Case studies illustrating the formulation development process in the pharmaceutical industry
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what is assessed in a biopharmaceutics risk assessment?
o API properties
o Formulation
o In-vitro data
o Identification of critical performance attributes
what are the in-vitro and in-silico strategies
o Dissolution workflow
o Biorelevant dissolution
o Precipitation investigation
o Development of PBBM model
what is in-vitro to in-vivo translation
o Combined use of in-vitro and in-silico methods to understand in-vivo performance
o Derisk clinical trials and prepare for regulatory submissions
what is lorlatinib for and why is it relevant?
- A precision medicine project in oncology, targeting ALK/ROS +ve tumour types
- A next generation version of Crizotinib can cross the BBB
- Rapidly accelerated project
- Acceleration is driven by early sign of efficacy
What are ALK mutations
- Oncogenic drivers
- ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) belong to the insulin receptor super-family of RTK’s
- Mainly expressed in adult brain tissue
- ALK mutations are identified in ~10% of neuroblastoma patients
- The NPM-ALK fusion gene was first identified in anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- Also found in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)
what is crizotinib for?
- Crizotinib is approved by the FDA for locally advanced or metastatic ALK+ NSCLC
why was there research going on for th next generation of ALKi?
- There is resistance in the kinase domain of EML4-ALK
- There is brain metastasis from lung cancer, increasing incidence
- Crizotinib has poor BBB permeability
what were the key lab objectives for an ALKi?
- Goal is to treat patients who progress on crizotinib
- Oral agent with qd or bd dosing
- Dual potency for EML4-ALK and mutants resistant to crizotinib
- CNS penetration
- The goal is to improve all 5 properties and avoid new issues
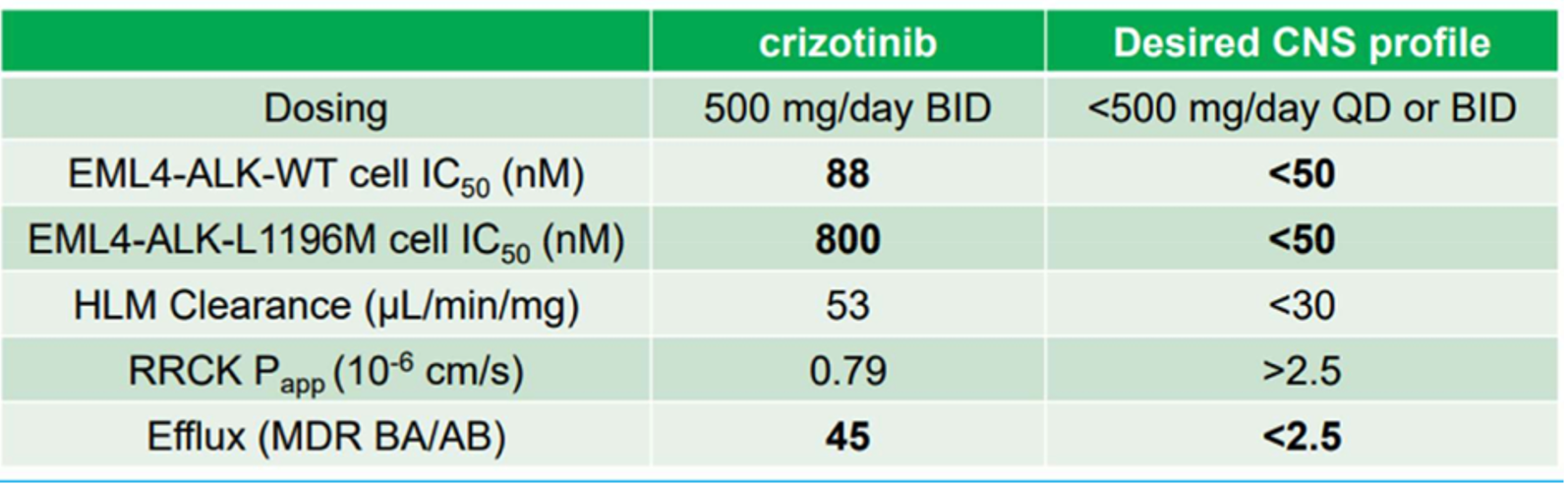
what is Pgp and BCRP?
- Both Pgp and Bcrp transporters limit brain penetration
- Avoiding transporter efflux is critical to achieve free brain penetration
- Designing inhibitors that will enter the brain:
o Ensures that molecular properties like logD, MW and the number of hydrogen bond donors are optimal
§ This allows for good penetration of the BBB through high permeability and avoidance of PGP and BCRP efflux
§ PGP and BCRP are transporters that limit access to the brain via the BBB
Is crizotinib brain permeable?
o Preclinical in-vitro and in-vivo data in rodents suggests that crizotinib is not brain penetrant
o Clinical data based on CSF exposure confirms crizotinib does not cross the BBB
Is lorlatinib macrocyclic. If so, what does it mean?
- In lorlatinib, the head and tail groups are in proximity (same for U binders), suggesting the macrocycle design
- Macrocycles are predicted to improve potency and efficiency through enhanced protein-drug interactions, stabilising bond conformation
- This helps against resistance and BBB limitations
- Lorlatinib enabled broad spectrum potency and excellent ADME and CNS penetration
- Lorlatinib is essentially the cyclised versioned of crizotinib
Why design within the same chemotype that is developing resistance
- Chemotype is validated in the clinic
- Potential for much greater ALK potency since crizotinib was optimised for cMET
- Acquired resistance may decrease affinity of crizotinib, but also enhances the enzymatic activity of ALK
- Lorlatinib 3rd generation ALKi provides key positive differentiation from crizotinib
what are the objectives of first in human studies?
o To determine in a strictly controlled and monitored subject population the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the drug over a range of doses and occasionally pharmacodynamics
what is FIP/TIM?
when the studies go directly to patients eg in oncology
what is a single ascending dose study?
o minimum dose ~10% predicted pharmacologic dose, where the maximum dose target 3-5x predicted efficacious dose with the top limit based on NOAEL
what is a multiple ascending dose study?
o typically 3-4 doses chosen based on SAD, dosed over a 14 day period, to achieve steady state
§ This determines whether the release profile stays the same and does the drug reach steady state
what are some phase 1 FIP study types?
§ Food effect, drug-drug interactions, relative bioavailability (to compare formulation performance)
for phase I what should the dose range for SAD be like?
large dose range
how should the dose flexibility be like for phase 1 FIP?
o modification to original doses may be required as data emerges from the study eg safety signals
§ This allows for the selection of dose strengths for tablets
what should th dose escalation plan be like for FIP?
§ Solid dosage form – number vs size
§ Liquid formulation – concentration vs volume
What are fit for purpose formulations like?
§ Less upfront investment
§ Enable more rapid FIH start
§ Further development work required (potential delay post-FIH)
what is a commercialisable formulation like?
§ More investment upfront
§ Longer timelines to FIH
§ Formulation ready for next clinical phase
what are the different phase I formulation approaches?
o Liquid formulations
§ Solutions/suspensions
o Powder in capsule (PIC)
§ API in capsule
o Powder in bottle
§ Aqueous dispersion
o Formulated product
§ Manufactured formulated dosage form for FiP§
what does accelerated development mean?
development in less than 5 years
o This however does not change quality or safety standards
o The product and processes must be consistently safe and effective and validated
what happens if the salt used in the API needs to be changed?
- the drug needs to be continually delivered to the patients in the clinical trial and continue to treat them during development
what is digital design and how Is it useful?
- Computational tools allowed for design and delivery of a robust commercial API in less than 6 months
what is dynochem or aspen modelling used for?
used to choose the optimal process solvents
what is materials studio used for?
design purge of select impurities
what is dynamic DOE used for?
identifies the best process parameters to assure robust manufacture in API facilities
what is filtration modelling
used for optimised isolations
why switch away from the research solid form?
- Solid form is used in material sparing tablets
- MST for phase I was an acetic acid solvate (the salt used in the tablet)
o Although it has favourable solid-state properties, data has shown that acetic acid solvate is physically unstable in the drug product at specific conditions (high temperatures)
o Solid form changes in the drug product is an issue, which is hard to fix in later stages
o Continuing with the acetic acid solvate carries a significant risk for commercial development in hotter countries so, a different salt had to be found
what do computational tools allow for?
- enabled a switch from the commercial solid form in time for Phase II study
o These enable the optimal API salt form for commercialisation
what do computational tools consider?
§ API processing control
§ Biopharm profile
§ Material science characteristics
§ Formulation
§ Stability
what are the risks associated with using computational tools to assess the biopharma profile?
o Compound may be a weak base so potential precipitation potential needs to be assessed
o Potential for negative food effect of with co-administration of ARA’s eg PPI
o Maintain dose-exposure relationship seen with the acetic acid solvate form
what isn’t stimulated with typical dissolution testing?
- Motility, transit, fluid distribution
- GI fluid complexity and variability
- Dynamic digestion processes
- Drug permeation
describe what the TIM-GI stimulator is like
o AN in-vitro model that stimulates the dynamic physiological conditions of the stomach and small intestine
o It has a gastric compartment and three small intestinal compartments to mimic transfer from stomach to duodenum, jejunum and ileum
o The removal of dissolved or solubilised drug molecules from the intestinal lumen by a semi-permeable membrane allows assessment of the bioaccessible fraction (fraction of drug, which is available for small intestinal absorption)
how was TIM-GI used for the development of lorlatinib?
o Used in lorlatinib development (commercial solid form, food and PPI predictions, solution dosing and particle size impact, higher strength tablet design, multiple vs single unit tablet equivalency)
§ Was able to predict comparable performance of alternative solid forms
§ Was able to predict absence of a negative food effect but clinically significant with ARA’s
§ Was able to predict equivalent performance to phase I material sparing tablet formulation with acetic acid
what are the benefits of an extemporaneously prepared drug product?
o Pharmacist prepares the medicine from high quality components
o Different countries have different EP interpretations
o The acceptable degree of manipulation:
§ Dilution
§ Simple reconstitution
§ Complex reconstitution steps
o Before using EP for clinical trials, it must comply with EP process in the country