Chemistry - Rates of Reaction
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
rate of reaction (2)
the time it takes for a reaction to complete
mol dm⁻³s⁻¹
Define rate in terms of A → B
the change in either A or B in respect to time
Describe the two perspectives to rate and their denotations(2/2)
The two respective to rate are instantaneous and average rate.
Instantaneous rate refers to rate at a particular time. In the equation A→B, rate is the loss of A with respect to time (-d[A]ₜ/dt) or the gain of B with respect to time (d[B]ₜ/dt)
Average rate refers to the overall rate for the entire reaction. It can be denoted as (amount of product formed/time taken)
rate law (2)
the mathematical equation that describes the rate of a chemical equation in respect to the concentration of its reactants
rate = k[A]ᵃ[B]ᵇ[C]ᶜ’ where A, B and C are reactants; a, b and c denote the order of reaction with respect to their respective reactant; k is the rate constant and [] refers to the molar concentration of the reactant
half-life (2)
time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to fall to half of its original value
t₁/₂
Describe how the equation is chosen for the rate law of a reaction (3)
The equation chosen is derived from the rate-determining step.
In the mechanism of a reaction, there are various steps which reactants take to form a final product. These steps are known as intermediates.
The intermediates which is an immediate conversion from the reactant is slow and is known as the rate-determining step.
order of a reaction
the extent at which the rate of reaction is affected by the concentration of a specific reactant
How do we determine the order of reaction with respect to a reactant using data from a table?
Through experimental data:
The order of the reaction is the exponent to which 2 is raised when determining the factor by which the rate changes upon doubling the concentration
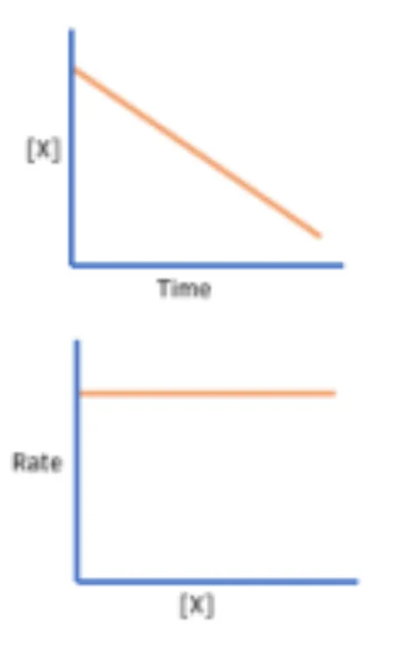
Determine the order of reaction in respect to a specific reactant as seen in these graphs
Zero order
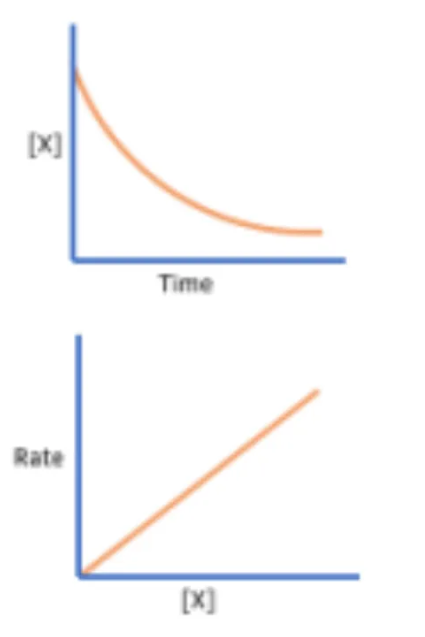
Determine the order of reaction in respect to a specific reactant as seen in these graphs
First order
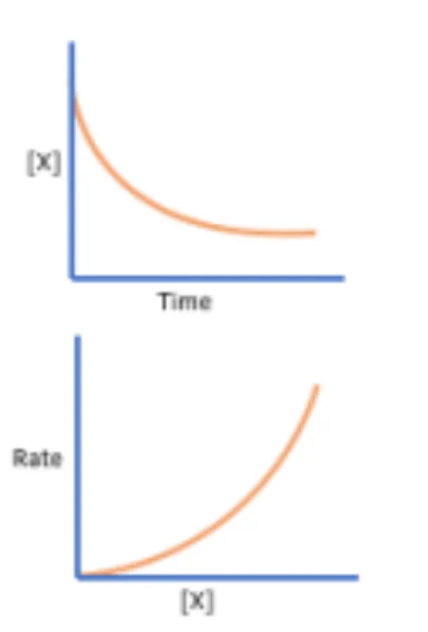
Determine the order of reaction in respect to a specific reactant as seen in these graphs
Second order
Define the overall order of a reaction
the sum of the orders of reaction with respect to each reactant in the rate law
rate constant
temperature-dependent proportionality factor which relays the rate of reaction to the concentration of the reactants
What are the units of k across the various orders of reaction? (3)
Zero - M/s
First - s⁻¹
Second - M⁻¹s⁻¹
What is the formulae for half-life in terms of rate constant? (3)
Zero - t₁/₂ = ln 2/k
First - t₁/₂ = [A₀]/2k
Second - t₁/₂ = 1/k[A₀]
What are the main factors which affect or are behind the reaction rate? (6)
Collision theory, concentration, surface area, Boltzmann distribution, temperature and catalysis
What is the collision theory? List its main postulates (1/3)
the hypothesis that states that in order to react particles must collide with each under certain conditions
1. Reactant particles must collide in order to form or break each other’s bonds
2. Reactant particles must have energy greater than their activation energy in order to react when colliding
3. Reactant particles must collide in the correct orientation in order to react
activation energy (2)
minimum energy needed for colliding particles to react
Eₐ
Explain how concentration affects rate of attraction
An increase in concentration increases as the frequency of collision and proportion of reactant particles with required activation energy increases and by extension so does effective collision
Explain how temperature affects rate of reaction
It increases the kinetic energy of the particles and increases collision and the amount of particles with required activation energy and by extension effective collision also increases
Explain how surface area affects rate of reaction
More particles are exposed and collide immediately — increasing the number of collisions and by extension effective collision
Describe how catalysts increase rate of reaction
They create a reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy without using themselves up by forming an intermediate product/surface on which reactant molecules can react more effectively
What are the two types of catalysts? Describe them (2/2)
The two types of catalysts are industrial and biological
Industrial catalysts are those which speed up the formation of products for manufacture or artificial synthesis
Biological catalysts are proteins called enzymes which aid in maintaining the necessary speed for chemical reactions in organisms by increasing their rate of reaction
List some examples of biological and industrial catalysis (3/3)
Industrial:
1. Harmful molecules such as nitrogen oxides and CO are converted into less harmful molecules (e.g. carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas) using metals like platinum, pallidum and rhodium
2. Sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide in the Contact process using vanadium oxide, V₂O₅, catalyst
3. Ammonia gas is formed via the Haber process by combining nitrogen and hydrogen under pressure at 450 degrees Celsius in the presence of an iron catalyst
Biological:
1. Carbonic anhydrase — zinc catalyst converts carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid
2. Hydrogenation of vegetable oils to margarine — reacting a carbon=carbon bond in vegetable oil with hydrogen in the presence of a Ni catalyst
3. Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas via a Manganese catalyst, MnO₄
The Boltzmann distribution
the instance in which the particles of a substance in a particular state of matter and fixed temperature have differing velocities
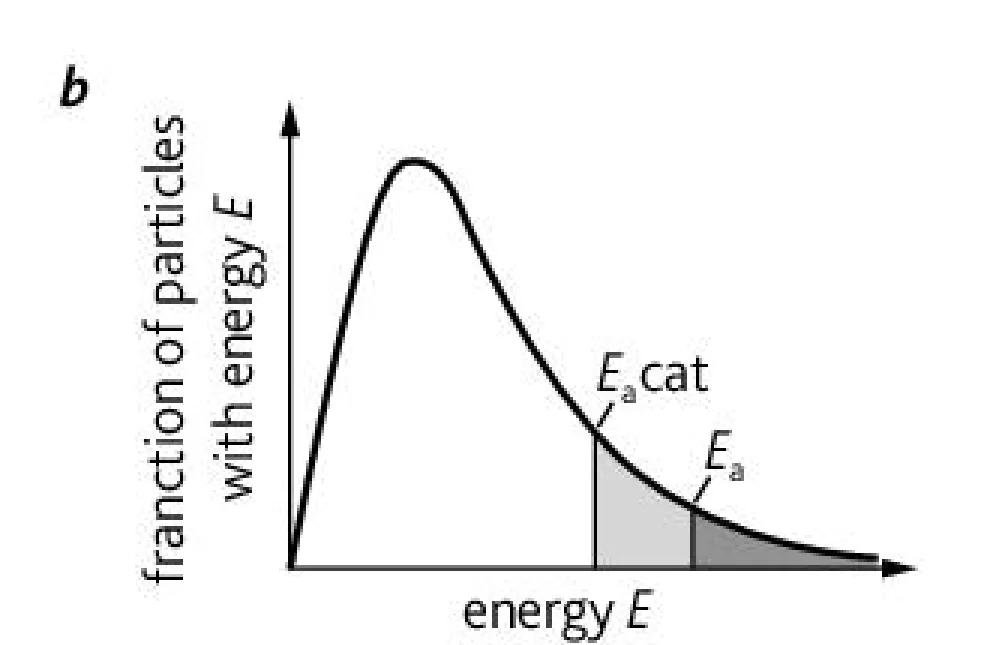
What is this graph representing?
A Boltzmann distribution graph representing the proportion of molecules that possess the activation energy required to effectively collide with and without a catalysis
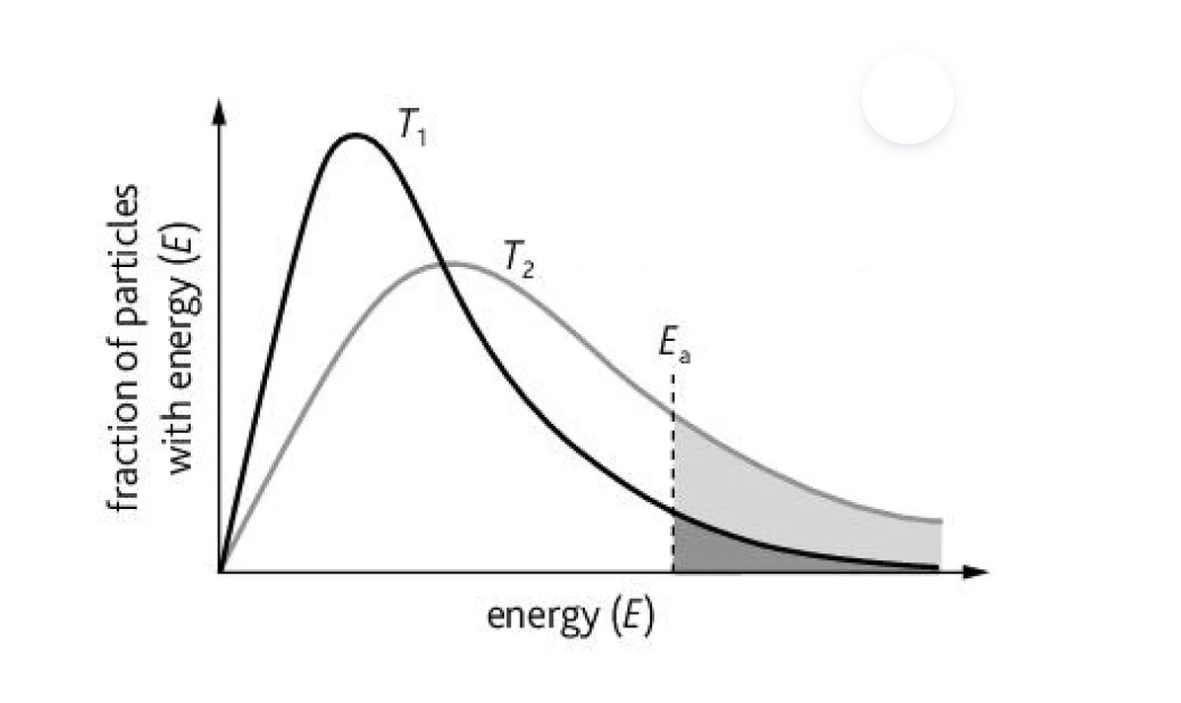
What is this graph representing?
A Boltzmann distribution graph representing the proportion of molecules that possess the activation energy required to effectively collide at a lower and higher temperature
Which order of reaction has a constant half-life?
1st order