revenge of the sigma official i hope please i hate this class
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
isometric
If we place a muscle under more load than it can lift and stimulate it, what type of contraction will we produce?
myofibrils
Bundles of protein filaments within a muscle cell are arranged into structures called:
frequency of stimulation
What experimental factor do we increase to produce tetany rather than simple wave summation?
aponeurosis
A flat, sheet-like bundle of connective tissue that connects a muscle to another muscle or to a bone is called:
fatigue
If we require a muscle to contract until it starts to run out of ATP, what do we call the state of the muscle at that point?
antagonist
what do we call muscles that oppose or reverse a particular movement?
Fixators
What do we call muscles that immobilize the origin of another muscle so that all of the tension is exerted at the insertion?
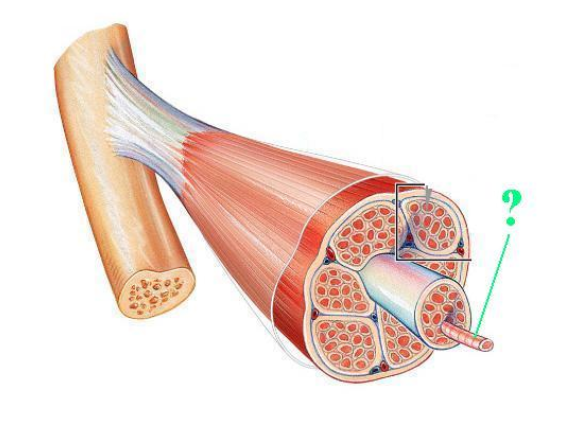
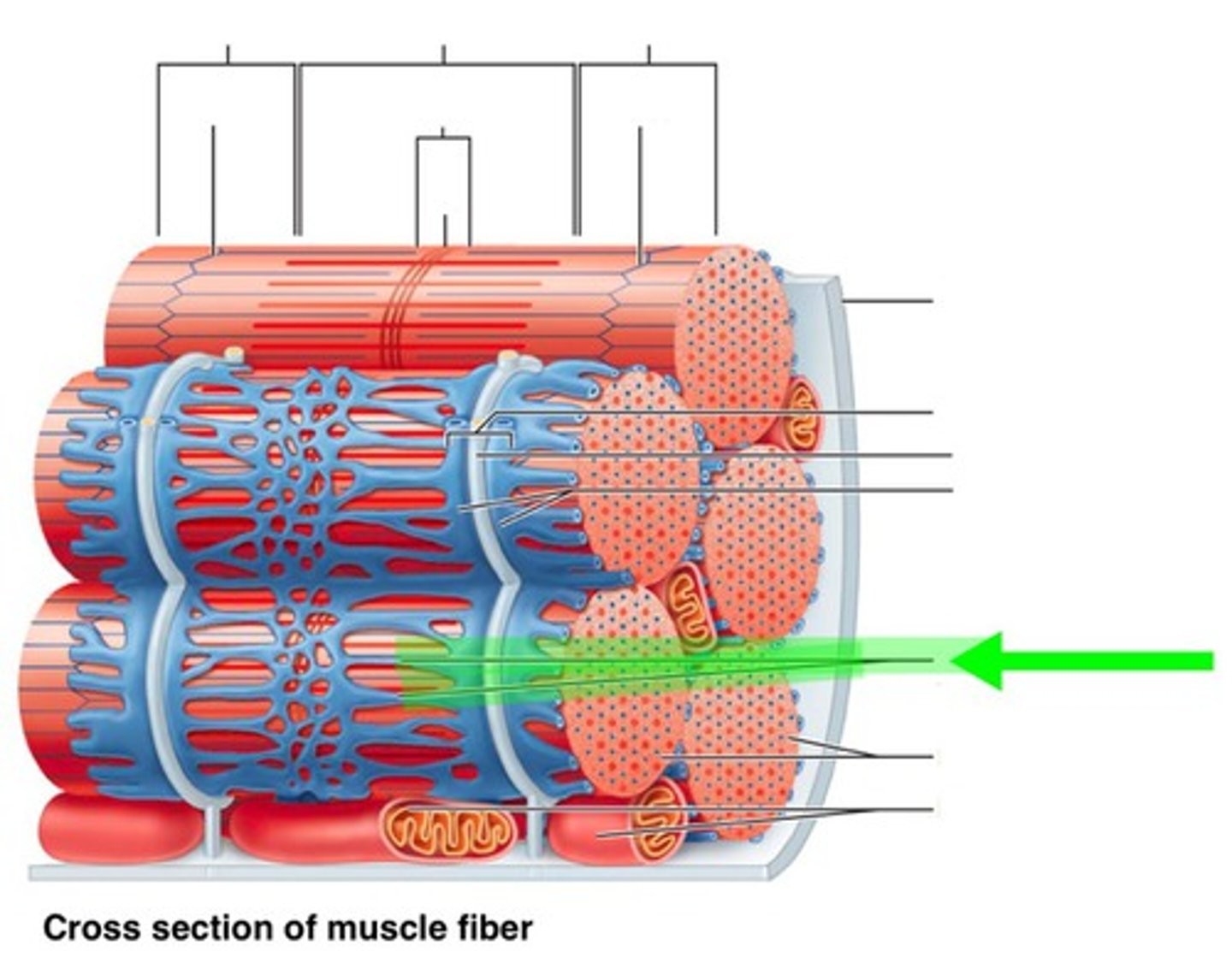
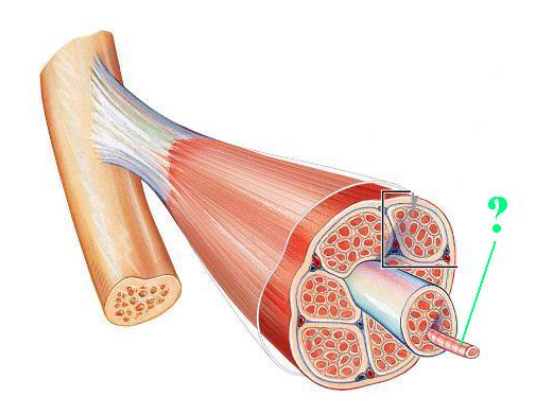
muscle fiber
Identify the indicated structure.
(very middle thing in muscle)
sarcoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum of a skeletal muscle cell is called:
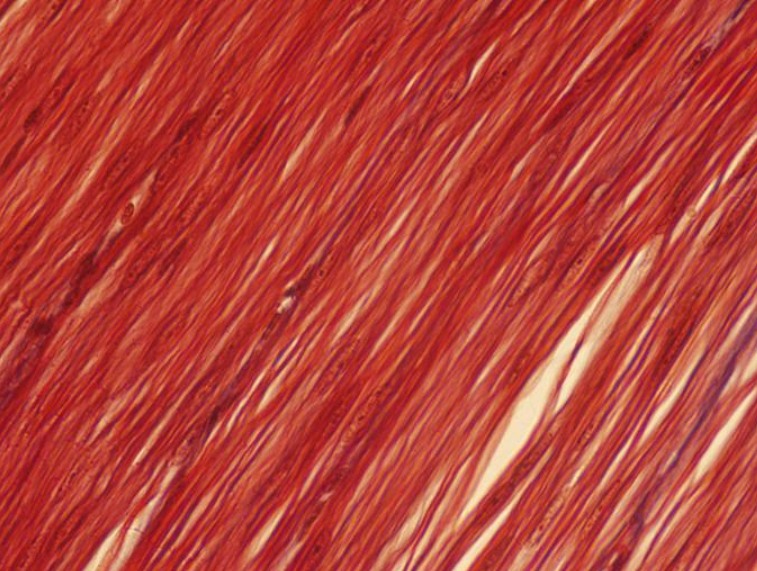
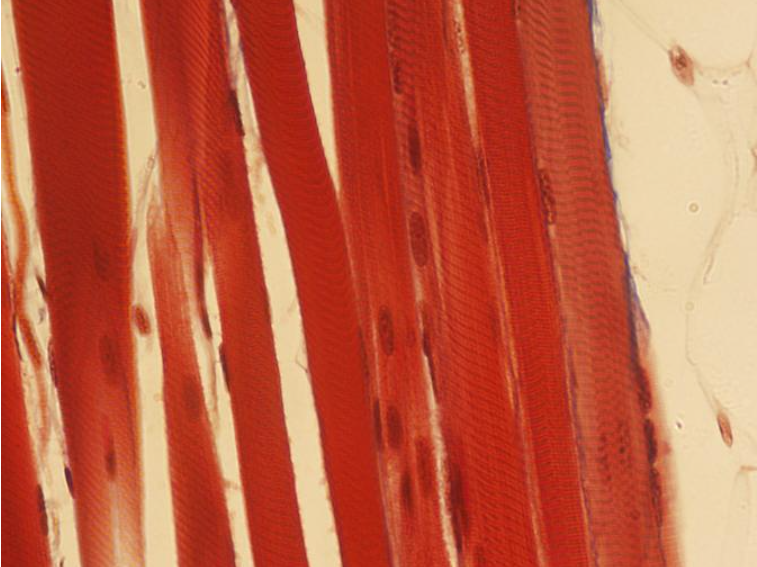
smooth
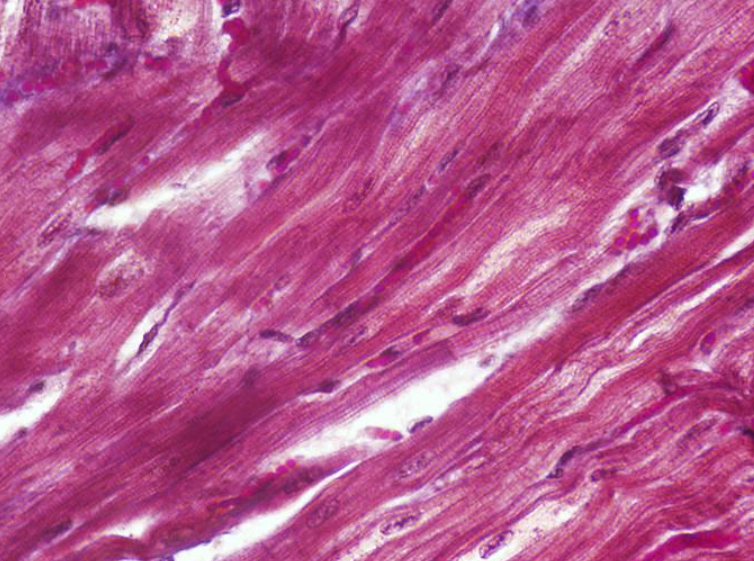
Identify the type of muscle tissue shown ho
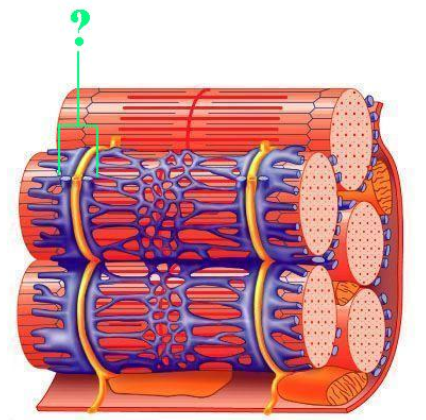
triad
Identify the indicated structure.
skeletal
Identify the type of muscle tissue shown?
(parallel)

synaptic vesicles
Acetylcholine in the axon terminal of a motor neuron is contained within membrane bound structures called:
latent phase
latent period
The three phases of a muscle twitch are the contraction period, the relaxation period, and the:
contraction period
The three phases of a muscle twitch are the latent period, the relaxation period, and the:
muscle fibers
Skeletal muscles cells are called:
acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter do motor neurons use to stimulate muscle cells?
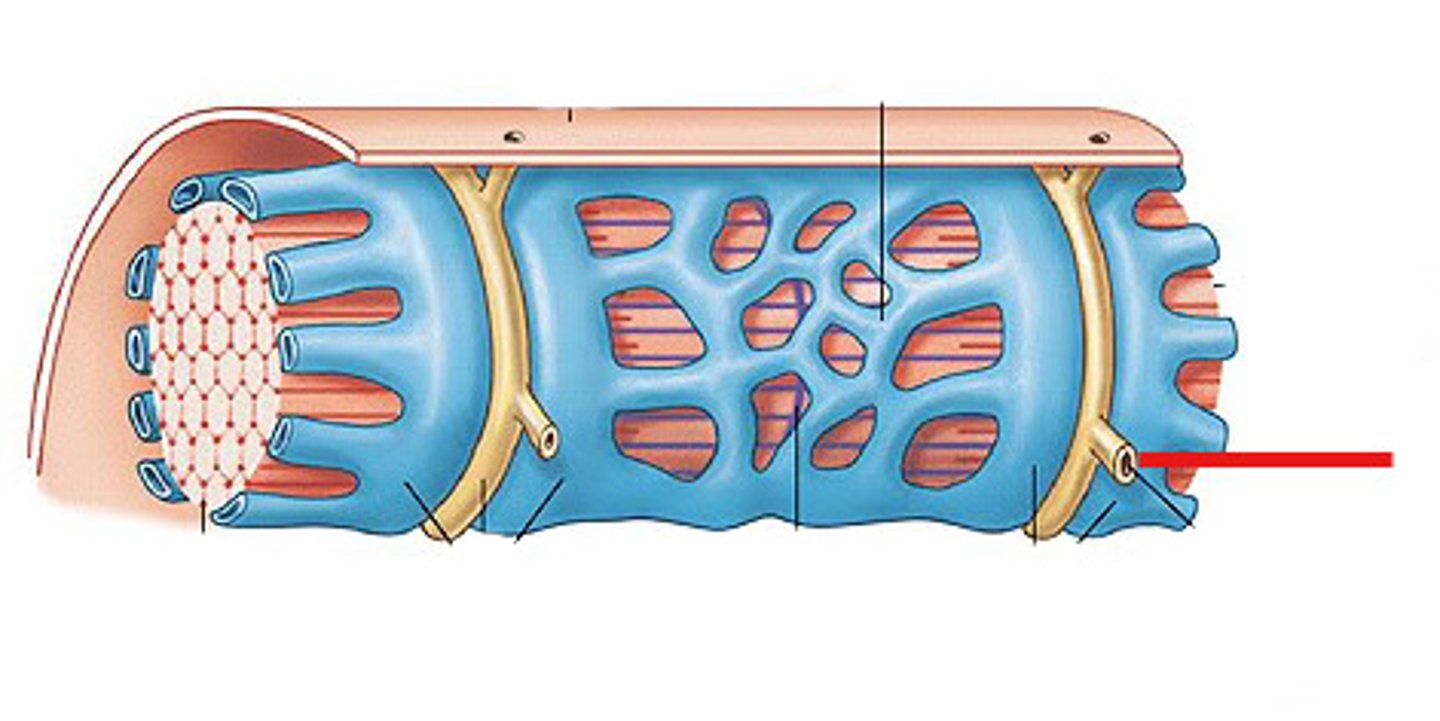
t-tubule
A portion of the plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle indents into the cytoplasm and surrounds the bundles of muscle filaments. This structure is called:
tetanus
What phenomenon is considered an extreme form of wave summation in which a steady, sustained contraction is acheived?
Motor Unit
A neuron and all of the muscle cells that it stimulates are together called a _________________?
Agonists
What do we call muscles that are primarily responsible for producing a specific movement?
movable attachment site of a muscle
Define "insertion" as it applies to skeletal muscles.
thick filaments
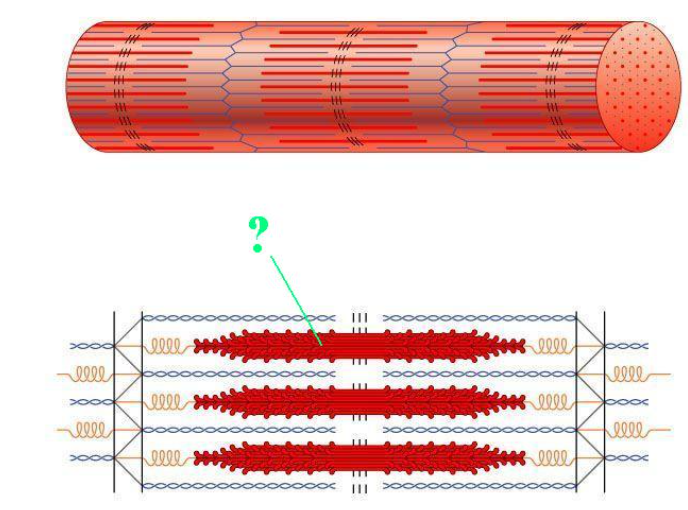
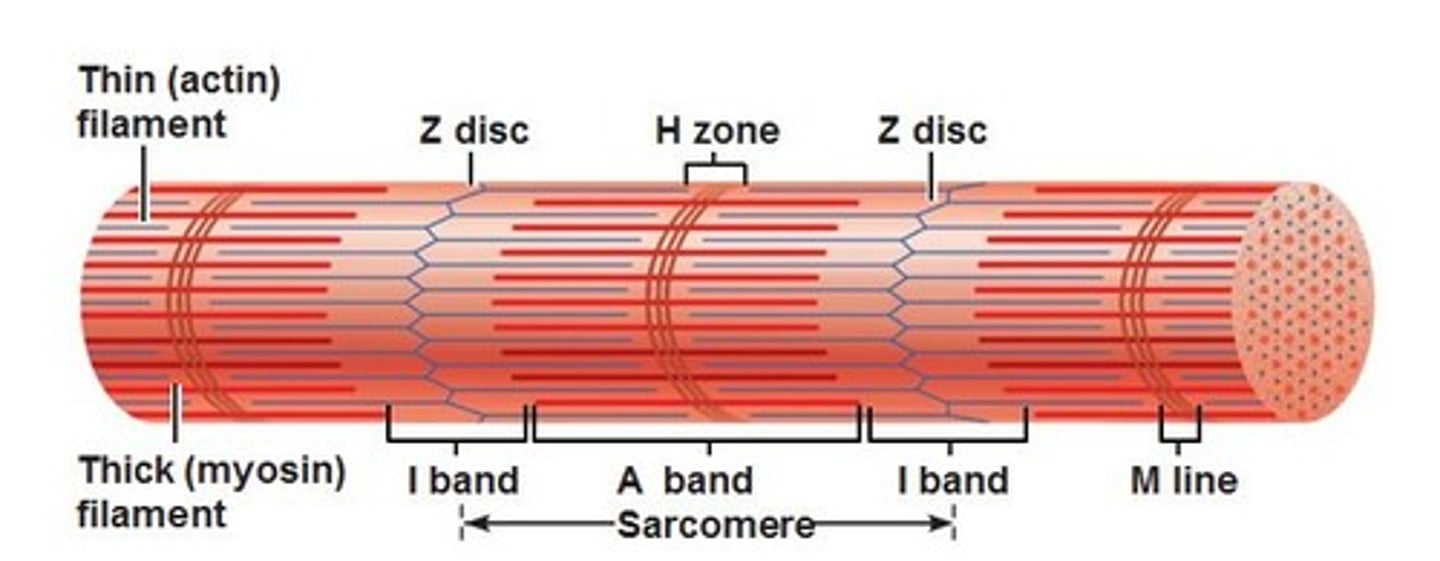
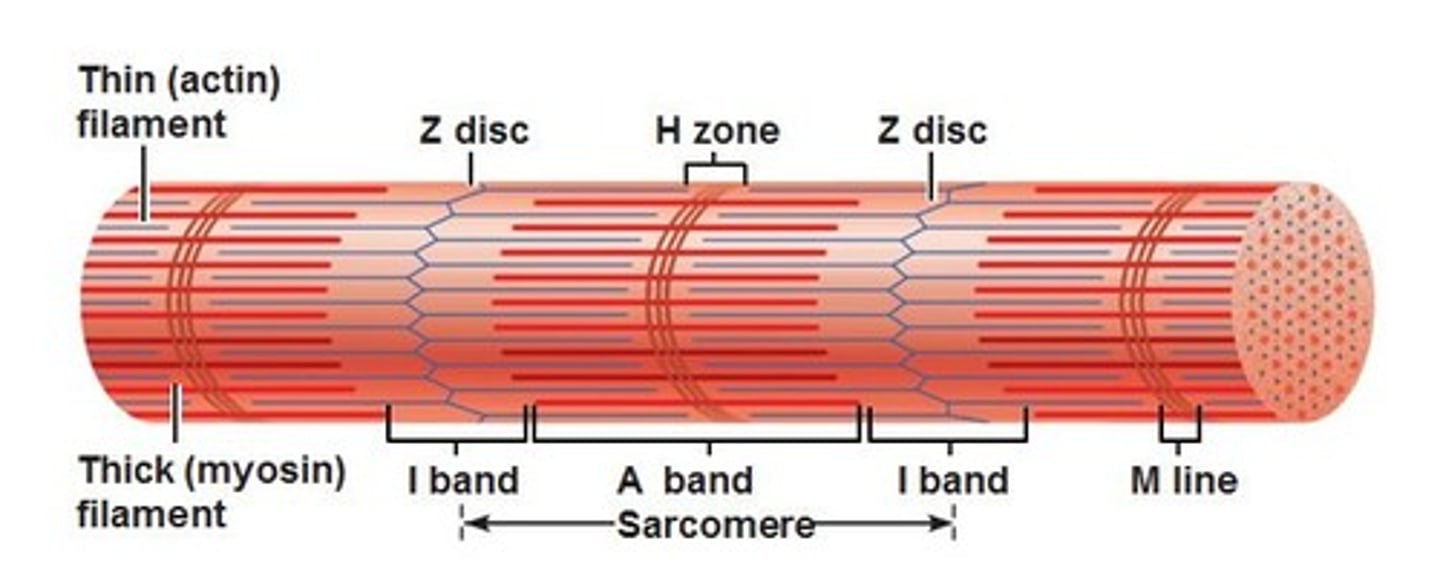
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere ho
terminal cistern of sarcoplasmic reticulum
Identify the indicated structure
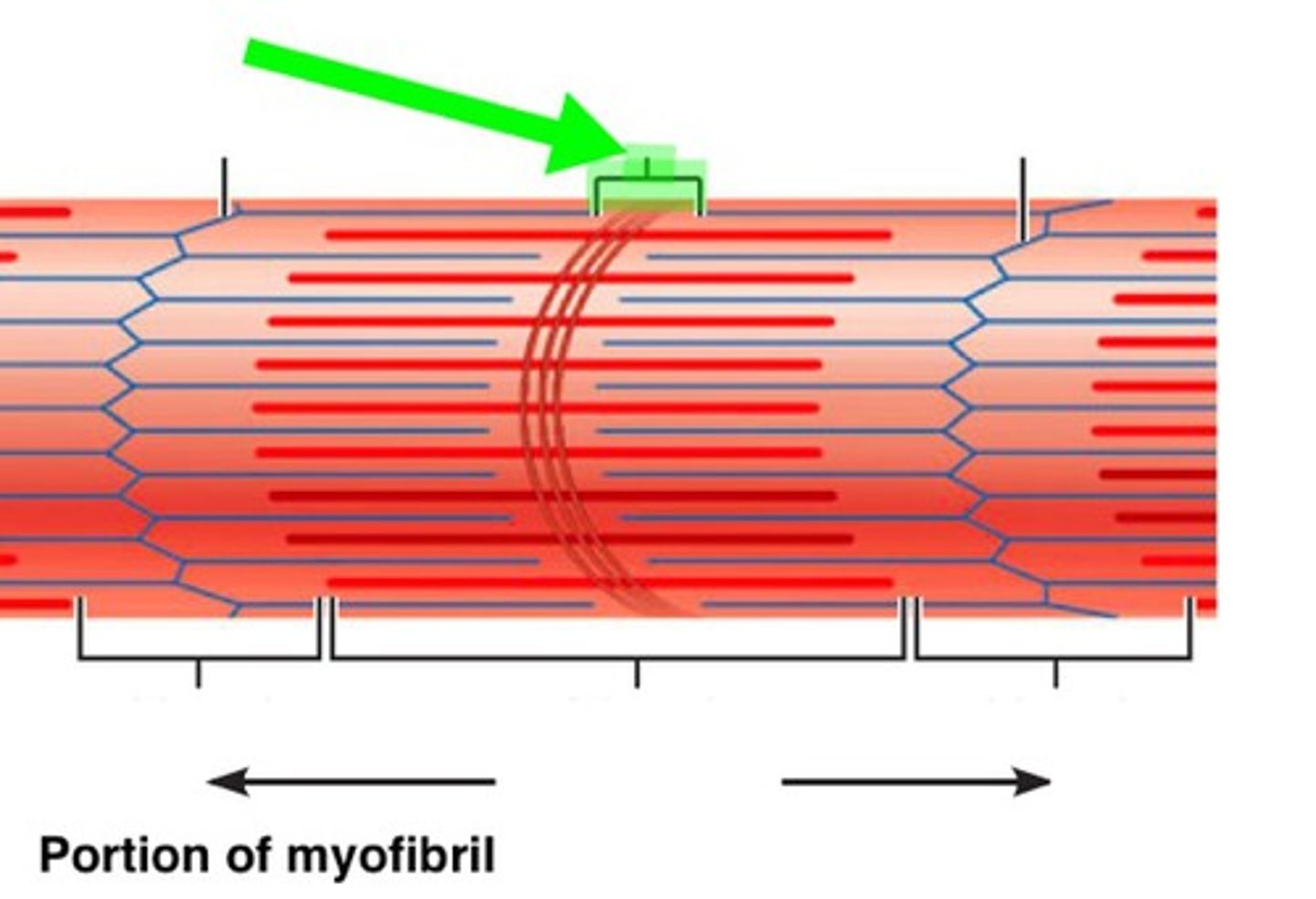
H-zone
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere ho
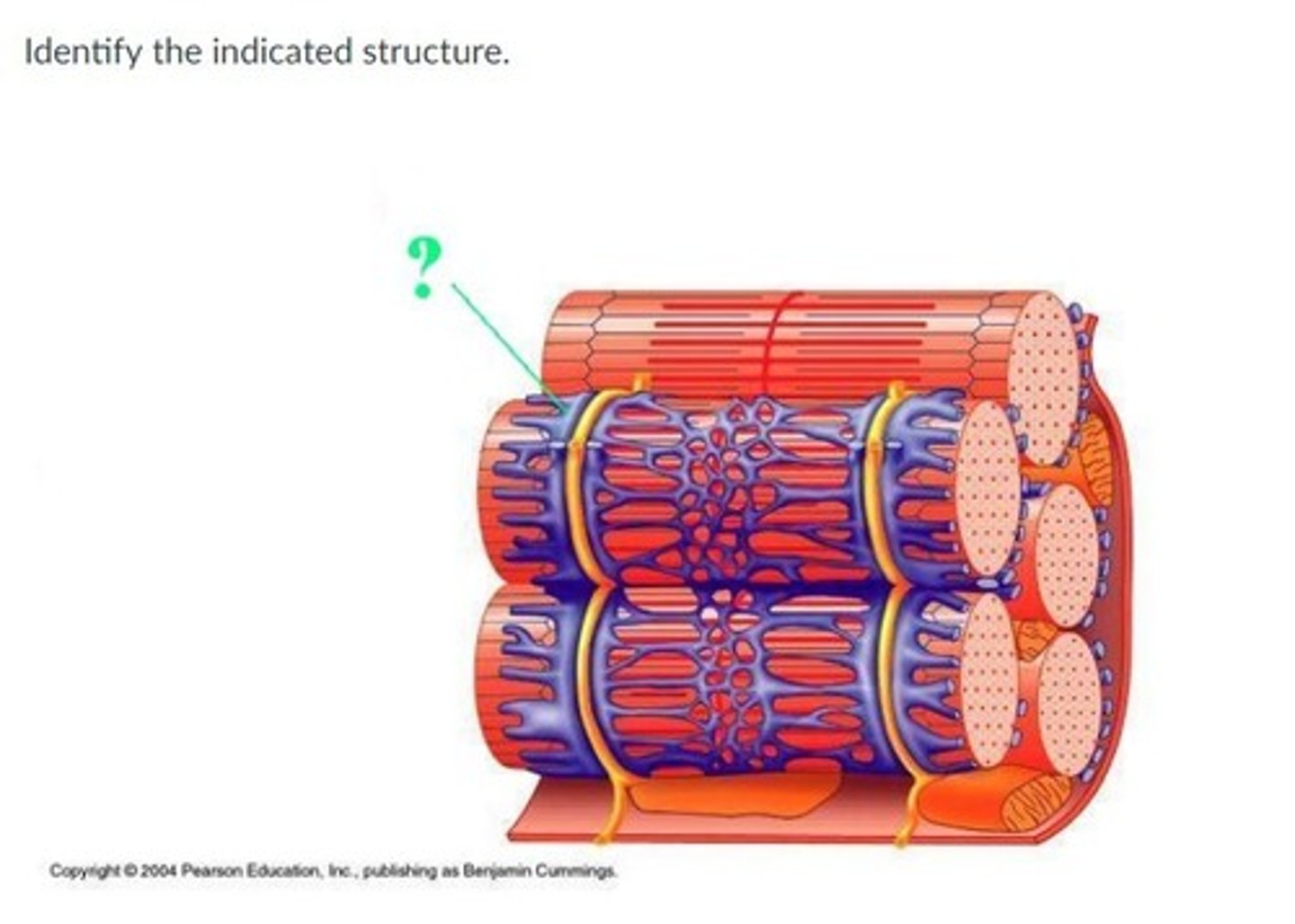
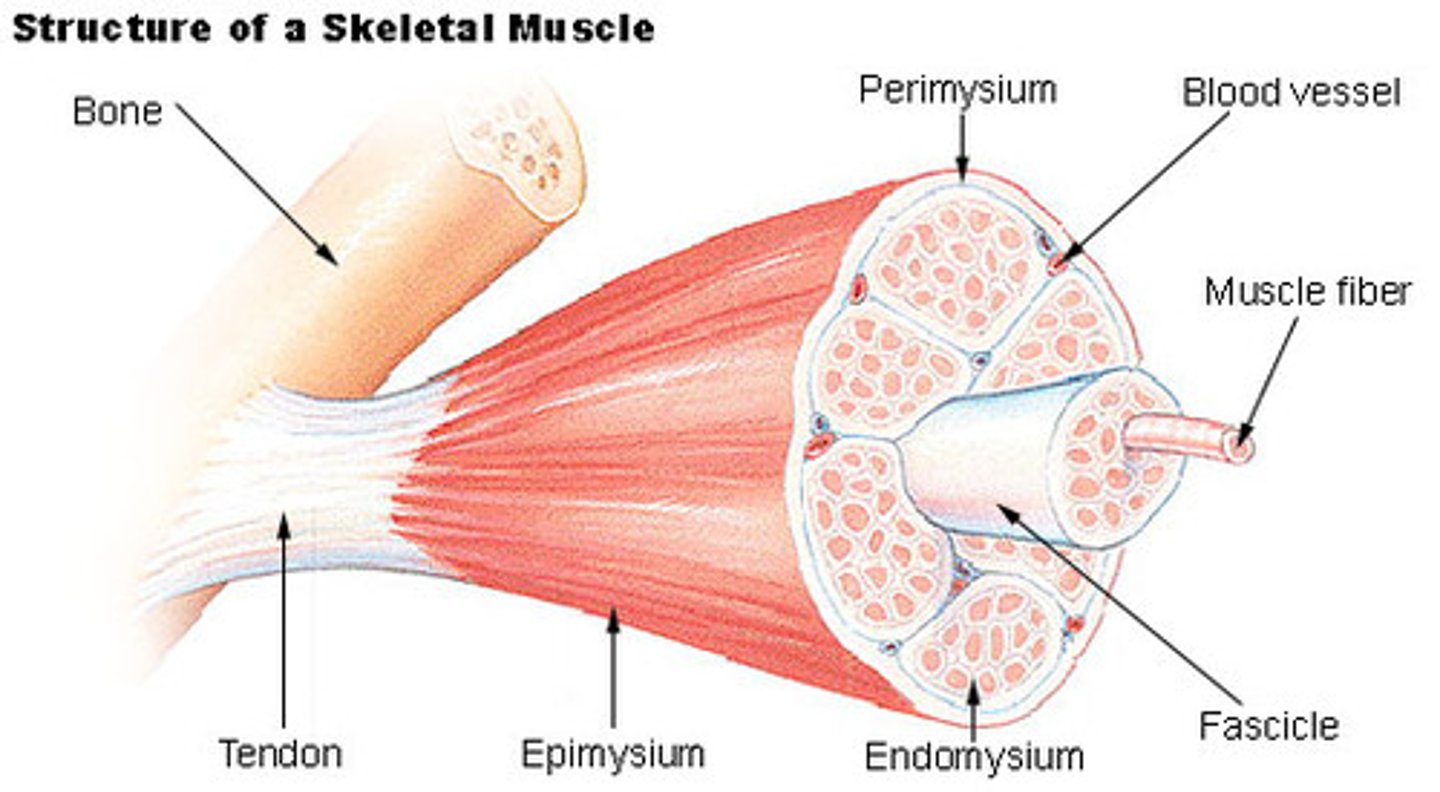
perimysium
Identify the indicated layer of connective tissue.
(the middle white-ish part of tube)
myosin
The indicated region of the sarcomere is composed of what protein?
(pointed at red part in the thing with 3 red parts on dynamite)
cardiac
Identify the type of muscle tissue shown?
tetanus
tetany
If we increase the frequence of stimulation of a muscle untill we acheive a steady sustained contraction, we will have caused what phenomenon?
epimysium
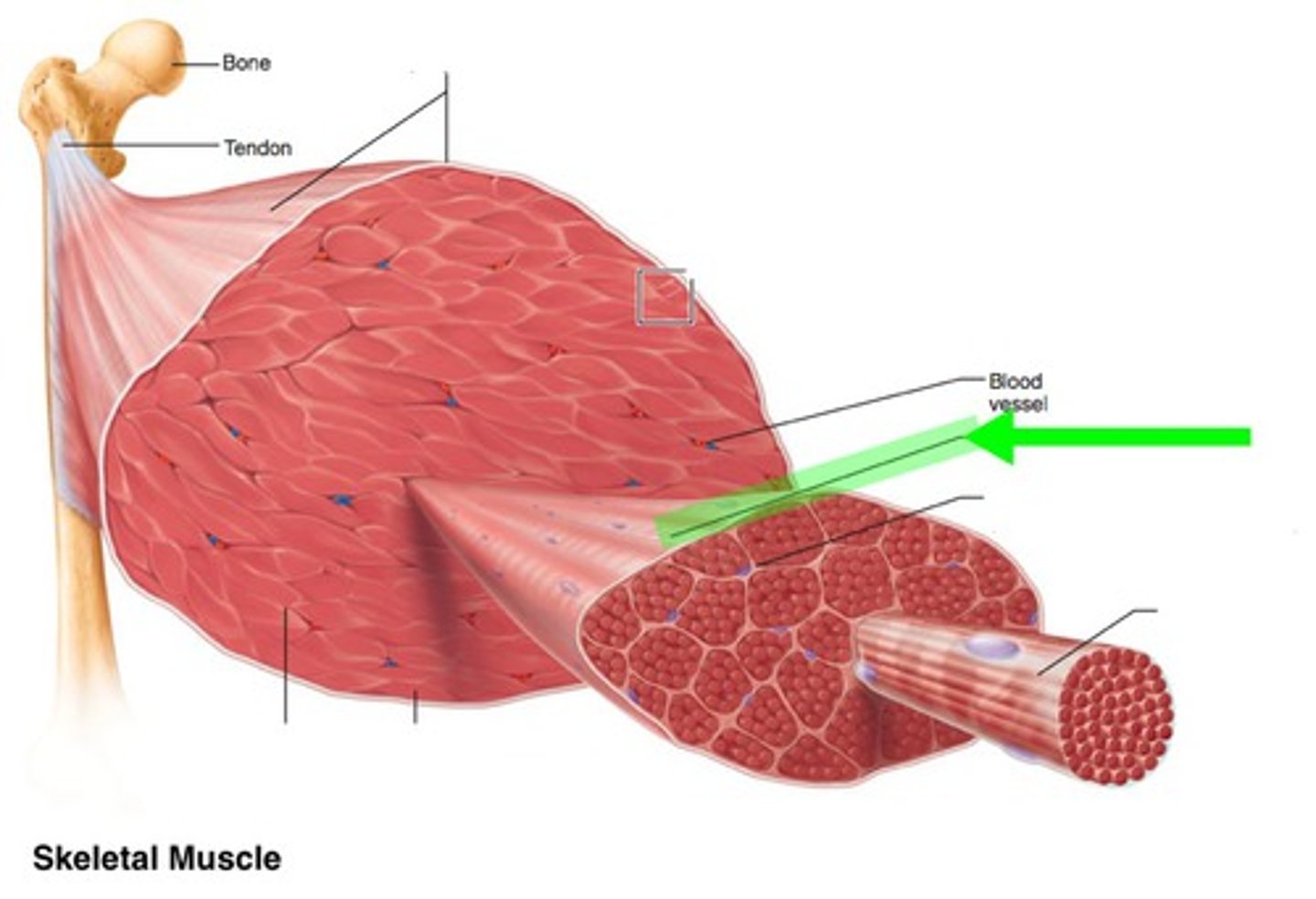
The connective tissue sheath that forms around an entire skeletal muscle is called:
tendon
A strong, cord-like bundle of connective tissue that connects a muscle to another muscle or to a bone is called:
epimysium
Identify the indicated layer of connective tissue.
(refer to pic)
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Identify the indicated structure.
(middle blue section on dynamite looking thing)
A-band
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
t-tubule
Identify the indicated structure.
(yellow line on dynamite)
endomysium
Identify the indicated layer of connective tissue
relaxation period
The three phases of a muscle twitch are the contraction period, the latent period, and the:
M-line
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere ho
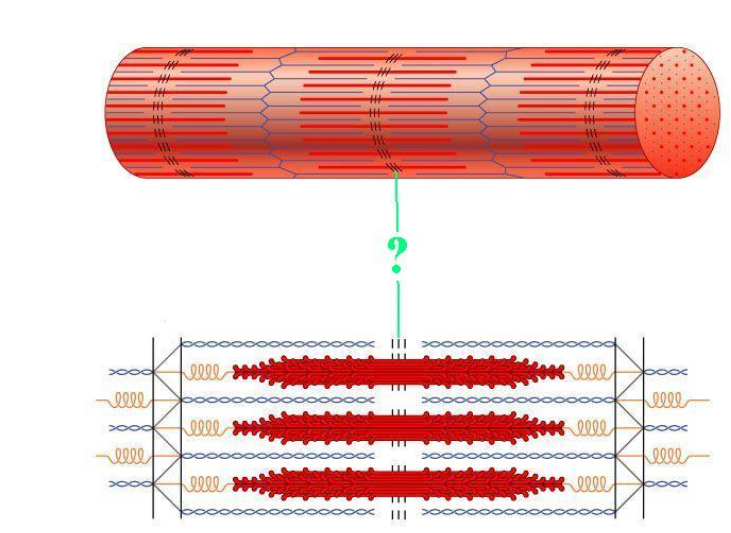
latent phase
latent period
What do we call the period of time between the application of a stimulus to a muscle and the first observable response or movement of the muscle?
A-bands
The dark segments of the striations of a skeletal muscle cell are called:
myofilaments
Chains of protein within the muscle cells are called:
I-band
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere
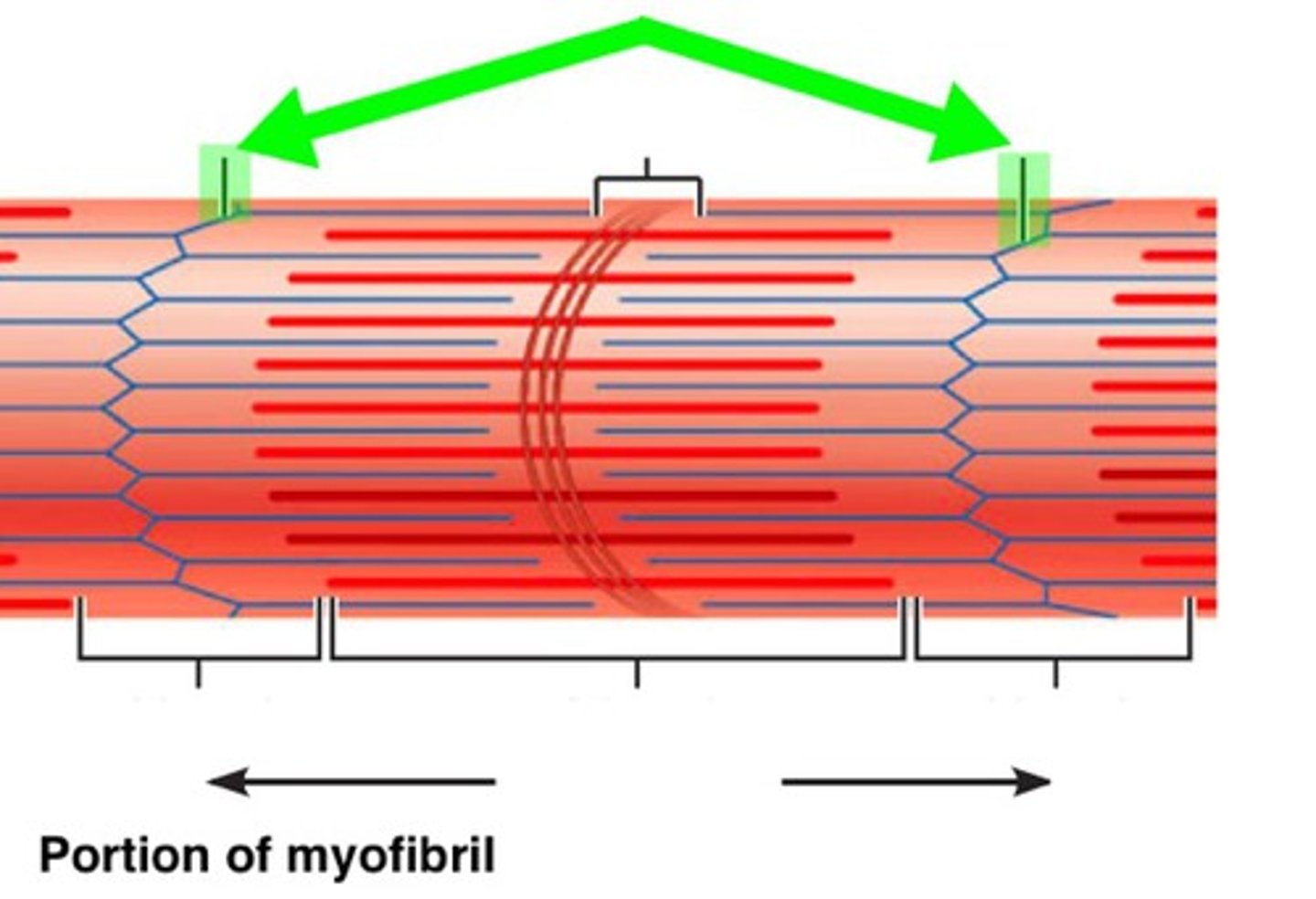
Z-disc
Identify the indicated region of the sarcomere.
(blue line on lighter red area of dynamite)
mhm
oh
active
What type of force is produced by the physiological contraction of a muscle rather than by elastic recoil?
passive
What type of force is produced by the elastic recoil of a stretched muscle?
triad
The structure formed by two terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and a transverse tubule is called:
endomysium
The connective tissue sheath that forms around an individual skeletal muscle cell is called:
perimysium
The connective tissue sheath that forms around a bundle of skeletal muscle cells is called:
treppe
If we stimulate a muscle, and then stimulate it again immediately after it has been allowed to relax, we observe that the second contraction of the muscle is slightly greater than the first. What do we call this phenomenon?
axonal terminals
The branches at the end of an axon of a motor neuron are called:
sarcoplasmic reticulum
From what cellular organelle is calcium released during the latent period of a muscle twitch?
twitch
A single contraction of a muscle is called a _____________?
motor unit
A single motor neuron, along with all of the muscle fibers that it innervates, is called:
isotonic
If we place a muscle under a load than it can lift and stimulate it, what type of contraction will we produce?
calcium
Although no force is generated by a muscle fiber during the latent period, chemical changes, such as the release of ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum do occur. Which ion is released
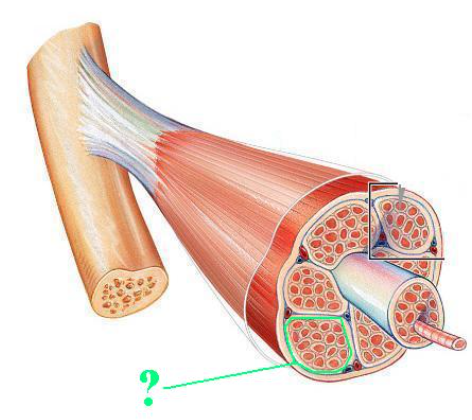
fascicle
what is it ho
ATP
The absence of what molecule is involved in the phenomenon of rigor mortis?
i-bands
The light segments of the striations of a skeletal muscle cell are called:
synaptic cleft
The space between a neuron axon terminal and the target cell is called:
isometric contraction
If a muscle contracts against a load that is too heavy for the muscle to lift, what type of contraction is the muscle demonstrating?
isotonic
If a muscle contracts against a load that it is able to lift, what type of contraction is the muscle demonstrating?
latent period
what do we call the period of time between the application of a stimulus to a muscle and the first observable response or movement of the muscle?
recruitment
By steadily increasing the number of motor units that are activated, we produce a steady increase in the force produced by a muscle. This process is called __________________?
muscle twitch
a single contraction of a muscle is called a _________?
fixator
what do we call muscles that immobilize the origin of another muscle so that all the tension is exerted at the insertion?
synergist
what do we call muscles that aid the action of other muscles by reducing undesirable or unnecessary movement?
shape, direction of muscle fibers, relative size, location, number of origins, location of origin and insertion, action
List the seven criteria listed in your lab manual that are used to name muscles?
sarcomeres
What are the individual contractile units of a muscle cell called?
immovable attachment site of a muscle
Define "origin" as it applies to skeletal muscles.