BSCI222: Mitosis + Meiosis
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Explain mitosis in prokaryotes
simple—generally single DNA; separates replicated copy with replicating cells
Explain mitosis in eukaryotes
complicated by division of genome organized into chromosomal pieces
complicated by two copies of chromosomes (homologous chromosomes)
What is a karyotype?
An individual’s complete set of chromosomes
What are two important chromosomes characteristics?
Centromere location (metacentric, subcentric, acrocentric, telocentric) and banding patterns
What are homologous chromosomes?
Similar genes but different chromosomes (maternal and paternal chromosomes)
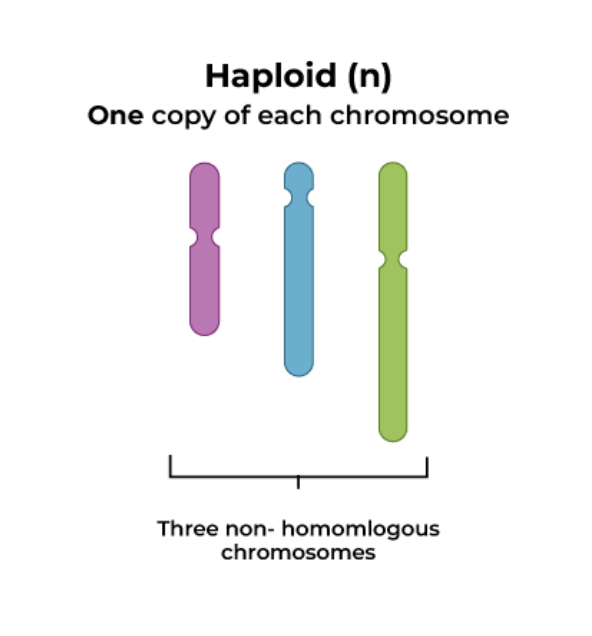
What are haploid cells?
number of unique chromosomes = n
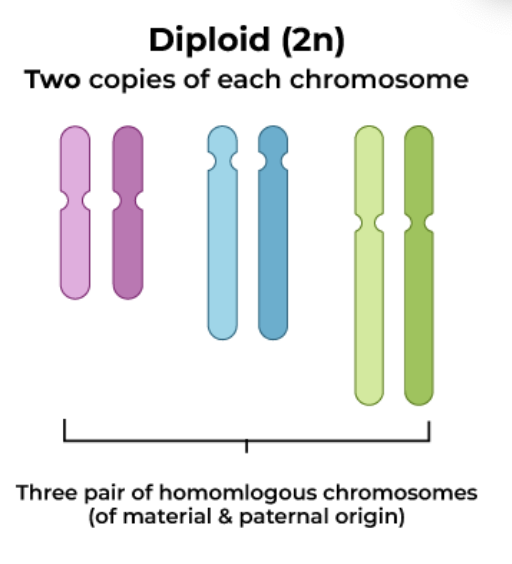
What are diploid cells?
2n chromosomes (each chromosome and its homologous pair)
What are sister chromatids?
Exact copies made from DNA synthesis (S phase)
What is mitosis?
Part of cell cycle!
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
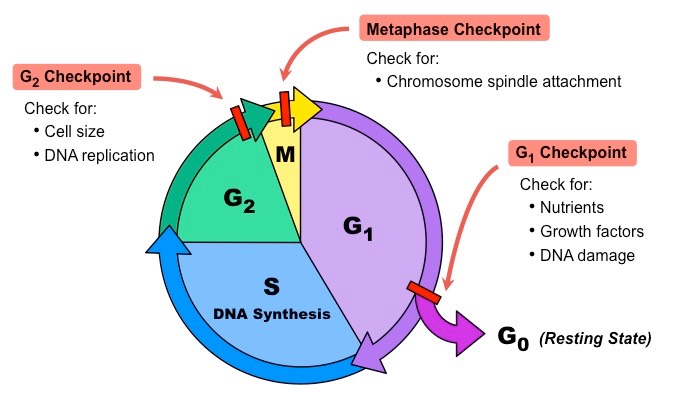
What are the interphase phases?
Four subphases:
G1: Cell growth (checkpoint for nutrients, growth factors, DNA damage)
S: DNA synthesis to make sister chromatids
G2: Continued growth of cell (checkpoint for cell size and no errors in DNA replication)
G0: Rest
What is prophase?
Chromosomes condense, spindle microtubules form centrosomes, nuclear envelope break down
What is metaphase?
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate in a line, each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber from opposite centrosomes
What is anaphase?
Cohesin proteins binding the sister chromatids together break down
Separation of sister chromatids (now chromosomes) to opposite sides due to pulling of spindle fibers at kinetochores
What is telophase?
Chromosomes reach opposite sides and decondense
Nucelar envelope reforms
What is cytokinesis?
Separation into separate cells
Plant cells: a cell plate separates daughter cells
Animal cells: a cleavage furrow separates daughter cells
What is are possible variations mitosis?
Skipping cytokinesis can produce multinucleate cell (multiple nuclei with 2n in one cell)
Skipping mitosis altogether or anaphase gives a nucleus with >2n chromosomes (synthesizing multiple copies of DNA in one nucleus)
What’s an example of what happens when there is a mistake in mitosis?
Leads to the formation of mosaic organism-differences between cells
What is meiosis?
Chromosome separation during gamete formation (gremline cells undergo mitosis)
What’s the purpose of meiosis?
To create haploid gametes
separate homologous chromosomes AND sister chromatids (create diversity in progeny)
What are the stages of meiosis?
Starts in cell cycle like mitosis (to form sister chromatids)
Two cell divisions via meiosis I and meiosis II
What happens in meiosis I?
Homologous chromosomes separate!
What happens in meiosis II?
Sister chromatids separate!
What is the synaptonemal complex?
Physical pairing of homologous chromosomes (mediate synapsis and recombination)
What is the chiasmata?
Physical connection after recombination that holds together individual chromatids of homologous chromosomes
What does crossing over do?
Homologous chromosomes (or more specifically, sister chromatids) are no longer exact; creates genetic variation
What is interkinesis?
The resting phase between meiosis I and meiosis II
How is genetic diversity created in gametes?
Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes
Crossing over on homologous chromosomes (recombination)
What is cohesin?
Holds the two sister chromatids like staple!
What is separase?
Digests the cohesin
What is shugoshin?
Protects cohesin at centromeres of sister chromatids in meiosis I
What are mistakes in meiosis?
Nondisjunction in anaphase I or II produces gametes that are n+1 (one extra chromosome) and n-1 (one less chromosome) “aneuploidy”
What is parthenogenesis?
Reproduction without male (can result from failure or reversal of meiosis or makes 2N cell from egg alone)
What are the different chromomsal shapes?
Given by where the centromere is:
Metacentric - in the middle
Submetacentric - not exactly the middle
Acrocentric - near the end
Telocentric - at the end
What is nondisjunction?
Failure of the chromosomes to separate during anaphase
What is Mendel’s law of segregation?
States that the two alleles for a gene separate from each other in the formation of gametes.
What is Mendel’s law of independent assortment?
Alleles of different genes segregate independently of one another during gamete formation.