Year 10 Science Motion
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Vector
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction, commonly used in physics to represent forces, velocity, and displacement.
Scalar
A quantity that has only magnitude, without any directional component, commonly used in physics for measurements like temperature, mass, energy, and distance
Displacement
A vector quantity that represents the shortest distance from an object's initial position to its final position, along with the direction of that distance.
Velocity
A vector quantity that measures the rate of change of an object's position with respect to time, including both speed and direction.
Acceleration
A vector, defining the rate at which an object’s velocity is changing, and in what direction.It is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²) and can indicate an increase or decrease in speed.
Distance formula
speed x time
Tickertape Timer
A device used to measure time intervals and record the motion of an object, often producing a continuous strip of paper with marks indicating distance traveled over time. A dot is placed at a frequency of 50Hz, which is every 0.02 seconds. The distance between dots can be used to calculate the speed of the object.
Average acceleration formula
(final velocity - initial velocity) / time
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion, remaining at rest or moving uniformly in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force.
Force
A push or pull on an object from another object; a vector equal to mass multiplied by acceleration.
Free Body Diagram
Shows forces in the positive and negative x and y axes. Arrows representing these forces show the magnitude and direction of the force, which are drawn from the centre of mass of an object.
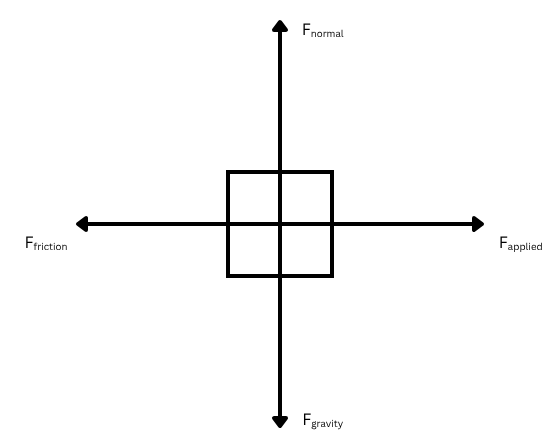
Newton’s First Law
An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object at motion will continue at motion, unless an external unbalanced force acts upon it.
Newton’s Second Law
The acceleration of an object due to a force varies depending on the mass of the object and the force applied. Expressed by F=ma.
Newton’s Third Law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Gravity
The acceleration towards a massive object due to its mass. On Earth, this acceleration is 9.81m/s.
Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
Weight
mass multiplied by acceleration due to gravity.