Kingdom Rhodoplantae (red algae)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what are the phylum of kingdom Rhodoplantae
Phylum Rhodophyta
Phylum Glaucophyta
monophyletic group
chloroplasts origin: primary endosymbiosis with a cyanobacterium
cells typically lack centrioles
cell wall compose of cellulose
store food: starch (of various types)
Supergroup Archaeplastida
unicells to complex filaments and parenchymatous thalloid plants
mainly of warm marine habitat
with phycobilin pigments
Chlorophyll a (absence of b or c)
no flagellate stages
food stored: floridean starch (alpha 1,4 glucan) similar to cyanophycean starch of the cyanobacteria
Phylum Rhodophyta: red algae
what is the class of Polysiphonia?
Class Florideophyceae
what is the order of Polysiphonia
Order Ceramiales
what is the family of Polysiphonia
Family Rhodomelaceae
what is the representative organisms of Phylum Rhodophyta
Polysiphonia
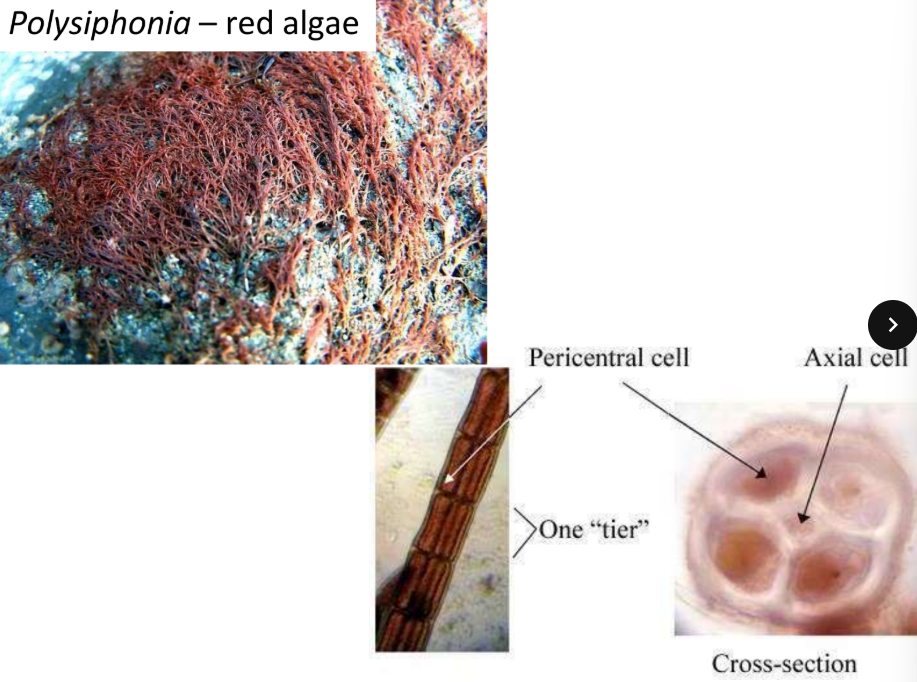
mostly branches, filamentous
attached by rhizoids or haptera
Thallus consists of fine branched filaments
central axial filament
supporting pericentral cells=4-24
Polysiphonia

describe the reproduction of Polysiphonia
typically diplohaplontic—alternation of haploid and diploid stages, some are haplontic
describe the oogamous reproduction of Polysiphonia
Oogamous
female gametophyte with carpogonium
contains the egg with receptive surface called trichogyne
male gametophyte produce spermatia
non-motile cells that function as male gametes
describe the triphasic life cycle of Polysiphonia
with gametangial, carposporangial and tetrasporangial phases
triphasic life cycle: describe the Gametangial phase
Gametangial phase-gametophyte phase (n)
male gametophyte produce spermatia that functions as male gametes
female gametophyte produce the carpogonium which contains the female gamete (ovum/egg)
after fertilization of gametes, the zygote migrates and fuses with a supporting cell in the carpogonium
Zygote grows and develops into carposporophyte (2n)
triphasic life cycle: describe the Carposporophyte phase
diploid phase of the life-cycle
origin: zygote
entirely parasitic on the parent female gametophyte
non-motile diploid carpospores are produced in the carposporangium by mitosis
carpospores are released from carposporangium, settles and grows to form diploid tetrasporophyte
triphasic life cycle: describe the Tetrasporophyte phase
develop tetrasporangium
produce tetraspores after meiosis
spores settle and grow to become the male and female gametophyte plants thus completing the cycle
describe the ecology of Polysiphonia
mostly marine, a few freshwater
typically live attached to surfaces
light harvesting is very efficient, and red algae can live at tremendous depths
Phycoerythrin accessory pigments allow absorption of blue and green lights which penetrates relatively far into the water
Corraline red algae build up calcium carbonate in their cell walls, and can be reef-building organisms
what is the economic importance of Polysiphonia
agar-agar is a jelly-like food delicacy in japan
agar used as culture medium in microbiology
cannot be digested by most microorganisms
Agarose—purified from agar-used in molecular biology
gel electrophoresis

paper thin glossy sheets or nori: mineral rich wrap for rice, vegetable and seafood in sushi

what is the ecological of Polysiphonia
corallines (calcified red algae) ]
regarded as keystone pigments (species whose decline could cause the collapse or loos of entire biotic communities)
what is the importance of corallines (calcified red algae) ?
help build and maintain coral reefs, which harbour diverse organisms
by forming hard, flat sheets that consolidate and stabilize reef crests, coralline algae protect reefs from wave damage
freshwater habitat
coccoid and occur in loose colonies formed by the persistent cell wall of the parent cell following division
have mitochondria with flat cristae
Phylum Glaucophyta
what are the chloroplasts known as in glaucophyta?
The chloroplasts are known as cyanelles
with peptidoglycan layer (relic of the endosymbiotic origin of plastids from cyanobacteria)
plastids contain chlorophyll a and phycobilins organized into phycobilisomes
what is the class of Glaucophyta
Class Glaucocystophyceae
what is the order of Glaucophyta
Order Glaucocystales
what is the family of Glaucophyta
Family Glaucocystaceae
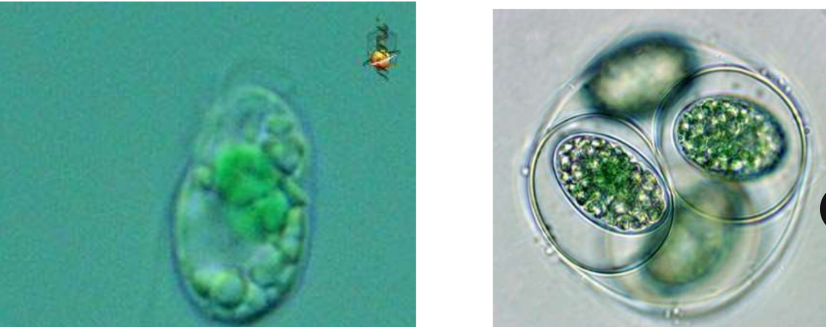
Glaucocystis
motile forms have two unequal flagella, which may have fine hairs