Intracellular & Extracellular accumulation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the 4 intracellular accumulations
Defect in metabolism, defect in protein folding/transport, Lack of inherited enzyme deficiencies, ingestion/inhalation of indigestible materials
What is defect in metabolism
Fatty change such as lipidosis/steatosis in the liver
What is defect in protein folding/transport
Accumulations can occur secondary to misfolded proteins or from an inability to transport proteins out of the cell
What does Lack of enzyme do
Failure to degrade a substrate due to inherited enzyme deficiencies
what is the mechanism of Ingestion/ inhalation of indigestible materials
accumulation of carbon
Intracellular accumulations: lipid is what?
Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides
causes include toxins, protein malnutrition, diabetes, obesity,decreased perfusion
What are the mechanisms of lipidosis/steatosis
Negative energy balance, decreased oxidation of FFA, decreased apoprotein synthesis, decreased/ineffective lipoprotein synthesis, ineffective lipoprotein transport outside the cell
Atherosclerosis
cholesterol accumulation in arteries, in smooth muscle and subintimal space of medium to large arteries, appear as clear lipid/ foamy macrophages
Intracellular accumulation: Glycogen
Source of stored energy in cell appears as clear vacuoles
Pigment Accumulation Red
Heme part of hemoglobin from vasodilation, hemorrhage, or hemoglobin imbibition
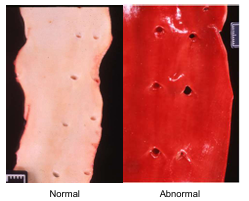
Pigment Accumulations: Green
Old hemorrhage(biliverdin) & eosinophilic infiltrate
Seen in birds chromic hemorrhage
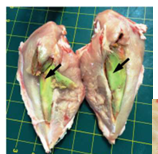
Pigment accumulation: Brown
Pathologic and non-pathologic
Hemosiderin, ceroid-lipofuscin, melanin
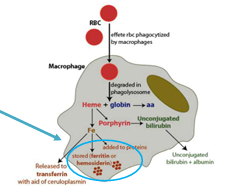
Hemosiderin
A hemoglobin break down product which discolors affected organs brown
Lipofuscin
Brown
Wear and tear pigment
Indicator of oxidative damage, age of cell
Ceroid
Pathological brown pigment
Indicator of oxidative injury
Nutritional panniculitis
Vit E deficiency
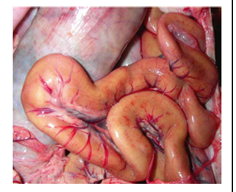
Pigment accumulation: Yellow
Bilirubin
End of product of hemoglobin metabolism
Produced within liver pre-hepatic, hepatic, post-hepatic
What are Carotenoids
Exogenous from diet, horses& some cattle breeds from leafy green plants
Product of erythrocyte breakdown
Heme—>biliverdin—>bilirubin—>conjugation in liver—>urobilinogen in GIT
Causes of hyperbilirubinemia/icterus
Prehepatic(hemolysis), Hepatic (liver dz), Post-hepatic (obstruction of bile)
Pigment accumulation: Black Melanin
Black brown pigment produced by melanocytes
ONLY endogenous black brown pigment
Non pathologic: skin, retina, meninges
Pathologic: melanocytic neoplasm, hyperpigmentation in skin
Amyloidosis
Protein-folding disorder resulting in deposition of misfolded insoluble protein (amyloid) between cells, causing tissue distortion and dysfunction
Extracellular
Local or systemic
Sharpei and Siamese cats=hereditary
Morphology of amyloid
Where is it found
Enlarged waxy pale dark brown
Liver,spleen,kidney
Intra/extra cellular accumulation: Mineral
What are the two forms
Deposition of calcium salts in tissue not normally mineralized
Dystropic-localized mineral deposition in areas of tissue injury and/or necrosis. Intracell=mitochondria Extracell=membrane bound matrix vesicles
Metastatic= result of ststemic Ca:P imbalance