Head, Face Neck Regional Lymphatics | NURS 122
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
the __________ is formed by vertebrae, ligaments, and muscles, providing support for the head and allowing for movement
head
what are the skulls bones?
two frontal bones
two parietal bones
two temporal bones
one occipital bones
what are the facial bones?
frontal (fused)
nasal
zygomatic
ethmoid
lacrimal
sphenoid
maxillary
mandible (moveable)
nasolabial fold
smile lines
palpebral fissures
the eye slit
sternocleidomastoid
muscle of the neck that attached to the mastoid process of the temporal bone and superior nuchal lines
extends from the upper sternum and medial third of the clavicle to the mastoid process
trapezius
muscle of the shoulder and upper back
large, flat triangular muscle
act to rotate the scapula upwardly adduct, raise, lower or retract the shoulder
extends from the scapula, the lateral third of the clavicle, and the vertebrae to the occipital prominence
Which bones compose the face?
Select all that apply.
Hyoid
Ethmoid
Lacrimal
Thyroid
Zygomatic
Ethmoid
Lacrimal
Zygomatic
photophobia
abnormal sensitivity to light, especially by the eyes
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
exophthalmos
protrusion of the eyeballs usually due to increase volume of the orbital contents caused by tumor or swelling
what is the different state of consciousness that a student nurse should ask when inquiring about a patient’s consciousness after an injury to the head/neck?
immediately
5 minute later
duration of unconsciousness
combative
confusion
alert
dazed
of course a lot of these are based on bystander and what is reported
REVIEW the different associated symptoms of a head/neck injury…
Photophobia
Phonophobia (sensitivity to sounds)
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Insomnia
Tinnitus
Headache, neck pain
Tenderness, warmth, redness
Breathing pattern change
Blurred or double vision
Ear/nose drainage
Impaired movement of extremities
Fever
Swelling
Voice distortion
Hearing loss
Dysphagia
Irritability
Exophthalmos
what are some of the common aggravating factors associated with head/neck injury?
light
sound
movement
what are some of the common alleviating factors associated with head/neck injury?
sleep
medication
position change
alternative measures (e.g., heat packs, neck brace)
what are some different types of medications that can be use to treat a head/neck injury (and review how they help…)?
analgesics - relieves pain (e.g., acetaminophen)
muscle relaxants - reduce muscle spasms and tension in the neck
anticonvulsants - treat nerve-related pain or seizures from head trauma
beta-blockers - manage symptoms like headaches or high blood pressure post-injury
NSAIDs - reduce inflammation and pain
narcotics - provide strong pain relief for severe pain
thyroid preparations - used if injury affects thyroid functions
review some of the characteristics that a patient might use to describe their symptoms post head/neck injury…
throbbing
pounding
boring
dull
nagging
pressure
pain with movement
relieved by movement
constant
intermitten
cramping
radiation
what are some medical predisposing factors for head/neck injuries?
seizures
hypoglycemia
poor vision
syncope
dizziness
what are some lifestyle/health states predisposing factors for head/neck injuries?
fever
fatigue
stress
food
fasting
alcohol
allergies
menstruation
what are some injury/work factors predisposing factors for head/neck injuries?
injury
strain
traumatic brain injury
poor work position
what key medical-surgical history should the nurse ask about for head/neck complaints?
think "HEAD-NECK":
Head/neck trauma
Epilepsy (seizure disorder)
Altered thyroid function
Dural issues (subdural hematoma, lumbar puncture)
Neck radiation or surgery (tumors/goiter)
Episodes of chronic headaches (migraines, vascular)
Conditions like fever, fatigue, or stress
Key surgeries or treatments
what are some conditions that have genetic prevalent among family members that is related to head and neck injury?
headaches (type and character)
thyroid dysfunction
graves diseases
Which question should the nurse ask a patient with a headache to assess aggravating and alleviating factors as part of the history of present illness?
“Does your headache worsen with loud noises?”
“How long has this headache been going on?”
“When did the pain begin?”
“Are you seeing any spots or floaters?”
“Does your headache worsen with loud noises?”
Which medical-surgical history question should the nurse ask a patient with headaches?
“What have you been taking for your headache?”
“How long have you experienced headaches?”
“Have any of your siblings needed sinus surgery?”
“Have you ever been diagnosed with migraines?”
“Have you ever been diagnosed with migraines?”
→ episode of chronic headaches (e in NECK)
What personal/social history question should the nurse ask the patient with neck pain?
“What makes the pain worse?”
“Have you had an injury to your neck?”
“When did the pain begin?”
“What type of physical activity or sports do you participate in?”
“What type of physical activity or sports do you participate in?”
what are some factors that student nurse should look for when inspecting the head and scalp?
symmetry
tenderness
movement
sutures/fontanels
hair texture/distribution
what are some factors that student nurse should look for when inspecting the neck?
tracheal positions
tracheal tug
movement of hyoid bone and cartilage with swallowing
lymph nodes
symmetry
fullness
what are some factors that student nurse should look for when inspecting the thyroid gland?
size
shape, configuration
consistency
tenderness
nodules
thrills
shouldn’t be visible or palpable if healthy
The nurse should begin the examination of the head by assessment of which physical characteristics of the patient?
Select all that apply.
Inspection of Thyroid gland
Inspection of Tracheal position
Inspection of neck muscles
Inspection of head position
Inspection of facial features
Inspection of head position
Inspection of facial features
Which structures of the neck should the nurse palpate for smoothness and tenderness?
Select all that apply.
Scalp skin
Hyoid bone
Trachea
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
Hyoid bone
How should the nurse describe the fontanels of a healthy infant on assessment?
Select all that apply.
Flat
Soft
Tense
Hard
Bulging
Depressed
Flat
Soft
review the expected finding during inspection of the head…
Head upright, midline, still
Variations in face shape depending on race, gender, age, build
Slight asymmetry of facial features
Symmetrical skull size, shape
Balding pattern in male patients
Salivary glands symmetrical without enlargement
review the expected findings during palpation of the head…
Symmetrical and smooth
Bones indistinguishable
Ridge of sagittal fissure may be palpable
Hair smooth, evenly distributed
Salivary glands symmetrical without enlargement, tenderness
No thrill felt over temporal arteries
NOTE: The nurse may also auscultate the temporal arteries and would expect no bruits on auscultation.
review the expected findings during inspection of the neck…
Bilateral symmetry of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Trachea midline
Smooth neck movement with flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral repositioning
review the expected findings during palpation of the neck…
Trachea in midline position
Hyoid, thyroid, and cricoid cartilage should be smooth and should move during swallowing
Lymph nodes not palpable
Thyroid gland symmetrical
Small lobes
Gland rises freely with swallowing
Right lobe may be up to 25% larger than left
Tissue firm and pliable
No palpable thrill over carotid arteries
NOTE: The nurse may also auscultate the carotid arteries and would expect no bruits on auscultation.
review the abnormal findings for inspection of the head and face…
Head tilted
Horizontal jerking/bobbing
Tics/nodding
Edema, puffiness
Unexpected alopecia
Coarsened features (e.g., enlarged forehead, nose, prominent veins)
Prominent eyes (exophthalmos)
Hirsutism
Lack of expression
excessive blinking
Excessive perspiration
Pallor
Pigmentation variations
Facial nerve weakness/paralysis
Scalp lesions, scabs (crusts), parasites, nits, scales, tenderness
Random areas of baldness
Ptosis
Nasal malalignment
review the abnormal findings for palpation of the head and face…
indentations or depressions
elevations
hair: splitting, cracked ends, coarse, dry, brittle or fine/silky
thickening, hardness, tenderness, thrill of temporal arteries
salivary glands
Asymmetrical
Tender
Enlarged
Nodules
review the abnormal findings when inspecting the neck…
Asymmetry
Torticollis (twisting of the head toward the sternocleidomastoid muscle)
Excessive posterior skinfolds
Unusually short
Jugular vein distention
Thyroglossal duct cyst (movable mass in the neck)
Branchial cleft cyst (mass along anteromedial border of sternocleidomastoid muscle)
Prominence of carotid arteries
Webbing
Edema
Masses
Pain, or limited movement with range of motion
Nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness - resist passive flexion)
review the abnormal finding when palpating the neck…
Trachea deviated to the right or left
Tenderness
Tracheal tug synchronous with pulse
Lymph nodes
Enlarged
Matted
Tender
Fixed
Warm
Thyroid gland
Asymmetry
Enlargement
Visible
Tender
Coarse tissue
Gritty sensation
Thrill palpated over carotid arteries
Which finding should the nurse note as normal on palpation of the head?
Tender salivary glands
Distinguishable bones
Thrill over temporal arteries
Palpable ridge of sagittal fissure
Palpable ridge of sagittal fissure
Which finding should the nurse note as normal on inspection of the neck?
Skinfolds
Pulsations
Symmetry of the muscles
Slightly displaced trachea
Symmetry of the muscles
Which findings would be considered abnormal on palpation of the head?
Select all that apply.
Slight depressions
Asymmetrical salivary glands
Thrill over temporal arteries
Thick hair
Nontender salivary glands
Slight depressions
Asymmetrical salivary glands
Thrill over temporal arteries
Which findings would be considered abnormal when the neck is assessed?
Select all that apply.
Edema
Webbing
Nuchal rigidity
Midline placement of trachea
Upward movement of the thyroid gland on swallowing
Edema
Webbing
Nuchal rigidity
torticollis
shortening or excessive contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Which information suggestive of a thyroid condition would be documented under family history?
Tachycardia
Neck pain on palpation
Spouse with Graves disease
Father with Graves disease
Father with Graves disease
The nurse notes that a 36-year-old patient has a mass in his neck at the midline. The patient reports a family history of lymphoma and a history of smoking two cigarettes a day. The patient complains of difficulty swallowing and pain when turning the head. Which should the nurse document as objective data related to the neck assessment?
Difficulty swallowing
Pain when turning head
Mass in neck
Family history of lymphoma
Mass in neck (OBJECTIVE!)
A 63-year-old patient reports a headache that began 3 days ago. The patient describes the headache as constant and severe. The patient denies photophobia or nasal discharge. The patient reports a personal and family history of migraine headaches. Which should the nurse document as part of the history of present illness?
Select all that apply.
Onset 3 days ago
Constant and severe pain
No photophobia or nasal discharge
Family history of migraines
Personal history of migraines
Onset 3 days ago (CORRECT)
Onset of the headache is subjective data and is part of the history of present illness.
Constant and severe pain (CORRECT)
Report of pain is subjective data and is part of the history of present illness.
No photophobia or nasal discharge (CORRECT)
The patient’s report of no photophobia and no nasal discharge is subjective data and is part of the history of present illness.
Family history of migraines
The patient’s family history of migraines is subjective data but is part of the family history, not history of present illness.
Personal history of migraines
The patient’s personal history of migraines is subjective data but is part of past medical history, not history of present illness.
what is the functions of the thyroid?
release thyroxine (T3) and triiodothyronine (T4) which helps stimulate how fast cells metabolize
where is the thyroid gland normally located in a person?
located just below a person’s adam’s apple
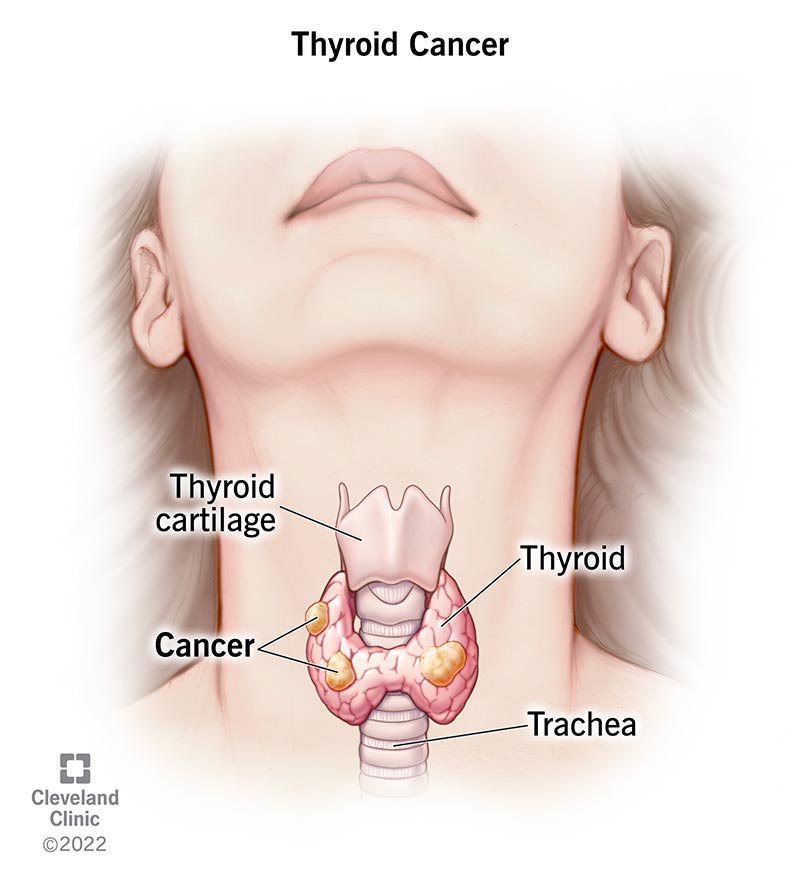
what gland and structure of the brain does the thyroid glands work with?
hypothalamus and pituitary
what is the function of the lymph nodes?
filter pathogens from the lymph preventing unwanted substances from entering the body’s circulation
what are the four areas that lymph nodes are accessible for examination?
head/neck (cervical)
arms
axillae
inguinal
the head and neck usually have ___________ lymph nodes
60-70
lymph nodes typically drain “__________”
downstream - that why looking upstream or above would help the student nurse find the problem
where are the preauricular lymph nodes located?
in front of the ear
where are the posterior auricular (mastoid) lymph nodes/
superficial to the mastoid process
where are the occipital lymph nodes located?
at the base of the skull
where are the submental lymph nodes located?
midline, behind the tip of the mandible
where are the submandibular lymph nodes located?
halfway between the angle and the tip of the mandible
where are the jugulodigastric (tonsillar) lymph nodes located?
under the angle of the mandible
where are the superficial cervical lymph nodes located?
overlying the sternomastoid muscle
where are the deep cervical lymph nodes located?
deep under the sternomastoid muscle
where are the posterior cervical lymph nodes located?
in the posterior triangle along the edge of the trapezius muscle
where are the supraclavicular lymph nodes located?
just above and behind the clavicle, at the sternomastoid muscle
what is the leading cause of acute pain and reason for seeking care?
headaches
true or false: migraines are more common in females than males with peak in midlife
true
headaches are classified by ___________
etiology
true or false: headaches are often misdiagnosed
true
migraines are more common in ________ than ________ (sex) with peak in midlife seen equally
females; males
true or false: chronic migraines are more prevalent among Caucasian and Hispanic populations
true
what are the common location and characteristic of tension headache?
location: both sides
character: bandlike tightness, non throbbing, nonpulsatile
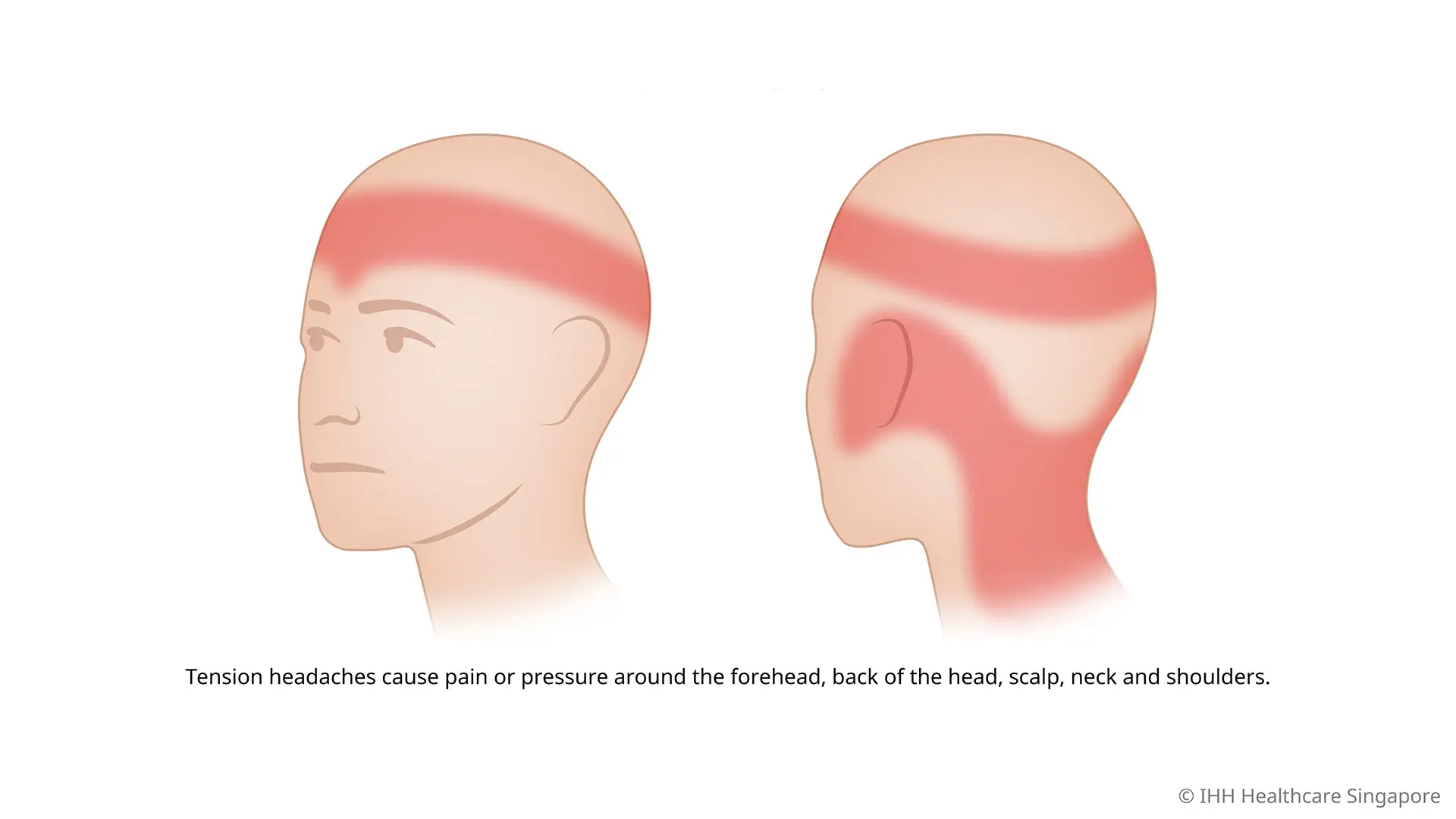
what are the triggers and associated symptoms of tension headache?
triggers: stress, anxiety, depression, poor sleep
associated symptoms: fatigue, anxiety, stress, sensation of a band of tightening around head
what are some common treatments for tension headache?
abortive - NSAIDs
preventive - tricyclic antidepressants
nonpharmacologic - reduce stress, biofeedback, cognitive behavioral therapies, physical therapy, message, acupuncture
what are the common location and characteristic of migraine headache?
commonly one-sides (but can be on both sides), behind he eyes, temple or forehead
character: throbbing, pulsating
what are the triggers and associated symptoms of migraine headache?
triggers: hormonal fluctuations, alcohol, caffeine, processed foods, salty foods, hunger, sleep changes, flashing lights
associated symptoms: nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia, family history of migraines
what are the common treatments of migraine headache?
nonpharmacologic - lay down, darken room, sunglasses, sleep
medications (abortive - NSAIDs, acetaminophen, triptans, preventive - beta-blocker, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, etc)
alternatives - acupuncture, cognitive behavioral therapy, lifestyles changes (e.g., exercise, regular sleep patterns, and meals)
what are the common location and characteristics of cluster headache?
location: always one sided, behind, or around the eye/temple
character: continuous, excruciating, sharp, burning, piercing
what are the triggers and associated symptoms of cluster headache?
triggers: worsened by alcohol, histamine, paint, and perfume
associated symptoms: nasal congestion, watery eye, eyelid drooping or swelling, facial sweating, feelings of restlessness, nausea, vomiting, phono/photophobia
what are some common treatments for? cluster headache?
abortive - inhaled oxygen, parenteral route medication (not by mouth but intradermal/muscular/venous or subcut)
preventive - calcium channel blockers, lithium carbonate, anticonvulsants, melatonin, nerve blocks
review all of the important sites for gathering objective data when doing a head/neck assessment…
Inspect the shape and size of the skull
Palpate the temporal artery
Inspect the face and neck (you should always be assessing for symmetry)
Assess the neck’s range of motion
Palpate for lymph nodes using gentle pressure
Inspect the position of the trachea (is it midline?)
if the thyroid is enlarged, auscultate the neck to assessment for a __________ as __________ may occur with hyperthyroidism
bruits
macrophaly
when the infant’s head circumference is significantly larger than average (often exceeding the 97th percentile)
microcephaly
when the infant’s head circumference is significantly smaller than average (often at or lower than the 3rd percentile)
nystagmus
conditions characterized by eyes moving rapidly in a repetitive, uncontrolled movements

what is a goiter and what causes it?
goiter is chronic thyroid enlargement
often caused by a low diet in iodine (common in regions with low iodine in the soil) but also from a number of autoimmune disease, nodules, pregnancy, or medications
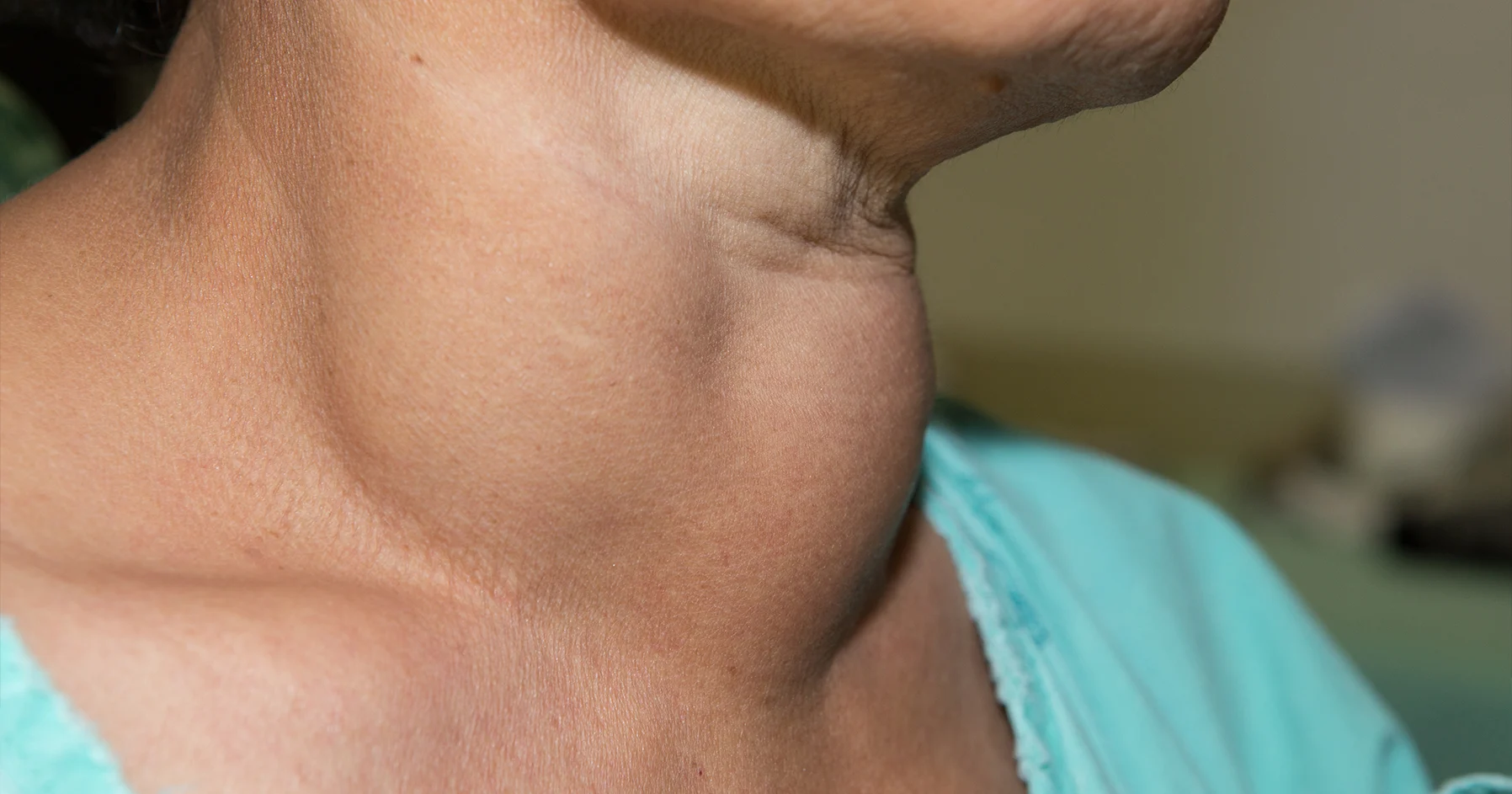
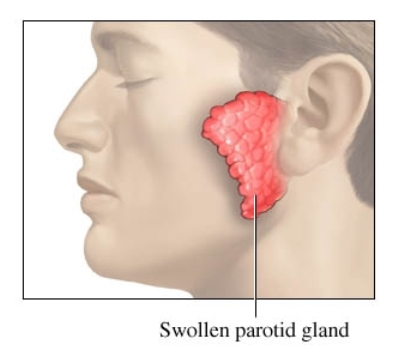
what conditions can cause parotid gland enlargement?
blockage of the durect
acute viral or bacterial infections
autoimmune diseases
neoplastic disease (tumors)
add in sherpath & workbook