GCSE Revision Physics
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
233 Terms
Radioactivity
unstable elements spontaneously emitting energetic particles by the decay of their atomic nuclei in order to become stable.
3 types of radiation
alpha - helium nucleus - 2 protons, 2 neutrons
beta - high speed electron
gamma - EM wave
Alpha particles
mass 4, charge 2+, most ionising, least penetrating, stopped by paper and smoke
Beta
stopped by aluminium, mass 1/2000 of a proton, charge -1
Gamma
uncharged, most penetratd ng, least ionising, stopped by lead
Alpha decay
loses 2 protons and neutrons, top number decrease by 4, bottom number reduce by 2, makes element + helium
beta decay
occurs when too many protons or neutrons, proton or neutron becomes electron, atomic mass stays same, atomic number increases by 1, makes new element and electron.
Gamma decay
just energy from nucleus, no change in numbers.
timeline of atomic model
john dalton - atoms can be created or destroyed
JJ Thomson - Plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford - Nuclear model, alpha scattering
neils bohr - planetary - electron shells, electrons move between them
Activity
number of unstable atoms in that source that decays per second. measured in becquerel
half life
time it taes for NO of nuclei of isotope to halve
the time it takes for the count rate to decrease by half.
count rate (after) =
count rate/ 2^n
n = number of half lifes
Nuclear Fission
nuclear fission can be induced by bombarding 2 atoms with neutrons, the nuclie of the atoms decay split into 2, neutrons are released
how does fission release energy
kinetic energy of the products in fission are greater than that of the bombarding neutron and target atom
Nuclear Fussion
2 small nuclei are fused together to make 1 heavy nuclei and this proccess creates heat energy and used to create electricity
Nuclear power
Uranium fuel rods under going fussion, rods surrounded by moderator to increase likelyhood of being absorbed, this generates heat to produce steam, this used by turbine to generate electricity
irradiation
exposure to a radioactive source outside the body
Contamination
when radioative stuff is inside your body and can cause damage
millisievert
measure of radiation dose
gear
a wheel with teeth that transmits the rotational effect of a force
force x distance =
force x distance
Refraction is
when light waves change direction when they pass from one medium to another
Waves travel
at different speeds through different densities
Higher density =
slower wave
Reflection- Angle of incidence=
angle of reflection
3 primary colours of light
red blue green
Red + Blue =
Magenta
Red + Green =
Yellow
Blue + Green =
Cyan
Blue + Green + Red =
White
why does a white shirt look white
because it reflects all colors of light
why does a red shirt look red
because it reflects the red light and absorbs the green and blue light
why does a green shirt look green
Because it absorbs red and blue light and reflects green light
why does a black blazer look black
because it absorbs all light
the 2 types of wave
Transverse, longitudinal
Examples of transverse waves include
Light waves, radio waves
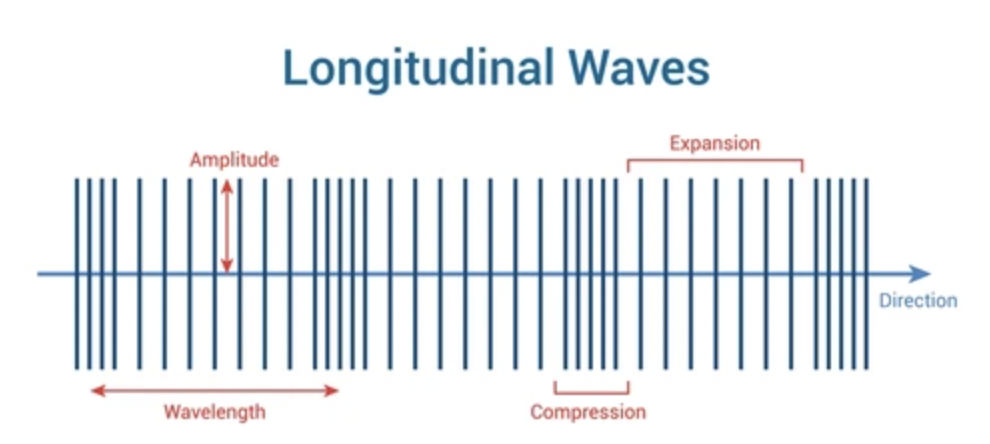
Examples of longitudinal waves include
Sound waves, seismic P waves
the wave equation
Wave speed = frequency X wavelength
Frequency
How many whole waves in a second
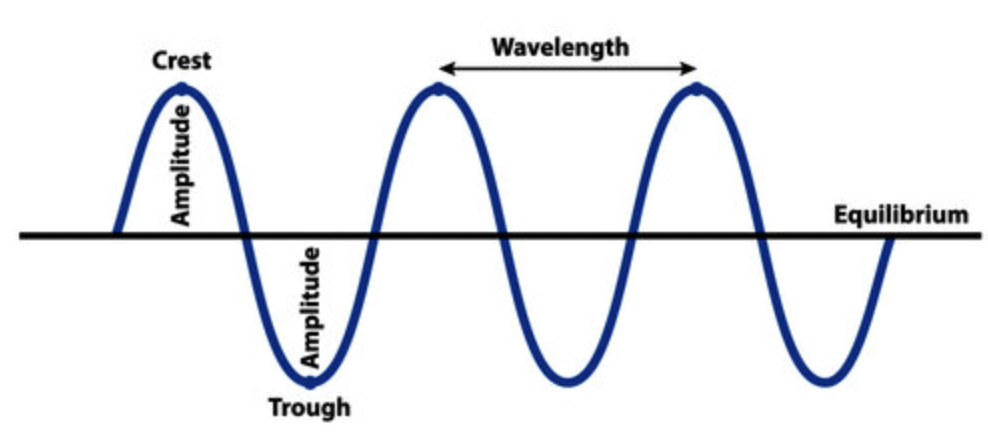
Amplitude
is the distance from the centre line (or the still position) to the top of a crest or to the bottom of a trough .
Wavelength
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between two waves
A light wave bend towards the normal when
less dense to more dense
a light wave bends away from the normal when
more dense to less dense
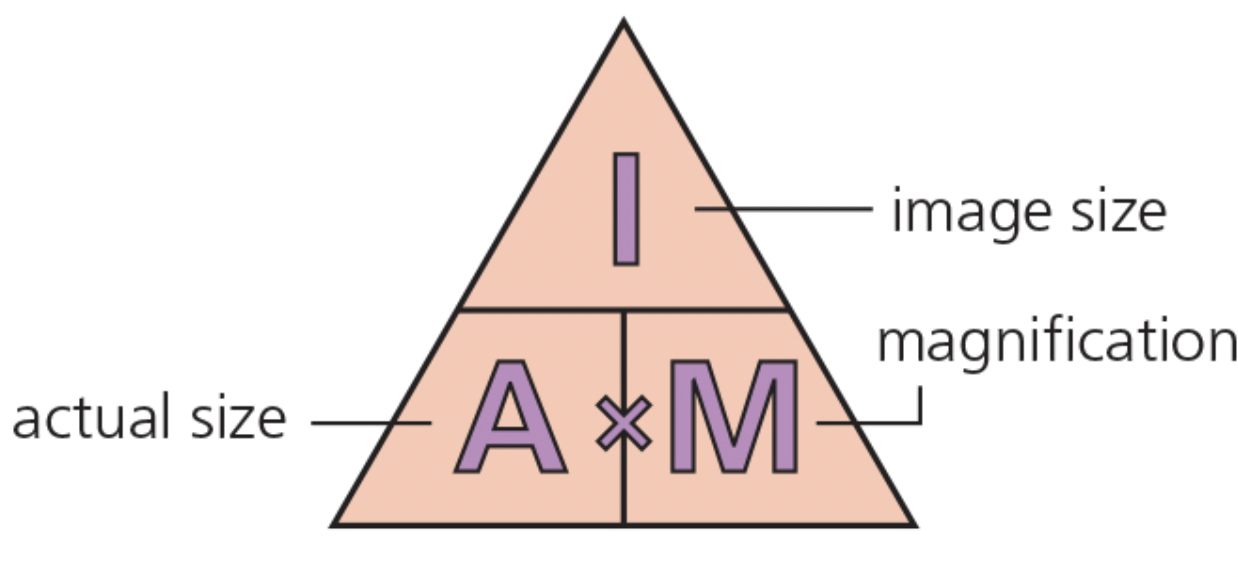
magnification =
image height
object height
Types of energy stores
thermal kinetic nuclear chemical gravitational elastic electrostatic magnetic
energy transferes are
mechanisms which allow energy to be moved from one location to another
Weight =
mass X gravity
Mass
is a measure of how much of an object there is and how mard is it to accelerate
Force
mg
GPE
mgh
work =
force X distance
Kinetic energy
½ mv²
Hookes law
The extension of a spring is directly proportional through the origin to the force applied, provided irs limit of proportionality is not exceeded
Hookes law equation
F = K X e
K=spring constant in N/m
Power =
work/time
Power also equals
Energy transfered/time
efficency =
useful power/total power input
When a current floes through a wire
a magnetic field is created around it
aNticlockwise
North
clockwise
south
LEFT hand grip rule
Thumb-Force , second-field, third-current
The motor effect
when a current flows through a magnetic field it will experience a force and it will move
Why do we get movement WITH THE MOTOR EFFECT
A CURRENT CARRYING WIRE WILL HAVE A MAGNETIC FEILD AROUD IT. THIS FEILD WILL INTERACT WITH THE MAGNETS AND BE PUSHED OUT OF THE FEILLD
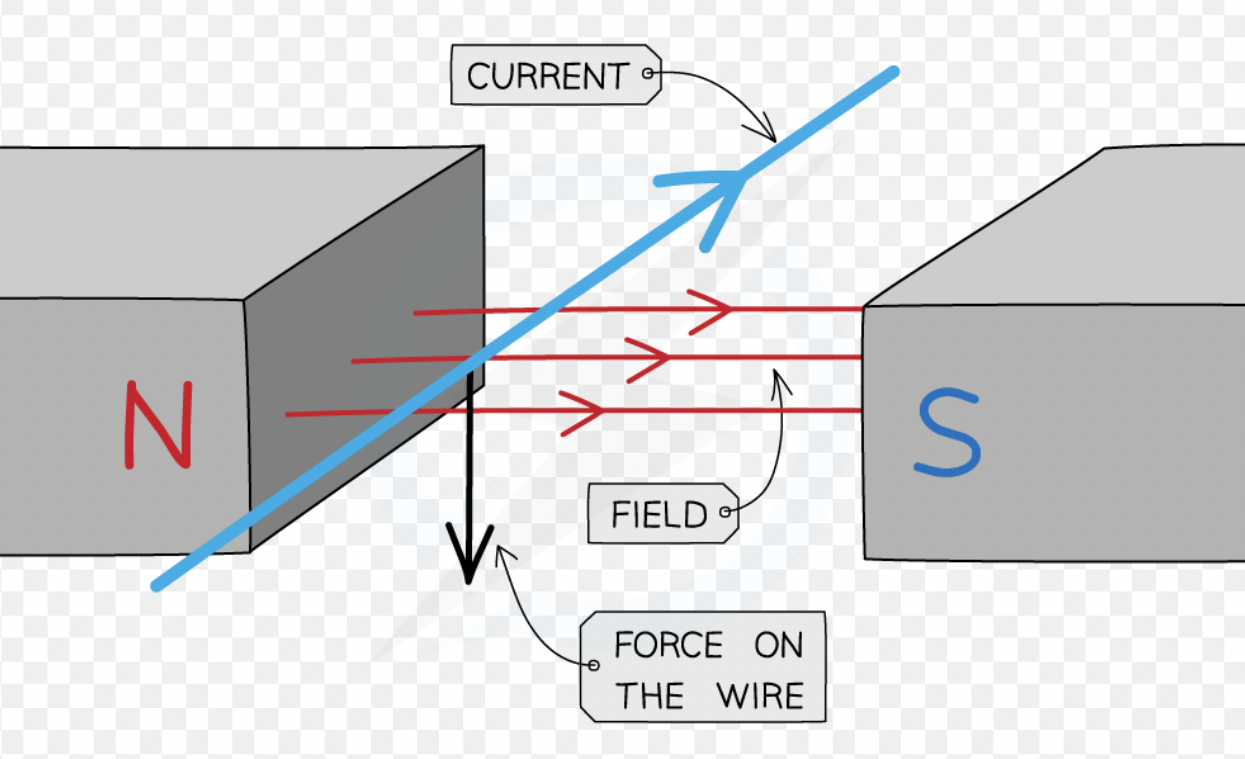
The biggest effect will be when
the current and field are at right angled to each other
If the current and field are parallel there will be
no force
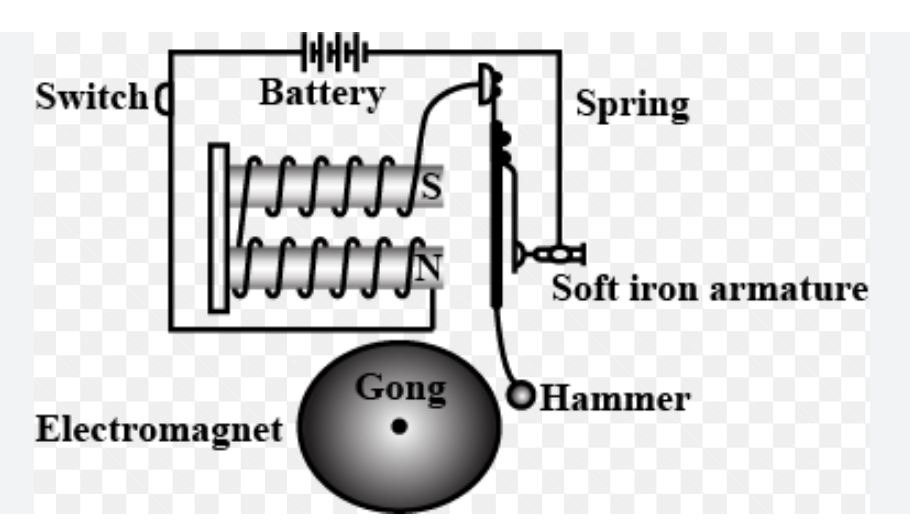
The electric bell
the current flows from the electromagnet because there is a complete circuit. This causes the iron core to become magnet and it attracts the soft iron armature this makes the hammer hit the gong.
The motor effect 3
A wire carrying a current creates a magnetic field . This can interact with another magnetic field, causing a force that pushes the wire at right angles.
An electro magnet
An electro magnet is a temporary magnet made by winding wire around an iron core.
Charge=
current x time
like charges
Different charges
REPEL
ATTRACT
Radial field
As you move away from the sphere the feild gets weaker
negitive sphere, - out + in
plus sphere, -in +out
Charge is measured in
Coulombs
Current is the
measure of the movement of charge and is measured in amps (coulombs per second)
Ametre
measures how much charge is moving around a current
Voltmetre
measure of p.d this is the measure of energy a cells gives to the charge§
Resistor
Resistance is a measure of hoe hard it is for current to flow through a component , measured in ohms.
V=
IR
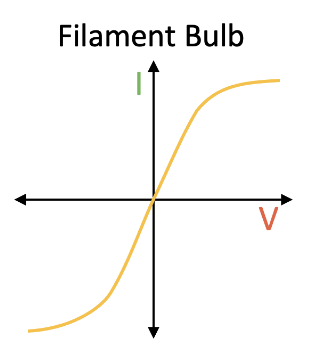
IV Graph filament bulb

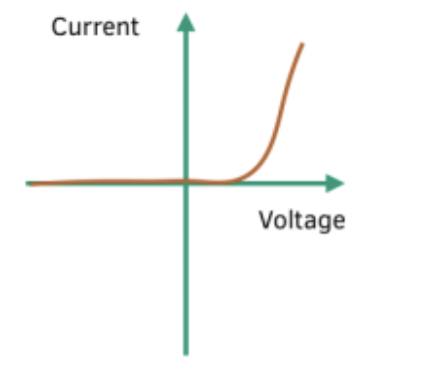
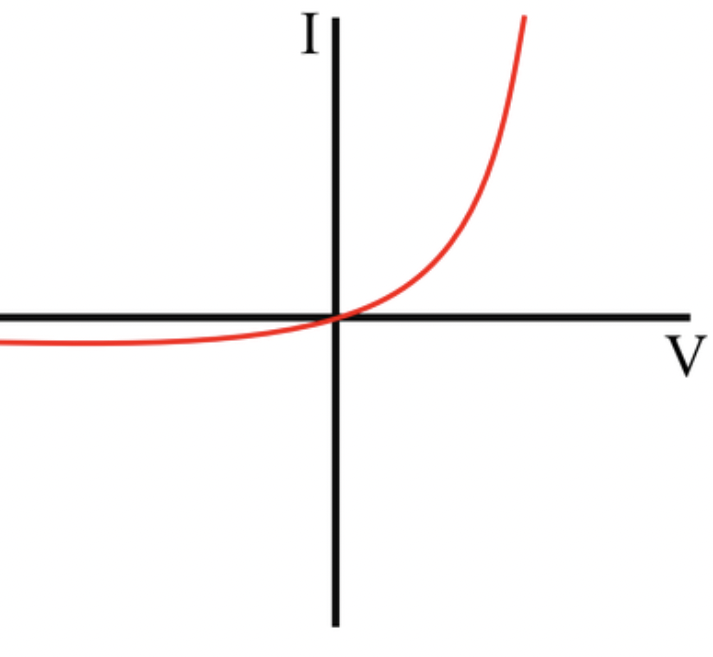
Diode

Light dependant resistor
As the light intensity increases the resistance falls
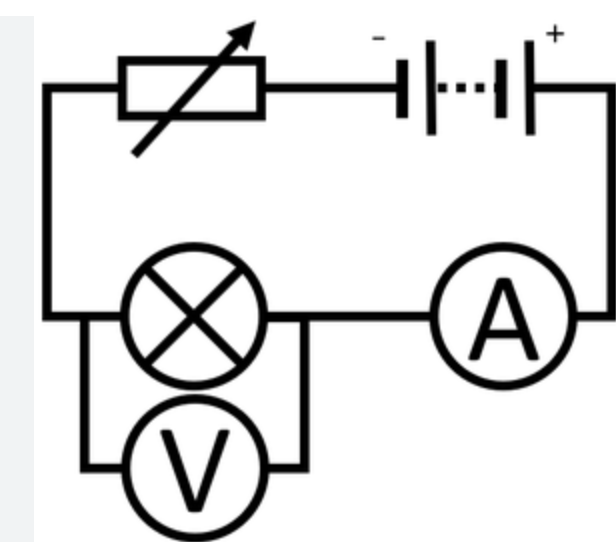
IV experiment
Variable resistor, bulb, ammeter in series, voltmeter in parallel
Change current and measure the P.d

Thermosistors
As temprature increases resistance falls
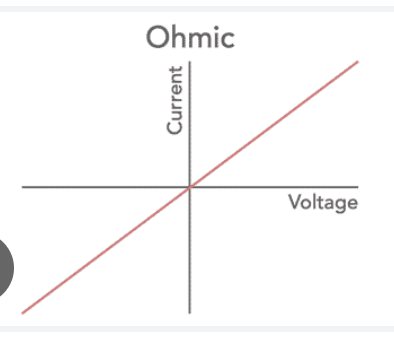
Ohmic resistor

LED graph

Series more bulbs=
more resistance
Parallel more bulbs =
more current and less resistance
Resistance in series and NO. of bulbs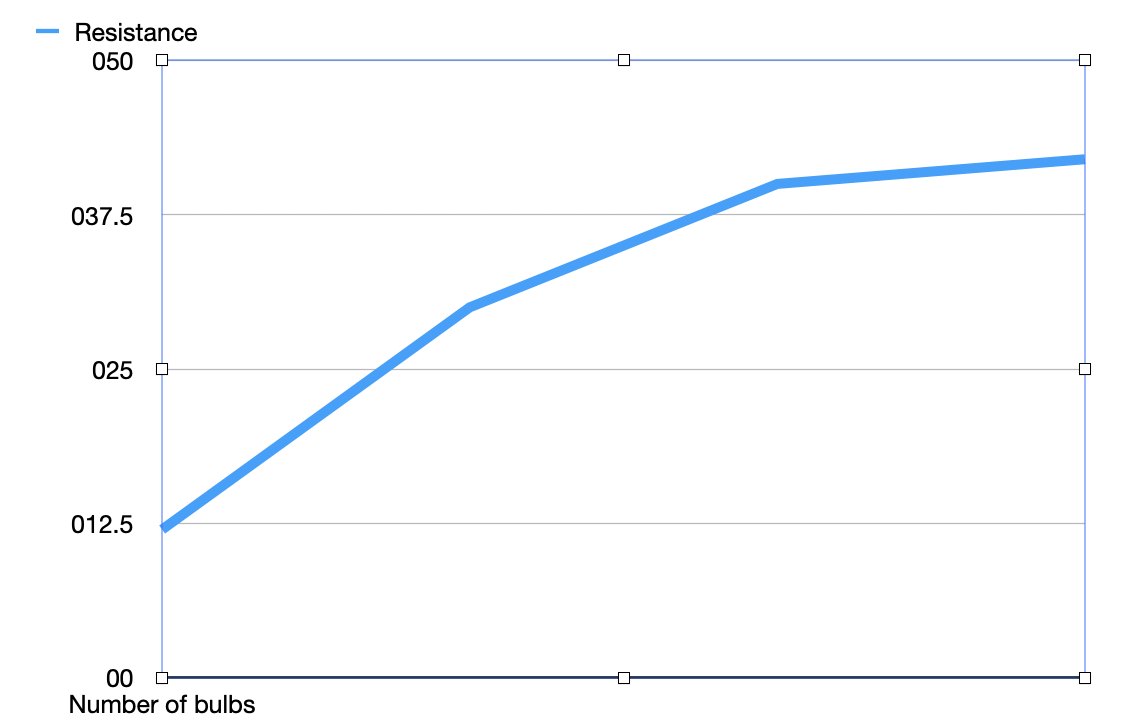
Graph goes up
Not straight because bulbs are less bright and cold.
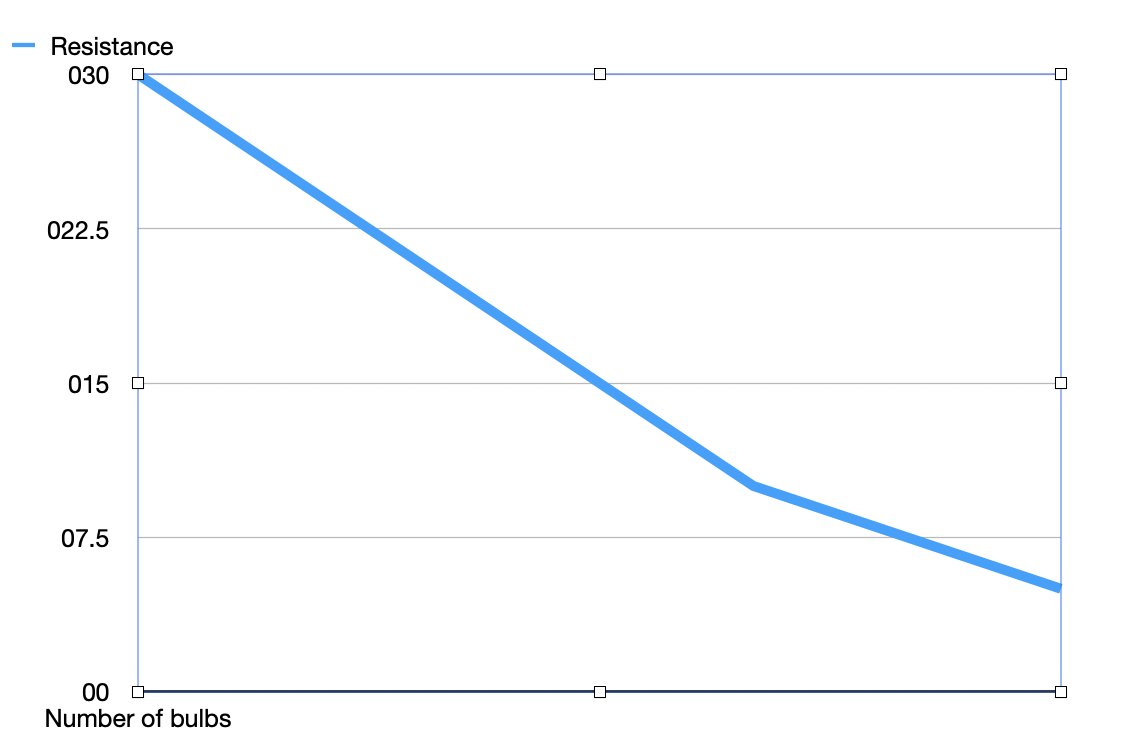
Resistance in parallel and NO. of bulbs

Series
resisatance can be added, current same everywhere, potential differences add to supply.
Parallel
Potential difference = same for all resistors, total current = all current added together.
Parallel Rtotal =
V/I total.
Using a LDR to measure light intensity
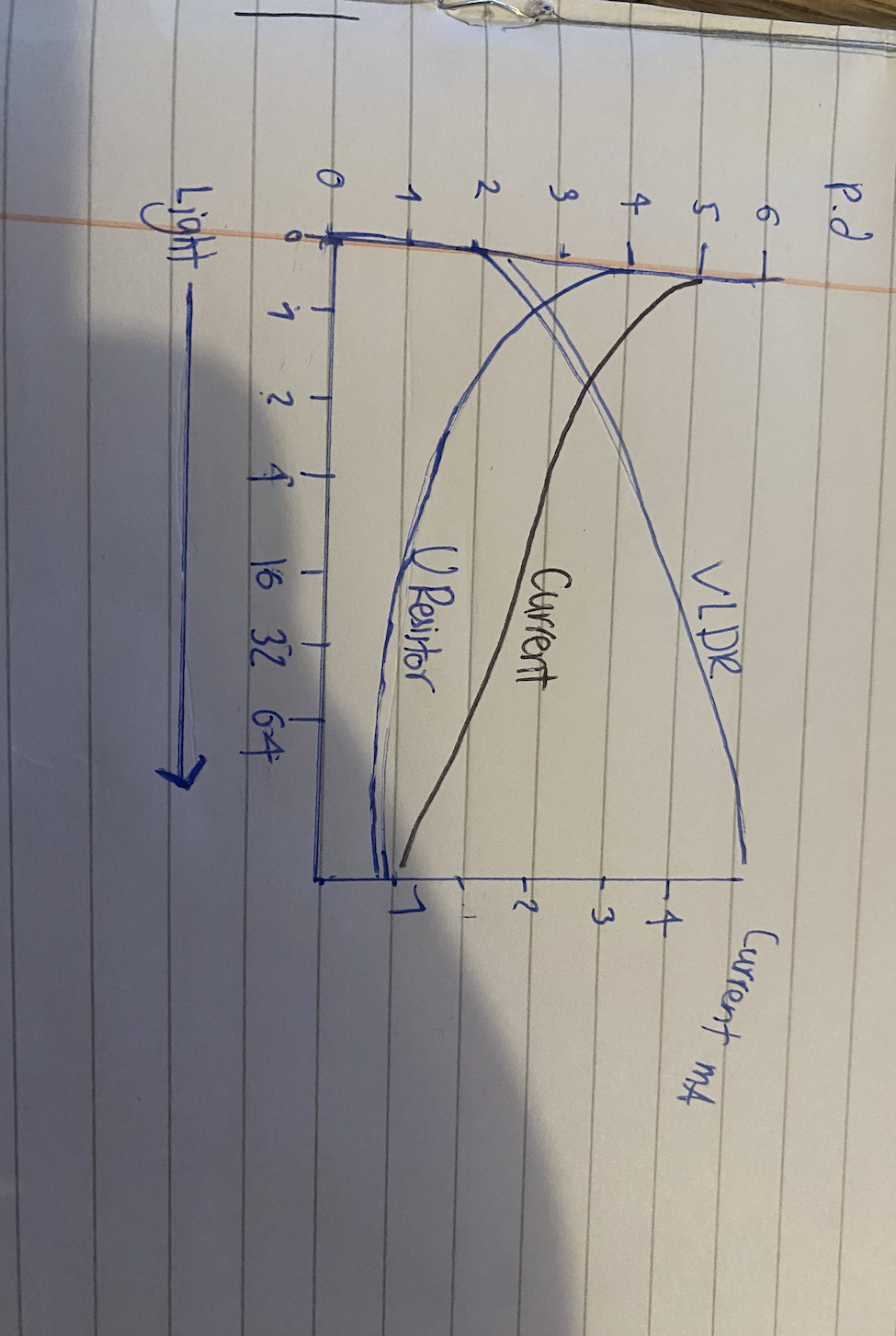
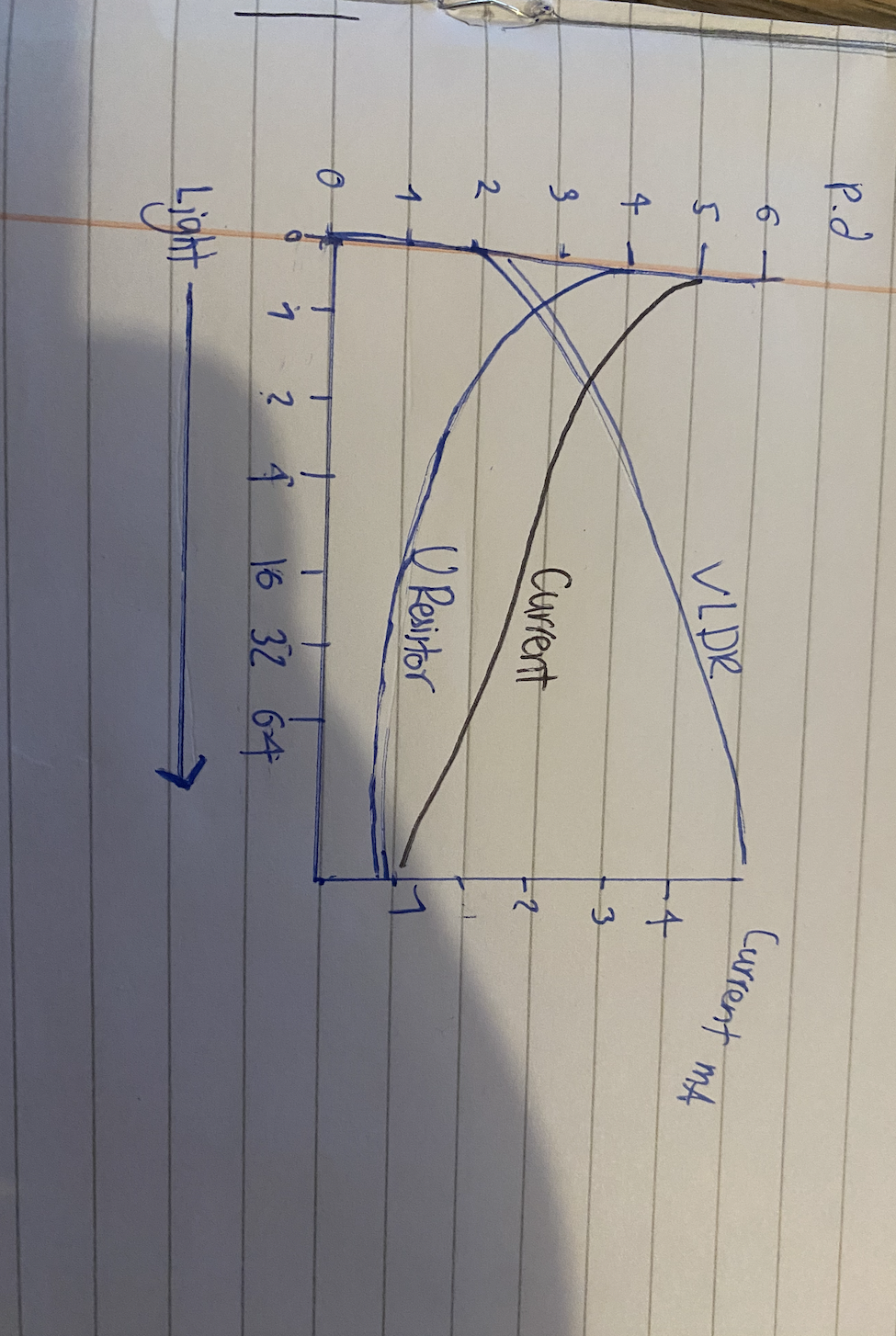
V =
E/Q
Energy transfered =
Charge x P.D
P=
E/T
I=
Q/T
Power =
I² x R
density =
mass/ volume
Density Eureka Can experiment
use balace to measure mass, submerge object into eureka can with water in it with a measuring cylinder underneath the spout, record the volume of water in the cylinder, work out density with d=m/v formula