Biochemistry of Erythrocytes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Hemolytic anemia
a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed and removed from the bloodstream before their normal lifespan is over
normal RBC structure and function
Red blood cells are disc-shaped and look like doughnuts without holes in the center
• Carry O2 to the body
• Remove CO2 from the body
rbc made in and lifespan
Are made in the bone marrow, live for about 120 days in the bloodstream and then die
Causes of hemolytic anemia
Intrinsic
extrinsic
intrinsic
(result from deficit within RBC itself)
1. Hemoglobinopathies
-Sickle cell anemia-
Thalassemia
2. Membranopathies
-Hereditary Spherocytosis
-Hereditary Elliptocytosis
3. Enzymopathies
G6PD deficiency
pyruvate kinase deficiency
Extrinsic
1. Immune (lupus)
2. Non-immune (burns, toxins, drugs)
3. Malaria (parasites enter rbc and rupture it)
4. Blood transfusion (agglutination, not compatible)
Membranopathies
Mutations in genes expressing membrane proteins cause RBCs to change shape
Dysfunctional membrane proteins leading to different shape:
-interfere with the cell's ability to be flexible to travel from the arteries to the smaller capillaries
-make the red blood cells more prone to rupture
-this can cause hereditary spherocyctosis and elliptocytosis
Spectrin
a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells
mutations in spectrin
can cause hereditary defects of the erythrocyte, including hereditary spherocytosis and hereditary elliptocytosis
Enzymopathies
Defective enzymes inside the RBC cause its premature breakdown
defective enzyme example
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase or G6PD deficiency
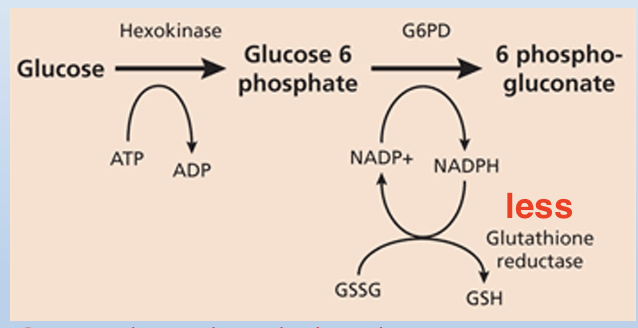
G6PD deficiency
RBCs do not have mitochondria: this is the only source for NADPH
NADPH is used in the RBC to make reduced glutathione
Reduction of NADPH → Reduction of Reduced Glutathione → Increased Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) oxidizes excess hemoglobin to make HEINZ bodies (aggregates of denatured, precipitated hemoglobin within erythrocytes) leading to premature destruction of RBCs
pyruvate kinase deficiency
less glycolysis, less ATP
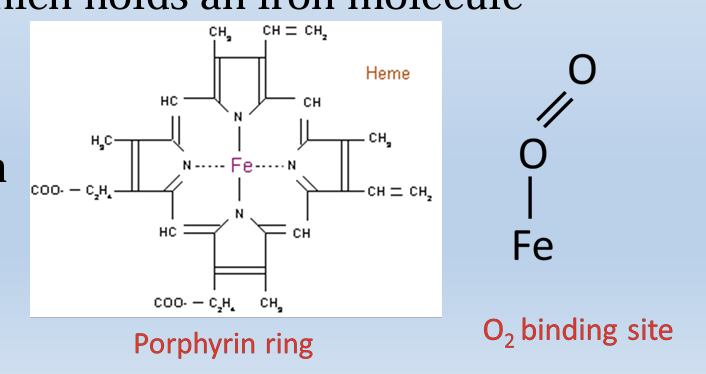
Hemoglobin structure
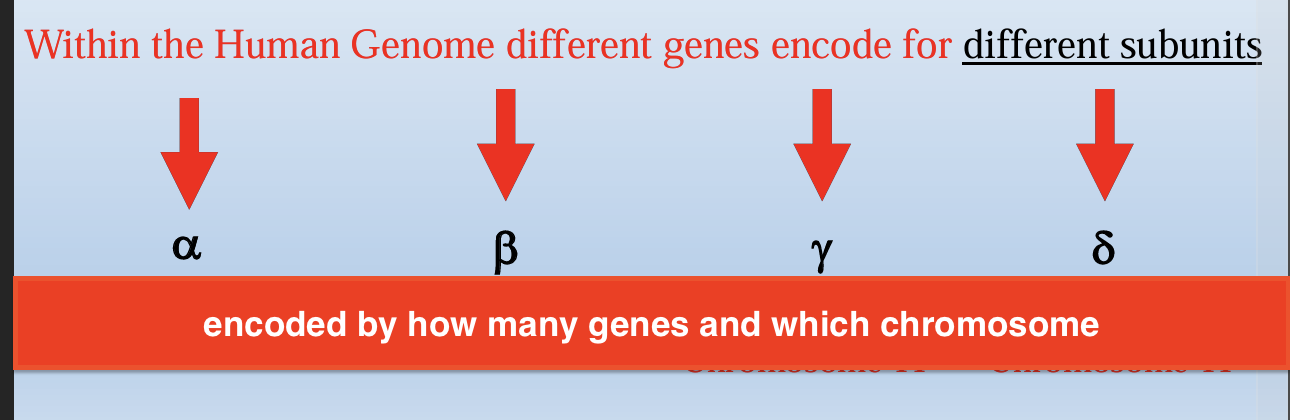
Hemoglobin is a tetramer composed of 4 subunits (2 of each type)
Each subunit has a porphyrin ring which holds an iron molecule
-This is the binding site of oxygen
why Hb inside the RBC
iron atoms could cause oxidative damage if they were not inside the cell membrane of the RBC
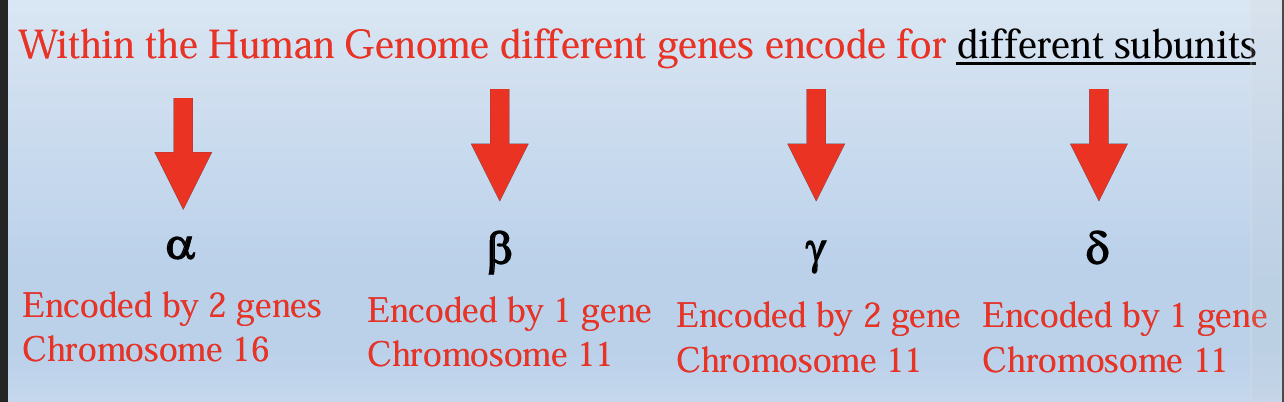
HbA chains
a2b2
HbA affinity and proportion
(A) stands for Adult Dominates in adult blood Range 95-98%
HbA2 chains
a2da
HbA2 proportion
Range 2-3%
HbF chains
a2g2
HbF proportion
F stands for Fetus Range 0.8-2% Higher affinity for O2
Qualitative Hemoglobinopathies
The amino acid sequence is altered due to DNA mutation (Sickle Cell Anemia)
Quantitative Hemoglobinopathies
Production of one or more globin chains is reduced or absent (Thalassemia)
-Hereditary persistence of Fetal Hemoglobin (HPFH)
Complete or partial failure of γ globin to switch to β globin
Sickle Cell Anemia mutation
point (substitution) mutation in B gene
Defective B subunit : Glutamic Acid switched to Valine position
glutamic acid is hydrophillic and negatively charged while valine is hydrophobic.
Under low O2 conditions they stick together hydrophbic patches
Clinical Findings of Sickle Cell Anemia
Clinical signs appear at 6 months of age
Have all physical symptoms of anemia
Growth and sexual maturation slower
Crisis - very painful. Anything that deoxygenates blood acts as trigger (exercise, illness and airplane flights) - Sickle cells get stuck in capillaries
Strokes
what drug is used in sickle-cell disease to decrease the number of attacks
Hydroxyurea taken orally
Hydroxyurea MOA
stimulates the body to produce more HbF in place of HbS that causes the pathology
- High levels of more HbF prevent more HbS to be produced
sickle cell and malaria
• Heterozygosity – 1 normal allele – 1 mutated allele
- Confers some resistance to malaria parasitization of red blood cells as RBCs are removed from circulation quickly not allowing parasite to replicate
Thalassemia
Production of a or B subunit is reduced leading to excess of the other subunit
a-subunit is encoded by
2 genes
2 a genes → 4 alleles


b-thalassemia
Production of B subunit is reduced
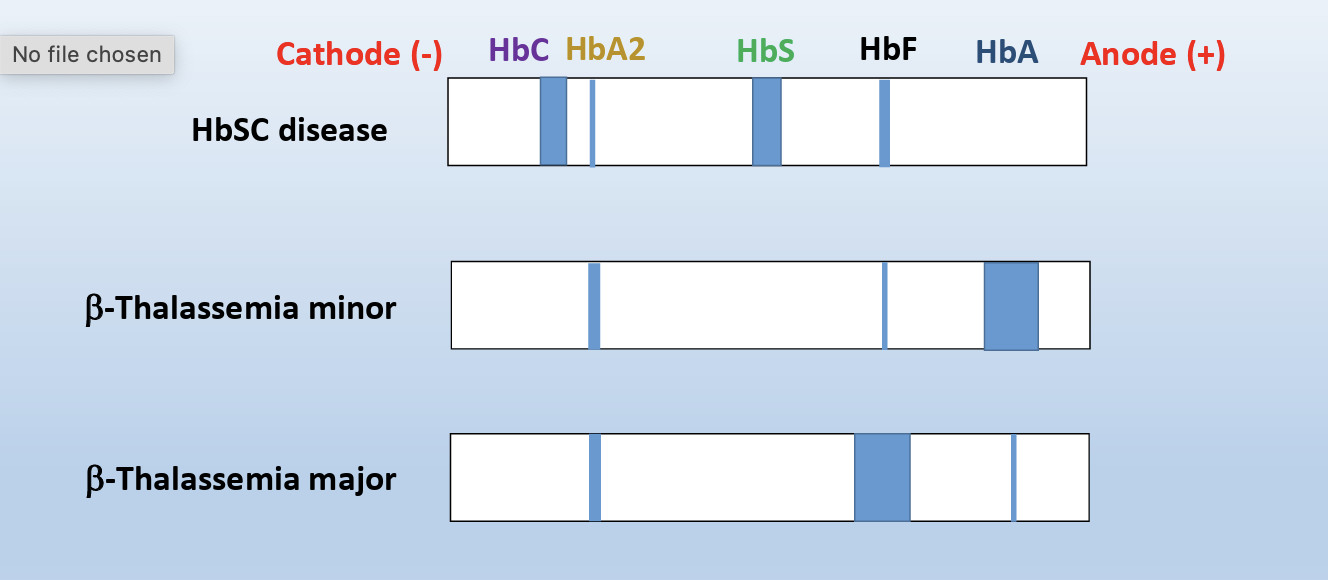
In β-Thalassemia minor:
Instead of B subunit the body produces delta Subunits forming HbA2- Good Marker for B-Thalassemia
β-Thalassemia major
increased HbF level, which is associated with stress erythropoiesis, which may result from the recruitment of erythroid progenitor cells that prematurely undergo terminal differentiation and are committed to producing γ-globin chains
Hemoglobin C
Hemoglobin C (Hb C) is one of the most common structural hemoglobin variants in the human population
• Individuals with hemoglobin C trait (Hb AC) are phenotypically normal, with no clinically evident limitations or symptoms
• Those with hemoglobin C disease (Hb CC) may have a mild degree of hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly and borderline anemia
-mutation in same position as B thalassemia where glutamic acid becomes lysine (hyrdophillic) in position 6
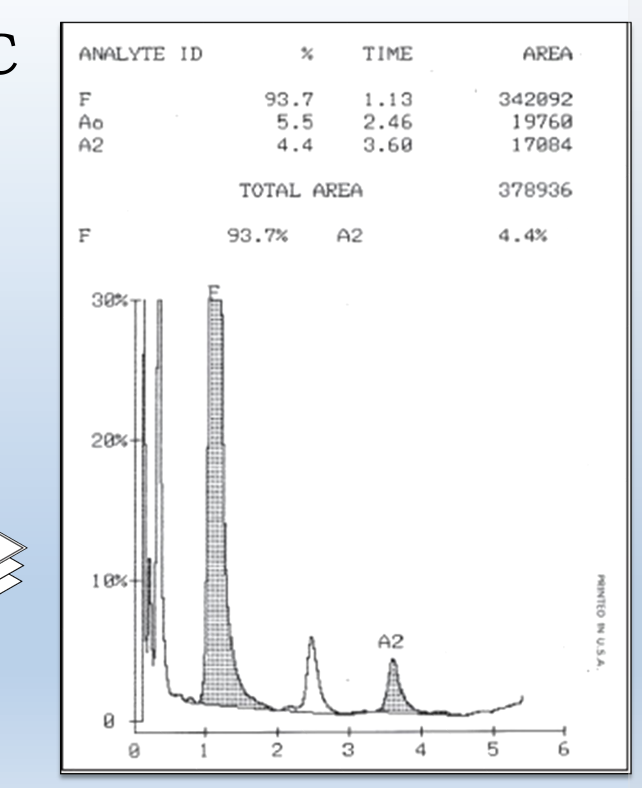
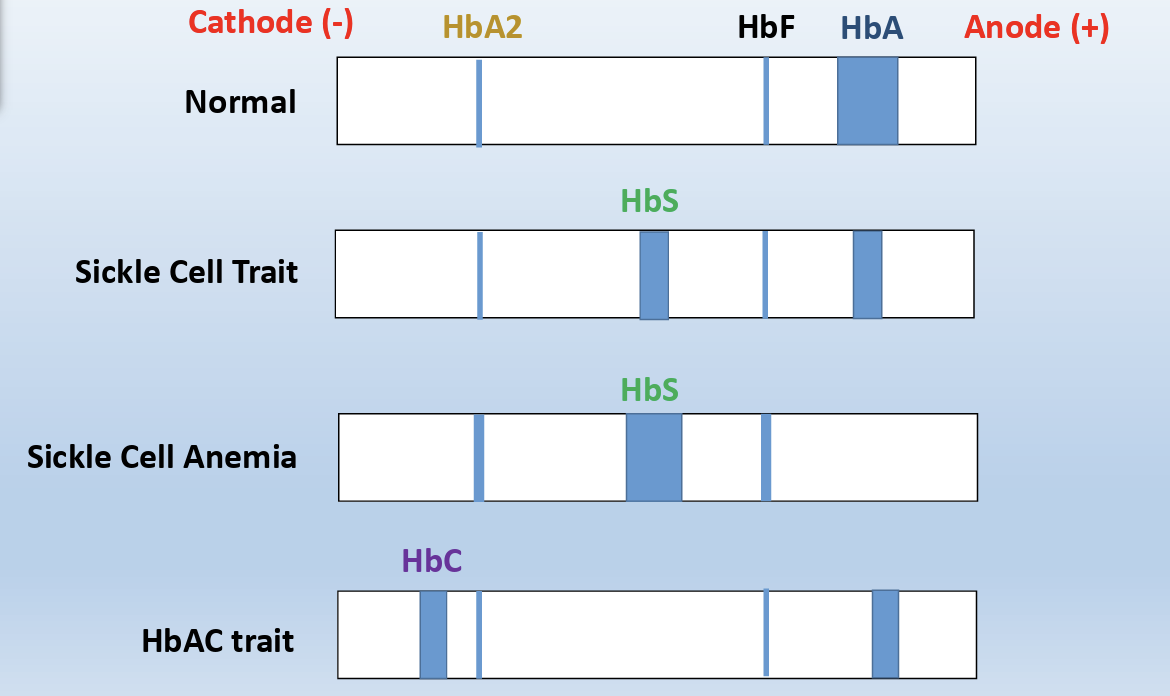
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a test that measures the different types of hemoglobin in the blood
• Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules, such as proteins based on their size and/or charge
It uses the principles of gel electrophoresis to separate the various types of hemoglobin
how is it done
• The sample (lysed red blood cells from the patient) is loaded into a well in the gel material
• The gel is placed in an electrophoresis tank filled with buffer solution
• The tank is then connected to a power supply in order for the molecules to start migrate from the cathode to the anode
Anelectric field is applied through a support medium (a gel) in a buffer at a fixed pH and the macromolecules migrate in that field, according to their size and/or net charge
• The electric field consists of a negative charge (cathode) at one end which pushes the molecules through the gel, and a positive charge (anode) at the other end that pulls the molecules through the gel
what buffer is used in thalassemia or hemoglobinopathy
When a thalassemia or hemoglobinopathy is suspected, a hemoglobin electrophoresis (alkaline or acid) is performed in order to identify different variants of hemoglobin • At the alkaline hemoglobin electrophoresis, the sample is loaded into a well of a cellulose acetate gel and is electrophoresed in a buffer at pH for the hemoglobin molecules to migrate from cathode to anode 8.4-8.6, in order • Separation of hemoglobins is based on the variable rates of migration of charged hemoglobin molecules in an electrical field


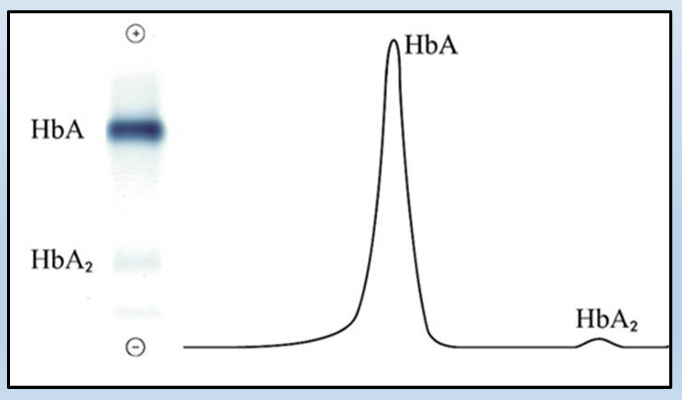
how is relative percent of each band is determined
The hemoglobin bands are visualized by the application of a dye, which also makes them measurable by densitometry. The patterns are scanned on a scanning densitometer, and the relative percent of each band is determined
Alkaline hemoglobin electrophoresis problem
s can be used to separate common variants such as HbA, HbF, HbS and HbC, but HbC and HbA2 are unresolved from each other
acid electrophoresis
Hemoglobins with identical mobility can be differentiated by acid haemoglobin electrophoresis. The acid hemoglobin electrophoresis, is similar to the alkaline hemoglobin electrophoresis with the exception that the sample (lysed red blood cells from the patient) is dispensed in a citrate gel and is electrophoresed in a buffer at pH 6.0-6.2
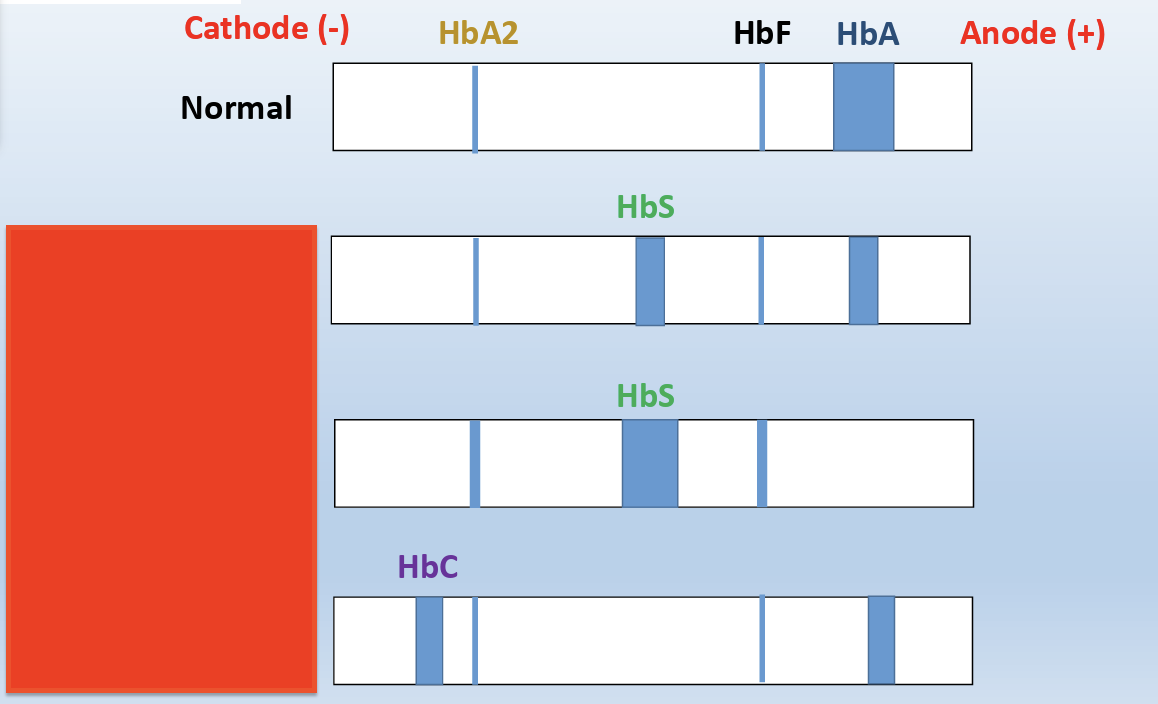
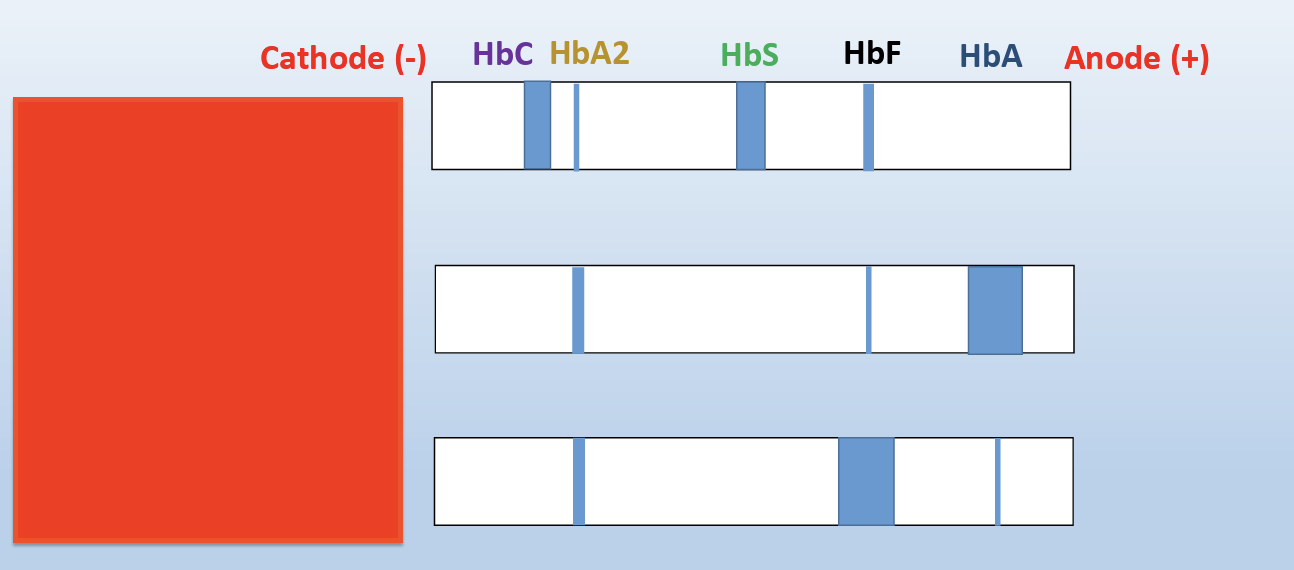
B-major can be normal newborn
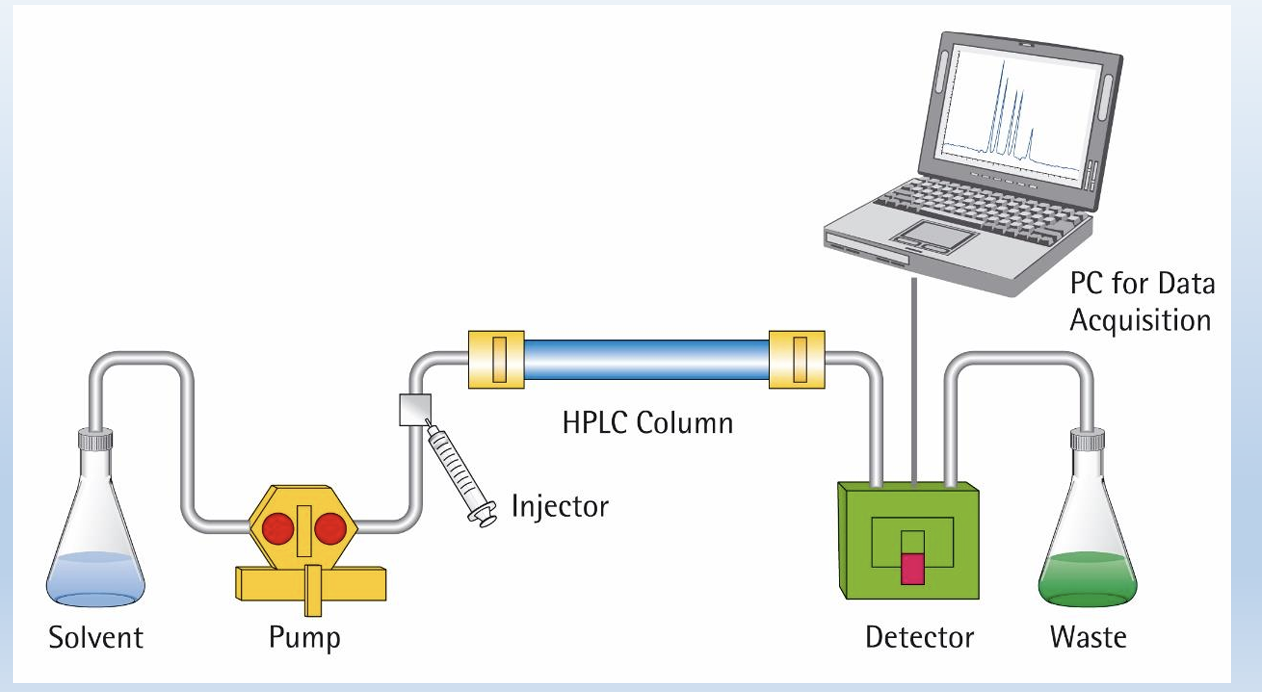
HPLC
• It relies on pumps to pass a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a column filled with a solid adsorbent material • Each component in the sample interacts slightly differently with the adsorbent material, causing different flow rates for the different components and leading to the separation of the components as they flow out the column
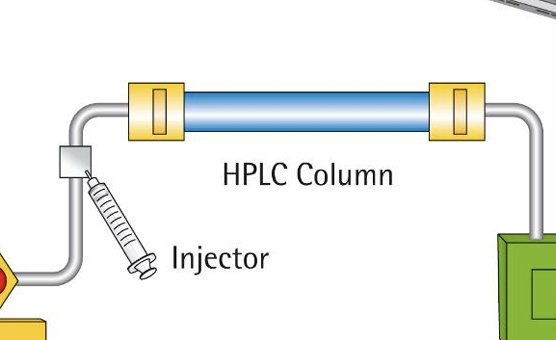
what is separation based on
in column, if has higher affinity to whats in the column it will be released last and you record the volume and the time of what was released