Chem Exam 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
l=0
s, 1 orbital
l=1
p, 3 orbitals
l=2
d, 5 orbitals
l=3
f, 7 orbitals
Calculatiing ml (number of orbitals from l value)
2l + 1
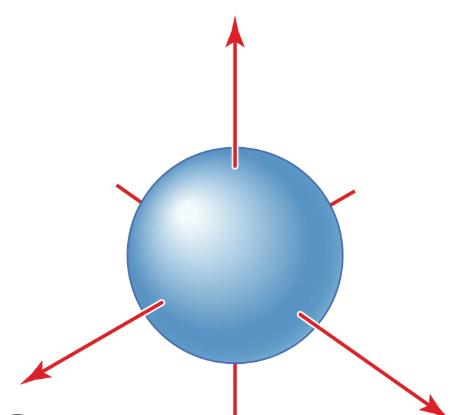
s

p

d
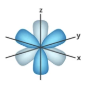
f
radial nodes
spherical nodes that have a change of phase on the orbital axis
node calculation
n-1
dxy
four lobes in x
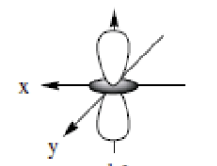
dz²
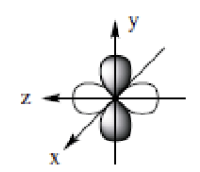
dyz
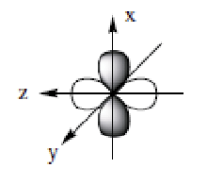
dxz
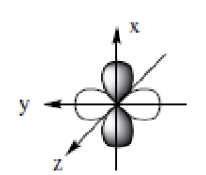
dxy
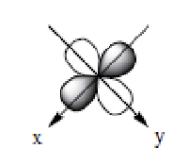
dx²-y²
electron notation rules
l<n, l=letter, ml is whole number range of l
de broglie wavelength
h/mv kg, m, s
radial node
spherical where finding electron probability is zero
planar node
symmetry
angular node
cone + planar
increasing wavelength
gamma rays, x-rays, ultra-violet, visible light (purple to red), infrared, radio waves
increasing energy
radio waves, infrared, visible light (red to purple), ultra violet, x rays, gamma rays
excited state
electron move to higher orbital
John Dalton
-elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms
-atoms of the same element are identical, but differ from those of other elements
-combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds
-chemical rxn does not change atoms of one element to a different one, just rearrange
JJ Thompson
Discovered electrons by deflecting bean in cathode ray tube, plum pudding, postive mass with equal negative
Ernest Rutherford
protons, most of mass in center of atom at nucleus, gold foil experiment, most of space in atom is empty,
Robert Millikan
oil drop experiments, microscopic oil droplets electrically charged by friction, fell from gravity, but could be altered by electric field, found charge on drops to get fundamental charge of electron
Nagaoka
saturn like, positive surrounded by ring of negative
isomers
same molecular formula but different structural
Newton
white light is combo of all colors (prism experiment), “corpuscular” view: light composed of stream of tiny particles travelling at high speeds
Thomas Young
light passing through narrow slits=interference patternsm can’t be explained in particles but in waves
James Clerk Maxwell
electromagnetic radiation, light is visible over vast spectrum of waves, partocle view discredited
wave particle duality
oscillation/ periodic movement, can transport energu, dont’t need to be restricted to travel through matter, contain electric field oscillating with perpendicular magnetic field
-can travel through vacuum at speed of light
quantization
energy only in discrete amounts, ex. quantum levels
inherent uncertainty
cannot know position and momentum of electron
aufbau principle
electrons fill lowest energy orbitals first before moving on to higher energy orbitals
Hund’s rule
electrons will singly occupy orbitals with same spin before putting two in same orbital
Pauli Exclusion Principle
two electrons cannot have the exact same set of quantum numbers
group 1
alkali metal
group 2
alkaline earth metals
group 15
Pnictogen
group 16
chalogens
group 17
halogens
group 18
noble gasses
interference
interaction of two waves, can be constructuve (crests align) or destructive (do not align), when trough align with crest: cancel each other
diffraction
waves bend around corners when opening similar to wavelength, can create pattern
photoelectric effect
electrons ejected when light of specific frequency strikes a metal, only light above threshold frequency can eject, increasing intensity increases number of electrons emitted but does not change kinetic energy
frequency changes velocity at which electrons ejected
intensity changes number of electrons ejected
standing waves
wavelength: 2L/n
1st harmonic: 2 nodes
blackbody radiation
emits radiation based on temperature, absorbs all electromagnetic radiation, continuous spectrum, hotter objects are bluer
ultraviolet catastrophe: classical physics predicted that a blackbody would emit infinite energy at short wavelengths, resolved by planck saying energu is quantized (discrete packets of energy)
line spectra
sharp, discrete lines, electrons moving between energy levels
emission lines: bright
absorption lines: dark
electron
outside nucleus, negative charge, smallest mass
proton
smaller mass than neutron (slightly), positive charge
neutron
largest mass by a little bit, neutral charge