NU 220: Chapter 16: Drug Therapy to Decrease Pain, Fever, and Inflammation
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Pain:
• Subjective (what the patient says)
• Cultural Influences
• objective (how to quantify pain)
• Pain assessment scales
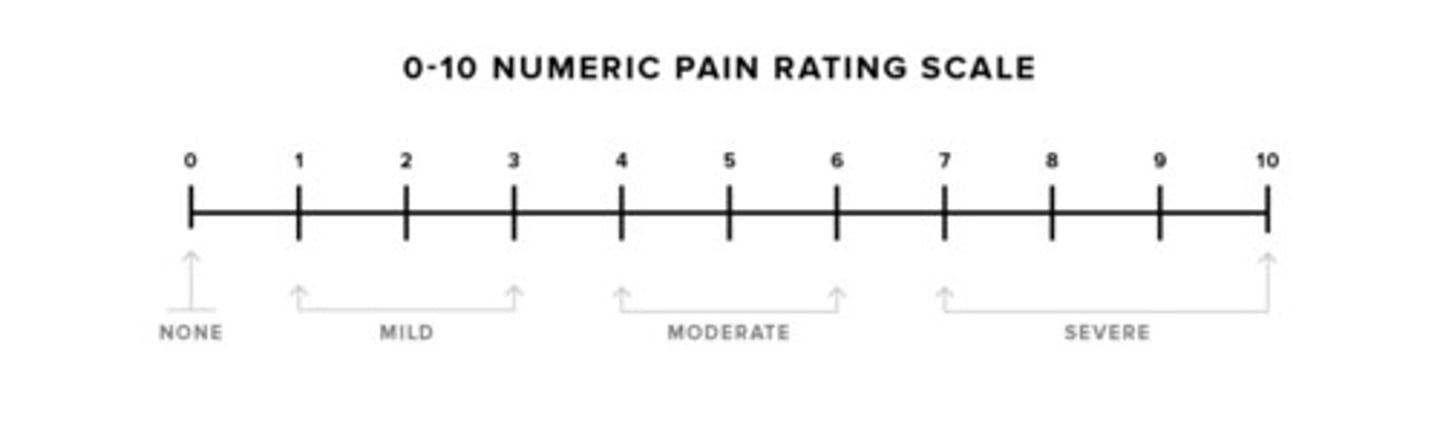
0-10 Numerical Scale
- someone cognitively intact
- over the age of 8
- 0 = no pain, ,5 = moderate pain, 10 = worst possible pain
Wong-Baker FACES scale
- kids ages 3 and under
- someone who cant speak English

Combo
- has numeric, faces, and different langauges
FLACC pain scale
F: Faces.
L: Legs.
A: Activity.
C: Cry
C: Consolability
based on what the nurse observes
- scores 0-2, goes up to 10
- used for infants or cognitively impaired
define fever:
Elevated body temperature beyond normal range (100.4 f) (38 c)
The set point of the hypothalamus is raised in response to pyrogens (anything that can cause a fever):
• Infection
• Toxins
• Injury
• Inflammation
• Dehydration
what are pyrogens?
substances that cause fever
Fevers are mediated by....
prostaglandins, they can either rise or lower a temperature
inflammation:
redness, swelling, pain, fever, anywhere in the body, could be caused because of an infection, injury
• Capillary dilatation
• Extravasation of edema
• White cells migrate to area
• Result in pain
• Result of prostaglandin release
define prostaglandins:
Chemical mediators found in most body tissues
• Assist in regulating many body functions
• Are formed when cellular injury occurs
• Participate in the inflammatory response
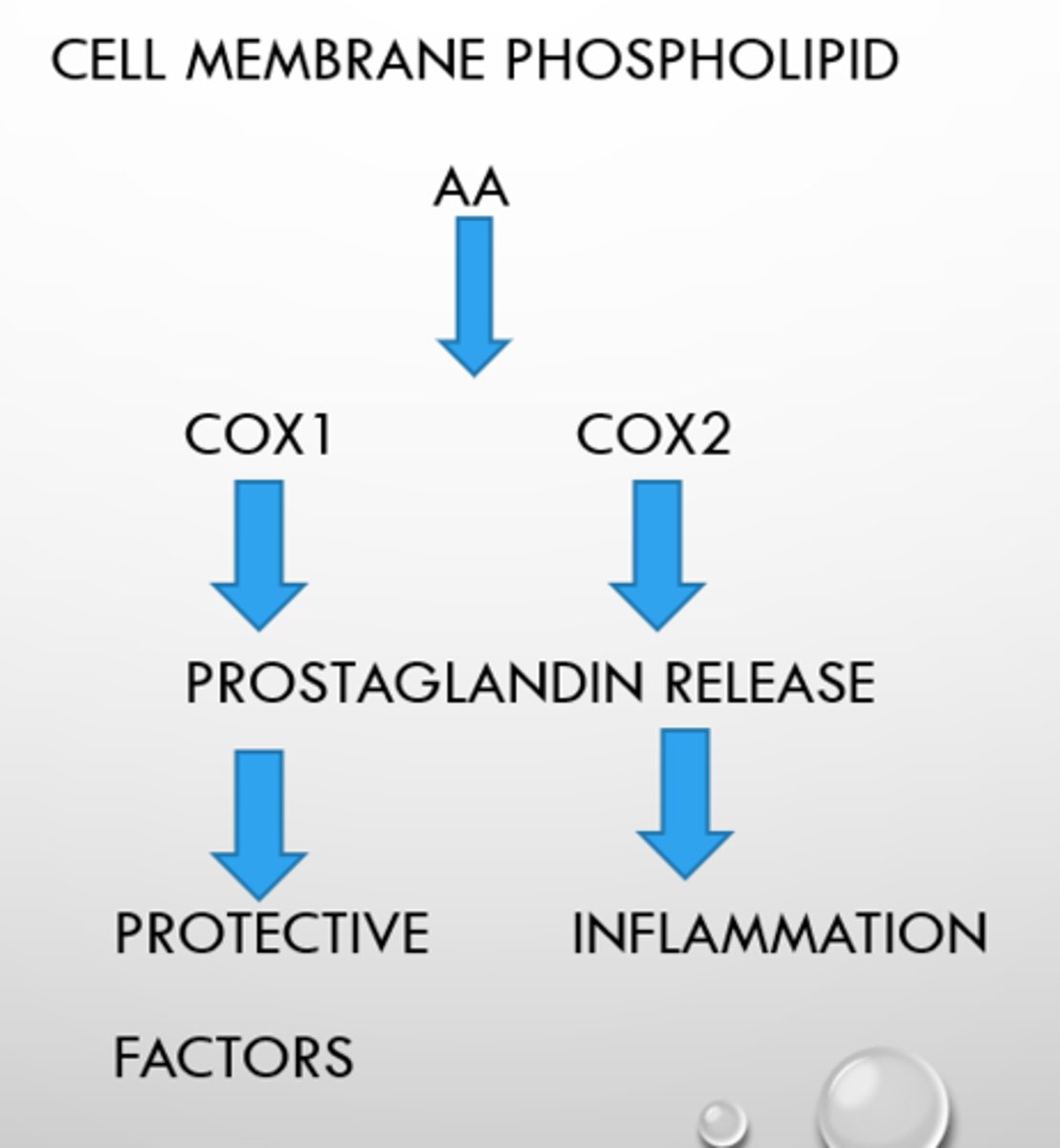
inflammatory cascade/pathway
- AA (arachidonic acid) release from cut, infection, injury
- this then releases into enzymes Cox 1 and Cox 2
- they cause the release of prostaglandins
- Cox 1 = protective factors
- Cox 2 - inflammation
Enzyme that converts arachidonic acid into prostaglandins and related compound prostacyclin:
Cyclooxygenase (Cox)
Cyclooxygenase is found in all tissues:
- Tissue injury: Catalyzes the synthesis of prostaglandins
- Stomach: helps protect gastric mucosa
- Platelets: helps stimulate platelet aggregation
- Kidney: promotes vasodilation and thus renal blood flow
- Uterus: promote uterine contractions at term
COX-1 (good):
- found in all tissues, housekeeping.
- protects gastric mucosa
- supports renal function
- promotes platelet aggregation. GOOD COX.
Inhibition causes:
- gastric erosion
- bleeding tendencies
- renal impairment
- protection against MI and stroke (secondary to reduced platelet aggregation)
COX-2 (bad):
• found at sites of tissue injury
• Mediates inflammation and sensitizes receptors to painful stimuli
• Brain: mediates fever
• Blood vessels: increases capillary permeability &promotes vasodilation
If you inhibit COX-1:
• Increase risk of gastric erosions and bleeding
• Increase risk of renal impairment
If you inhibit COX-2:
• Suppress inflammation
• Relieve pain
• Reduce fever
Types of Cox Inhibitors: Drugs that have an anti-inflammatory property
- First Generation
- Second Generation
First generation:
• Salicylates (ASA), Ibuprofen, Naproxen (Aleve)
• Inhibit both cox 1 & 2
Second generation:
• Cox-2 inhibitors Celecoxib (Celebrex)
• Inhibit primarily cox 2
Drugs that inhibit Cox I & II are Anti-prostaglandins:
• Work by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins
• How are Prostaglandins inhibited >>blocking effects of Cox1 & Cox II
Examples:
• Aspirin
• Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)
Non-Selective NSAIDs - Mechanism of Action:
• Inhibit prostaglandin synthesis
• Inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes
• Relieve pain by decreasing inflammatory response
• Relieves fever by decreasing inflammatory response and the concentration of pyrogens
• hypothalamis or "thermostat" is reset
• Has good and bad effects
Classification: NSAIDs to know:
* aspirin
* celecoxib (Celebrex)
* ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil)
* indomethacin (Indocin)
* ketorolac (Toradol - discontinued brand)
* naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprelan, Naprosyn)
NSAID: Indications for Use: to relieve pain and inflammation
• To relieve pain & inflammation
• NSAIDs effective in treating mild to moderate pain
• pain
• HEADACHE, minor trauma, minor surgery, other acute or chronic conditions
• Not recommended for visceral or neuropathic pain
NSAID: Indications for Use: to reduce fever
• NSAIDs
Aspirin not used with children because of risk of Reye's syndrome
NSAID: Indications for Use: to suppress platelet aggregation
• Regular low-dose ASA effective for patients with history of ischemic stroke, TIA, angina, acute MI
• Reduces risk of death or recurrent event
NSAID: Indications for Use: Inflammatory disorders
• NSAIDs are widely used to prevent/treat mild to moderate pain and inflammation
• Osteoarthirits
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Other autoimmune disorders
Contraindications for NSAID Use:
• Hypersensitivity to Aspirin or other NSAid
• Chronic alcohol abuse
• Gastric bleeding
• Children and adolescents- NO ASPIRIN
• Presence of viral infections
• Due to its connection with Reye's syndrome
Contraindications for NSAID Use: Increased risk of serious GI adverse events
• Bleeding
• Ulceration
Perforation of stomach and intestines
Contraindications for NSAID Use: Contraindicated in the presence of
- Peptic ulcer disease
- GI or other bleeding disorders
- Impaired renal function
Contraindications for NSAID Use: pregnancy and fetus
• Pregnancy
•Potential for anemia from GI blood loss
•Potential for postpartum hemorrhage
• Potential risks to the fetus
•Low birth weight, renal toxicity
•Premature closure of ductus arteriosus (needed for fetal circulation)
•Intracranial hemorrhage, stillbirth
Salicylates prototype:
ASPIRIN - acetylsalicylic acid (bayer, bufferin)
Salicylates indications:
Pain, fever, inflammation
Salicylates action: Inhibits PgE by blocking Cox I & Cox II
• Analgesic
• Anti-inflammatory
• Antipyretic
• Decreases platelet aggregation by blocking Thromboxane A synthesis
Salicylates contraindications:
• Hypersensitivity to aspirin
• Bleeding disorders or thrombocytopenia (reduced blood clotting cells, bleeds)
- Children or teens with viral infections
Salicylates Adverse reactions / side Effects:
• Salicylism - toxicity due to salicylates & may be associated with chronic use
• Signs include dizziness, tinnitus, difficulty hearing & mental confusion Nephrotoxicity- aspirin can cause kidney damage in high doses (20,000 - 25,000 mg)
• GI Bleeding
Salicylates interactions:
Drug-drug = aspirin may increase risk of bleeding with antiplatelet drugs
Salicylates route/dosage:
• PO/ Rectal-
• Low doses for antiplatelet effects - 81 mg daily
• FDA does not recommend unless history of (hx of) a stroke or heart attack (MI)
• Antipyretic - 325- 650 mg every 4 hours
• Anti-inflammatory - Larger doses -Maximum daily 8000mg
Salicylates pharmacokinetics:
• Metabolized by liver
• Excreted by kidneys
• Half-life: 3 hours, up to 30 hours with very large doses
Salicylates pregnancy category:
D (should be avoided, esp during 3rd trimester)
Salicylates assessment:
• question allergies
• Assess for rashes
• Pre-medication pain assessment
• Post-medication pain assessment
• Reduction of fever
Salicylates administration:
• Full glass of water or other fluid
• With or just following food
• Have patient Sit upright for 15-30 minutes after administration
• Do not crush enteric coated tablets
• Chewables should be chewed
Salicylates patient teaching:
• Instruct to take with full glass of water and sit up for 15-30 minutes after taking this med
• Report tinnitus, unusual bleeding of gums, bruising, black tarry stools
• Do not drink alcohol with this medication- may increase risk of gi bleeding
• Notify provider if rash occurs
• Advise patients on long term therapy to inform provider of medication regimen- aspirin may need to be held for 1 week prior to surgery
• Do not give aspirin to children or teens
Salicylates black box warning:
Reye's Syndrome
- affects children and teens recovering from a viral infection like the flu
- Causes swelling in liver and brain
Salicylates mild overdose:
decrease the dose
Salicylates severe overdose:
• Discontinue
• Prevent further absorption- lavage and activated charcoal
• Increase urinary excretion
• Correct fluid, electrolyte
• Correct acid/base imbalance > sodium Bicarbonate
Propionic Acid Derivatives prototype:
Ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil)
Propionic Acid Derivatives other drugs in catergory:
Naproxen sodium (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprelan)
Propionic Acid Derivatives indications:
• Mild to moderate pain
• Fever
• Inflammation
Propionic Acid Derivatives action:
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, blocks cox-1 and cox-2
Propionic Acid Derivatives contraindications:
• In persons with known allergies to NSAIDS and salicylates
• Renal disease / renal transplant
• Pain after CABG
Propionic Acid Derivatives adverse reactions / side effects:
• Dyspepsia / nausea
• GI Bleeding
• Fluid retention
• HTN
Propionic Acid Derivatives interactions:
Drug-drug = additive gi effect if taken concurrently with aspirin or other nsaids
Propionic Acid Derivatives route/dosage:
PO or IV 200-800 Mg
Propionic Acid Derivatives pharmacokinetics:
- Metabolized by liver
- Excreted by the kidney
- g every 6-8 hours
- topical
Propionic Acid Derivatives pregnancy category:
B second trimester, D third trimester
Propionic acid derivatives assessment:
• Question allergies
• Assess for s/s of gi bleeding: black tarry stools, hypotension
• Assess for rashes
• Pre- and post-pain medication assessment
• Reduction of fever
Propionic acid derivatives patient teaching:
• Take with full glass of water and remain upright 15-30 minutes after taking this med
• Do not double doses
• DO not take with history of renal impairment or history of transplant
• Do not take more than 10 days unless instructed by provider
Propionic acid derivatives black box warning:
Contraindicated for the treatment of pain after coronary artery bypass graft
Acetic Acid Derivatives prototype:
Indomethacin (Indocin, Indocin SR)
Acetic Acid Derivatives other drugs in category:
Ketorolac (Toradol)
Acetic Acid Derivatives indications:
short term management of pain (<5 days) or long-term use in gouty arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
Acetic Acid Derivatives action:
inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic actions; inhibits both Cox I & Cox ii
Acetic Acid Derivatives contraindications:
• Hypersensitivity to aspirin
• History of gi bleeding
• Renal impairment
• Pain following CABG
Acetic Acid Derivatives: Adverse reactions / side effects:
• GI bleeding
• Anaphylaxis
• Drowsiness/dizziness (vertigo)
• Rashes
• Fluid retention
• HTN
Acetic Acid Derivatives interactions:
drug-drug- should not be taken with probenecid (often prolongs effect of many drugs), aspirin or other NSAIDS
Acetic Acid Derivatives route/dosages:
• PO, IM, IV, intranasal
• Ketorolac dosage is 10-30 mg depending on route, every 4-8 hours
• Parenteral is reported to be comparable to morphine & other opioids in effectiveness of moderate or severe pain.
• Duration should not exceed 5 days
Acetic Acid Derivatives pharmacokinetics:
• Metabolized in liver
• Excreted by kidneys
• Half-life= 4.5 hours, higher in geriatric patients (see beers criteria)
Acetic Acid Derivatives pregnancy category:
b, c, or d depending on specific drug
Acetic Acid Derivatives assessment:
•Question allergies
•Assess for rashes
•Pre- and post-pain medication assessment
•Qsen alert- assess for gi pain, rapid pulse and diaphoresis in those who receive ketorolac- indicative of gi perforation
•Observe for bleeding tendencies and peptic ulcer
Acetic Acid administration:
•Indomethacin po with food or antacid to prevent GI upset
•Ketorolac First dose should be iv or im
•Assess compatibility if giving iv
•Administer iv over at least 5-10 seconds
Acetic Acid patient teaching:
•Instruct patient to ask for pain meds as needed
•Do not double doses
•Report rash
•Keep po meds out of light
Acetic Acid black box warning:
not for use after cabg
Celecoxib (Celebrex) is the only COX-2 Inhibitor on the market in the US
Celecoxib (Celebrex) is the only COX-2 Inhibitor on the market in the US
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor indications:
acute and long-term treatment of inflammation & Pain
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor action:
inhibits cox-2 enzyme to decrease PgE (prostaglandin) & inflammation
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor contraindications:
• hypersensitivity to nsaids, ASA, sulfonomides
• Renal impairment
• In those with hepatic impairment, dose should be reduced 50%
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor adverse reactions/side effects:
•anaphylaxis
•fluid retention, htn, liver effects
•MI (heart attack) & stroke
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor interactions:
• drug-drug- may decrease effectiveness of ace inhibitors (lowers blood pressure), thiazide diuretics and furosemide
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor route/dosage:
PO- 100 mg to 400 mg twice daily
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor pharmacokinetics:
•slow onset of action d/t highly protein bound
•Metabolized in liver (p450 enzymes)
•Excreted in the urine
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor pregnancy category:
C, d in the third trimester
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor black box warning:
concerning cardiac & vascular risks
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor assessment:
•Question allergies to aspirin, nsaids or sulfa drugs= should not take if so
•Assess range of motion, degree of swelling, and pain in affected joints
•Assess for rashes
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitor administration:
• May be administered without regard to meals
• Capsules may be opened and sprinkled on applesauce (not on anything dairy)
Non-narcotic (not on the schedule) analgesic antipyretic prototype:
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen indication:
•Reduce pain and fever
•Equal to ASpirin in analgesic and antipyretic effects
•Lacks anti-inflammatory activity
•Drug of choice for children with fever and mild pain (no reyes syndrome)
Acetaminophen mechanism of action:
unknown, directly acts on hypothalamus
Acetaminophen advantages:
Does not cause nausea, vomiting, GI bleeding, or interfere with blood clotting
Acetaminophen contraindications:
Hypersensitivity
Liver & Kidney impairment
Alcoholism
Patients on antiepileptic drugs
Acetaminophen route/dosage:
•po tablets or liquid, rectal suppository, iv
•325-1000 mg every 4 hours
•Not > 4 grams per day
Acetaminophen pharmacokinetics:
•Metabolized in the liver
•Excreted in Urine
Acetaminophen Overdose:
• Acute or chronic overdose can result in liver damage or fatal liver necrosis
• Usual therapeutic doses may cause or increase liver damage in those who abuse alcohol
Acetaminophen Toxicity:
•Prevention: Maximum daily dose is 4 grams from all sources
•Overdose causes hepatotoxicity
•Accidental or intentional
•Signs/symptoms are nonspecific
•24 to 48 hours after overdose, liver function tests begin to show increased levels
•Later manifestations may include jaundice, right upper quadrant pain, palpate big liver, vomiting, CNS stimulation with excitement, and delirium followed by coma and death
Acetaminophen Toxicity Treatment:
• Draw blood for liver function tests and acetaminophen levels, but do not wait to treat!
Gastric lavage and activated charcoal
• If overdose detected within 4 hours after ingestion
Antidote
• Acetylcysteine (Mucomyst)
• Oral or IV
• Most beneficial if given 8 hours after ingestion, may be helpful within 36 hours
• Does NOT reverse damage already sustained
Gout
Arthritic condition characterized by hyperuricema
three stages of gout:
• First: Acute gouty arthritis or "Gout attack"- hyperuricemia, pain, and swelling of the joints (especially great toe, usually at night)
• Second: symptom-free period of several years, then recurrence of above
• Third: chronic- solid deposits of urate crystals (tophi) in the joints and elsewhere
• Can form renal calculi (kidney stones), can result in permanent kidney damage
gout treatment:
nsaids and corticosteroids, and Uricosuric or mitotic agents
mitotic agent prototype:
Colchicine (Colcrys)