experimental design: exam one examples
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
which type of IRB review?
An anonymous online survey asking adults about their favorite study strategies (e.g., flashcards vs. highlighting).
exempt
which type of IRB review?
A reaction time experiment where participants respond to visual stimuli on a computer.
expedited
which type of IRB review?
A study involving exposure therapy for participants with diagnosed phobias (e.g., gradual exposure to spiders in a controlled setting).
full review
Mill’s Inductive Logic Example:
Rose, Donna, and Martha all order different entrees at dinner, and all get the pie for dessert. All three get food poisoning.
method of agreement (sufficiency)
Mill’s Inductive Logic Example
Jack plants two fields of tomatoes. He fertilizes only one. The field that received the fertilizer grows. The field which didn’t get the fertilizer doesn’t grow
method of difference (necessity)
In a study of the effects of problem difficulty (easy or hard) and reward size ($1 or $5 for each solution) on an anagram problem-solving task, what are the independent and dependent variables?
IV = problem difficulty (easy or hard), reward size ($1 or $5)
DV = # analogue problems solved
*2×2 Factorial Design
What are extraneous variables and what happens if they are not controlled properly?
factors other than IV that could impact exp results
If not controlled, they can introduce noise, create systematic differences between groups, and mask or exaggerate effects, leading to flawed conclusions and a lack of internal validity
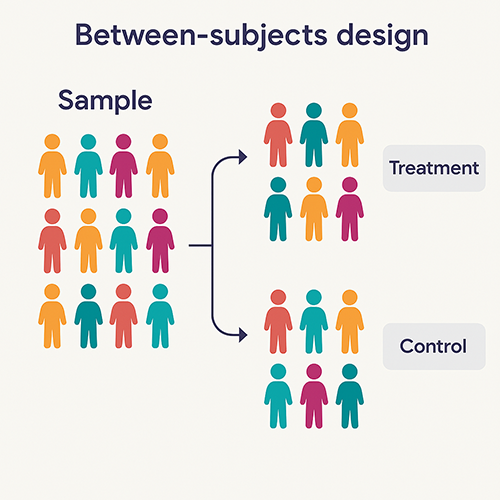
Draw a diagram that illustrates the between-subjects design
(reference image)
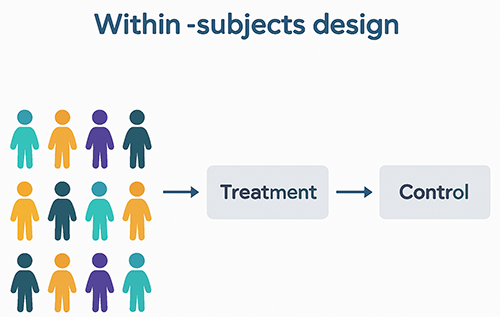
Draw a diagram that illustrates the within-subjects design
(reference image)
which type of study?
IV = type of social skills training (*matching variable autism quotient)
direct teaching
play activities
DV = social interaction observation code
between-subject, single-factor, two-levels: matched groups
which type of design?
IV = whether or not TBI occurred
experimental group: TBI
control group: no TBI
DV = ability to detect insincerity in others
between-subject, single-factor, two-levels: ex post facto
which type manipulated IV?
A helping behavior study: the effect of the number of bystanders on the chances of help
situational
which type of manipulated IV?
study of reasoning: give ppl different kinds of logic probs to determine kinds of errors ppl make
task
which type manipulated IV?
memory task on how to memorize list 1) form visual images of the words 2) form associations between adjacent pairs of words 3) repeat each word three times as its presented
instructional
construct a table based on this data:
A memory study with a 2 (type of training) × 2 (presentation rate) factorial, like the example used a moment ago, has these results (DV = words recalled):
Imagery/2‐sec rate = 20 words
Imagery/4‐sec rate = 20 words
Rote/2‐sec rate = 12 words
Rote/4‐sec rate = 12 words
what is the main effect? interaction effect?
main effect:
training type: there is a ME
avg words recalled for imagery was 20
avg words recalled for rote was 12
presentation rate: no ME
avg words recalled for both 2 sec and 4 sec was 16
construct a graph based on this data:
A memory study with a 2 (type of training) × 2 (presentation rate) factorial, like the example used a moment ago, has these results (DV = words recalled):
Imagery/2‐sec rate = 20 words
Imagery/4‐sec rate = 20 words
Rote/2‐sec rate = 12 words
Rote/4‐sec rate = 12 words
graph this data:
IVs:
laboratory self‐discovery course vs straight lecture course
Students from different majors: Science vs Humanities
DV: Score from 1 to 100 on a standardized test of knowledge of General Psychology
Score Results:
lab emphasis, science major: 80
lab emphasis, humanities major: 70
lecture emphasis, science major: 70
lecture emphasis, humanities major: 80
Interaction effect?
construct a table for this data:
IVs:
laboratory self‐discovery course vs straight lecture course
Students from different majors: Science vs Humanities
DV: Score from 1 to 100 on a standardized test of knowledge of General Psychology
Score Results:
lab emphasis, science major: 80
lab emphasis, humanities major: 70
lecture emphasis, science major: 70
lecture emphasis, humanities major: 80
what is the main effect?
major
no ME
both avgs were 75
learning style “emphasis”
no ME
both avgs were 75
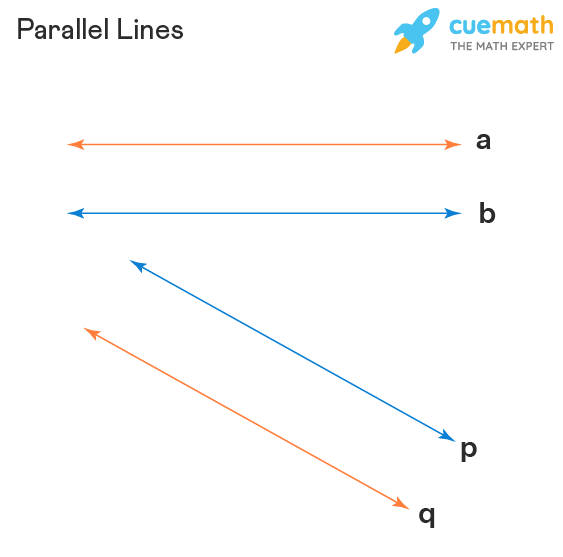
graph w/ no interaction present?
parallel lines
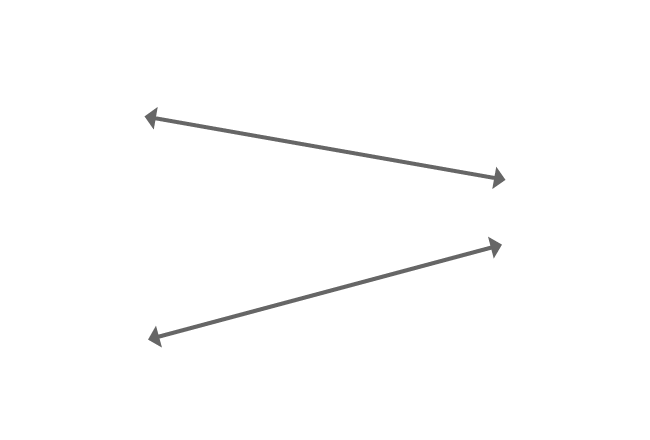
graph w/ interaction present?
non-parallel lines
6 assumptions when analyzing factorial designs
#1: Dependent variable at the continuous level (i.e., they are interval or ratio variables, Called Scale in SPSS)
#2: Independent variables categorical
#3: Independence of observations
#4: No significant outliers.
#5: Dependent variable approximately normally distributed (Shapiro-Wilk test for normality)
#6: Homogeneity of variances (Levene’s test)
what type of study is this?
IV-Manipulated type of note-taking:
1) Laptop note-taking;
2) Handwritten note-takingDV: performance on memory test
single-factor, between subject, two level design
what type of study is this?
IV-Type of social skills training:
1) Direct teaching;
2) Play activitiesDV: Social Interaction Observation Code
single-factor, between subject, two level design
what type of study is this?
IV-Whether or not traumatic brain injury (TBI) had occurred:
1) Experimental group: had experienced TBI
2) Control group: no TBI
DV: Ability to detect insincerity others
single-factor, between subject, two level design
ex post facto
what type of study is this?
IV-Whether or not the color of print and word match:
1) Match
2) Mismatch
DV: Speed and accuracy
single-factor, within-subjects, two level design
*stroop effect
Bradford + Johnson’s 1972 study:
One IV, three levels, independent groups
No context (no topic presented)
Context before (topic presented before reading paragraph)
Context after (topic presented after reading paragraph)
DV: recall of paragraph’s ideas
what type of study is this?
single factor, between-subject, multilevel design
what type of study is this?
IV = Heart rate training program
DV = Resting heart rate
Resting Heart Rate 1 Month Before Training Program
Resting Heart Rate 1 Month during Training Program
Resting Heart Rate 1 Month After Training Program
single-factor, within-subject, multilevel design