Topic 3: Integumentary System
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Functions of Epidermis
Protection
Regulation of body temperature
excretion
provides sensory information
synthesis of vitamin D3 and of lipid reserves
coordinates immune responses of the skin
Layers of the Integumentary system
Epidermis
Surface Layer
Dermis
Blood Vessels and nerves present
Hypodermis
aka subcutaneous layer, subcutaneous fat
Types of skin (epidermis)
thick skin (5 layers) (found on palms, soles of feet)
thin skin (4 layers)
keratinized skin
keratin = protein
5 layers of epidermis
stratum germinativum (stem cells)
Stratum spinosum (bundles of protein filaments) (callus)
Stratum granulosum (keratination layer (keratohylalin, keratin)
Stratum lucidum (thick skin only)
Stratum corneum (15-30 layers)
Main cell type in integumentary system
Keratinocyte (stratified squamous epithelium)
Melanocyte
Produce melanin which prevent skin damage by absorbing UV radiation
UV exposure causes melanocytes to increase melanin synthesis and transfer
Skin color is due to the amount of melanin and skin vascularization
Dermis Layers
Papillary layers (under epidermis)
Loose CT proper
contains capillaries and nerve endings or sensory apparatus (Merkel cells and dendrites)
Reticular layer
Dense irregular CT proper
contains blood vessels, hair follicles, nerves, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, collagen fibers
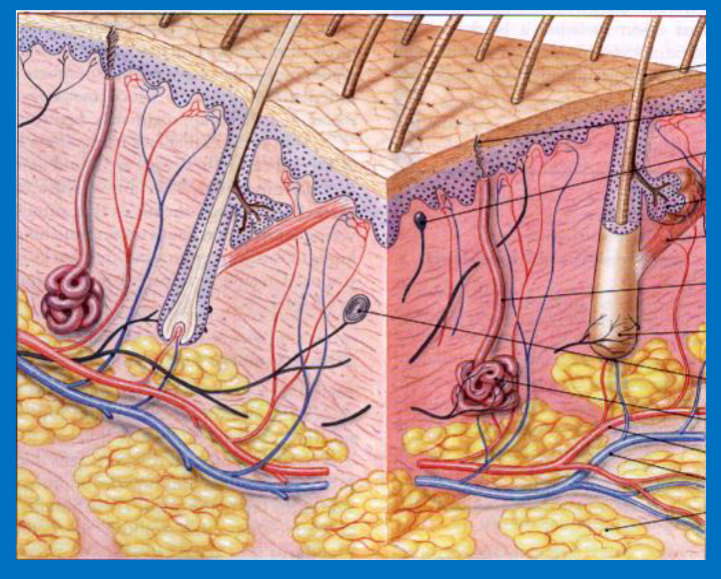
Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer)
Loose CT proper
Contains abundance of fat cells (adipose) — energy store
Distribution/accumulation of adipose tissue in hypodermis is sex dependent
Important in stabilizing the position of the skin in relation to underlying tissue
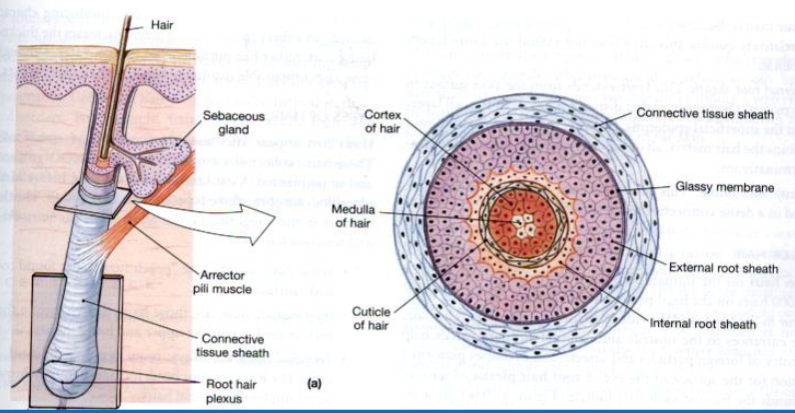
Hair Follicle
An accessory structure of the integumentary system.
Deep into the dermis
features root hair plexus: nerve ending to sense movement of hair
Sebaceous glands and sebaceous follicles
accessory structure: produce sebum: a natural oil secretion that is vital to health of skin and hair
Sweat Glands
apocrine and merocrine glands.
Coil-like structures in the integumentary system, deep in subcutaneous
Merocrine glands: up to 300 glands per square inch in palms and soles of feet
Apocrine in armpits, releasing stinky secretions
Nails
Nail body covers the nail bed
Nail root: production of nail begins
features lunula: small visual at bottom of nail, palish coloration, in area where blood vessels are comprimised
pick up on mineral or vitamin deficiency by feeling and texture (cap refill)
Aging and the Integumentary system
Thin epidermis
slows repair
decreased vitamin D
reduced number of Langerhans cells(immune cells)
Fewer Melanocytes
Pale skin
reduced tolerance for sun exposure
Reduced sweat glands
tendency to overheat
Reduced blood supply
Slow healing
reduced ability to lose heat