Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
Key Idea: Cognitive development occurs in four universal, sequential stages. Each stage is characterized by distinct ways of thinking and understanding the world.
Order is fixed: All children go through stages in the same order.
Onset age may vary: Cultural and environmental factors can influence when a child enters a stage.
Classification of Piaget’s Theory
Dimension | Classification | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Stage Type | Discontinuous | Each stage reflects a qualitative shift in thinking (not just more of the same) |
Development Role | Active | Children are active participants who learn by interacting with their environment |
Reflexive Reactions (0–1 mo)
🔑 Keyword: Reflexes
🧠 Mnemonic: Born to react
💡 Meaning: Baby uses inborn reflexes (e.g., sucking, grasping) to respond to stimuli—no intentional control yet.

Primary Circular Reactions (1–4 mos)

🔑 Keyword: Body
🧠 Mnemonic: Me, myself, and loop
💡 Meaning: Repeats body movements that feel good (e.g., thumb sucking). Focus is on own body and pleasure.

Secondary Circular Reactions (4–8 mos)

🔑 Keyword: Object
🧠 Mnemonic: Toy makes noise—I do it again!
💡 Meaning: Repeats actions involving external objects. Begins interacting intentionally with the world (e.g., shakes rattle).

Coordination of Secondary Circular Reactions (8–12 mos)

🔑 Keyword: Goals
🧠 Mnemonic: Two tricks, one purpose
💡 Meaning: Combines actions to achieve a goal (e.g., knocks over a box to get a toy). First signs of intentional problem-solving.

Tertiary Circular Reactions (12–18 mos)

🔑 Keyword: Experiment
🧠 Mnemonic: What happens if...?
💡 Meaning: Actively experiments with cause-and-effect (e.g., drops ball from different heights). Begins flexible thinking.
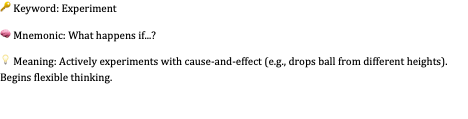
Internalization of Schemas (18–24 mos)

🔑 Keyword: Think
🧠 Mnemonic: Mind over motion
💡 Meaning: Begins mental representation. Can think about actions before doing them. Starts symbolic play and problem-solving in mind.

Preoperational Stage (2–7 yrs)

🧠 Mnemonic: Pretend, but not logical
💡 Key Features:
· • Make-believe play, imaginary friends, role play
· • Transductive reasoning: assumes causation where there is none
· • Egocentrism: can't understand others' perspectives
· • Magical thinking and animism
· • No conservation due to centration and irreversibility

Concrete Operational Stage (7–12 yrs)

🔑 Keyword: Logical Thinking (Concrete)
🧠 Mnemonic: Rules and real things
💡 Key Features:
· • Can classify, order, and perform math operations
· • Conservation develops (number → length → liquid → mass → weight → volume)
· • Uses decentration (can attend to multiple aspects)
· • Understands reversibility
· • Horizontal décalage: conservation skills appear gradually

Formal Operational Stage (12+ yrs)

🔑 Keyword: Abstract Thought
🧠 Mnemonic: Ideas and ideals
💡 Key Features:
· • Can reason about abstract concepts like justice
· • Uses hypothetical-deductive reasoning
· • Understands propositional logic
· • Adolescent egocentrism: imaginary audience and personal fable
