Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
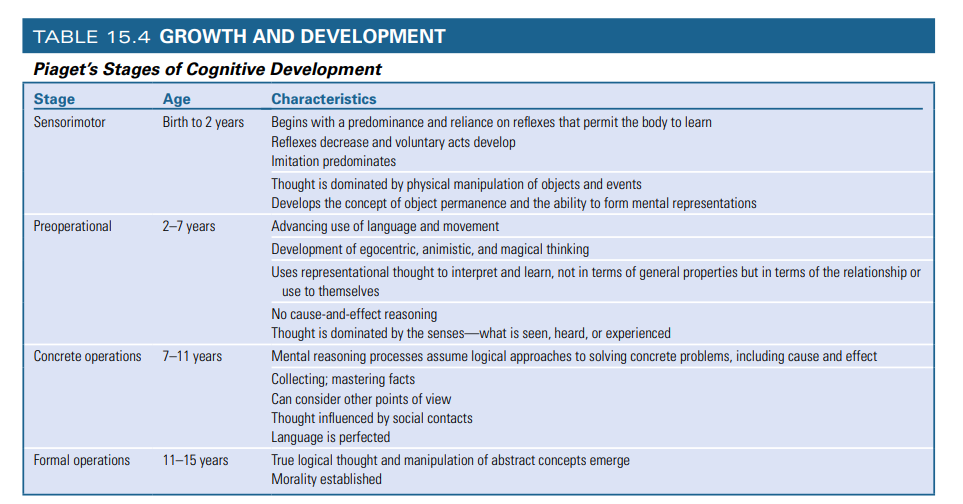
Birth to 2 years
they explore the world through ? (5 senses)
What is object permanence?
infants learn what about their actions?
What type of reasoning?
Sensorimotor
Explore the world using sight, sound, touch, taste, and movement. Their own POV
Object Permanence: Understanding that objects continue to exist even when they are out of sight
Example: A toy hidden under a blanket is still there.
Infants learn that their actions can produce results.
Example: Shaking a rattle makes a sound.
Primitive Reasoning
2-7 years stage
advance use of?
Development of ? (3 things)
Interpret and learn about the world based on ?
Develop what type of functions and what thoughts, engage in ?
Preoperational
Advancing use of language and movement
Development of egocentric, animistic, and magical thinking
Children interpret and learn about the world based on how things relate to themselves, not in terms of general logical properties.
develop symbolic functions and intuitive thoughts; engage in pretend play.
7-11 years
Develop ____ _____ operations?
Engage in what type of reasoning?
They understand that their thoughts are? (2 things)
Concrete Operations
develop concrete cognitive operations, such as the ability to sort objects in a certain order and understand the concept of conservation.
engage in inductive reasoning, make generalizations, and reverse actions by doing the opposite.
understand that their thoughts and feelings are unique and different, allowing them to develop empathy and perspective-taking skills.
11-15 years
Ability to think more ? About? (2 things)
What type of reasoning? _____ generalizations?
Deeper meaning of ?
Formal operations
develop the ability to think more rationally about abstract concepts and hypothetical events.
deductive reasoning, make logical generalizations, and think about thinking itself.
develop a deeper understanding of their own identity, morality, and the behavior of others. egocentric thoughts may still be present, and some may experience an imaginary audience watching them.
What did Piaget conclude after observing younger children making different types of mistakes than older children?
They must think differently
Piaget calls the intuitive age the birth of ——————reasoning.
deductive