T4:Atomic Structure
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Card 25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is the radius of an atom?
1×10^-10
What is the basic structure of an atom?
A positively charged nucleus composed of both protons and neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
Where is most of the mass of an atom concentrated?
The nucleus
What is the radius of a nucleus compared to the radius of an atom?
The radius of a nucleus is 1/10 000 of the radius of an atom.
What do electrons lie on that it means that they are different distances from the nucleus?
Different energy levels
What happens if an electron absorbs electromagnetic radiation?
The electron moves further away from the nucleus to a higher energy level
What happens if an electron emits electromagnetic radiation?
The electron moves closer to the nucleusto a lower energy level.
In an atom,what is the number of electrons equal to?
The number of protons in the nucleus.
Do atoms have an overall electrical charge?
No
What do all atoms of a particular element have?
The same number of protons.
What is the number of protons in an atom of an element called?
The atomic number.
What is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom called?
The mass number.

What does 23 and 11 represent for Sodium?
23:Mass number
11:Atomic number
What is it called when atoms of the same element have different number of neutrons?
An isotope
When do atoms turn into positive ions?
When they lose electrons.
What may lead to a scientific model being changed or replaced?
New experimental evidence.
What did James Dalton think about atoms before the discovery of the electron?
Atoms were thought to be tiny spheres that could not be divided
Which model did the discovery of the electron lead JJ Thompson to create?
The plum pudding model.
What did the plum pudding model suggest?
The atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded throughout it.
What three conclusions did the results from the Alpha Scattering experiment lead to?
Most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus
The nucleus has a positive charge
Most of the atom is empty space
Which model replaced the Plum Pudding model?
The nuclear model
How did Neil Bohr adapt the Nuclear model?
By suggetsing that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances.
What sub-particle was discovered after later experiments?
The proton.
What did James Chadwick disocver 20 years after the nucleus became an accepted scientific idea?
The Neutron.
Plum Pudding vs Nuclear model?
What is the random process of radioactive decay?
When unstable nuclei give out radiation as they change to become more stable
What is Activity?
Activity is the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays.
What is Activity measured in?
Becquerel (Bq)
What is count rate?
Count-rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector.
What is an alpha particle (α)?
A helium nucleus
What is a beta particle (β)?
A high speed electron ejected from the nucleus as a neutron turns into a proton
What is a gamma ray?
electromagnetic radiation from the nucleus
What is the fourth type of radiation?
A neutron
What is an alpha particle’s range in air?
A few cm
What is an beta particle’s range in air?
A few m
What is an gamma ray’s range in air?
A few km
How ionsing is an alpha particle?
Strongly ionising.
How ionsing is a beta particle?
Moderately ionising.
How ionsing is an a gamma ray?
Weakly ionising
What are alpha particles absorbed by?
Paper.
What are beta particles absorbed by?
A sheet of Aluminium around 5mm.
What are gamma rays absorbed by?
Metres of concrete.
What are nuclear equations used to represent?
Radioactive decay.
Should the total mass be equal on both sides in a nuclear equation?
Yes.
What is the symbol for an alpha particle in a nuclear equation?
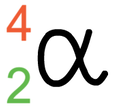
What is the symbol for an beta particle in a nuclear equation?
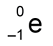
What is the symbol for a gamma ray in a nuclear equation?
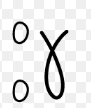
Does the emission of a gamma ray cause the mass or charge of the nucleus to change?
No
Radioactive decay is….
Random and spontaneous.
What is a half-life of a substance?
The Half-life is half the time taken for the number of radioactive nuclei in an isotope to halve.
What is radioactive contamination?
Radioactive contamination is the unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials.
What is the hazard from contamination due to?
The hazard from contamination is due to the decay of contaminating atoms.
What is irridation?
Irradiation is the process of exposing an object to nuclear radiation.
Does an irradiated object become radiactive?
No.
Give two things that exposure to radiation can cause:
Cancer
Cell damage
What two precautions can be taken against an irradiated/contaminated object?
Stand behind a barrier
Use gloves/tongs
What is it called when Scientists check other scientist’s work?
Peer-review.
What are 6 forms of background radiation?
Radon Gas
Buildings and the ground
Cosmic rays
Food and drink
Medical
Fallout from nuclear weapon testing
What is radiation dose measured in?
sieverts (Sv)
How many milisieverts is 1 sievert?
1000 millisieverts (mSv) = 1 sievert (Sv)
How does a short half -life affect the hazards associated with it?
The activity falls quickly
because the nuclei are very unstable/rapidly decay
so are dangerous due to the high amount of radiation emitted at the start
but quickly become safe.
How does a long half -life affect the hazards associated with it?
The activity falls more slowly
beacuse most of the nuclei won’t decay for a long time
so are dangerous as the source
releases small amounts of radiation over millions of years
What 2 ways is nuclear radiation used in medicine?
exploration of internal organs
control or destruction of unwanted tissue.
What is Nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a large and unstable nucleus.
Why is spontaneous fission rare?
Usually, for fission to occur the unstable nucleus must first absorb a neutron.
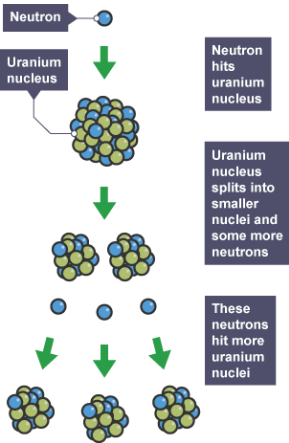
What isthe process of nuclear fission?
The nucleus undergoing fission splits into two smaller daughter nuclei
and emits two or three neutrons
plus gamma rays
Energy is released by the fission reaction.
What do all of the fission products have?
Kinetic energy.
What can the nergy not transferred by the gamma rays and carried away by the gamma rays be used for?
heat water
to make steam to turn turbines and generators
What can the spare neutrons go on to start?
A chain reaction.
What is the explosion of a nuclear weapn caused by ?
An uncontrolled chain reaction.
How is a chain reaction controlled in a nuclear reactor?
Lowering control rods
to absorb neutrons to
slow down the chain reaction
and control the amount of energy released.
Draw a diagram to represent a chain reaction:
What is nuclear fusion?
Nuclear fusion is the joining of two light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus.
Why are the nuclei produced lighter in nuclear fusion?
Some of the mass may be converted into the energy of radiation.
Which releases more energy nuclear fission or nuclear fusion?
Nuclear Fusion.
What is needed for fusion reactors that makes them very expensive to build?
High temperatures
High pressure