Unit 5: Land and Water Use
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Types of GMOS
Bt crops (make its own pesticide), Golden rice (high vitamin A)
Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizer
Organic: has micro nutrients, makes soil healthier, can be expensive, hard to know how much of one nutrient is being applied
Synthetic: does not have needed micro nutrients, cheaper, amount of nutrients easier to control, damages soil (less absorbed > runoff)
Tilling
Turning over soil to prepare for planting, which can improve soil aeration and weed control but may lead to soil erosion and degradation.
Slash and burn agriculture
Farming technique that involves cutting down and burning vegetation to clear land for crops, often leading to temporary soil fertility but long-term environmental degradation.
No-till farming
A farming practice that reduces soil erosion and degradation by not plowing the soil, thus maintaining soil structure and health.
Drip Irrigation
Most expensive, 5% of water lost, best method
Furrow Irrigation
Digging trenches or furrows to direct water to crops, worst method, 33% water lost
Spray Irrigation
Uses pumps and pipes that spray water over the plants, 25% water lost, second to worst
Flood Irrigation
Water flows over the field and saturates the soil, 20% water lost, efficient for rice and other crops, second to best
Water logging
Too much water is left to sit in soil > raises water table > inhibits plants ability to absorb oxygen through roots (Flood Irrigation leads to this)
Ogallala Aquifer
Largest Aquifer in the US that supplies water to eight states, crucial for agriculture and irrigation. Located in the Great Plains.
POPs (Persistent Organic Pesticides)
Toxic chemical compounds that persist in the environment, bioaccumulate in living organisms, and can cause adverse health effects. Examples include DDT and PCBs.
CAFOs (Concentrated animal feeding operations) / Feedlots
Crowded, animals feeded grains not grass, generates large amounts of organic waste, used to quickly get livestock ready for slaughter. Uses more antibiotics/chemicals because disease spreads faster.
Free Range Grazing
Meat from free range tends to be free from chemicals used in feedlots, and allows animals to roam, higher quality meat. More expensive for consumer but cheaper for farmer. Requires a lot of land.
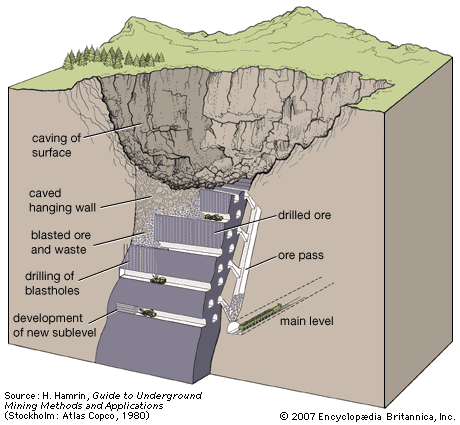
Strip Mining (Surface)
Removal of soil and rock to access minerals near the earth's surface.
Open-pit Mining (Surface)
A surface mining technique where a large excavation is made to access minerals, resulting in a terraced pit.
Placer Mining (Surface)
A method of extracting valuable minerals from alluvial deposits using water to separate heavier materials from lighter ones. Least impact on environment.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Biological, chemical, physical methods to reduce pests without immensely hurting the environment
Contour Farming
Plowing of land along the contours of a slope to reduce soil erosion and water runoff.
Windbreaks
Rows of trees or shrubs planted to protect crops from wind damage and reduce soil erosion.
Perennial Crops
Plants that live for multiple years, providing yields over time without the need for replanting each season. Eliminates tilling + leaving the ground empty. Reduces soil erosion.
Terrace Farming
Steep slopes, dig into the slopes to make a flat surface to plant on (like stairs/steps). Slows water, increases absorption, reduces soil erosion.
Strip Cropping
Alternating strips of different crops are planted to improve soil health and reduce erosion. This technique also helps manage pests and enhance biodiversity.
Fish Farming vs Fish Ranching
Farming: kept in cages where they are cared for until they are harvested
Ranching: hatched at a fishery then released into the wild to grow + mature, they are harvested when they return to spawn as adults
Shelterwood Cutting
Removing mature trees in a series of cuts, leaving some trees standing to provide a shelter for the regeneration of new trees.
Selective Cutting
Cutting down only some trees in a forest while leaving others intact. Best tree cutting technique.