Week 4: Random sampling error, bias, confounding
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:27 PM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
strong evidence:
1) lowest possible random sampling error
2) based on a good design
- high validity: of the study and measures association, Not the validity of the measure of events or exposure
2) based on a good design
- high validity: of the study and measures association, Not the validity of the measure of events or exposure
2
New cards
Internal Validity
- do the observed results accurately reflect the true association?
*if a study lacks internal validity, external validity is irrelevant
*we do not compromise internal validity in an effort to achieve external validity (generalizability)
*if a study lacks internal validity, external validity is irrelevant
*we do not compromise internal validity in an effort to achieve external validity (generalizability)
3
New cards
External validity (generalizability)
- to whom can results be applied?
- requires internal validity
Will be achieved by a sample that represents the target population
- requires internal validity
Will be achieved by a sample that represents the target population
4
New cards
observing an association
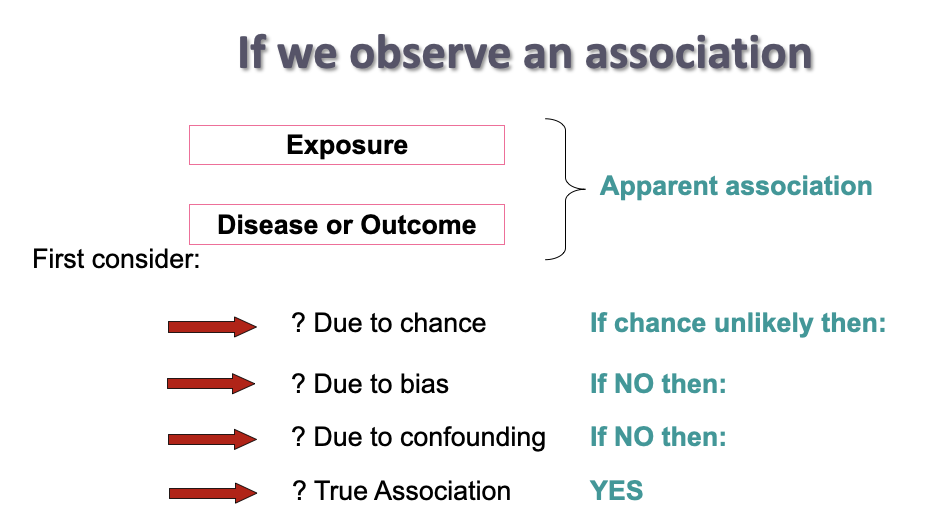
5
New cards
Validity is:
having fewer errors
error = measured value - true value
sources of error:
- chance (random sampling error)
- bias
- systematic error in selection of participants and/ or measurement
error = measured value - true value
sources of error:
- chance (random sampling error)
- bias
- systematic error in selection of participants and/ or measurement
6
New cards
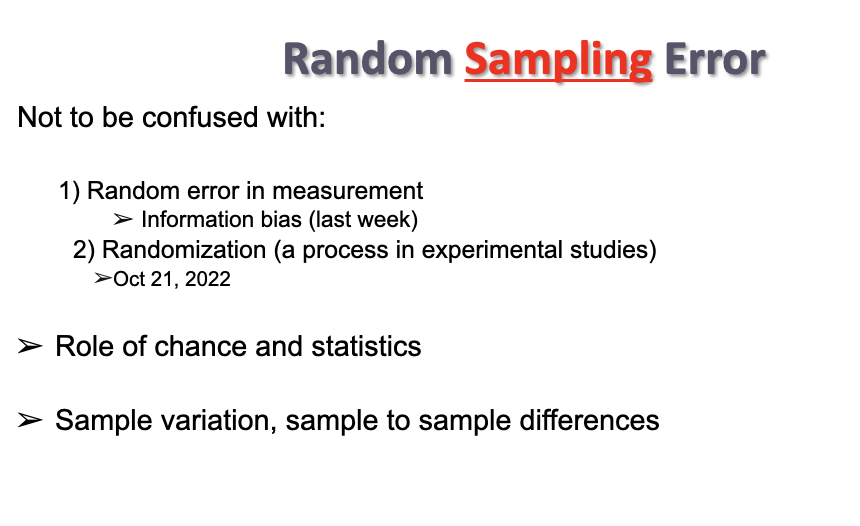
Random sampling error
- random
- sample variation, sample to sample differences
p value shows how likely the observed results might be due to chance
-best way to minimize random sampling error is to increase sample size
- sample variation, sample to sample differences
p value shows how likely the observed results might be due to chance
-best way to minimize random sampling error is to increase sample size
7
New cards
P value
- NOT an error
- calculated as a guide for rejection or acceptance of null hypothesis
- calculated as a guide for rejection or acceptance of null hypothesis
8
New cards
Bias
refers to a systematic error in the design or conduct of a study
- when bias occurs in a study, the observed association between the exposure and outcome will be different from the true association
- when bias occurs in a study, the observed association between the exposure and outcome will be different from the true association
9
New cards
confidence interval
how confident we are, that our research does not include bias
large sample size - confidence interval smaller
large sample size - confidence interval smaller
10
New cards
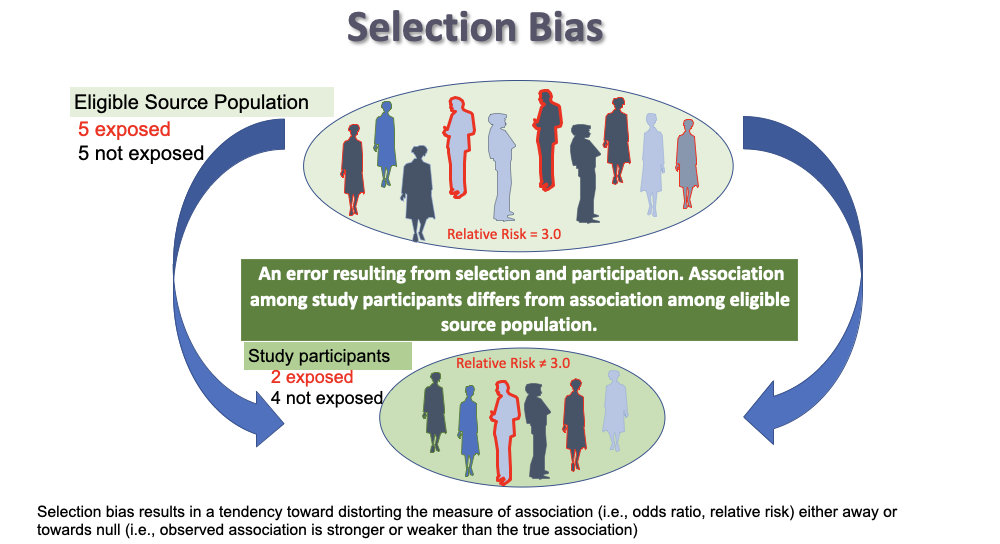
Selection bias
refers to a systematic study error in the way participants are selected or retained in a study
* occurs when individuals have different probabilities of being included or retained in the study according to the exposure and/or outcome
* if you see the word __**recruit**__ -----> selection bias
\*PARTICIPATION DIFFERS ON EXPOSURE AND DISEASE
* occurs when individuals have different probabilities of being included or retained in the study according to the exposure and/or outcome
* if you see the word __**recruit**__ -----> selection bias
\*PARTICIPATION DIFFERS ON EXPOSURE AND DISEASE
11
New cards
Types of selection bias:
1. Inappropriate control selection (control-selection bias)
2. Differential participation (case-control cohort)
3. Differential loss to follow up (cohort, experimental)
2. Differential participation (case-control cohort)
3. Differential loss to follow up (cohort, experimental)
12
New cards
Volunteer bias
Volunteers are more health-conscious or from a different socio-economic group
- Differential exposure
-Effect of interventions for enhancing physical activity in older adults
- Differential exposure
-Effect of interventions for enhancing physical activity in older adults
13
New cards
Non-response bias
those suffering from a disease with a particular belief
- differential outcome
- differential outcome
14
New cards
membership bias
Healthy worker effect
eg. Service in Vietnam reduced mortality rates
eg. Service in Vietnam reduced mortality rates
15
New cards
Loss to follow-up bias
in clinical trials or longitudinal studies, the sickest usually leave the study early
16
New cards
Reducing selection bias
little or nothing can be done to fix selection bias once it has occurred
* CANNOT be reduced by increasing sample size
* CANNOT be reduced by increasing sample size
17
New cards
information bias
Interviewer asks to many questions - answers become inaccurate
eg. measurement error
eg. measurement error
18
New cards
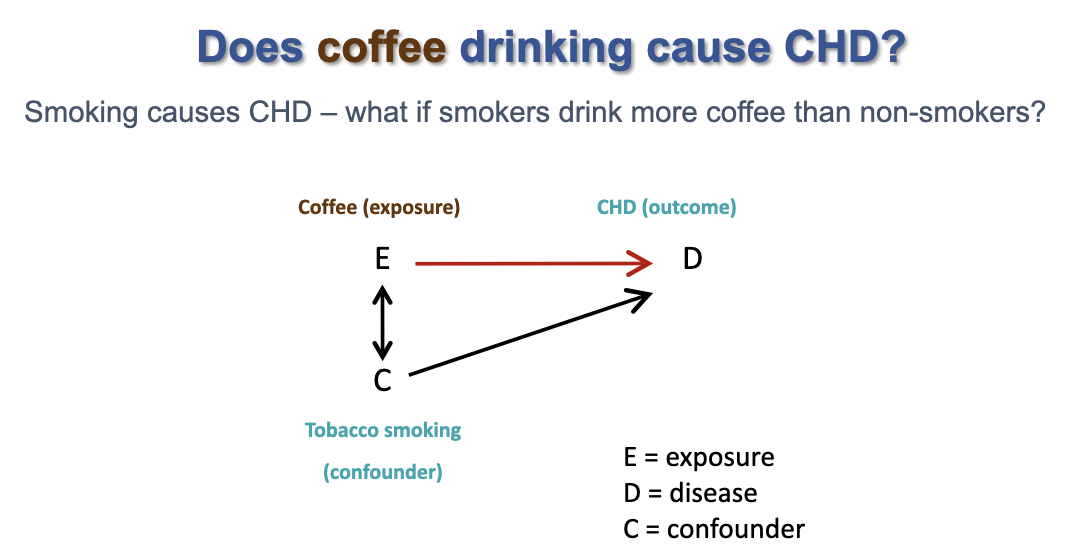
Confounding bias
- occurs when the exposed group and the unexposed group are not exchangeable
19
New cards
Defining a confounding variable:
1. Causally associated with the outcome (a true risk factor)
2. non causally or causally associated with the exposure
3. not an intermediate in the causal pathway between exposure and outcome
2. non causally or causally associated with the exposure
3. not an intermediate in the causal pathway between exposure and outcome
20
New cards
how to identify a confounding variable
- literature review of comparable studies
- consult experts
- statistical tests
- consult experts
- statistical tests
21
New cards
How to deal with confounding, at design stage:
1. restriction
- limit study inclusion criteria
2. matching
- produce case and control groups that have similar characteristics
3. randomization
- limit study inclusion criteria
2. matching
- produce case and control groups that have similar characteristics
3. randomization
22
New cards
How to deal with confounding, at the analysis stage:
1. standardization
- age standardization is in fact 'adjustment' for age
2. stratified analysis
3. confounding factor in a multivariate regression model
- age standardization is in fact 'adjustment' for age
2. stratified analysis
3. confounding factor in a multivariate regression model
23
New cards
So the big 3 threats to validity:
CBC
1) Chance
2) Bias - selection/information
3) confounding
1) Chance
2) Bias - selection/information
3) confounding
24
New cards
low P-value vs High P-value
low = more likely results are valid and reliable (not up to chance)