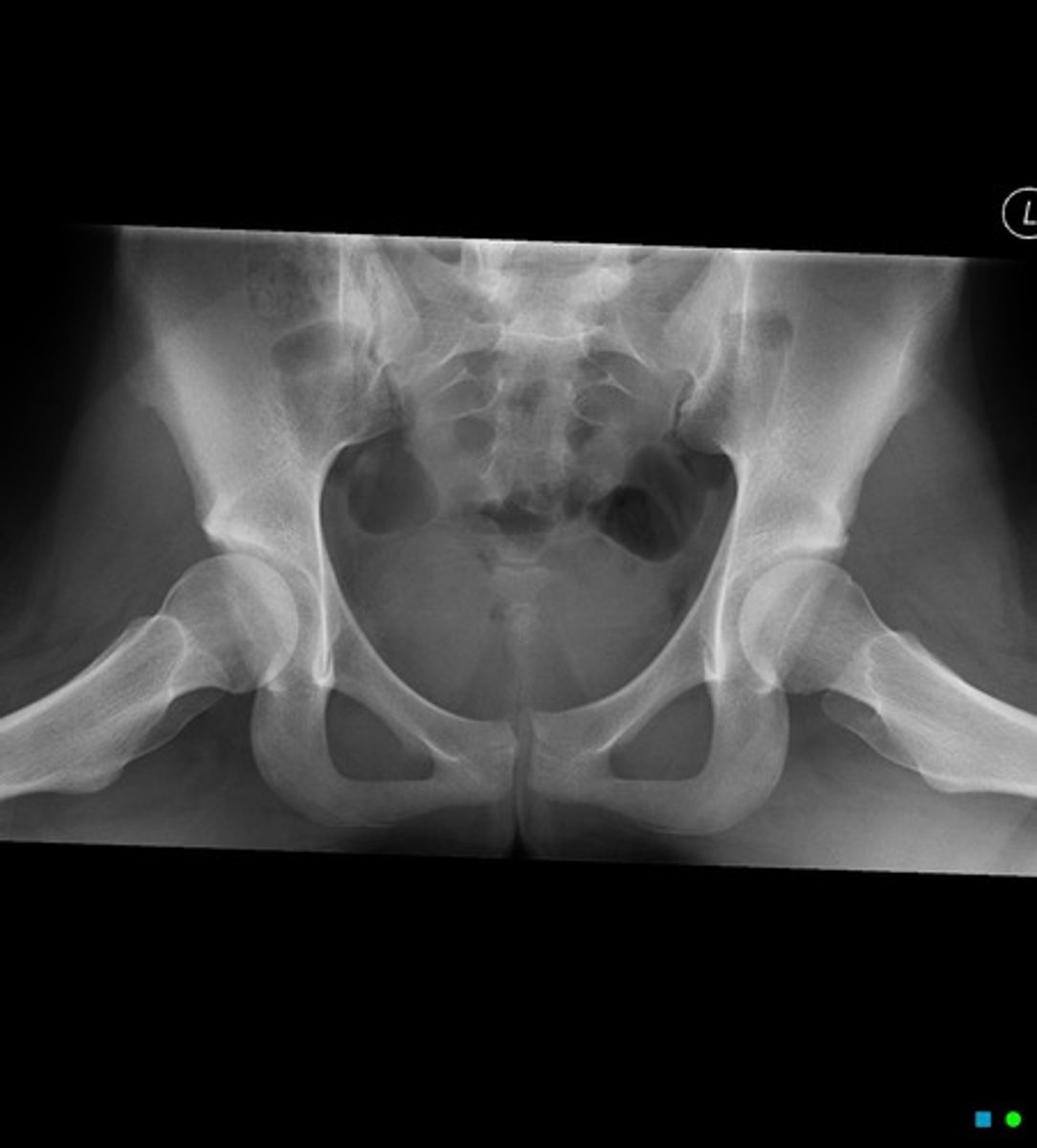
frog leg view
Plain films include an AP view and _______________ (abducted)
MVC's
Hip dislocations – usually the result of _________
Posterior
______________ dislocation is the most common hip dislocation
- Displaced superiorly and laterally on film
Anterior
__________ dislocation can also occur
- Displaced inferiorly and medially
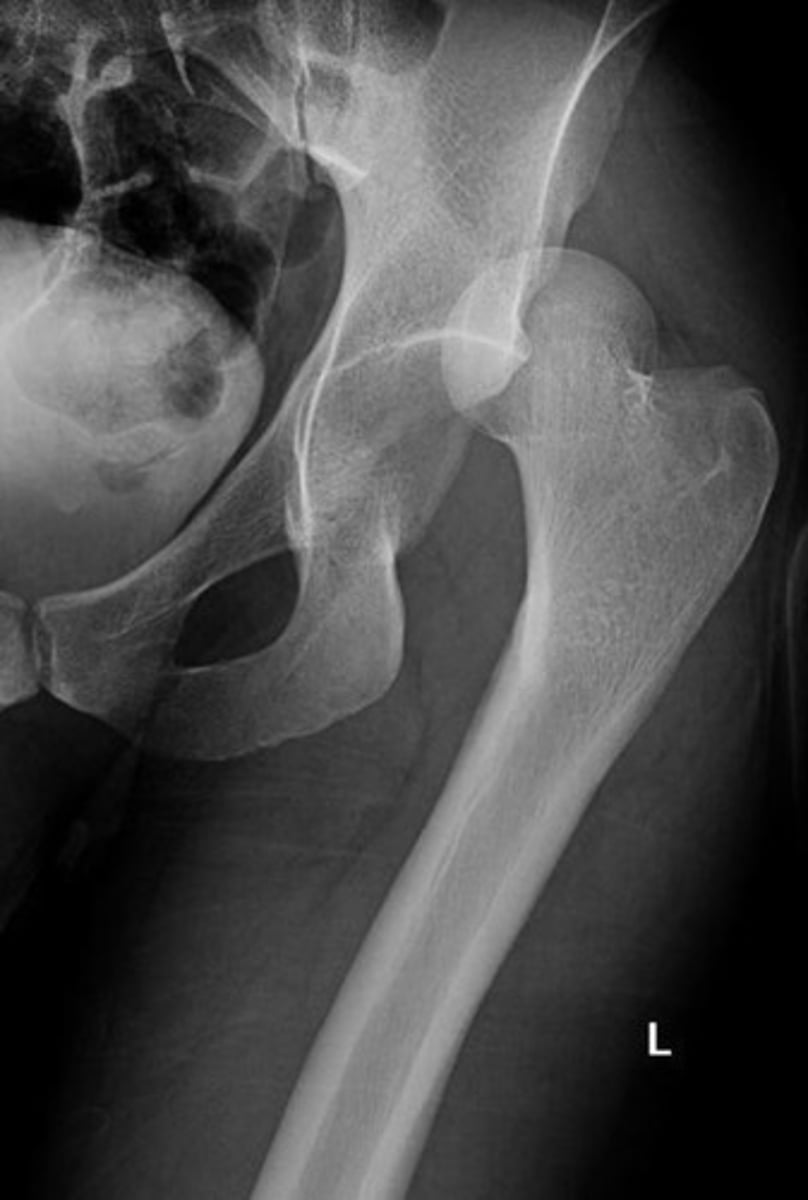
Left Posterior Dislocation
Trauma pt comes in s/p MVC. VSS. Pt CC is hip pain. nSuperior and lateral to the acetabulum. What's going on?
Anterior Dislocation
Anterior dislocation- Right
Inferior and medial to acetabulum
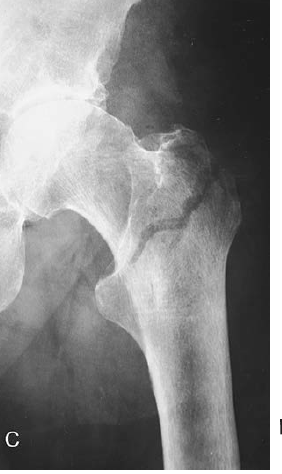
femoral neck
M/C hip fractures are
Fx’s of the _____________ (90%)
- Often due to osteoporosis
- Stress fx’s of the femoral neck may appear sclerotic
intertrochanteric region
Fx’s of the __________________
- Often due to trauma
***Shortened leg with internal rotation
CT scan
Nondisplaced hip fractures are best evaluated by ____
Femoral neck fracture
Fracture of the neck of the femur
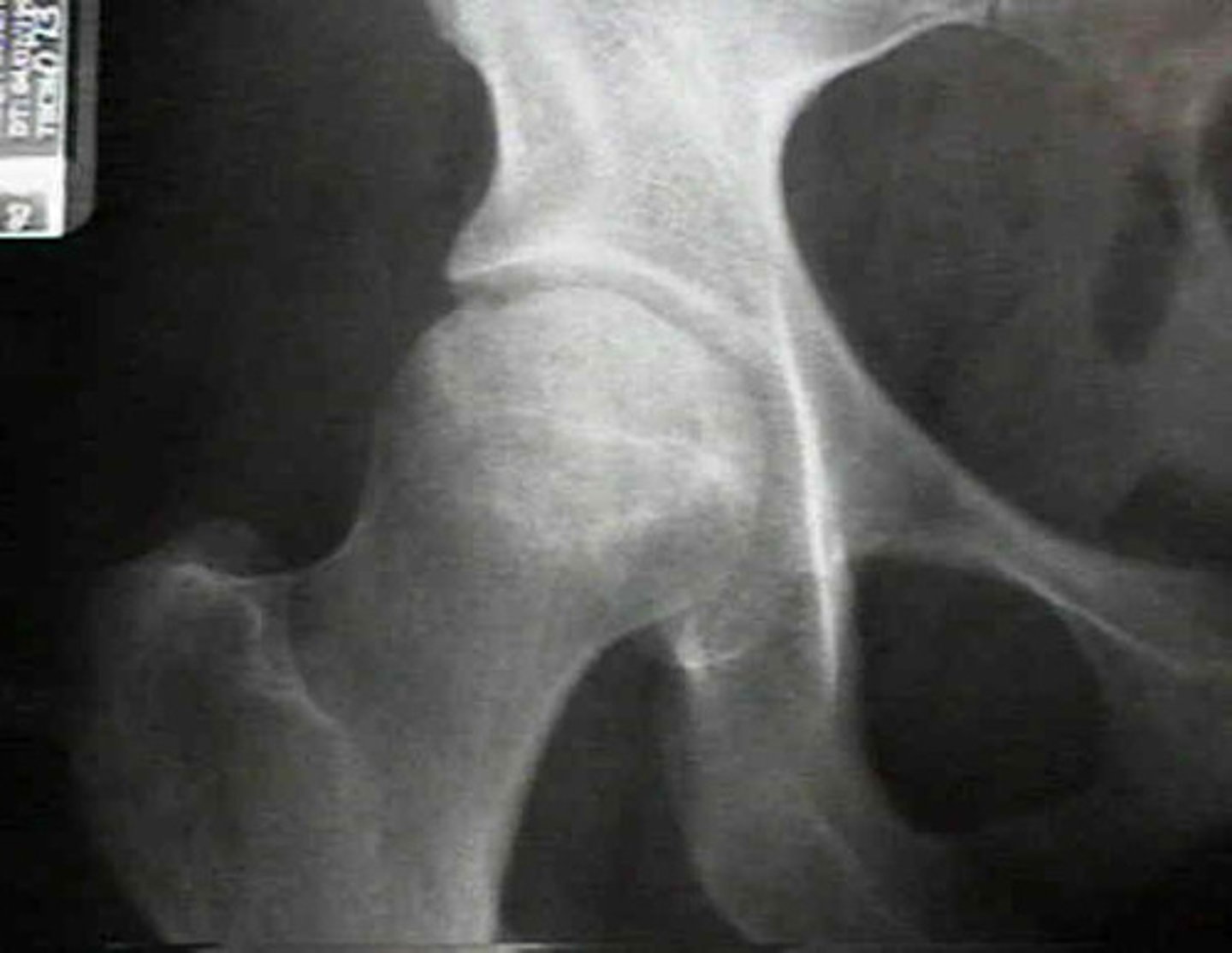
Intertrochanteric fracture
fracture that occurs between the greater and lesser trochanters of the hip
Osteoarthritis
_____________ is the most common cause of chronic hip pain
- Patient presents with pain and loss of mobility, starting with internal rotation.
- 90% of patients over 40 have some DJD of the hips
- DJD changes include joint space narrowing, subchondral cysts, and osteophyt
Avascular necrosis
_______________ of the hip
- Femoral head is flattened, irregular and sclerotic
- Crescent sign may be seen
Best study is an MRI
(**Steroid use, EtOH abuse...)
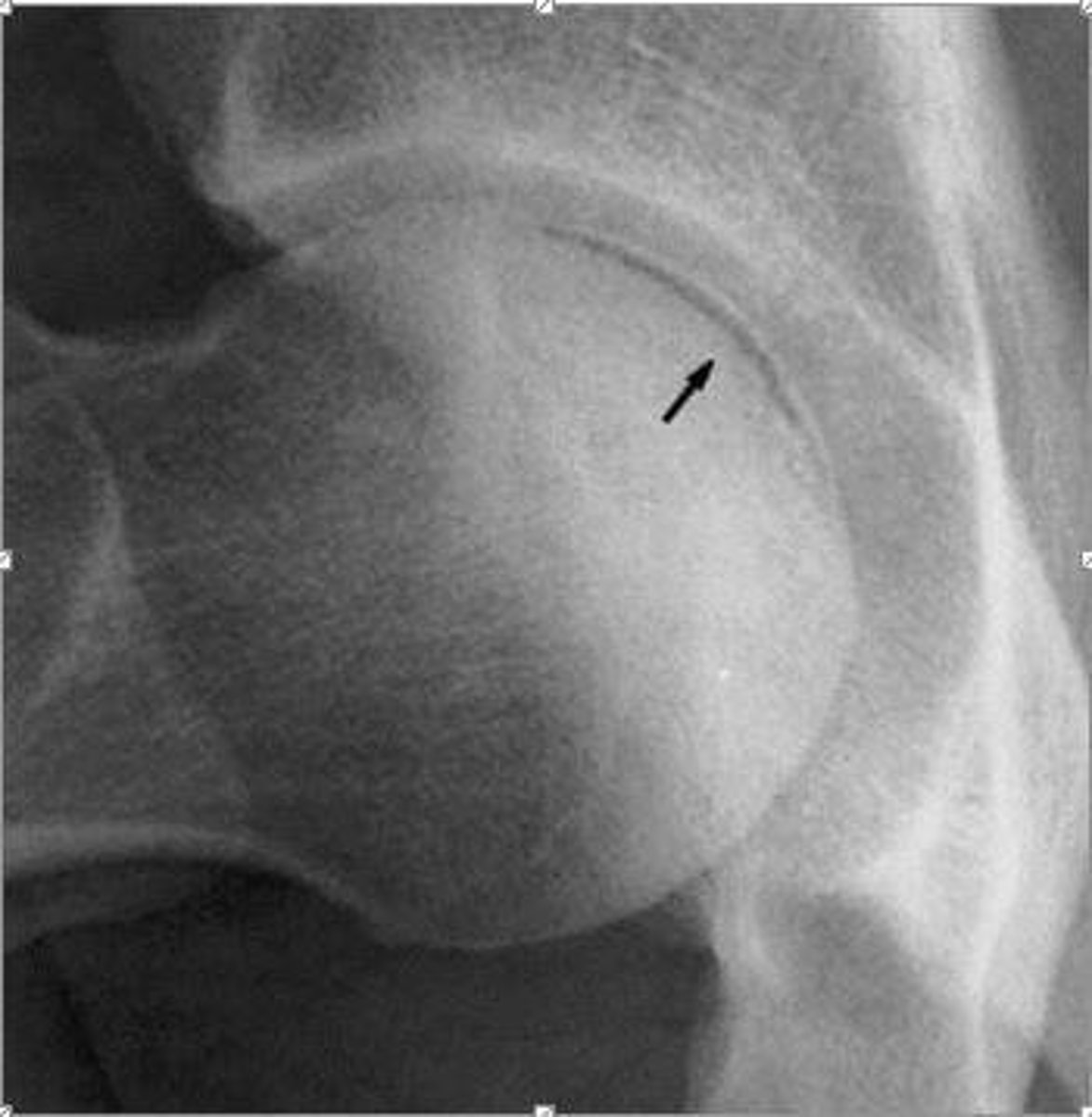
crescent sign
Your pt is a chronic alcohol abuser with hip pain. What sign might you see if they have avascular necrosis?
(Radiologist says: "Subarticular lucency of the femoral head")
Benign
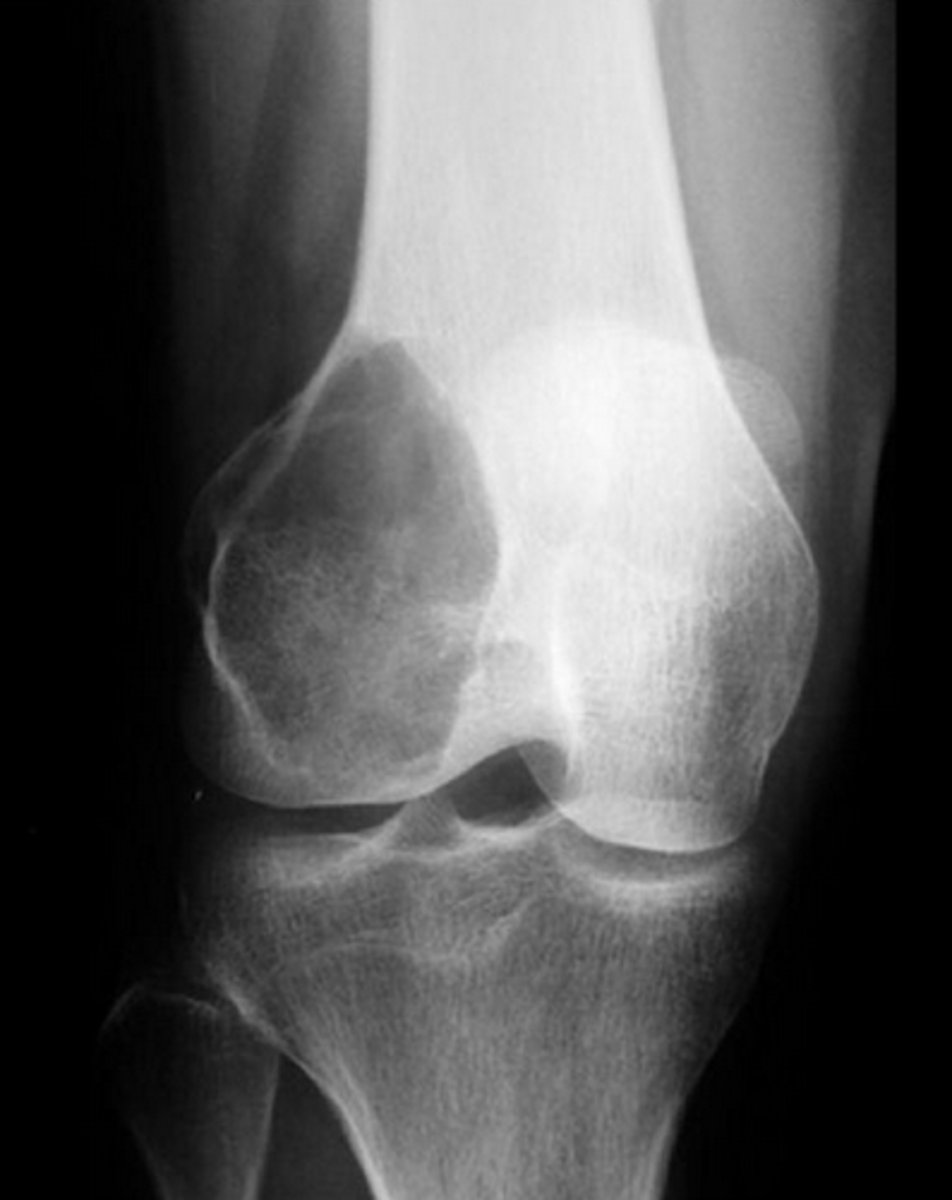
The femur is prone to tumors – benign and malignant
__________ – fibrous cortical defects, fibrous dysplasia, non-ossifying fibroma
Malignant
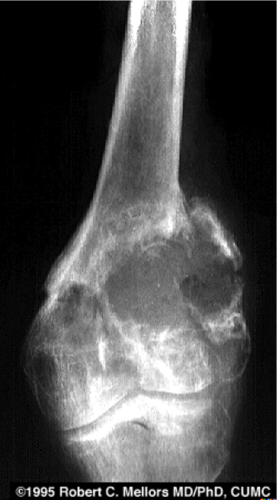
The femur is prone to tumors – benign and malignant
___________ – chondrosarcoma, metastases
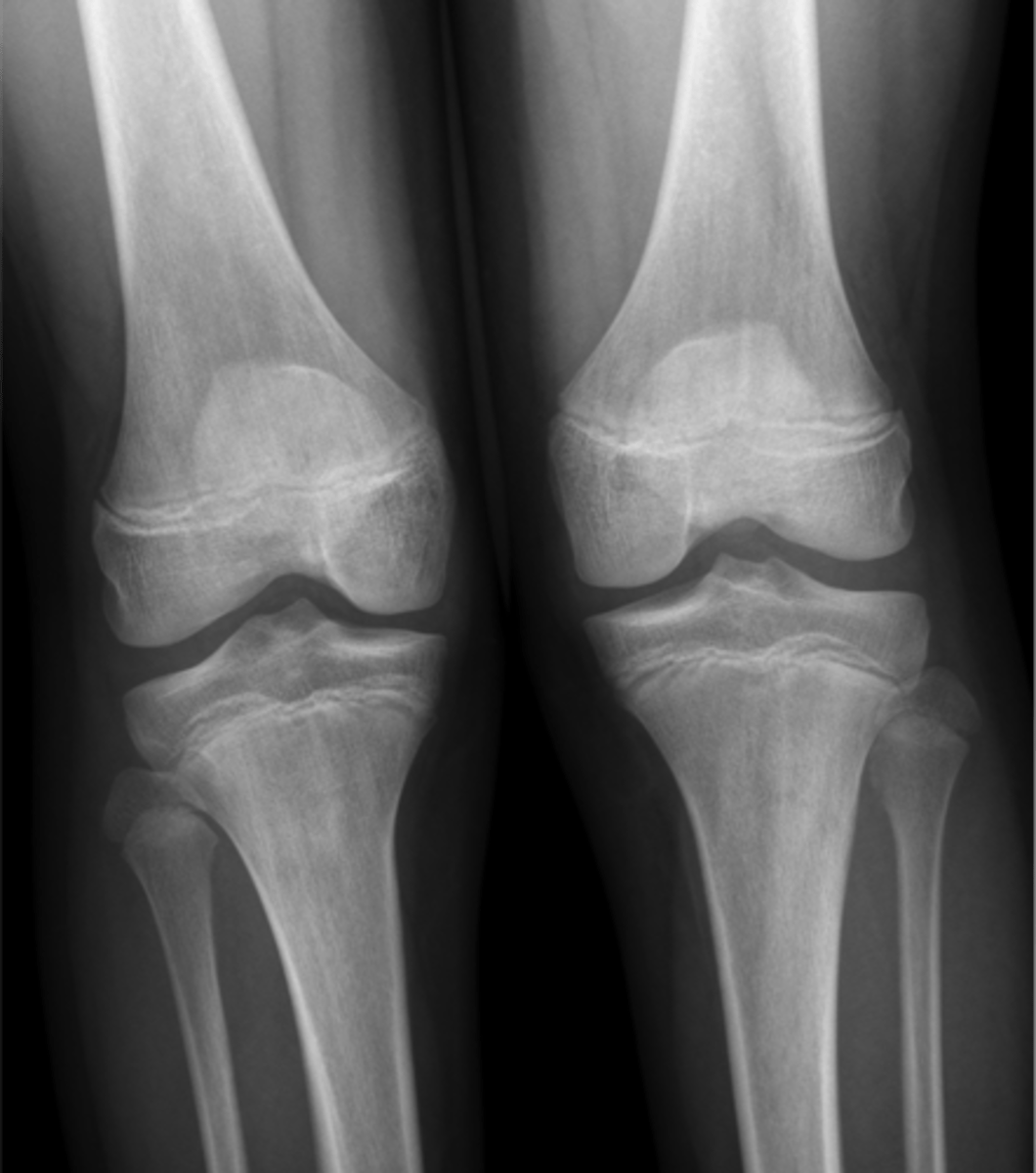
AP view
Lower Extremity Knee Plain films include:
_________ – joint space narrowing or calcification of the cartilage
lateral view with partial flexion
Lower Extremity Knee Plain films include:
_________________ – patella and joint effusions
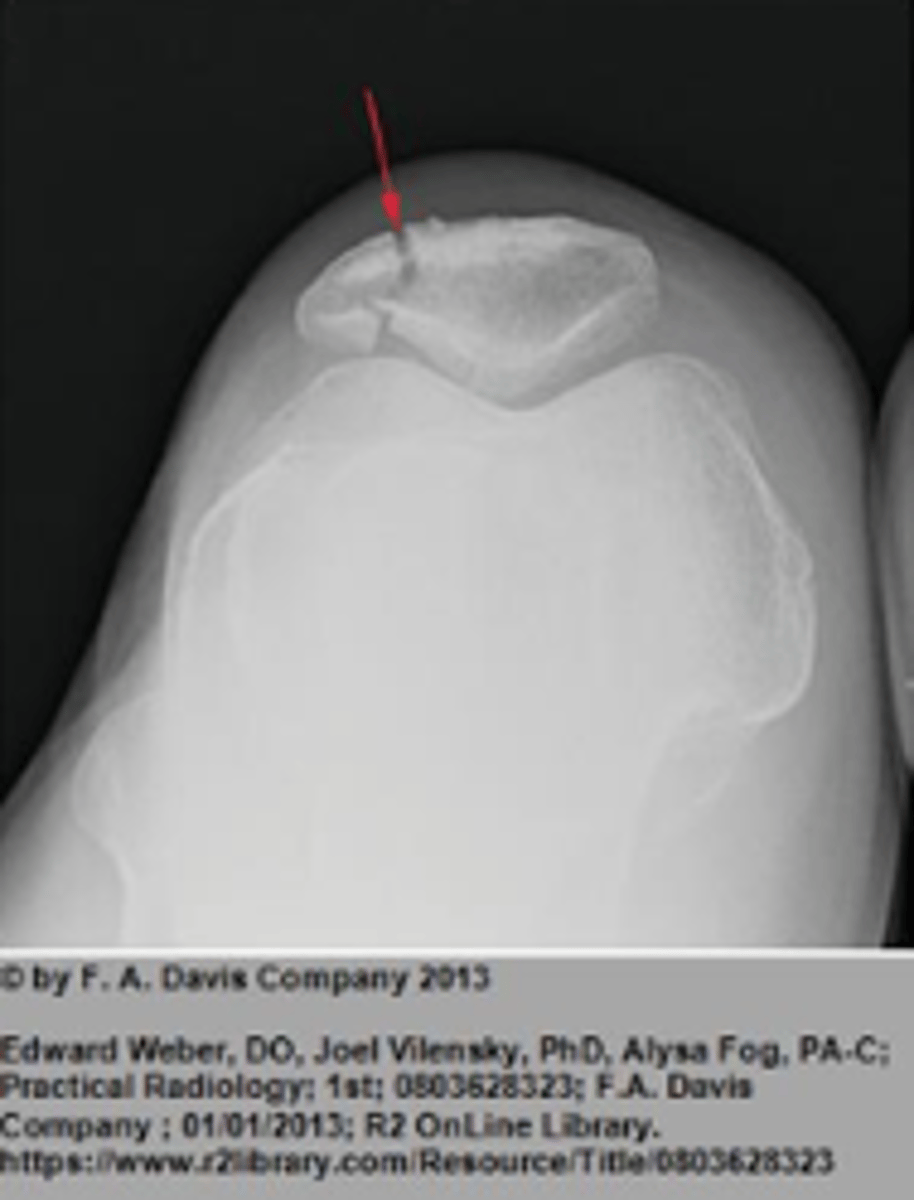
Sunrise or Merchant view
Lower Extremity Knee Plain films include:
__________________ – relationship of patella to the anterior femur
Tunnel view
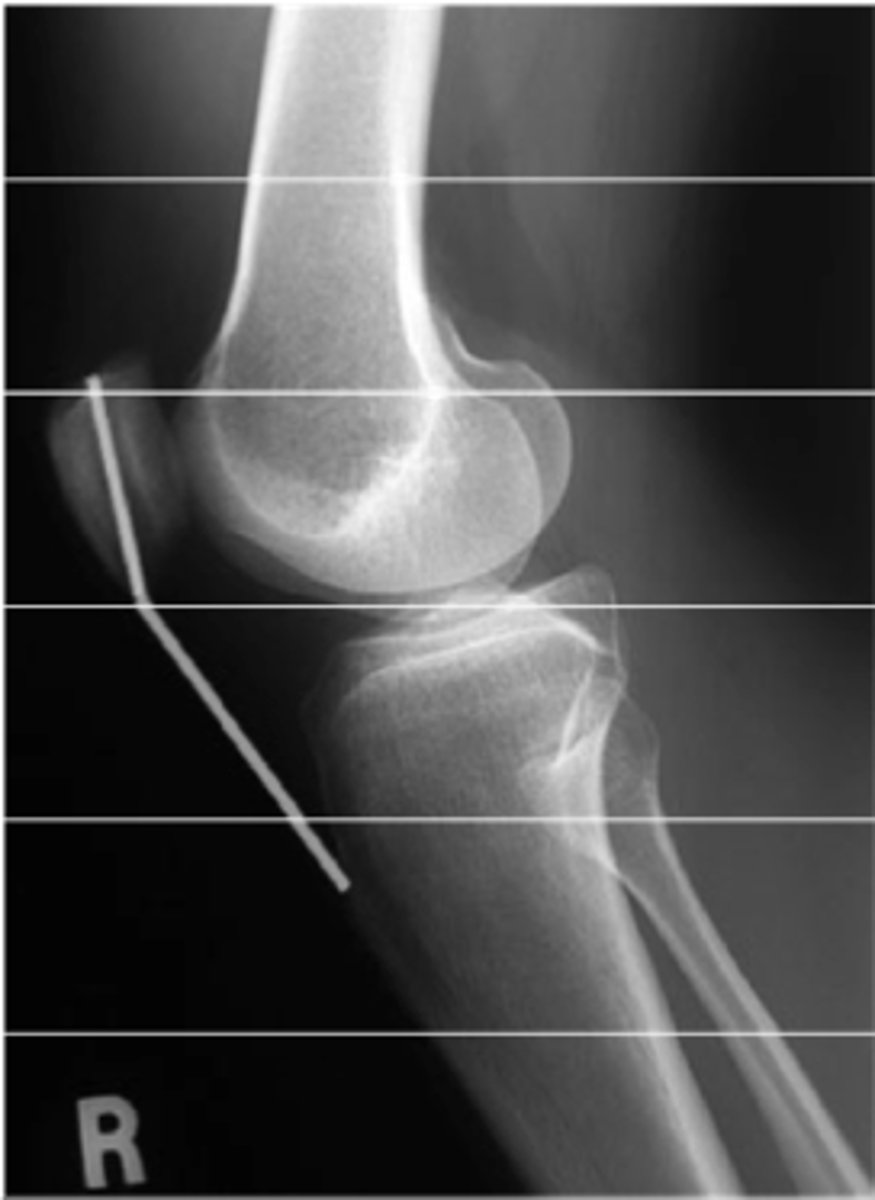
Lower Extremity Knee Plain films include:
____________ – tibial spines and femoral condyles

MRI
_______ is the best study for ligaments, cartilage and tendons (of the knee)
Joint effusion
_____________ is best seen on a lateral view superior to the patella and anterior to the femur
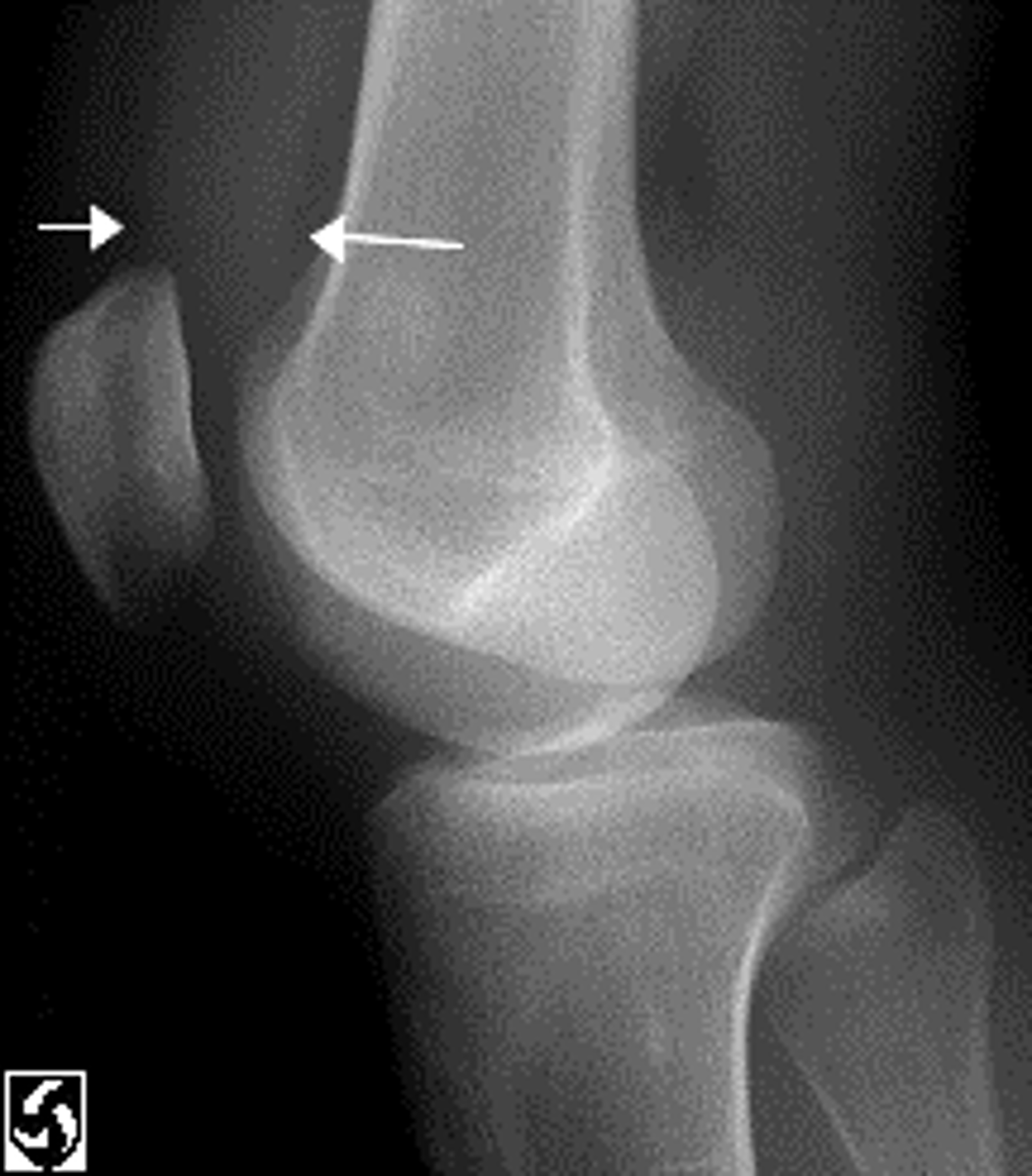
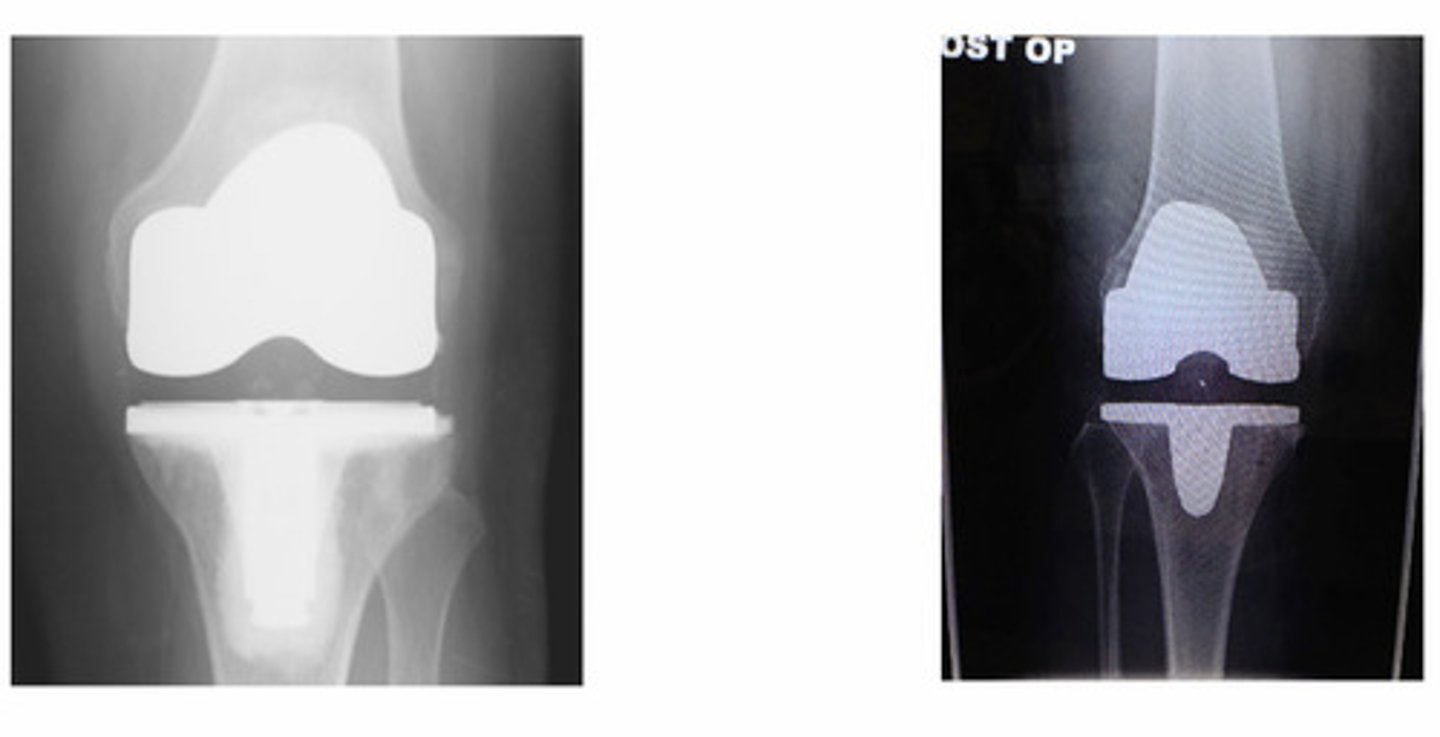
Knee DJD
What's goin on here?
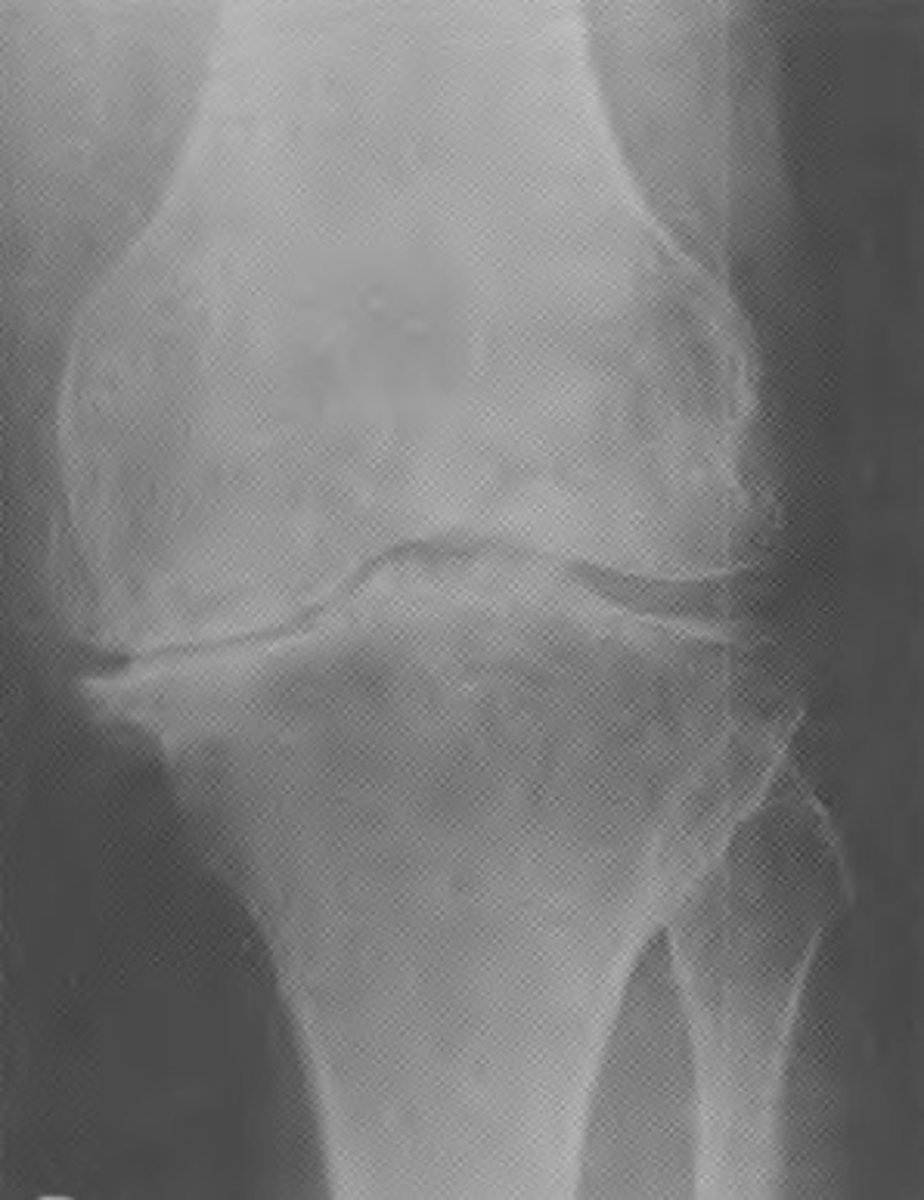
Total knee replacement
What procedure was done to this pt?
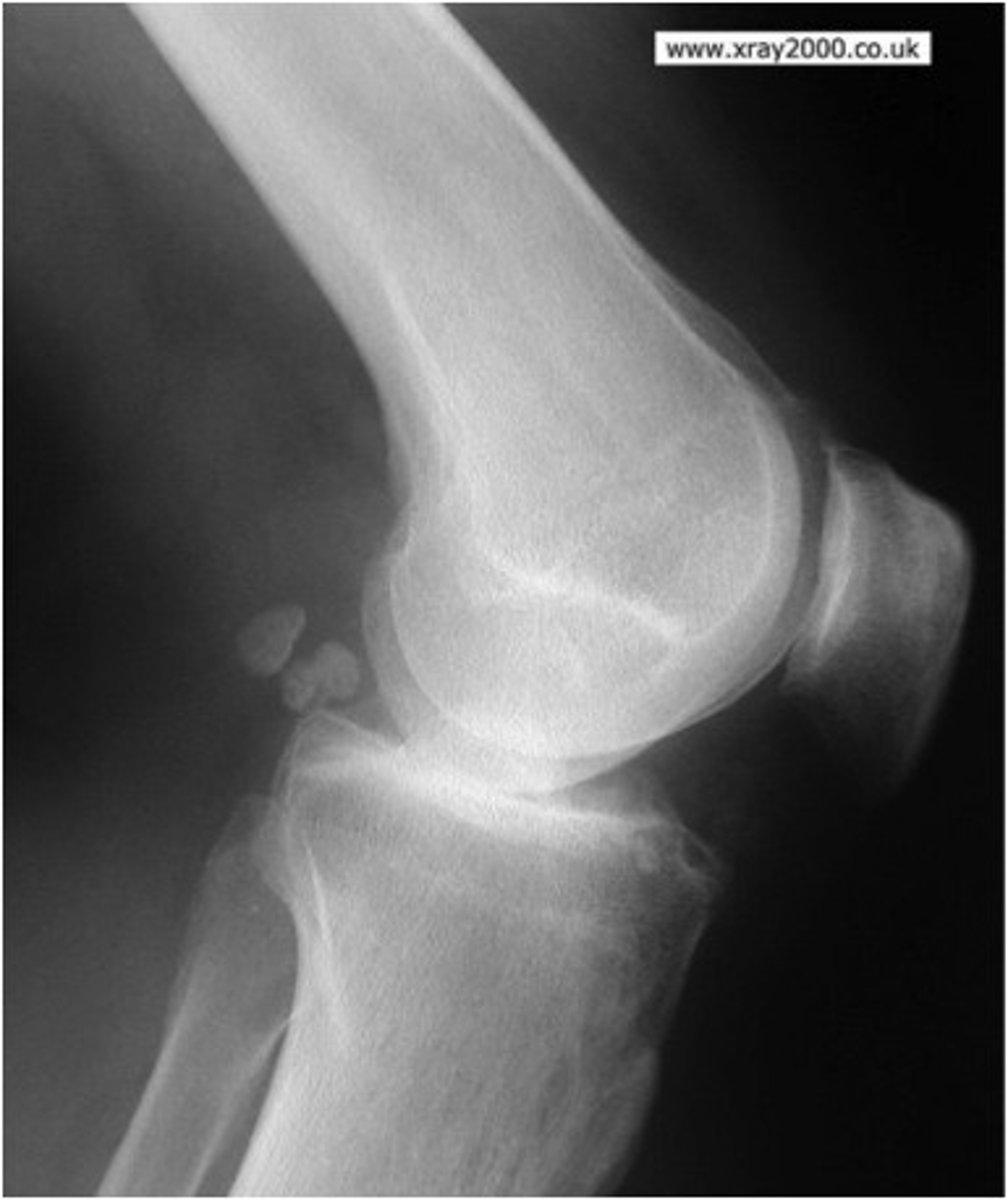
Loose bodies (NOT a Fx)
Is this a fracture?
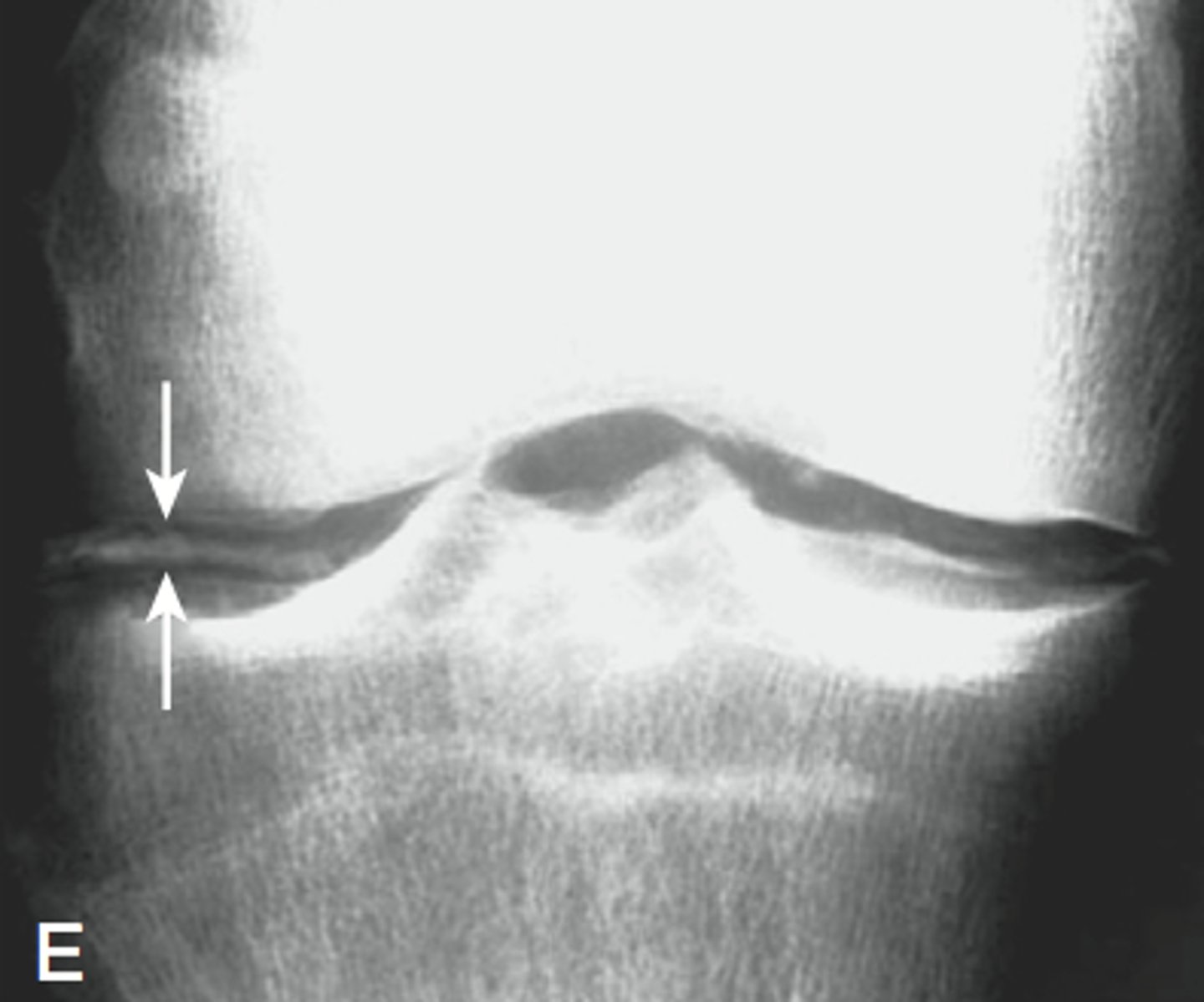
Chondrocalcinosis
Calcification of the articular cartilage
AP view
Tibial plateau fractures can be difficult to see
- Best seen on ___________
o If films are negative and still suspect fractures-MRI or CT is indicated
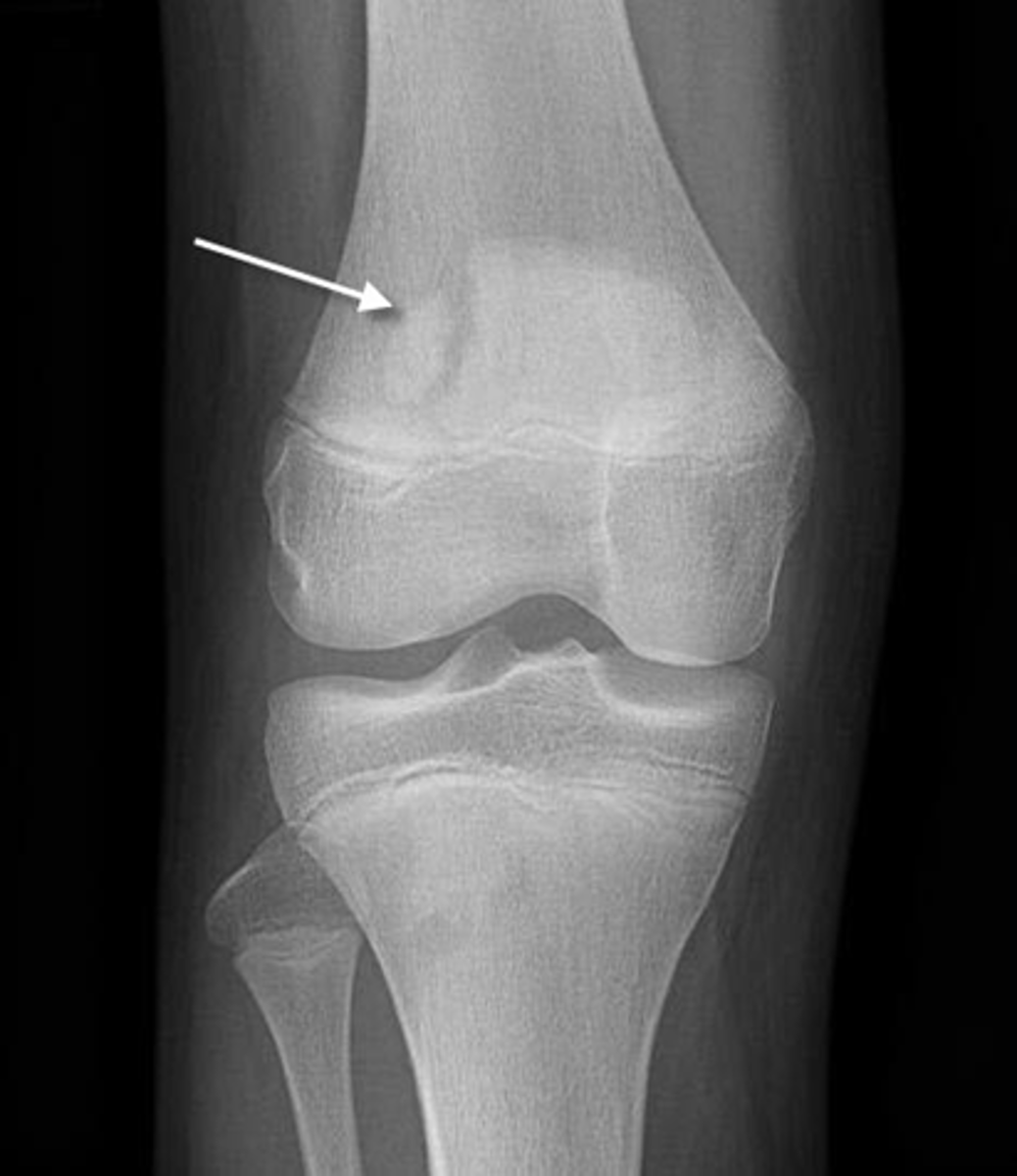
Bipartite patella
______________ is a normal variant that may appear to be a fracture
Patellar fracture
MOI: direct fall, direct hit, forceful extension
Surgery is typical
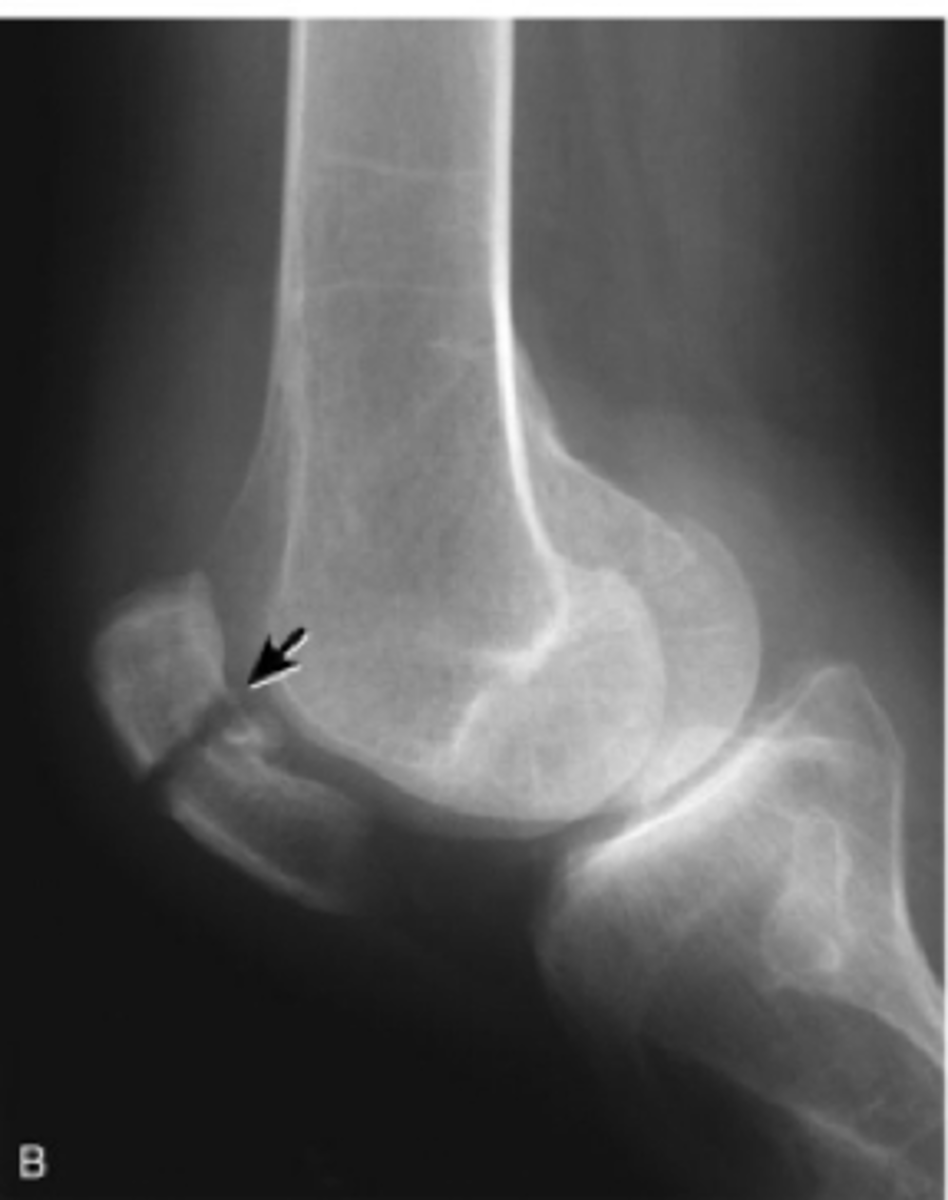
Tibial plateau fracture
valgus and compressive forces to knee with knee in flexion. often in conjunction with MCL injury.
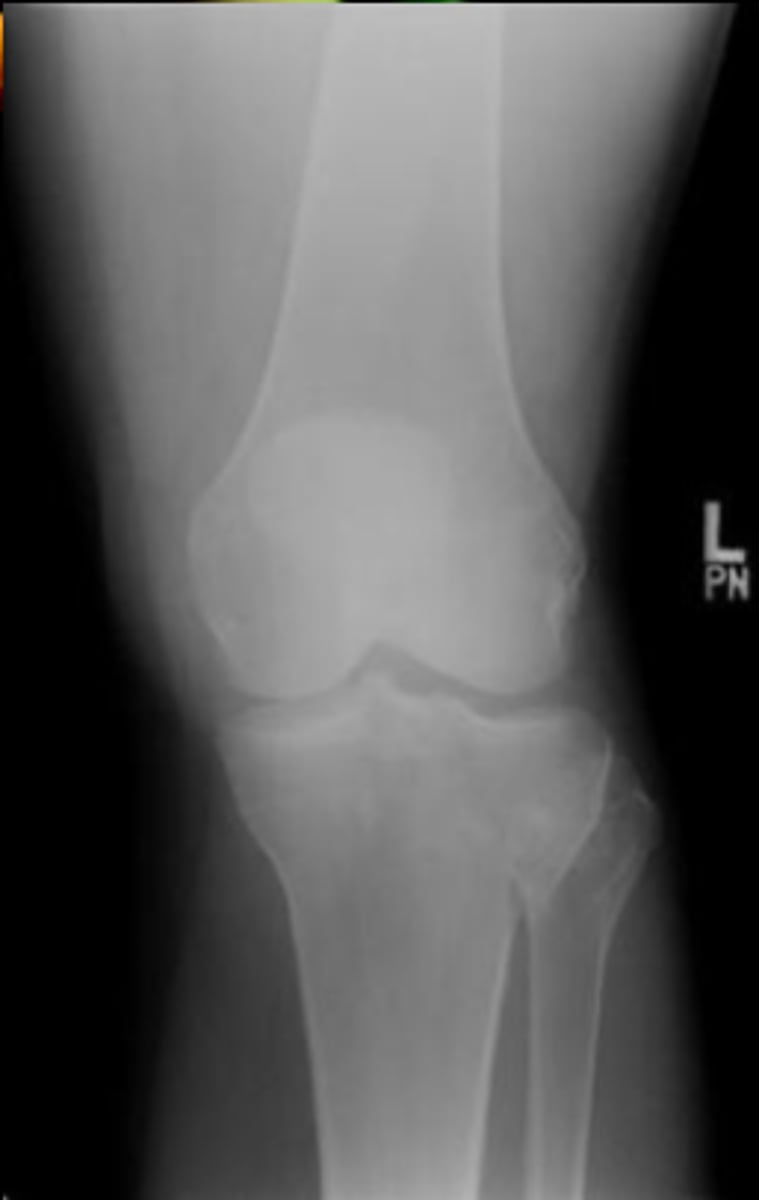
Supracondylar fracture of femur
Occur after Severe Impaction Injury to the Femur
May be associated with Hip Fracture/Dislocation
Transverse or Oblique Orientation
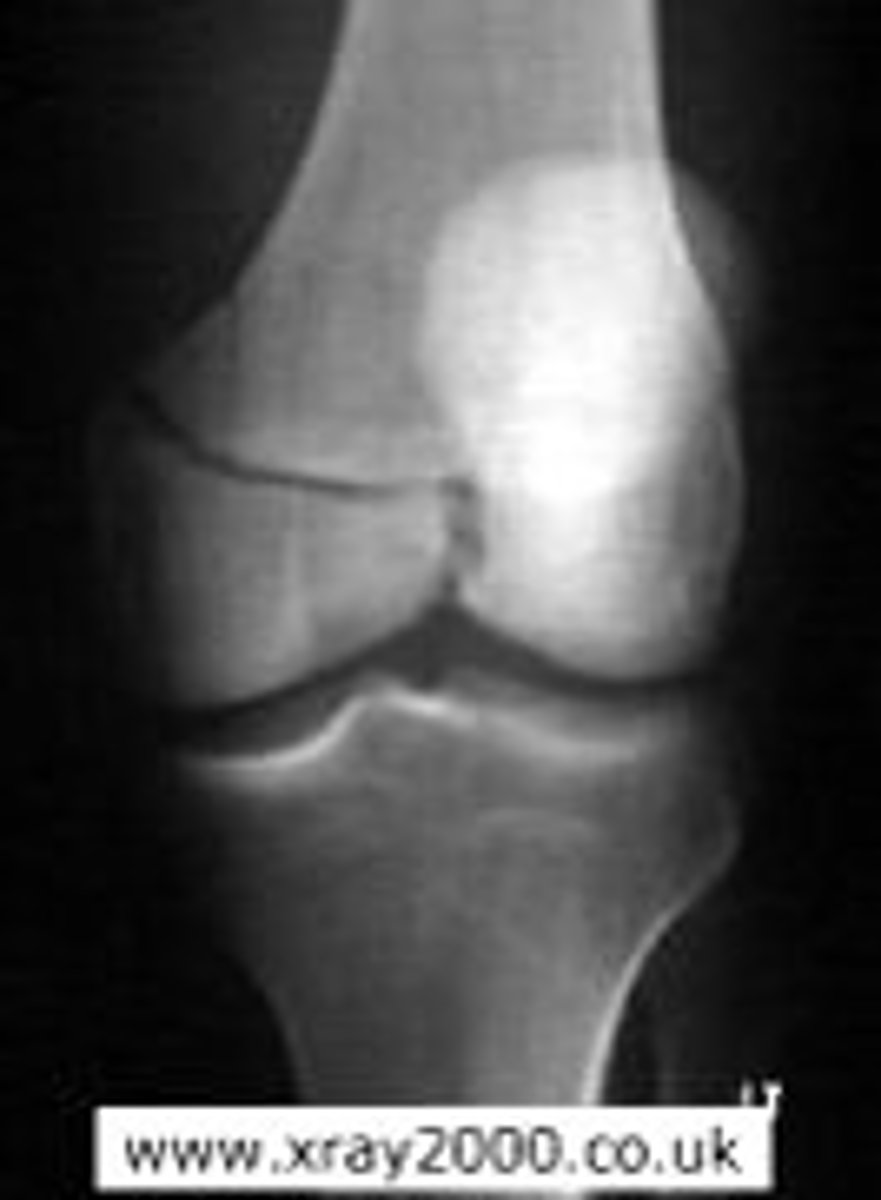
Dislocated patella
athlete may have tight lateral tissue, weak VMO, or forced to outside by contact with another object
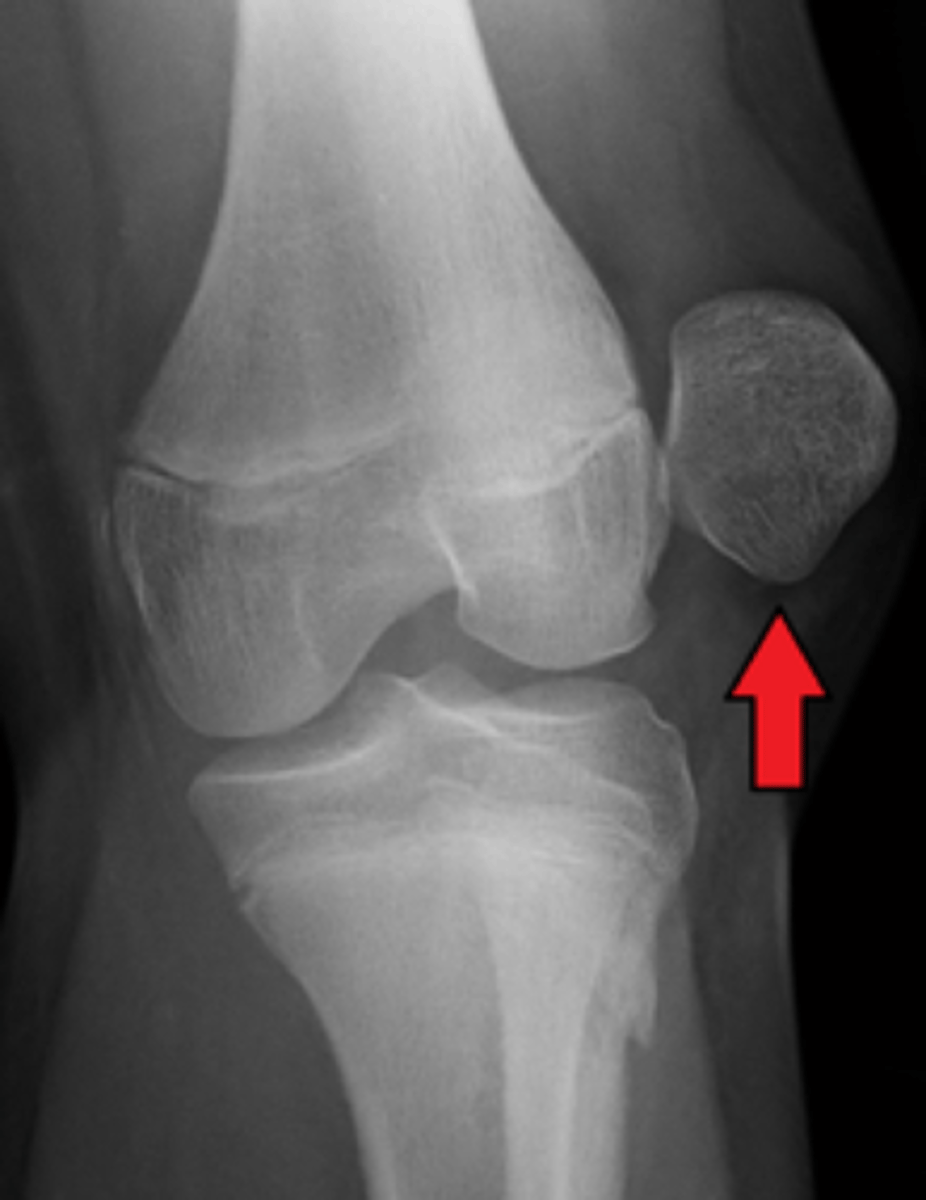
Giant cell tumor
_____________ is a benign tumor that commonly occurs in the knee – often in the proximal tibia
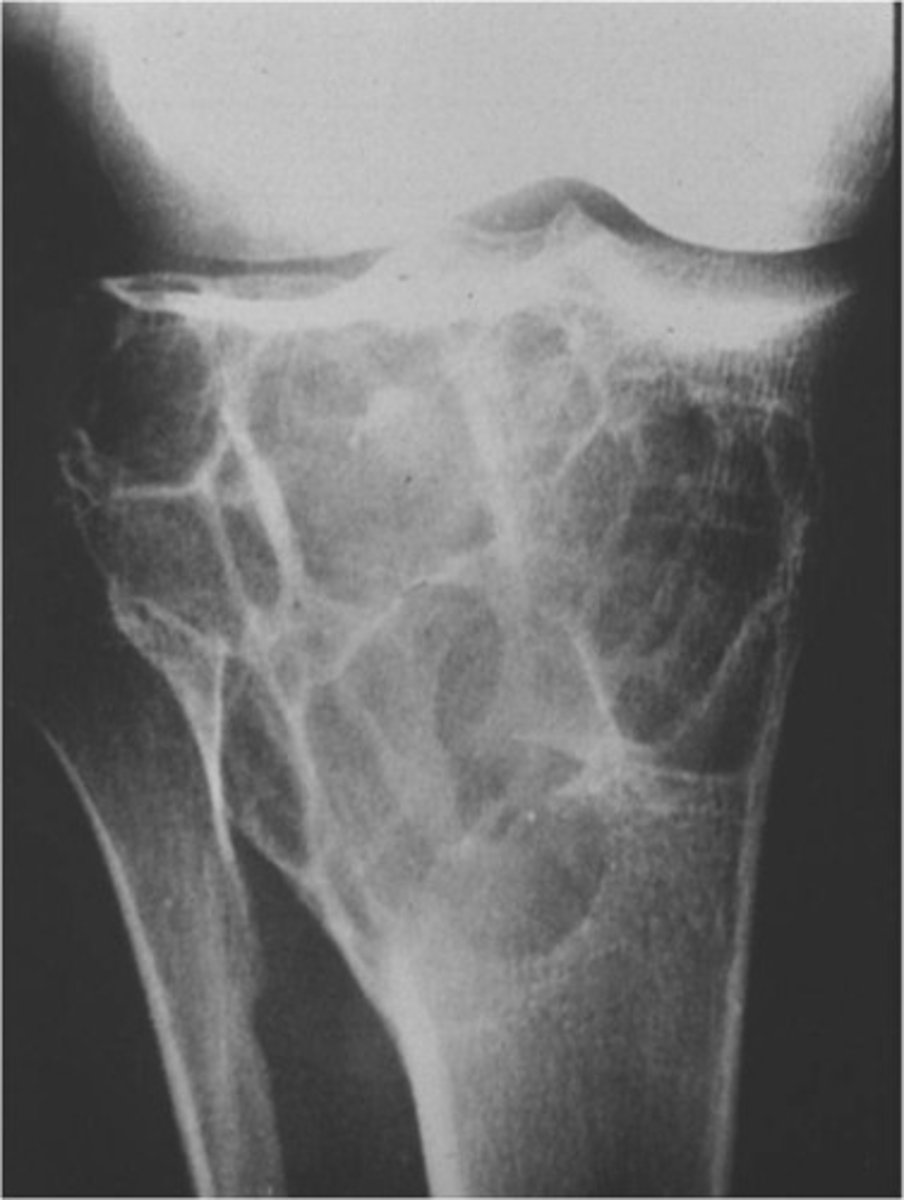
Spiral fractures
_____________ are common to the tibia – often has an associated fibula fracture
Tibia Fracture
1. Mechanism: direct force to fibula or indirect -- tibial torsion (skiing)
2. Symptoms: sudden pain and loss of function
3. Signs: a) possible deformity and crepitus, b) rapid swelling, c) delayed ecchymosis, d) possible false joint motion, e) painful weight bearing
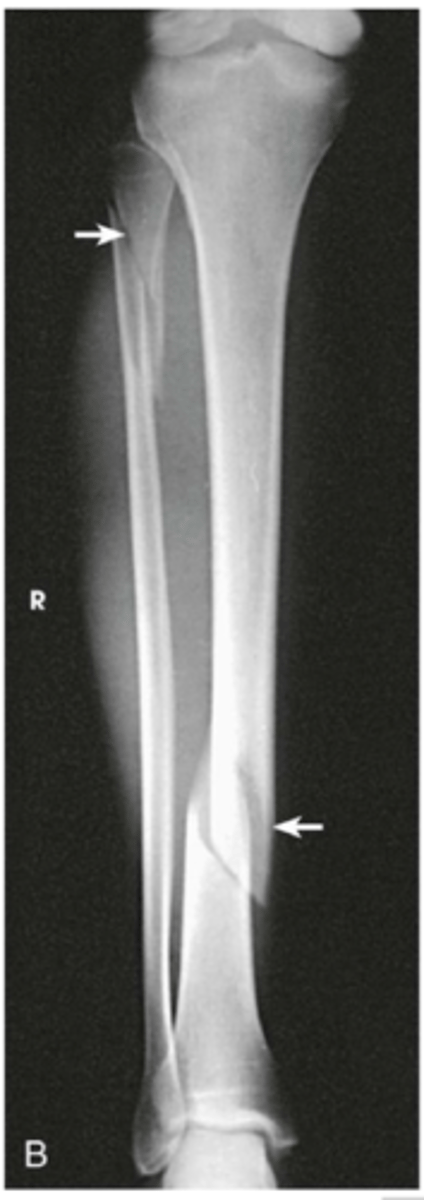
Fibula Fracture
- caused by a direct blow to the outside of the leg
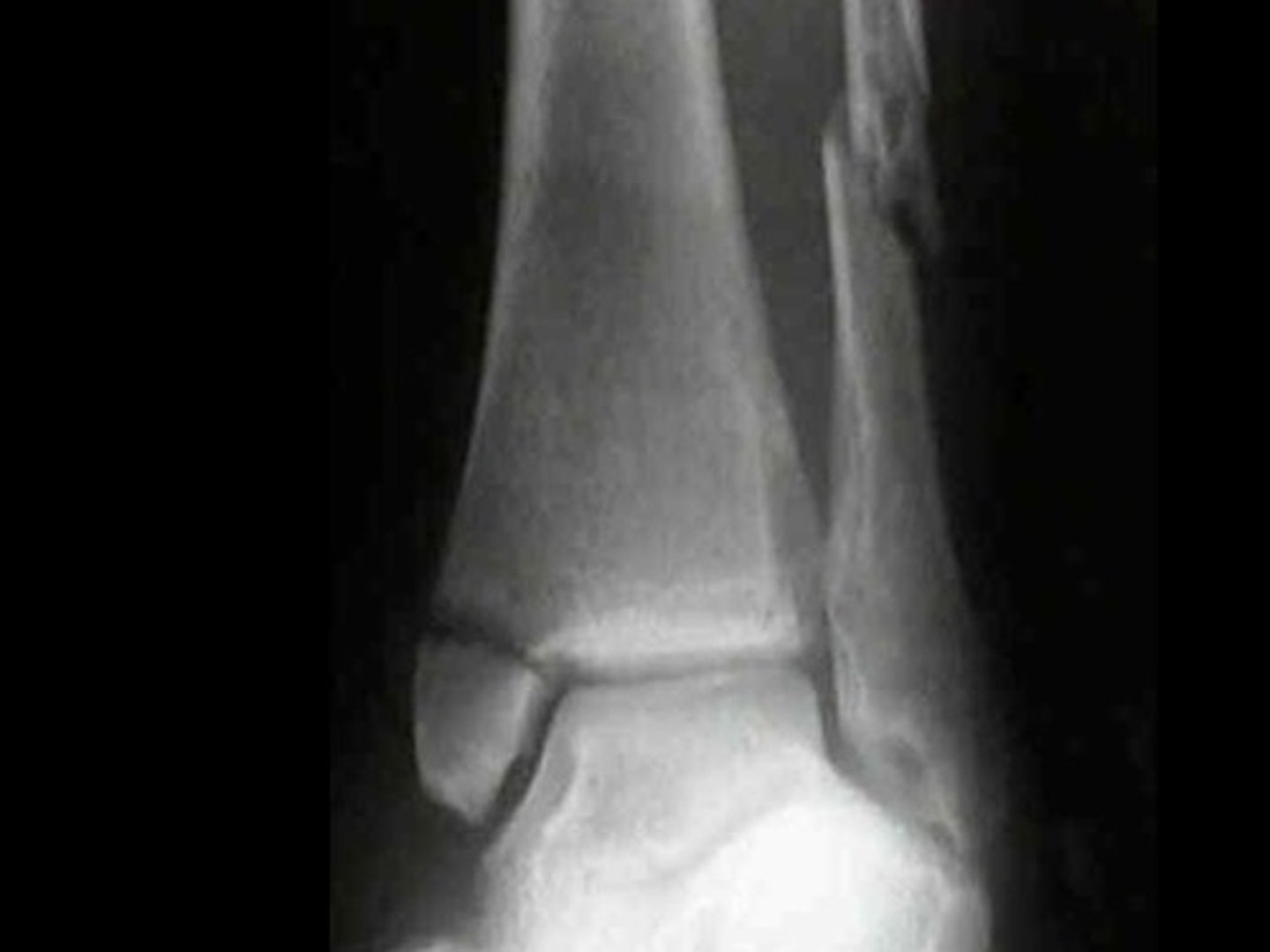
ankle effusion
An __________ appears as an anterior fat line in front of the joint space on the lateral view
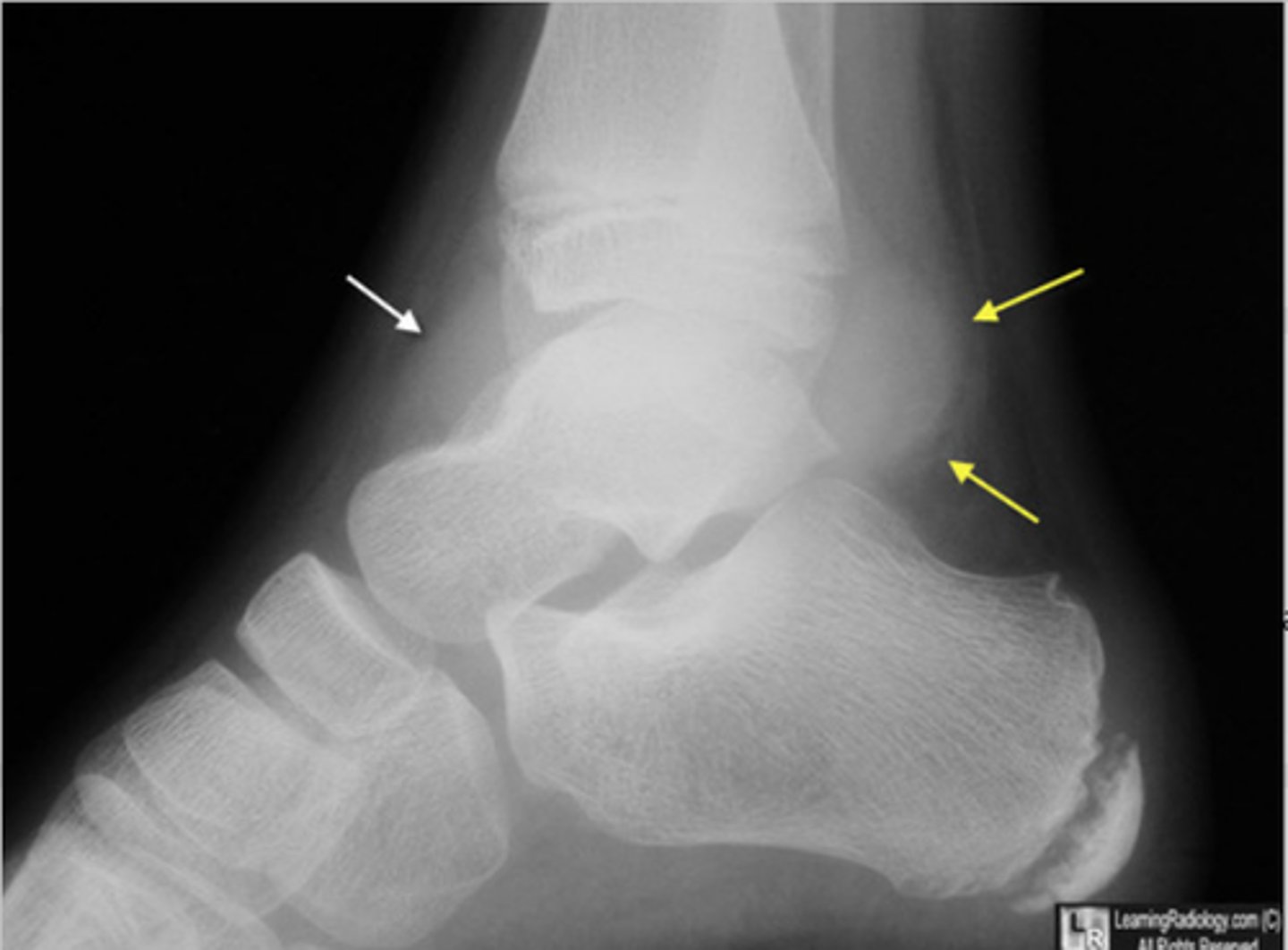
lateral malleolus fracture
1. MC distal fibula fx
2. oblique or spiral fx m/c
3. result of outward or external rotation of foot
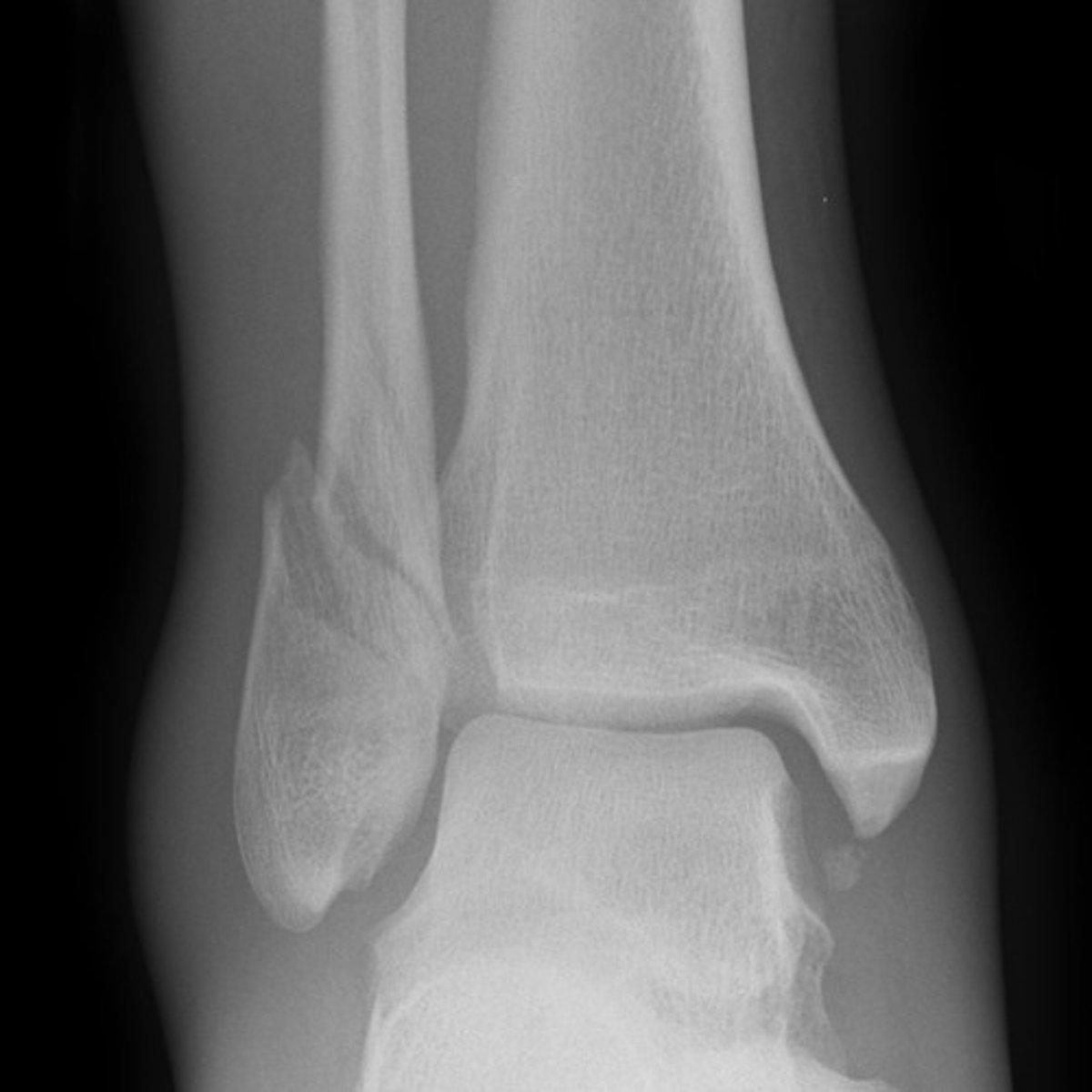
medial malleolus fracture
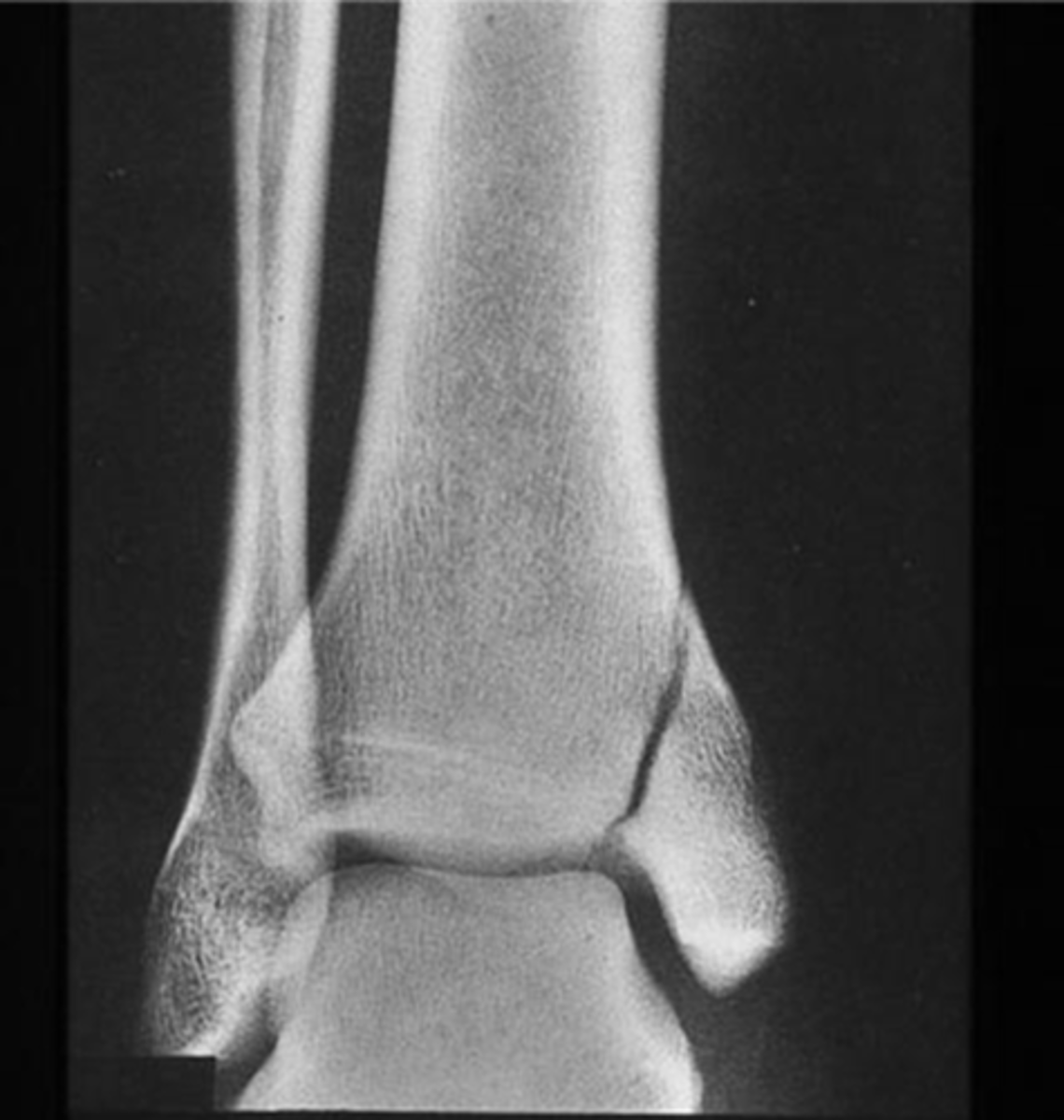
Bimalleolar fracture
Fractures of both the medial and the lateral malleolus.
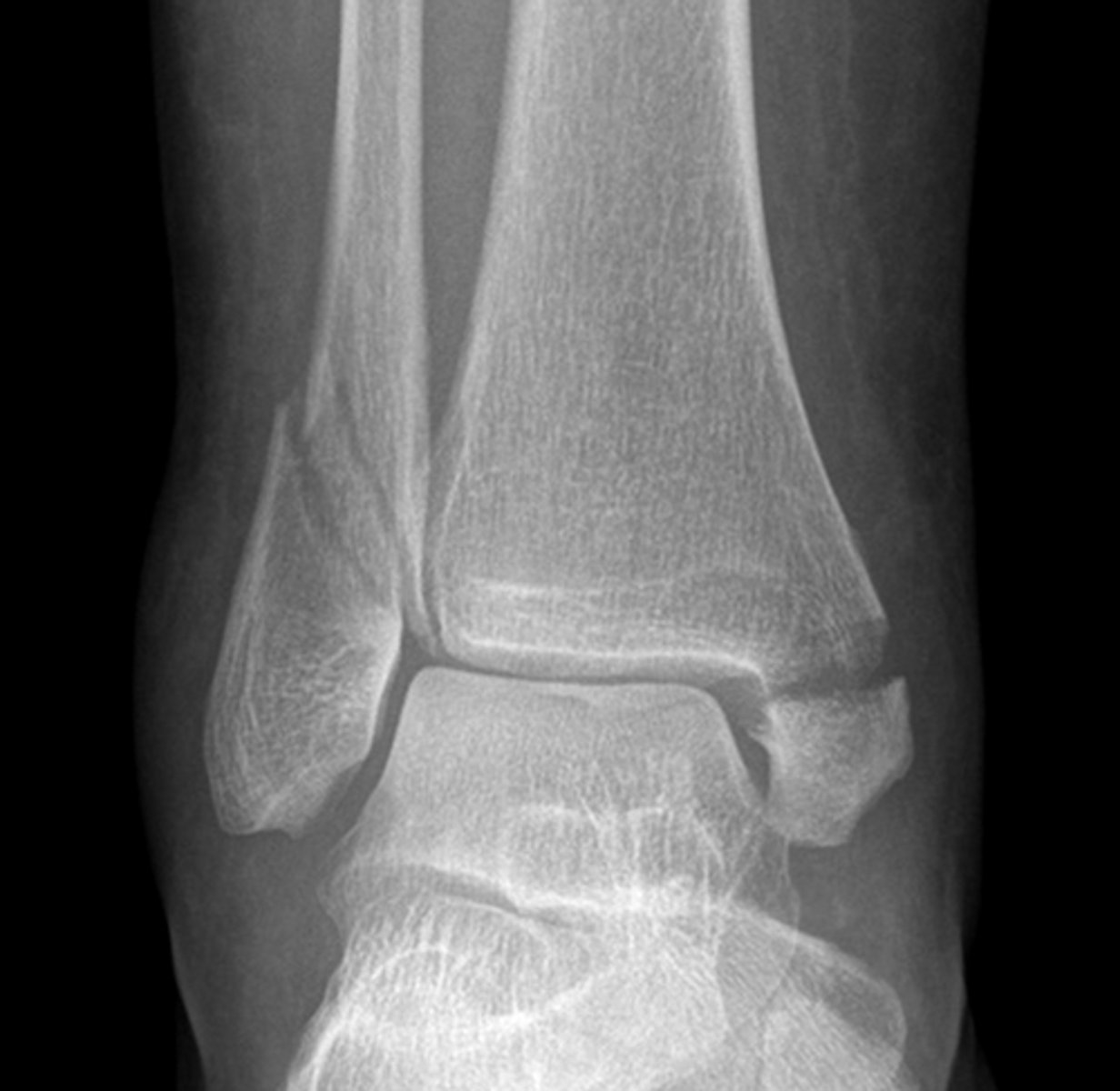
Growth arrest lines
_____________:
oOccur in the distal tibia
oDue to a period of arrested growth – perhaps sickness
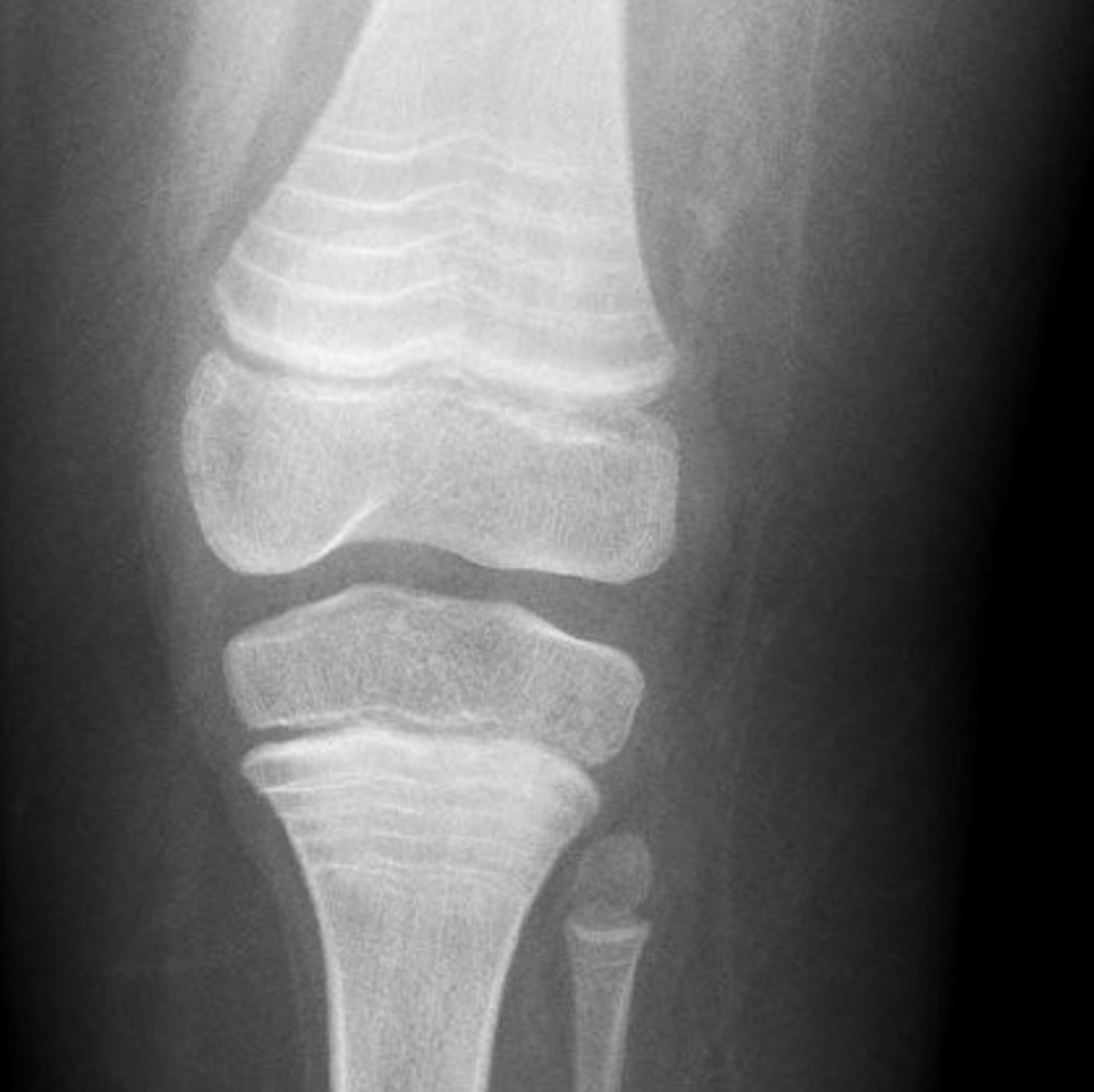
Bone islands
___________ – benign finding
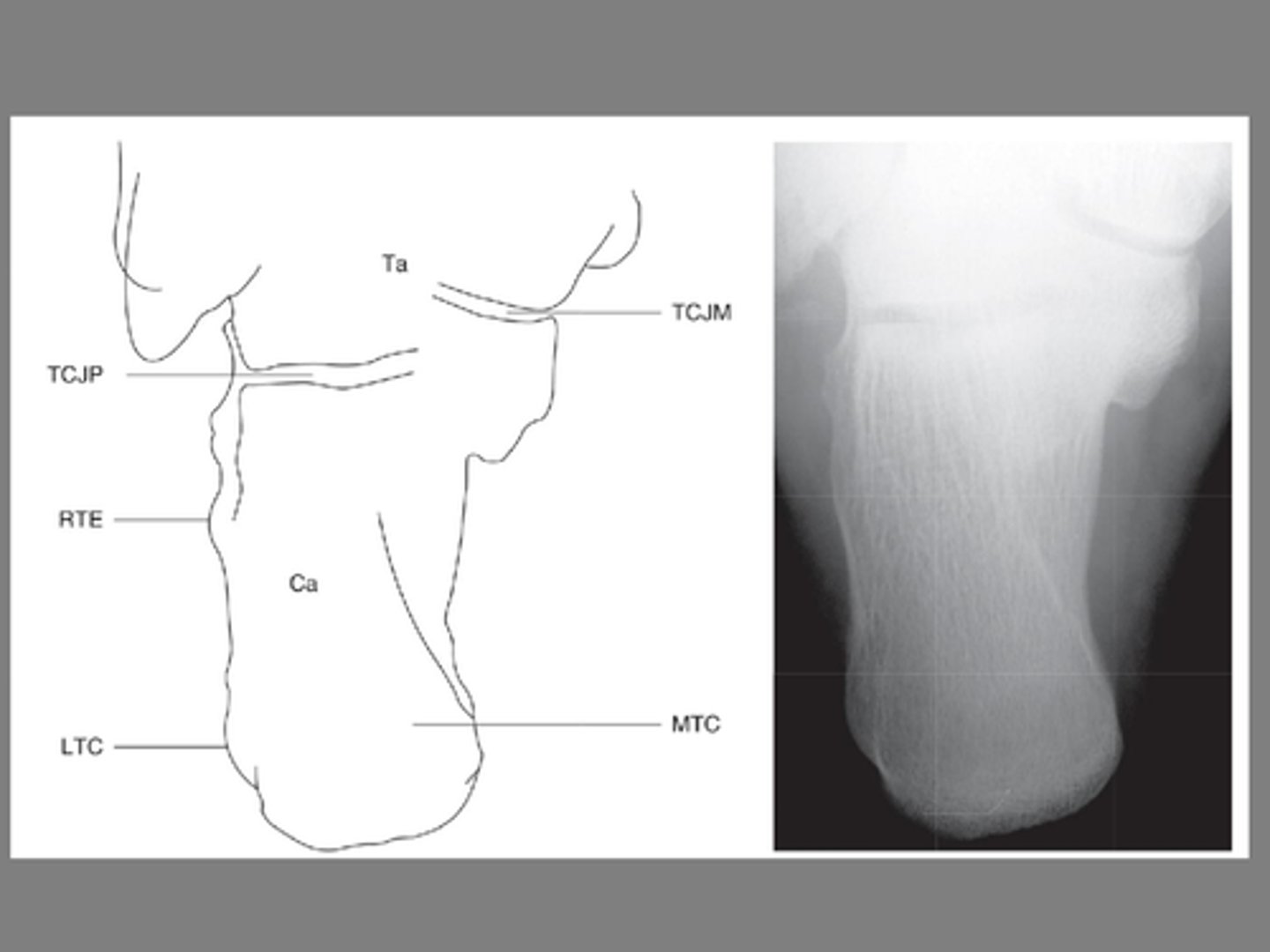
Calcaneal view
Plain films include an AP view, lateral view and oblique view
- ______________ is needed for suspected calcaneal fracture
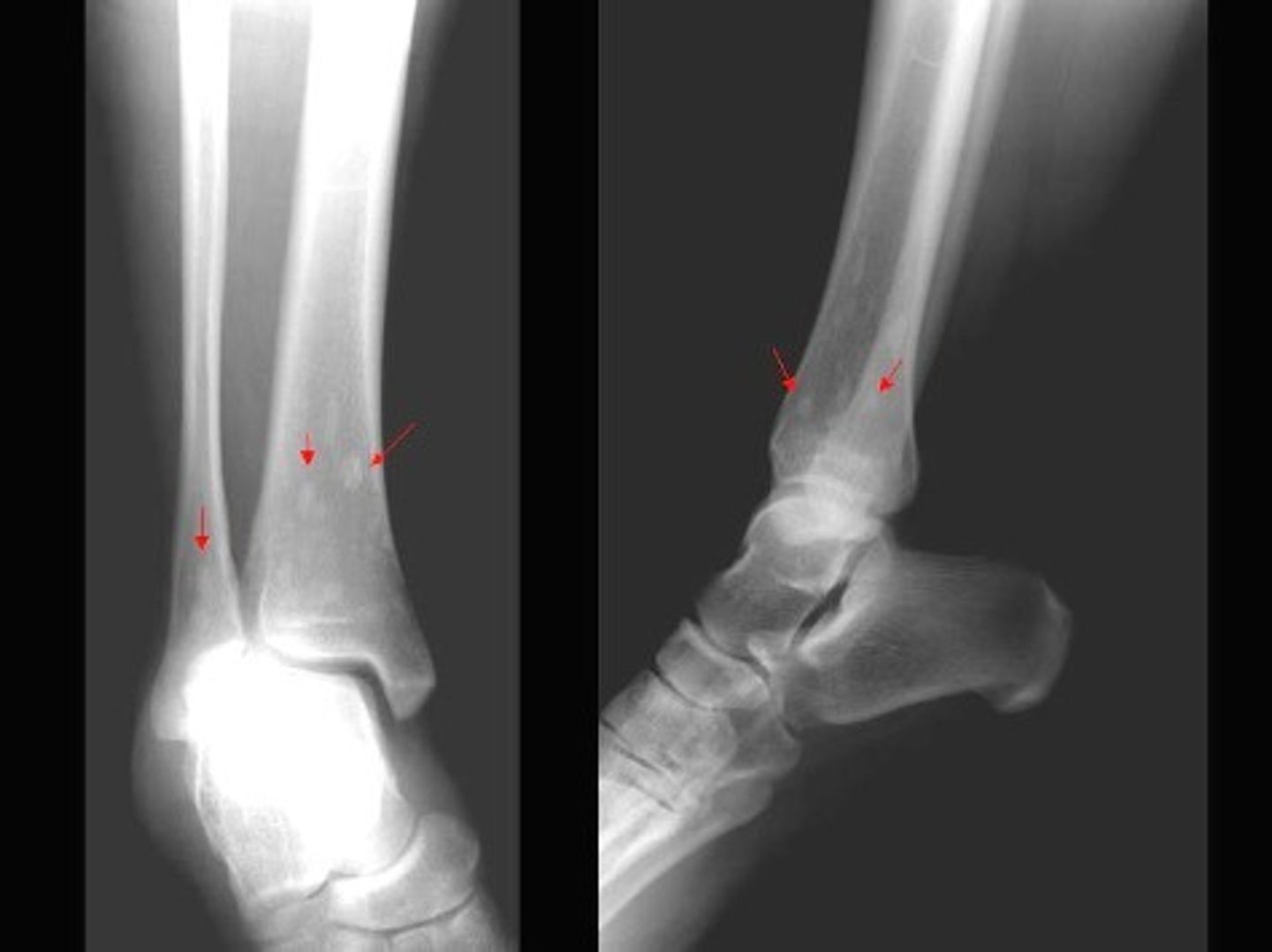
Talar fracture
____________ – always involves the neck of the talus
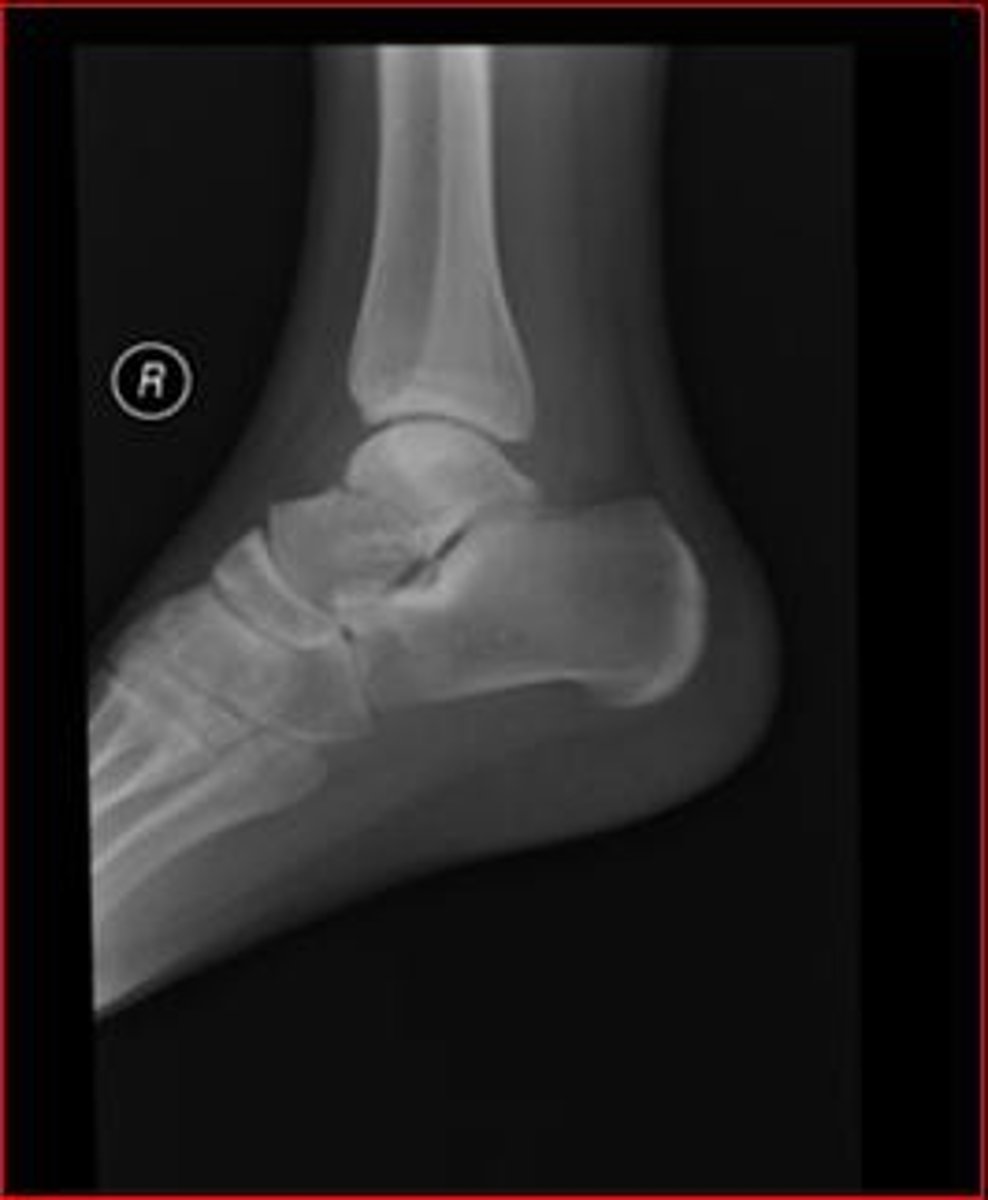
Calcaneal fracture
- AKA "lover's fracture"; usually the result of a fall from height.
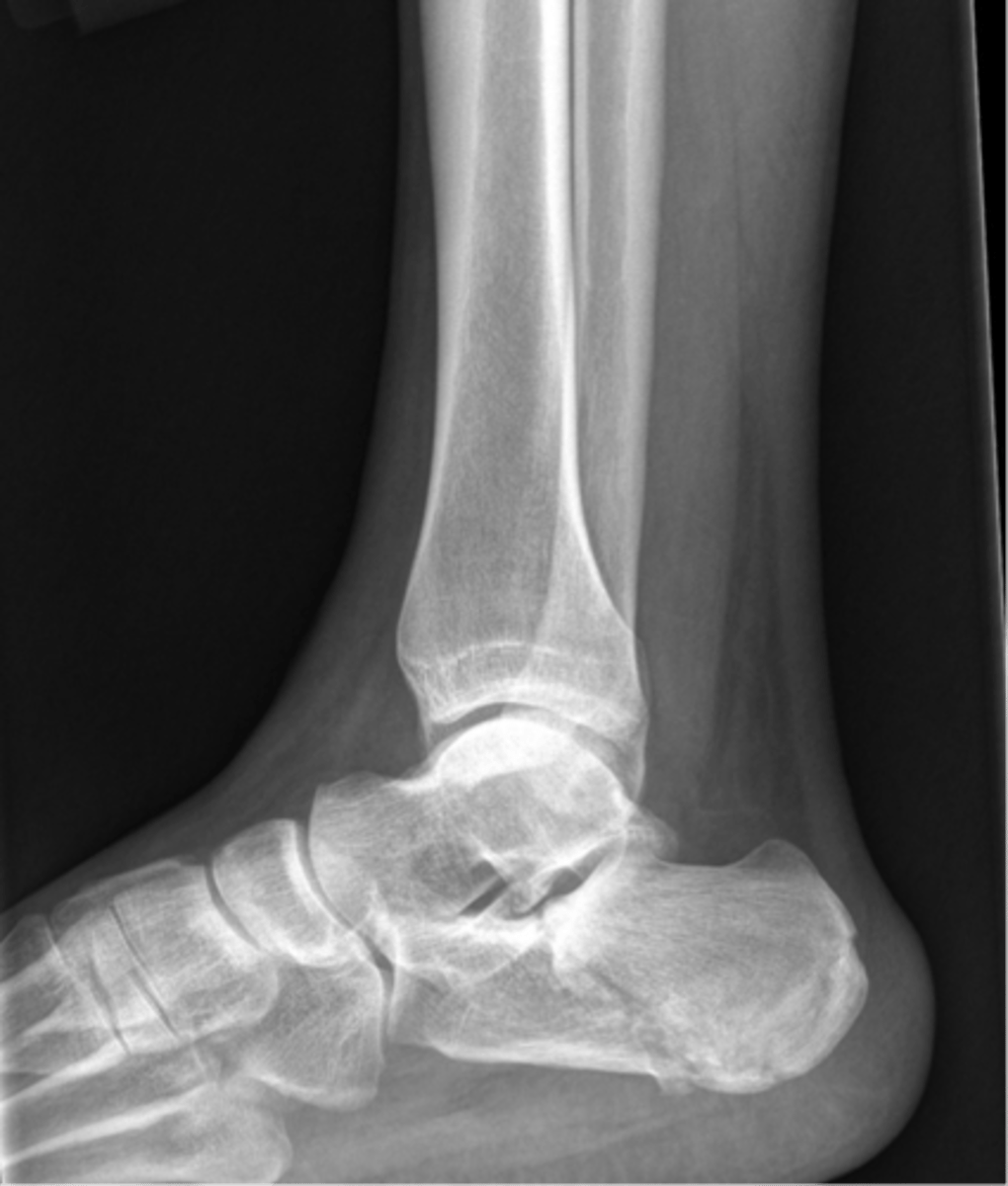
Calcaneal spur
"heel spur"
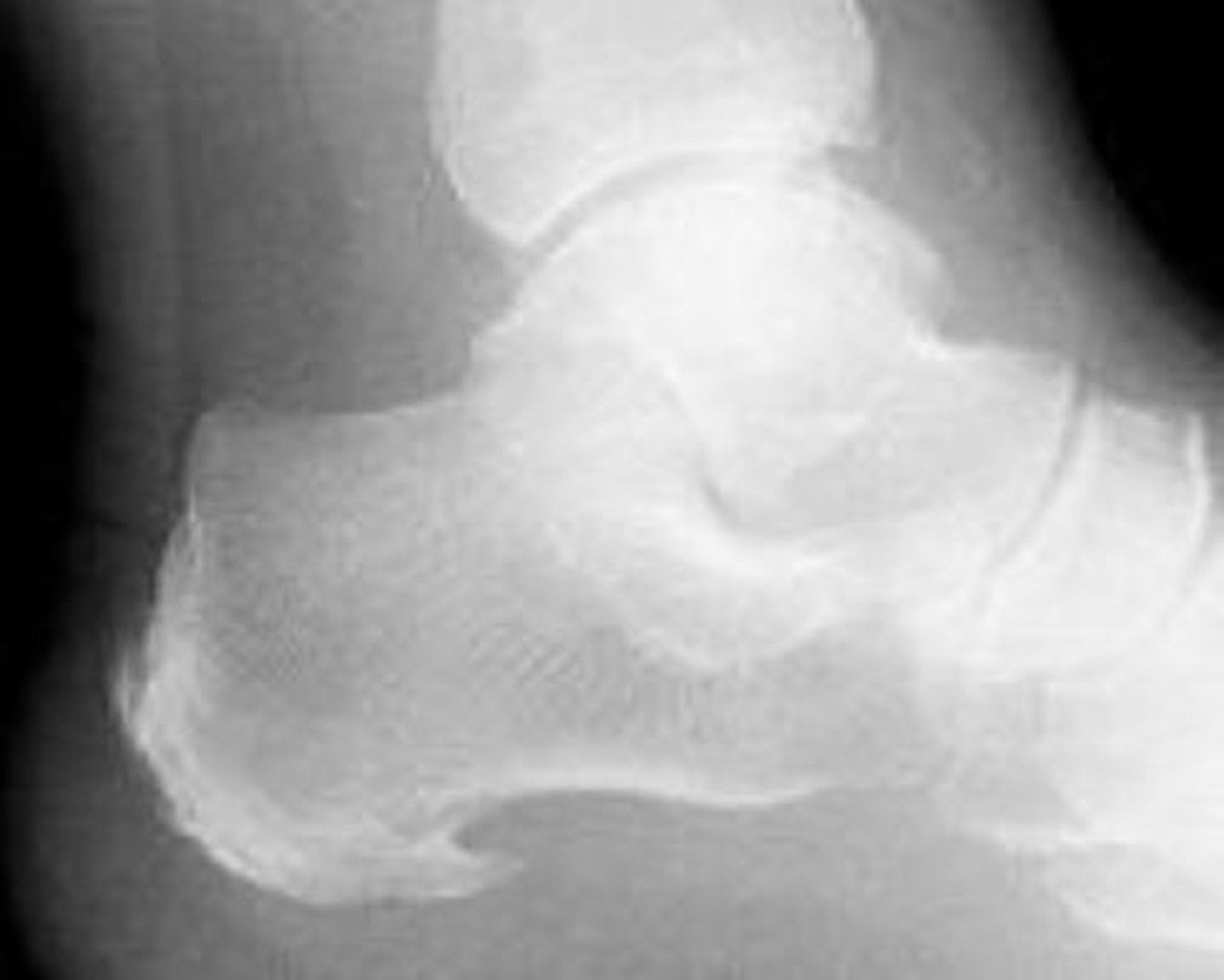
Jones fracture
______________ – base of 5th metatarsal
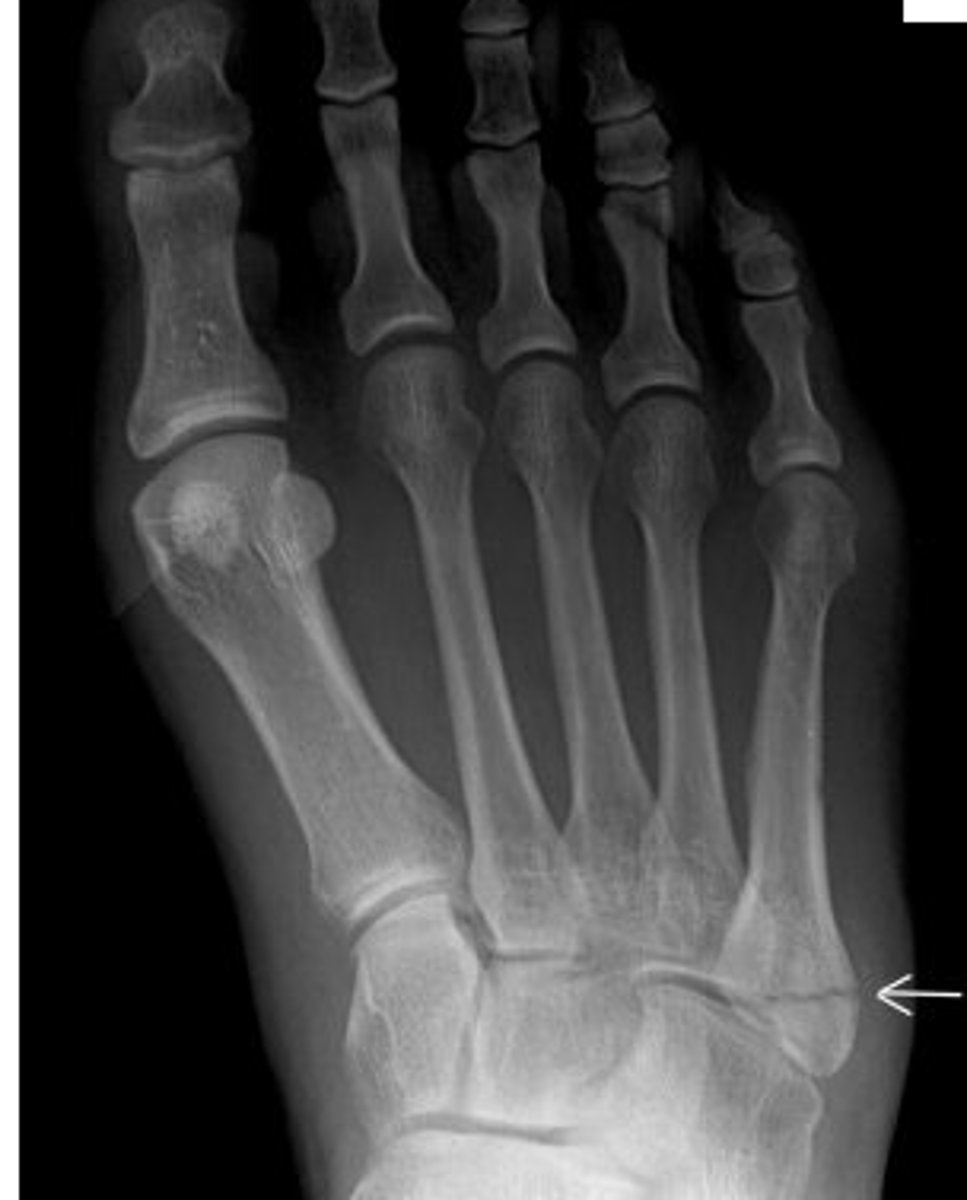
Lisfranc fracture
_____________ – fx of 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th MT with lateral dislocation
o MOI – foot caught in stirrup
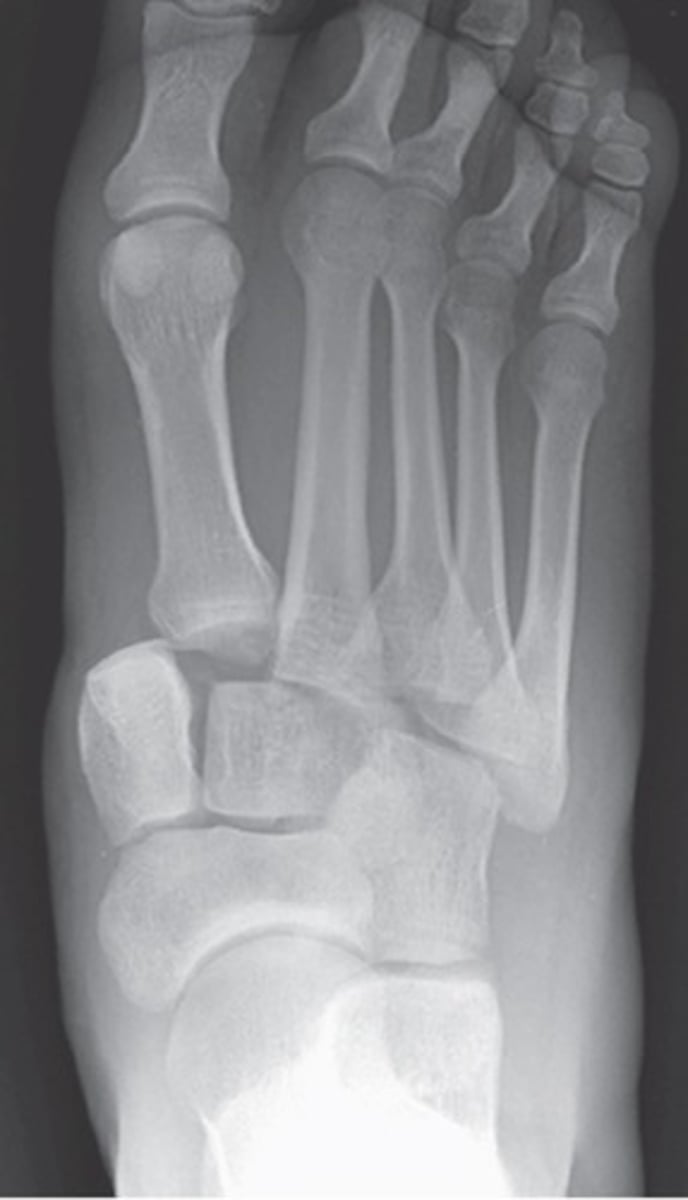
March fracture
______________ – stress fracture of 2nd, 3rd, or 4th MT
Seen in new recruits, athletes and dancers
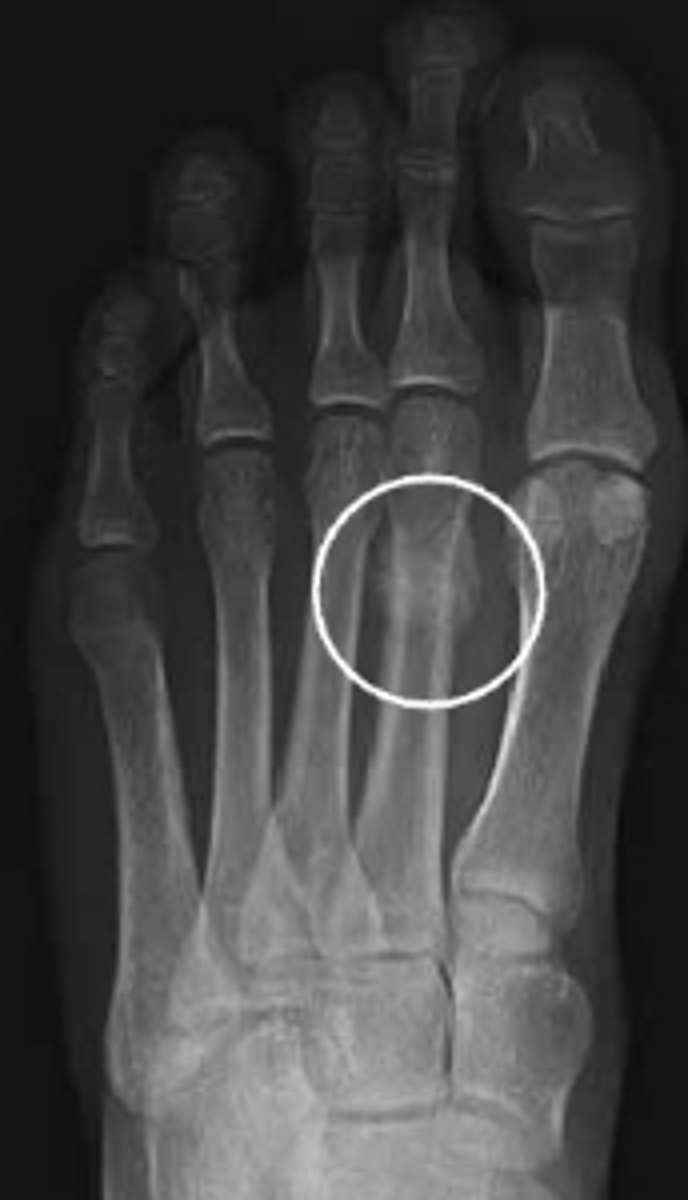
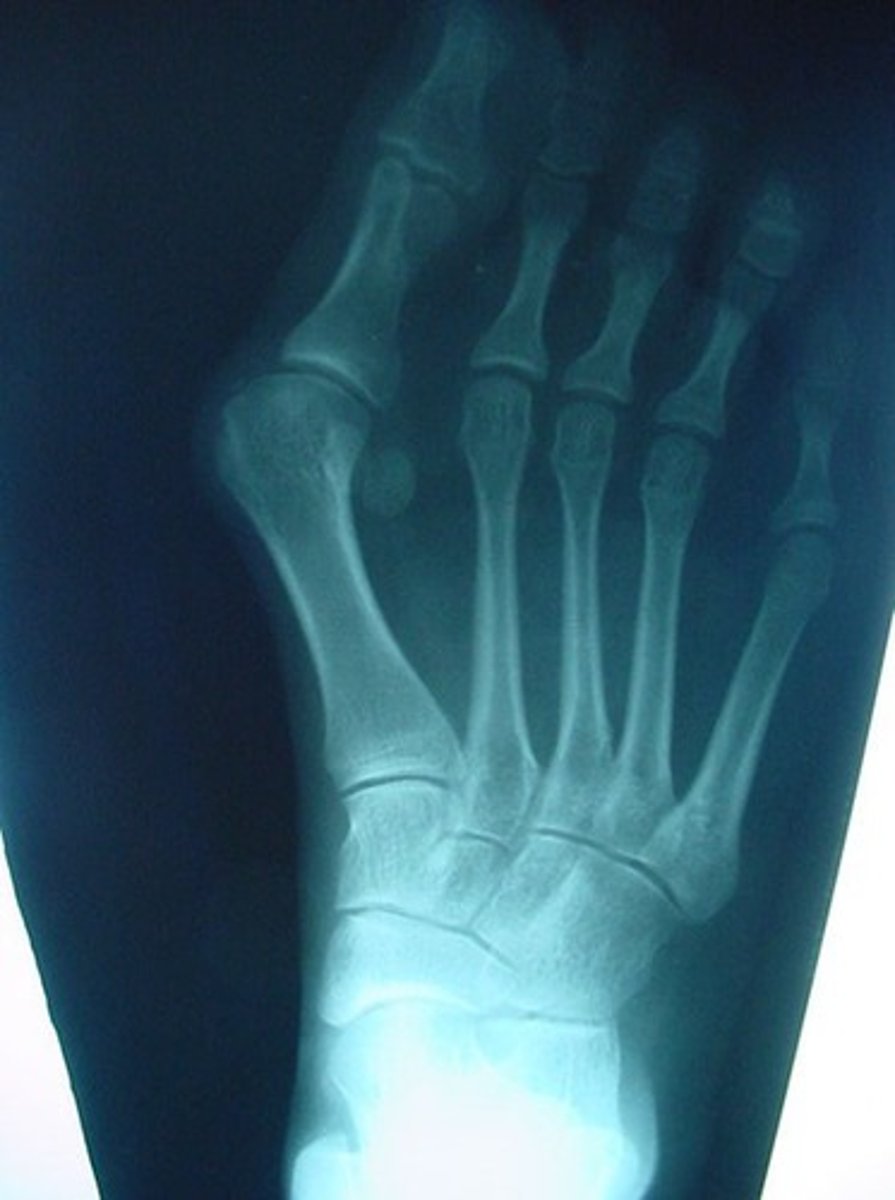
Gout
_________ – involves the 1st MCP joint
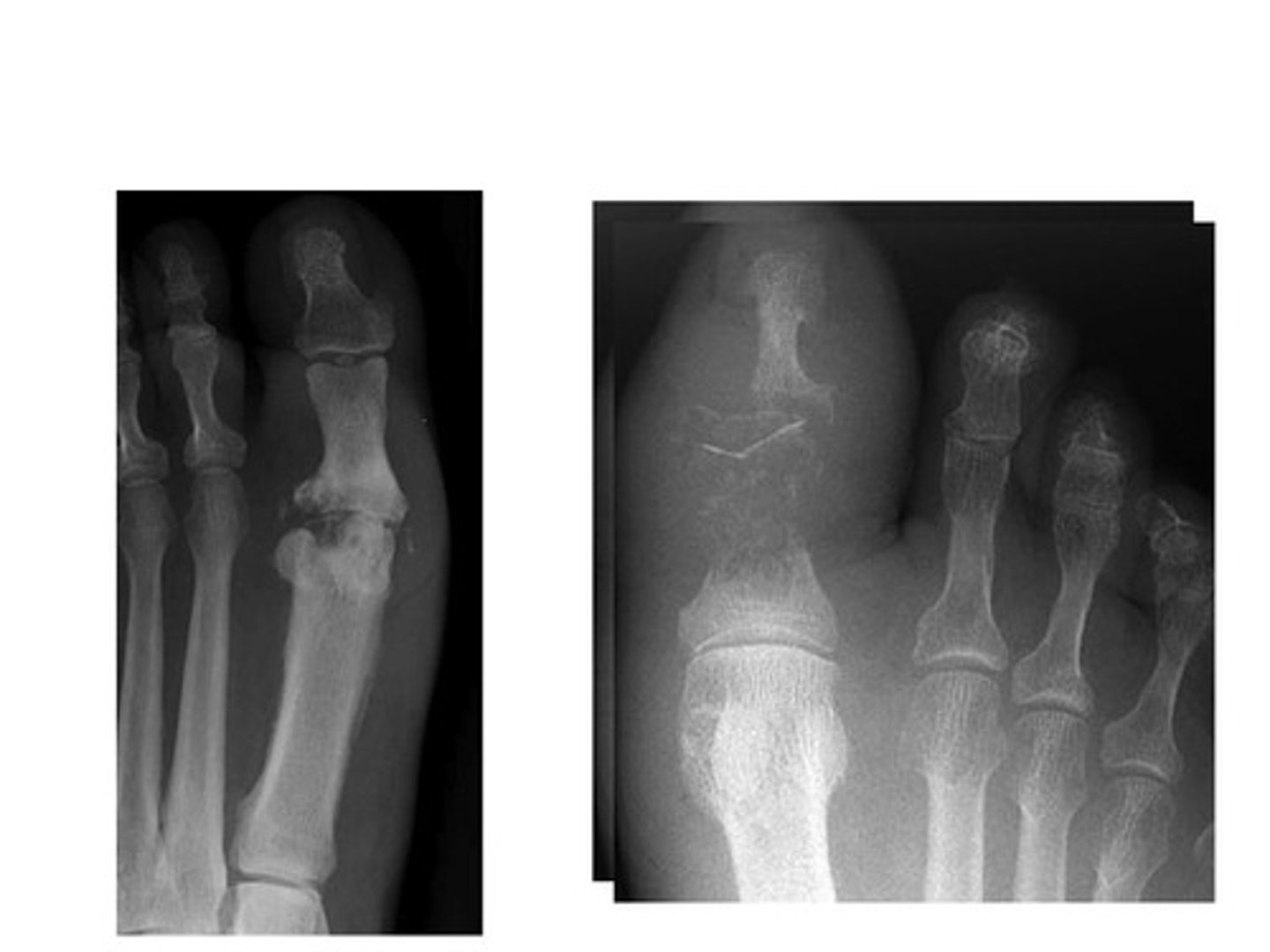
Osteomyelitis
infection of the bone
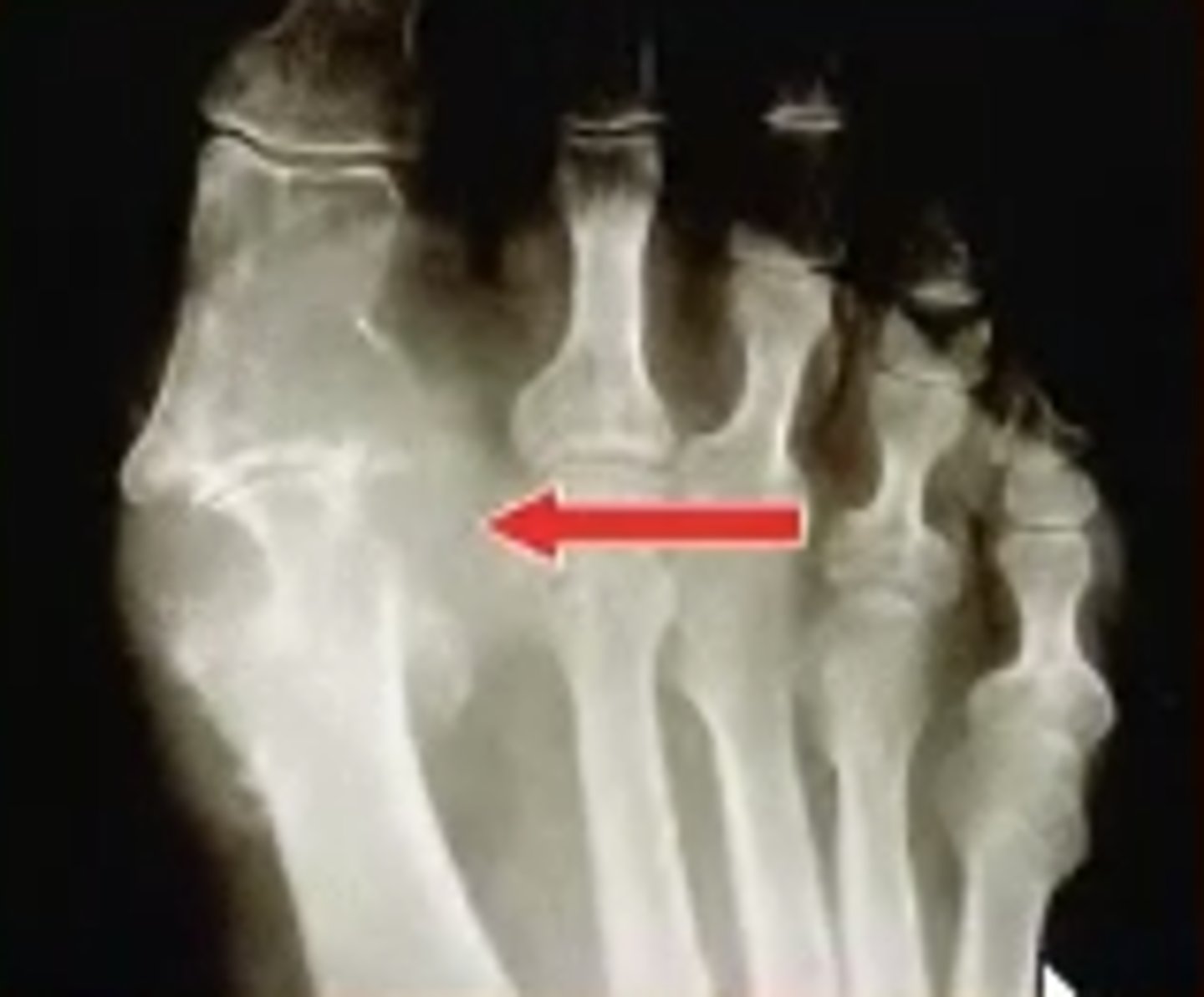
Bunions
__________ – Hallux Valgus