unit 3: production, costs, and perfect competition
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
what is marginal product? what is its formula?
marginal product is the difference of product after one more resource (the additional output generated). change of TP/change of inputs
marginal product is the slope of what?
slope of TP
what does total physical product (TP) refer to?
it refers to the total amount of products made from all resources
what is average product (AP)? what is its formula?
the average product (or output) per resource (labor). TP/units of labor
what are input resources called?
factors
what are fixed resources?
fixed resources are resources that don’t change w/ the quantity produced
what are variable resources?
variable resources are resources that change with the quantity produced
more workers result in more what?
more marginal product
what does the law of diminishing marginal returns explain?
law of diminishing marginal returns explains how as variable resources are added to fixed resources, the additional output produced from each additional worker will eventually fall
what are the 3 stages of diminishing marginal returns?
increasing marginal returns
decreasing marginal returns
negative marginal returns
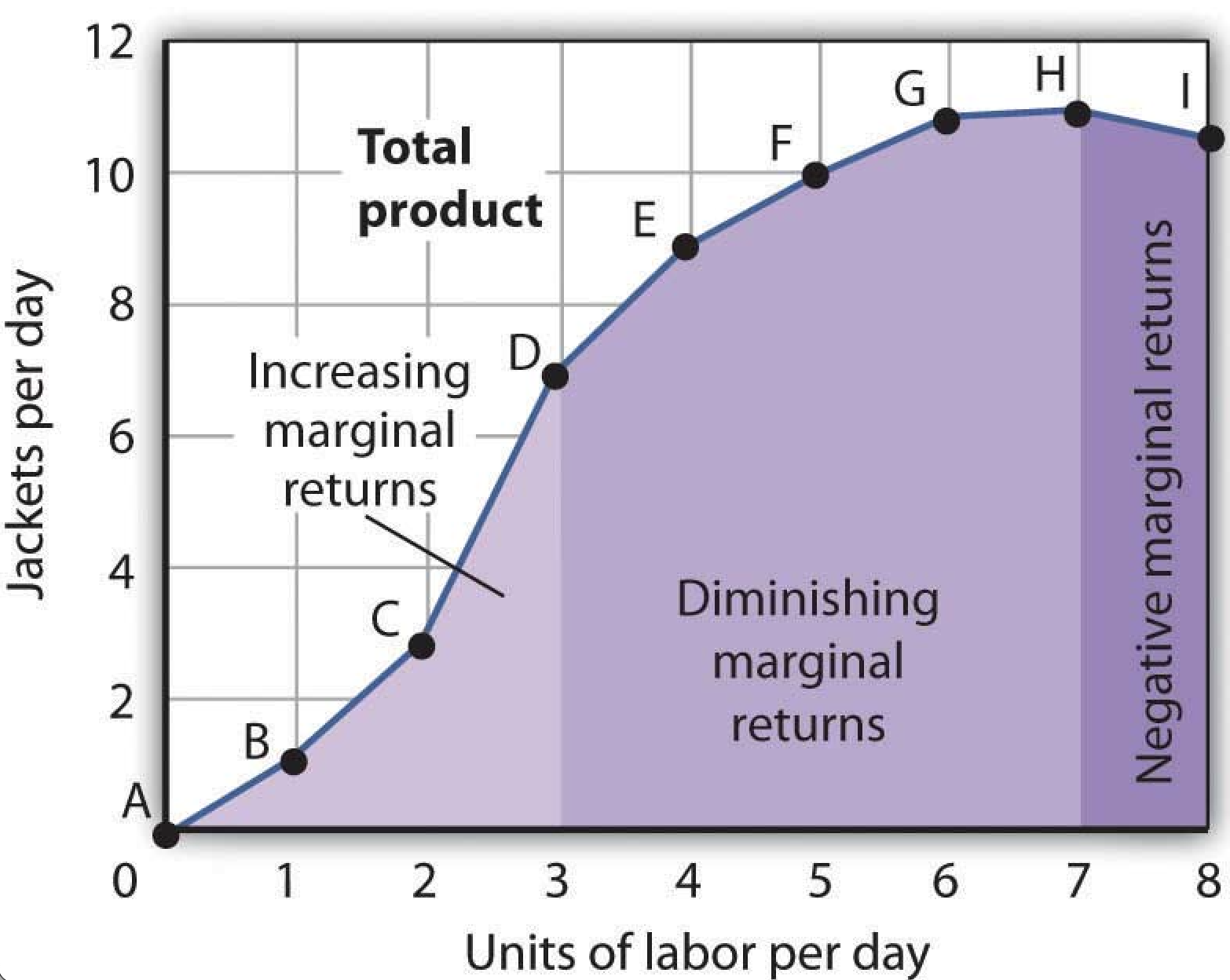
how is increasing marginal returns depicted?
in increasing marginal returns, marginal product is rising and total product is increasing at an increasing rate
how is decreasing marginal returns depicted?
in decreasing marginal returns, marginal product is decreasing and total product is increasing at a decreasing rate (on its way to downhill)
how is negative marginal returns depicted?
in negative marginal returns, marginal product is negative and total product is decreasing (too many workers)
total product is at a maximum when?
when marginal product is at 0
what does short-run (production costs) refer entail? what are its characteristics?
short-run refers to a period in which at least one resource is sized or fixed. in short-run time is not fixed but plant capacity/size is fixed
what does long-run (production costs) entail? what are its characteristics?
long-run entails all resources are variable. there are no fixed resources and plant/capacity size is not fixed
what is the formula for total cost?
fixed costs (FC) + total variable costs (VC)
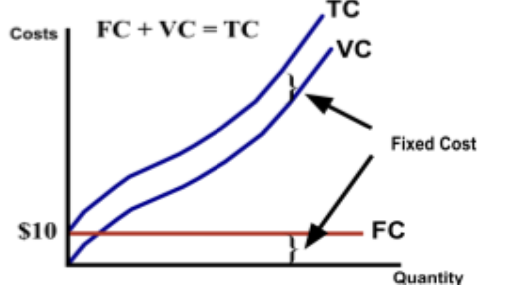
what are the 4 per units costs?
average fixed costs (AFC)
average variable costs (AVC)
average total costs (ATC)
marginal cost (MC)
what is the formula for ATC?
average total cost = average fixed costs + average variable cost
what do fixed costs include?
fixed costs are costs for fixed resources that don’t change w/ the amount produced (e.g. rent, insurance)
what do variable costs include?
variable costs are costs for variable resources that change as more or less is produced (raw materials, labor, electricity)
what is the formula for average costs?
total (respective) cost/quantity
what is marginal cost?
marginal cost is the additional cost of an additional output
what is the formula for marginal cost?
change in total cost/change in quantity
what does specialization mean?
specialization makes things go down, then up
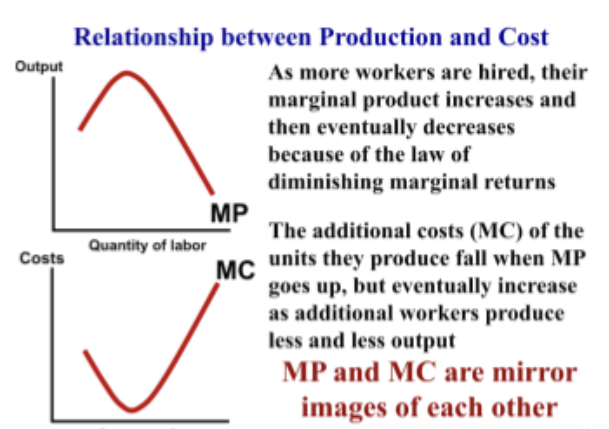
what is the relationship btwn production and cost? (in terms of MP. MC, and MR)
MP and MC are mirror images. MR equals MC (think: in order for there to be revenue, there needs to be cost)
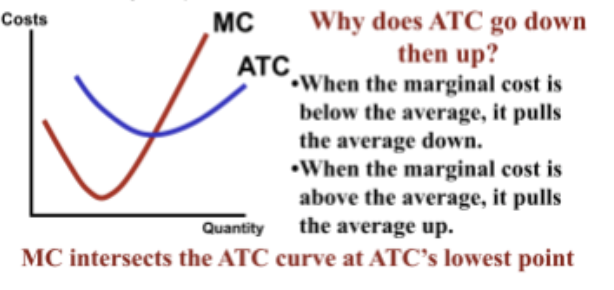
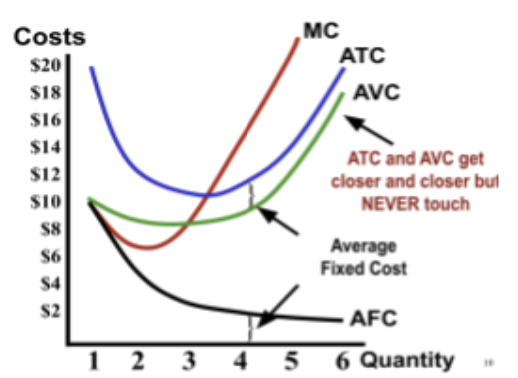
Why does ATC go down then up?
Because when the marginal cost is below the average, it pulls the average down. (note how MC intersects ATC at the vertex)
what is the relationship btwn ATC and AVC?
Average total cost is always above average variable cost
when is long-run used?
long-run is used to identify which size factory results in the lowest per unit cost
what happens in returns to scale?
input is doubled
what are the 3 returns to scale? And what does each scale mean?
increasing returns to scale: output more than doubles
constant returns to scale: output doubles
decreasing returns to scale: output less than doubles
what happens to the ATC of a product when a firm increases its plant capacity? (AKA what happens to the ATC of a product in the long-run?)
the ATC curve becomes made up of all the different short-run ATC curves of different plant sizes
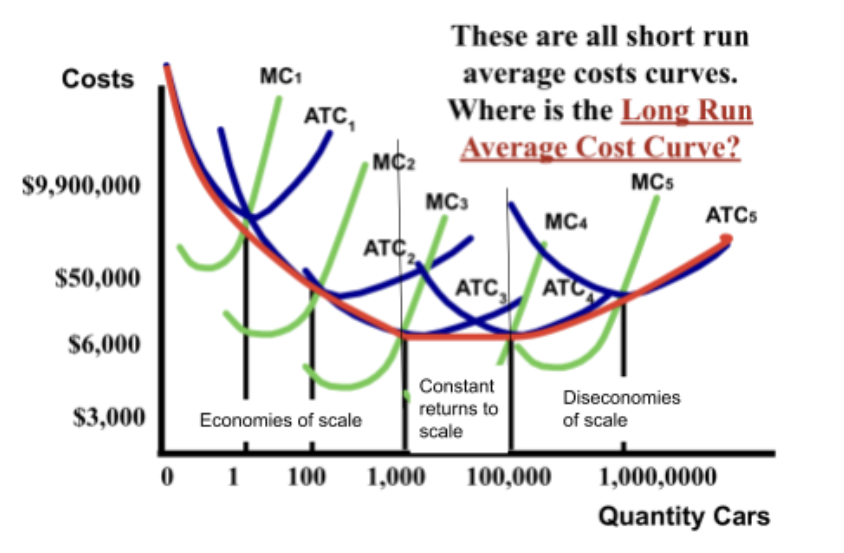
define economies of scale
shows that long-run average cost falls because mass production techniques are used (cheaper to produce due to mass production)
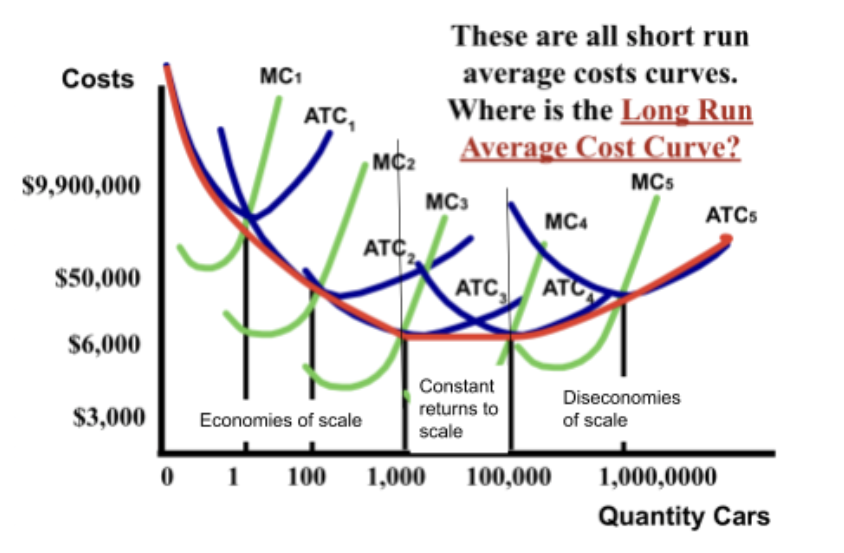
how does mass production affect TC and AC?
mass production causes total cost to be high but average cost per unit to be low
how does low volume production affect TC and AC?
low volume causes TC to be low but AC per unit to be high.
what does constant return to scale show?
it shows ATC is as low as it can get
define diseconomies of scale
diseconomies of scale is when average cost increases as the firm gets too big and difficult to manage (similar concept to diminishing marginal returns)
does law of diminishing marginal returns apply in long-run?
no, because there are no fixed resources in the long-run.
per unit tax or subsidy causes what to shift and affect or not affect what?
it will cause marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost to shift since it affects the variable costs. It will also affect the quantity produced.
lump sun tax or subsidy causes what to shift and affect or not affect what?
it will cause average fixed cost and average total cost to shift since it affects fixed costs. It will not affect marginal cost, profit, or quantity produced.
what is the difference btwn per unit tax/subsidy and lump sum tax/subsidy (in what they affect)?
per unit tax affects variable costs while lump sum affects fixed costs
what is the formula for accounting profit?
total revenue - accounting costs (explicit costs: rent, wage, material)
what is the formula for economic profit?
total revenue - economic costs (explicit and implicit costs: forgone wage, rent, time)
when does positive accounting profit occur?
when economic profit is zero
if MR > MC, the firm should
the firm should produce more output
if MR < MC, the firm should
produce less output (since they’re losing more than they are getting back)
how to maximize profit?
MC shoul dbe close to the product price or MR
when should a firm shut down? why?
If the price is below the average variable cost. this means the firm has a loss bigger than their fixed cost, which is a no.
when is the firm earning profit, earning normal economic profit, producing at a loss, and shutting down? (list answers)
profit: price above ATC
normal economic profit: price at ATC vertex
producing at a loss: price at AVC vertex
shutting down: price below AVC
Short run supply curve: MC and AVC
MC is above AVC in a short run supply curve
what do sunk costs explain?
they explain why people will continue to spend despite losing money
what are barriers to entry?
they are factors that prevent new firms from entering a given market
what do low barriers mean? what do high barriers mean?
low barriers mean the market has more competition and individual firms make less profit. high barriers mean the market has less competition and individual firms make more profit
what does normal profit mean in an efficient competitive market?
it means firms that have identical products will break even and make no economic profit
what are 5 characteristics of perfect competition and what is one market example?
many small firms
identical products (perfect substitutes)
low barriers
seller has no need to advertise
firms are price takers— they have no control over price
one example is a strawberry market
what are 4 types of barriers to entry?
economies of scale (e.g. there being only one electric company)
superior technology
geography or ownership of raw materials
government created barriers (patents, copyrights)
demand for perfectly competitive firms: what is the relationship btwn MR, D, AR, and P?
they are all equal— MR. D AR P
what are the 3 characteristics of Mr = MC rule
MR = MC applies to all market structures
MR = MC only applies if price is above AVC
MR = MC is also P = MC for competitive firms