ESS SPACED REPETITION
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Stages of the demographic transition model
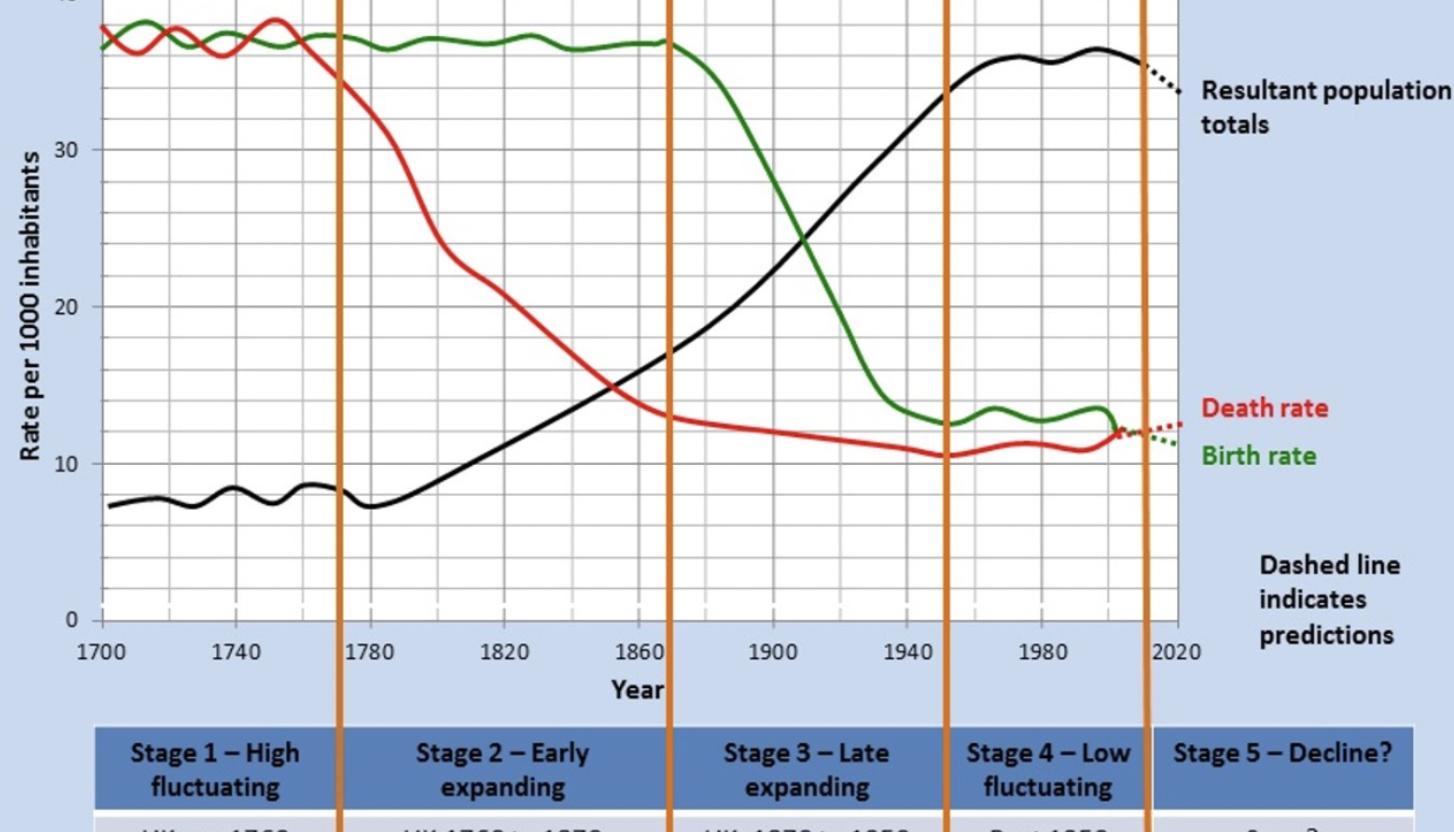
Stage 1: high fluctuating (BR AND DR, low population)
Stage 2: Early expanding (high BR falling DR)
Stage 3: late expanding (falling BR still above DR)
Stage 4: low fluctuating (low BR>LOW DR)
Stage 5: DECLINE (DR>BR)
Doubling time
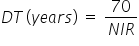
NIR
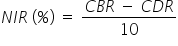
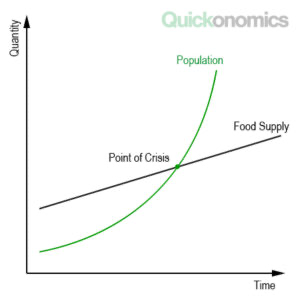
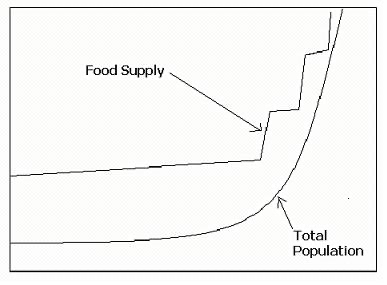
Malthusian theory
Population grows exponentially (doubles rapidly).
Resources grow linearly (slower).
Result: Population outpaces resources, leading to shortages. Shortages only for the poor / food unevenly distributed
Natural checks: Famine, disease, war reduce population.
Preventative checks: Voluntary measures like delayed marriage limit growth.
Criticism: Did not account for technological advances like modern farming. Too simplistic

Boserupian theory
Population pressure drives innovation (e.g., better farming methods).
Human ingenuity increases resource availability.
Dynamic relationship: More people → more innovation → more food.
Result: Population growth can stimulate solutions.
Criticism: Innovation may not always keep up with population growth/ not all areas are as suitable for tech developments. / land may simply be running at maximum output / assumes tec advances are possible

speciation
the generation of new species through evolution, or when populations of a species become isolated and evolve differently from other populations.

factors affecting the sustainability of terrestrial food production systems
scale;
industrialization;
mechanization; led to these small farms being combined into bigger farms, with fields combined to provide large uniform areas for agriculture.
fossil fuel use;
seed, crop and livestock choices;
water use;
fertilizers; greater intensification of products was achieved. They supply additional nutrients such as nitrogen or phosphorus, thus increasing crop yield. fertilizer manufacturing consumes about 3–5 per cent of the world’s annual natural gas supply.
pest control; kill insects that eat crops, again increasing the overall biomass of crop that is harvested.
pollinators;
antibiotics; can lead to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
legislation;
