MCB3020 Lab Midterm Topics
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for MCB3020 Lab Midterm Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What does the Catalase test detect?
Detects the presence of the catalase enzyme, which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. (H₂O₂ → H₂O + O₂)
What is the reagent added after incubation in the Catalase test?
3% hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is added to a bacterial sample to observe the reaction.
What indicates a positive result in the Catalase test?
The formation of bubbles indicates a positive result, showing the presence of catalase enzyme.
What does a negative result look like in the Catalase test?
The absence of bubbles indicates a negative result, meaning the bacteria lack the catalase enzyme.
What is the primary distinction made by the Catalase test?
The Catalase test primarily differentiates Staphylococcus species (which are catalase-positive) from Streptococcus species (which are catalase-negative).
What does the Nitrate test detect?
Detects the ability of an organism to reduce nitrate (NO₃⁻) to nitrite (NO₂⁻) or further to nitrogen gas (N₂).
What reagents are added in the Nitrate test?
Nitrate A (sulfanilic acid) and Nitrate B (dimethyl-alpha-naphthylamine) reagents are added to the bacterial culture after incubation.
What indicates a positive result in the Nitrate test?
A red color development after adding Nitrate A & B reagents indicates the presence of nitrite, meaning the organism reduced nitrate to nitrite.
What happens if there is no color after adding zinc powder in the Nitrate test?
If no color develops after adding zinc powder, it indicates that the organism completely reduced nitrate to nitrogen gas (N₂). Zinc reduces any remaining nitrate to nitrite, which would then react with the reagents to produce a red color if nitrate were still present.
What does the Oxidase test detect?
Detects the presence of cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme in the electron transport chain that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen.
What reagent is used in the Oxidase test?
dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine hydrochloride
What indicates a positive result in the Oxidase test?
A purple or dark blue color development within 10 seconds indicates a positive result, showing the presence of cytochrome c oxidase.
What is a key tip for the Oxidase test?
It's important to use a plastic loop (instead of metal) to transfer the bacteria to avoid false positive reactions due to the metal reacting with the reagent.
What does the Urea test detect?
Detects the presence of urease, an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. ( (NH₂)₂CO + H₂O → 2NH₃ + CO₂).
What reagent is used in the Urea test?
Phenol red is used as a pH indicator in the Urea test to detect the production of ammonia.
What indicates a positive result in the Urea test?
A cerise or pink color indicates a positive result, showing that urease is produced, leading to alkaline conditions due to ammonia production.
What indicates a negative result in the Urea test?
A red, yellow, or orange color indicates a negative result, meaning urea was not hydrolyzed and the medium remains acidic or neutral.
Which species are typically positive in the Urea test?
Proteus species are typically positive in the Urea test due to their rapid urease production.
What does the Gelatin test detect?
Detects the production of gelatinase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes gelatin into amino acids.
What should you do to observe results in the Gelatin test?
After incubation, the gelatin medium must be refrigerated to observe for solidification. Gelatin is liquid at higher temperatures, so refrigeration is necessary.
What indicates a positive result in the Gelatin test?
The gelatin medium remains liquid (not solidified) after refrigeration, indicating that the gelatin has been hydrolyzed by gelatinase.
What indicates a negative result in the Gelatin test?
The gelatin medium solidifies when cold, indicating that the gelatin has not been hydrolyzed.
What does the Phenylalanine test detect?
Detects the production of phenylalanine deaminase, an enzyme that deaminates phenylalanine to phenylpyruvic acid and ammonia.
What reagent is used in the Phenylalanine test?
10% ferric chloride (FeCl₃) is added to the medium after incubation to detect the presence of phenylpyruvic acid.
What indicates a positive result in the Phenylalanine test?
A green color indicates a positive result, showing the presence of phenylpyruvic acid.
What does a negative result look like in the Phenylalanine test?
No color change indicates a negative result, meaning phenylalanine deaminase was not produced.
Which species are characteristic for a positive Phenylalanine test?
Proteus and Providencia species are characteristic for a positive Phenylalanine test due to their ability to produce phenylalanine deaminase.
What does the SIM test detect?
detects three different bacterial activities: hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) production, indole production, and motility.
What reagents are used in the SIM test?
Lead acetate is used as the H₂S indicator, and Kovac's reagent is used to detect indole production from tryptophan.
What indicates a positive result for H₂S in SIM?
A black color in the medium indicates a positive result for H₂S production.
What indicates a positive result for Indole in SIM?
A red ring at the surface of the medium after adding Kovac's reagent indicates a positive result for indole production.
What indicates a positive result for Motility in SIM?
Growth radiating away from the stab line indicates that the organism is motile.
What does the Methyl Red test detect?
Detects mixed acid fermentation, where bacteria produce stable organic acids (such as lactic, acetic, and formic acids) from glucose.
What reagent is used in the Methyl Red test?
Methyl red indicator is added to the medium after incubation to detect the presence of these organic acids.
What indicates a positive result in the Methyl Red test?
A red color indicates a positive result, showing that the organism produces stable organic acids from glucose fermentation, lowering the pH.
What indicates a negative result in the Methyl Red test?
A yellow color indicates a negative result, meaning the organism does not produce enough stable acids to lower the pH.
What does the Voges-Proskauer test detect?
Detects the production of acetoin (acetylmethylcarbinol), a precursor in the production of butanediol, via the fermentation of glucose.
What reagents are used in the Voges-Proskauer test?
VP reagents A (alpha-naphthol) and B (potassium hydroxide) are added to the medium after incubation to detect acetoin.
What indicates a positive result in the Voges-Proskauer test?
A red/pink color development indicates a positive result, showing the presence of acetoin.
What indicates a negative result in the Voges-Proskauer test?
No color change indicates a negative result, meaning acetoin was not produced.
What does the Tryptone Broth test detect?
Detects the ability of an organism to produce indole from the degradation of tryptophan in tryptone broth.
What reagent is used in the Tryptone Broth test?
Kovac's reagent is added to the tryptone broth after incubation to detect indole.
What indicates a positive result in the Tryptone Broth test?
A red ring at the surface of the broth after adding Kovac's reagent indicates a positive result for indole production.
What indicates a negative result in the Tryptone Broth test?
The absence of a red ring indicates a negative result, meaning indole was not produced.
What does the Simmons Citrate test detect?
Detects the ability of an organism to utilize citrate as its sole carbon source, leading to alkaline products.
What indicator is used in the Simmons Citrate test?
Bromothymol blue is used as a pH indicator to detect alkaline conditions resulting from citrate utilization.
What indicates a positive result in the Simmons Citrate test?
A blue color indicates a positive result, showing that the organism utilized citrate, producing alkaline compounds.
What indicates a negative result in the Simmons Citrate test?
A green color indicates a negative result, meaning the organism couldn't utilize citrate, and there is no growth.
What does the Sugar Fermentation test detect?
Detects the ability of an organism to ferment specific carbohydrates, producing organic acids (with or without gas production).
What indicator is used in the Sugar Fermentation test?
Phenol red is used as a pH indicator to detect acid production from carbohydrate fermentation.
What indicates a positive result in the Sugar Fermentation test?
A yellow color indicates a positive result, which means acid production from fermentation. A gas bubble in the Durham tube indicates gas production.
What indicates a negative result in the Sugar Fermentation test?
A red or pink color indicates a negative result, meaning the organism didn't ferment the sugar, and alkaline products may have been produced.
What does Kligler's Iron Agar test detect?
Detects glucose/lactose fermentation and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) production.
What indicators are used in Kligler's Iron Agar?
Phenol red indicates acid production from sugar fermentation, and ferrous sulfate detects H₂S production.
What indicates a positive result in Kligler's Iron Agar for acid?
A yellow color indicates acid production due to the fermentation of glucose and/or lactose.
What indicates a positive result for H₂S in Kligler's Iron Agar?
A black color indicates H₂S production, which reacts with ferrous sulfate to form ferric sulfide.
What does the Litmus Milk test detect?
Detects multiple reactions including acid or alkaline production, gas production, proteolysis, and reduction in litmus milk medium.
What indicator is used in the Litmus Milk test?
Litmus is used as a pH and oxidation-reduction indicator in litmus milk.
What does a positive result look like in Litmus Milk?
Various results are possible: acid clot (acid production and coagulation of milk proteins), alkaline reaction (litmus turns blue), peptonization (proteolysis and clearing of the medium), and reduction (litmus turns colorless).
What does the Starch Agar test detect?
Detects the activity of amylase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes starch into glucose.
What reagent is used in the Starch Agar test?
Iodine solution is used to detect the presence or absence after incubation.
What indicates a positive result in the Starch Agar test?
A clear zone around the bacterial growth indicates that the starch has been hydrolyzed by amylase.
What indicates a negative result in the Starch Agar test?
A blue-black color indicates the presence of starch, meaning it was not hydrolyzed by amylase.
What does the Milk Agar test detect?
Detects the activity of casease, an enzyme that hydrolyzes casein (milk protein).
What is the appearance of a positive result in the Milk Agar test?
A clear zone around the colonies indicates that casease has hydrolyzed the casein, resulting in the clearing of the milk agar.
What does a negative result look like in the Milk Agar test?
No clear zone around the colonies indicates that casease was not produced, and the casein remains intact.
What does the Lipase test detect?
Detects the activity of lipase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes lipids (fats) into fatty acids and glycerol.
What indicates a positive result in the Lipase test?
A clear zone around the growth on the lipid medium indicates that lipase has hydrolyzed the lipids.
What indicates a negative result in the Lipase test?
No clear zone around the growth indicates that lipase was not produced, and the lipids remain intact.
Is Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA) selective or differential?
Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA) is a selective medium used to inhibit the growth of Gram-negative bacteria.
What is the inhibitor in PEA?
Phenylethyl alcohol inhibits the DNA synthesis of Gram-negative organisms.
What does PEA select for?
PEA selects for the growth of Gram-positive bacteria by inhibiting Gram-negative bacteria.
What is a positive result on PEA?
The presence of colonies indicates that the organism is Gram-positive and can grow on PEA.
What is a negative result on PEA?
The absence of growth indicates that the organism is Gram-negative and inhibited by PEA.
Is MacConkey Agar selective or differential?
MacConkey Agar is both selective and differential, used to isolate and differentiate Gram-negative bacteria.
What are the inhibitors in MacConkey Agar?
Crystal violet and bile salts inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria.
What does MacConkey Agar select for?
MacConkey Agar selects for Gram-negative bacteria by inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria.
What is the indicator in MacConkey Agar?
Neutral red is a pH indicator that differentiates lactose fermenters from non-fermenters.
What does MacConkey Agar differentiate?
MacConkey Agar differentiates lactose fermenters from non-lactose fermenters based on their ability to ferment lactose.
What does a positive result look like on MacConkey Agar?
Growth on MacConkey Agar indicates a Gram-negative organism. Pink or red colonies indicate lactose fermentation, suggesting the production of acid.
What is a negative result on MacConkey Agar?
No growth indicates a Gram-positive organism. Colorless colonies indicate a non-lactose fermenter.
Is Blood Agar selective or differential?
Blood Agar is a differential medium used to differentiate bacteria based on their hemolytic capabilities.
What is the indicator in Blood Agar?
Red blood cells in the agar act as an indicator to visualize hemolysis.
What does Blood Agar differentiate?
Blood Agar differentiates bacteria based on their ability to cause hemolysis: beta (complete), alpha (partial), and gamma (none).
What is a positive result on Blood Agar?
A clear zone around the colonies indicates beta hemolysis, which is the complete lysis of red blood cells.
What is a negative result on Blood Agar?
No change around the colonies indicates gamma hemolysis, which is the lack of hemolysis.
Is Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar selective or differential?
both selective and differential, used for the isolation and differentiation of Gram-negative bacteria.
What are the inhibitors in EMB Agar?
Eosin and methylene blue dyes inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria.
What does EMB Agar select for?
EMB Agar selects for the growth of Gram-negative bacteria by inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria.
What is the indicator in EMB Agar?
Eosin and methylene blue differentiate lactose fermenters from non-fermenters.
What does EMB differentiate?
differentiates lactose fermenters based on their ability to ferment lactose and produce acid, which causes color changes in the colonies.
What does a positive result look like on EMB Agar?
Dark purple/black colonies = lactose fermenter;
Metallic green sheen = strong fermenter (e.g., E. coli)
What is a negative result on EMB Agar?
No growth = Gram-positive
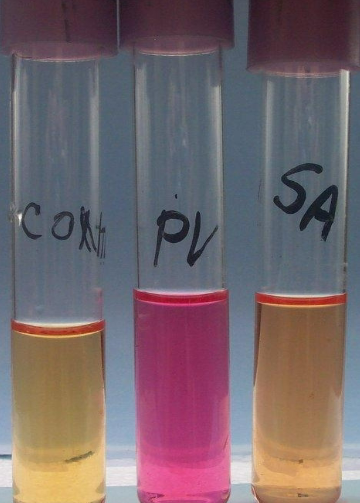
What test is this?
Urease test

What test is this?
Phenylalanine test

What reagent are used in this test?
10% Ferric Chloride (FeCl3)

What test is this?
SIM- Sulfide, Indole, Motility

What reagents are used in this test?
Indole uses Kovac’s reagent, Sulfide already has reagents incorporated in the medium (Fe), and Motility does not require a specific reagent.

What test is this?
Methyl Red test MR
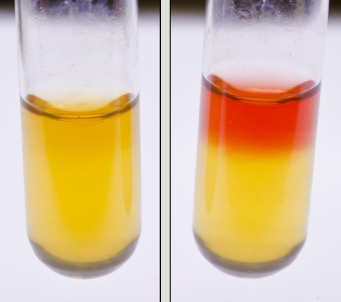
What test is this?
Voges-Proskauer (VP)