CBL 4: The Poorly Performing Horse
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lung
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What are the 3 equine olympic disciplines?
dressage, show jumping and eventing

What discipline?
Polo

What discipline?
Showing

What discipline?
racing

What discipline?
endurance

What discipline?
dressage

What discipline?
driving

What discipline?
show jumping

What discipline?
vaulting

What discipline?
eventing
What horse breed is commonly used for racing?
thoroughbred
What horse breed is commonly used for polo?
thoroughbred
What horse breed is commonly used for endurance?
Arab horses
What is the typical age when horses start flat racing?
2-4 yrs
What is the typical age when horses start national hunt racing?
4-5 yrs
Do flat or national hunt races involve the horse jumping obstacles?
national hunt
How long are national hunt races typically?
2-4 miles
How long are flat races typically?
5 furlongs to 2.5 miles
When is the main season of flat racing?
mid march to mid november
When is the main season of national hunt racing?
november to end of april
Are flat or national hunt races typically faster?
flat
How are flat races started?
using a tape barrier
How are national hunt races started?
stalls
What are horses vaccinated against?
equine influenza, tetanus, equine herpes virus and rota virus
When should horses first be vaccinated against equine influenza?
5 months, 21-92 days later, 150-215 days after
How often should equine influenza booster vaccines be given?
annually
When should horses be given their first tetanus vaccines?
5 months
When should horses be given their first tetanus booster vaccine?
12 months (and then at 2 yr intervals)
When should horses get their first equine herpes virus vaccine?
5 months, 4-6 weeks after
When are the booster vaccines for equine herpes virus?
6 month
What horses are recommended to be vaccinated against rota virus?
broodmares
When are broodmares due rota virus vaccines?
8th,9th and 10th month pregnancy
Define ‘gelding’
neutered male horse which has had its testicles surgically removed
Why may horses be gelded?
calmer temperament, less sexually aggressive, easier to train, better suited to riding
What does ‘poor performance’ mean?
when a ridden horse’s athletic abilities fall short of the riders’ expectation
How may air quality be improved in a stable?
windows, ventilation slats, high roofs
What do windows and ventilation slats do to improve air quality?
provide sufficient air circulation without draughts being created
Name the 4 standard gaits of the horse in the UK
walk, trot, canter and gallop
Define the footfall sequences for the horse’s gait
left hind, left front, right hind, right front
Why/when is using animals in sport and for human pleasure acceptable?
supports people’s livelihoods, provide opportunities for high standards of vet care, health benefits
When is using animals in sport and for human pleasure not acceptable?
when it compromises animal welfare
What are the 5 domains for horse’s daily management which need to be followed to ensure horse’s welfare is being managed to a high level?
nutrition, environment, health, behavioural interactions and mental state
What inspiratory noise is associated with vocal cord collapse?
whistle
What inspiratory noise is associated with left arytenoid cartilage collapse?
roar
What expiratory noise is associated with rostral plate (soft palate) instability?
gurgle
What connect the laryngeal cartilages to eachother?
intrinsic muscles of the equine larynx muscles
What are the intrinsic muscles of the equine larynx muscles innervated by?
laryngeal nerve
What is laryngeal hemiplegia?
damage to the laryngeal nerve
What is the term used to describe damage to the laryngeal nerve?
laryngeal hemiplegia
What is laryngeal hemiplegia caused by?
paralysis of the dorsal cricoarytenoid muscle
Which side of the horse does laryngeal hemiplegia usually happen on?
left
What can laryngeal hemiplegia cause?
roaring
What is used to check the diagnosis of laryngeal hemiplegia?
endoscopy
What surgery can be used to help laryngeal hemiplegia?
tie back surgery (prosthetic laryngoplasty)
What happens to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles during inspiration?
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract
What happens to volume of the thoracic cavity during inspiration?
increases
What happens to alveolar pressure during inspiration?
decreases (so air moves into lungs down pressure gradient)
What happens to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles during expiration?
relax
What happens to alveolar pressure during inspiration?
increase (forces air out of lungs)
What happens to volume of the thoracic cavity during expiration?
decreases
Where do the guttural pouches extend from?
eustachian tubes connecting pharynx and middle ear
What are the guttural pouches lined with?
thin pseudostratified ciliated epithelial mucous membrane
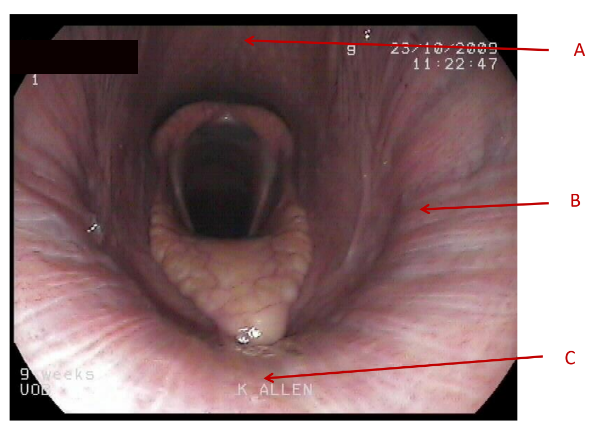
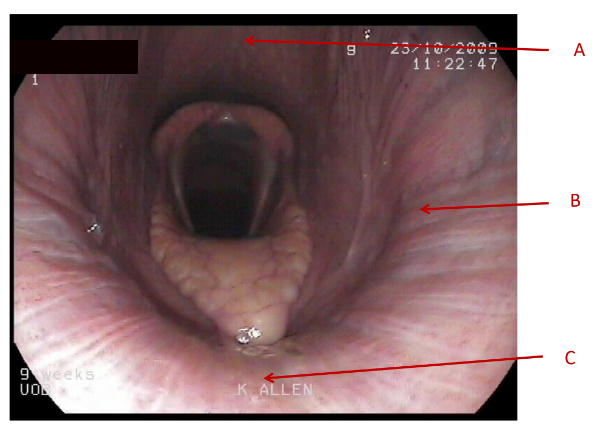
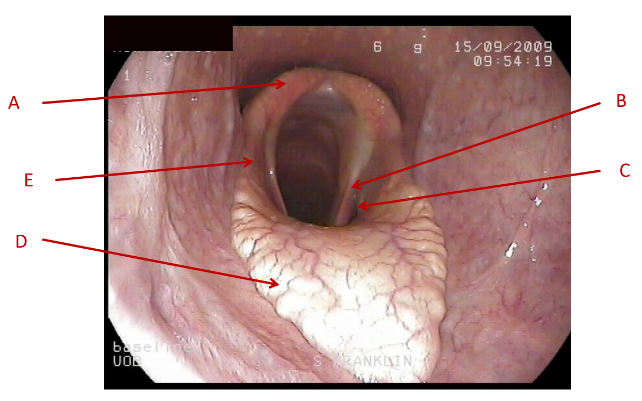
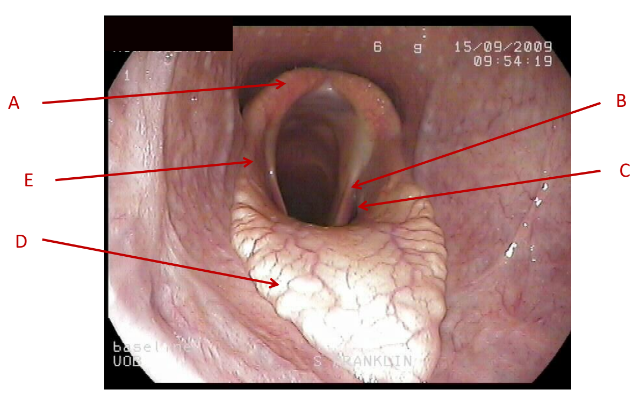
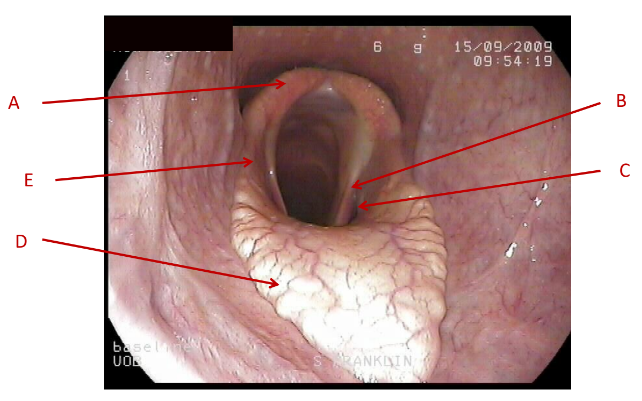
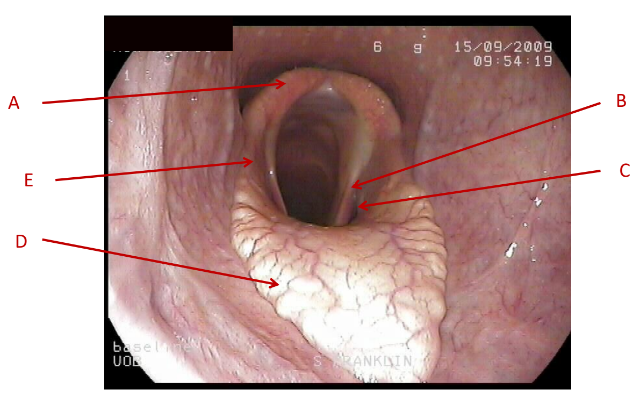
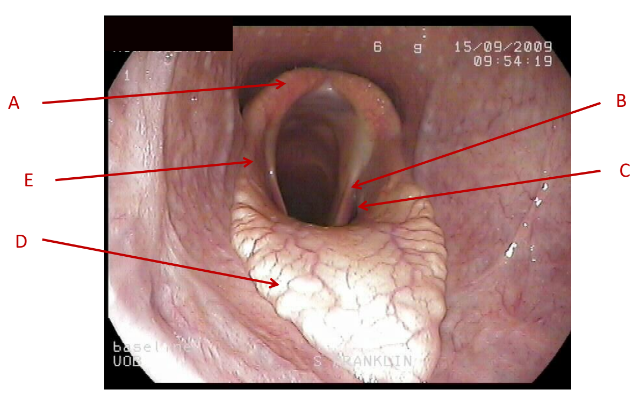
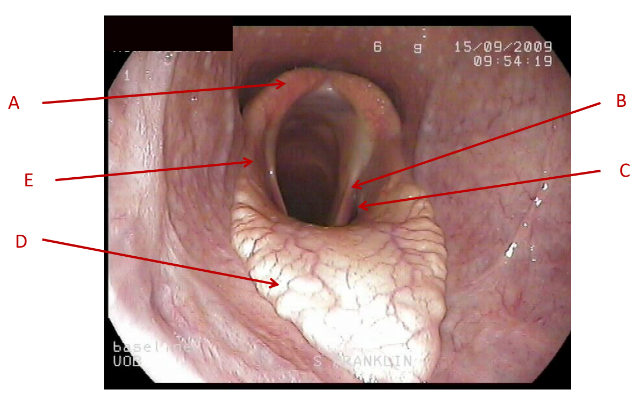
A
Dorsal pharyngeal wall
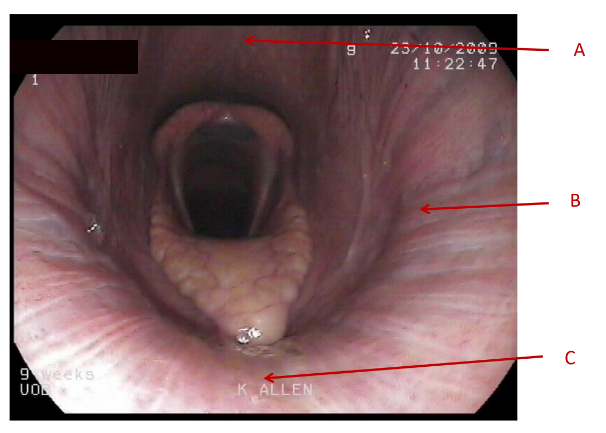
B
lateral pharyngeal wall
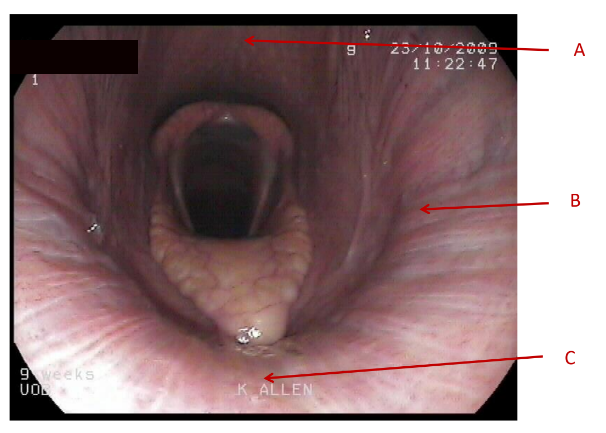
C
Soft palate
What does this image show the anatomy of?
pharynx
What does this image show the anatomy of?
larynx
A
arytenoid cartilage
B
vocal fold
C
ventricle
D
epiglottis
E
aryepiglottic fold
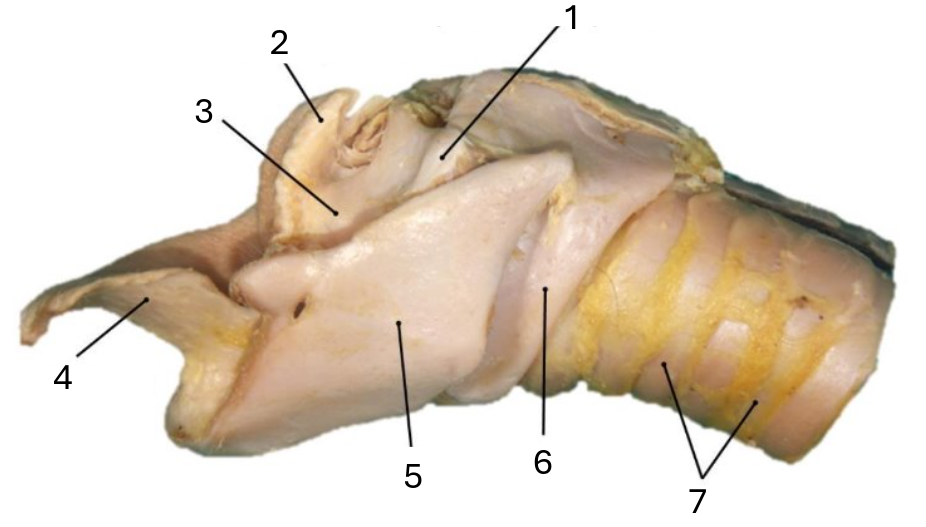
1
muscular process of arytenoid
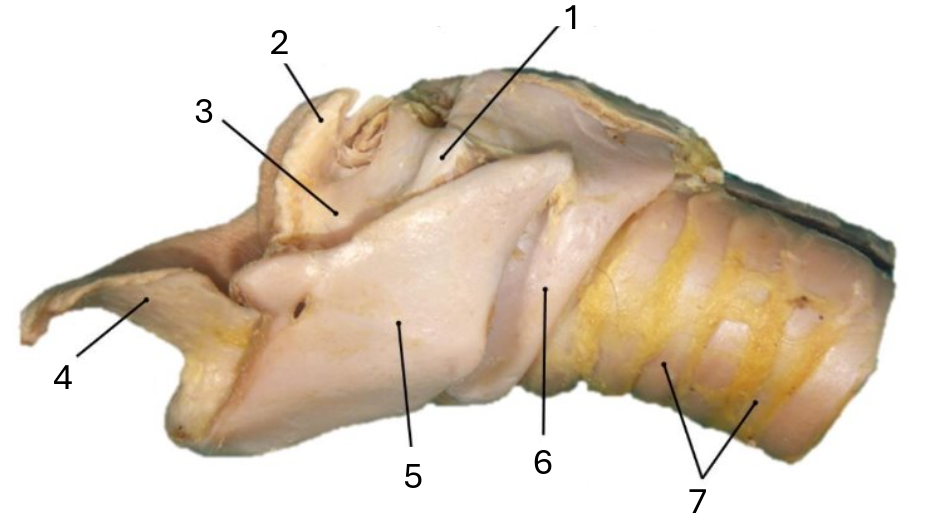
2
corniculate process of arytenoid
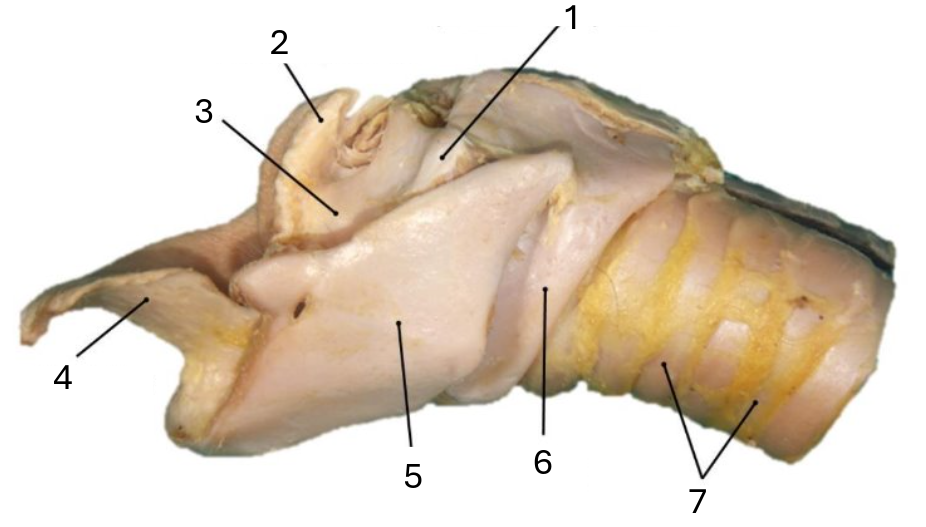
3
arytenoid cartilage
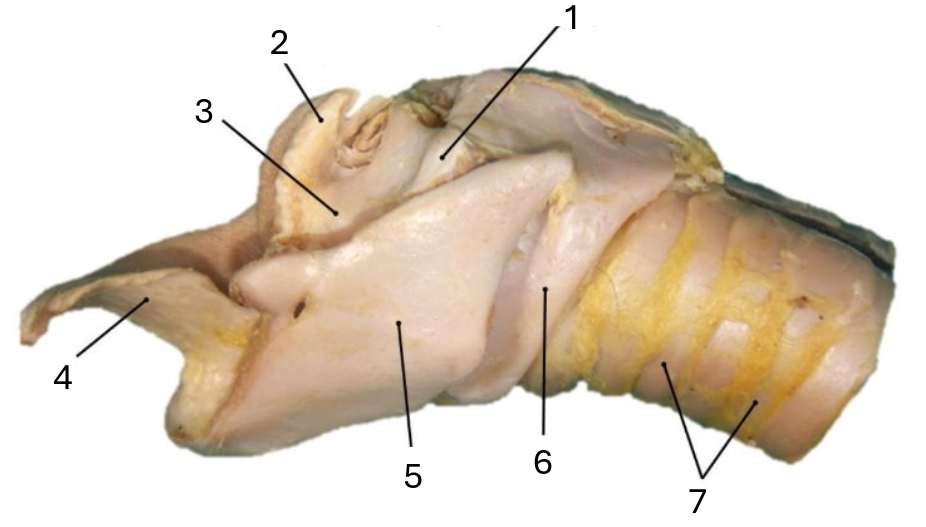
4
epiglottic cartilage
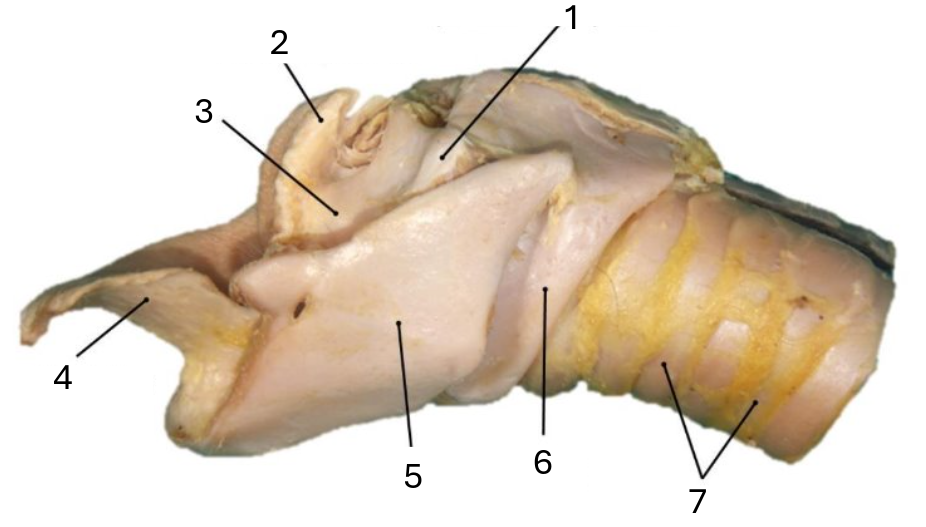
5
thyroid
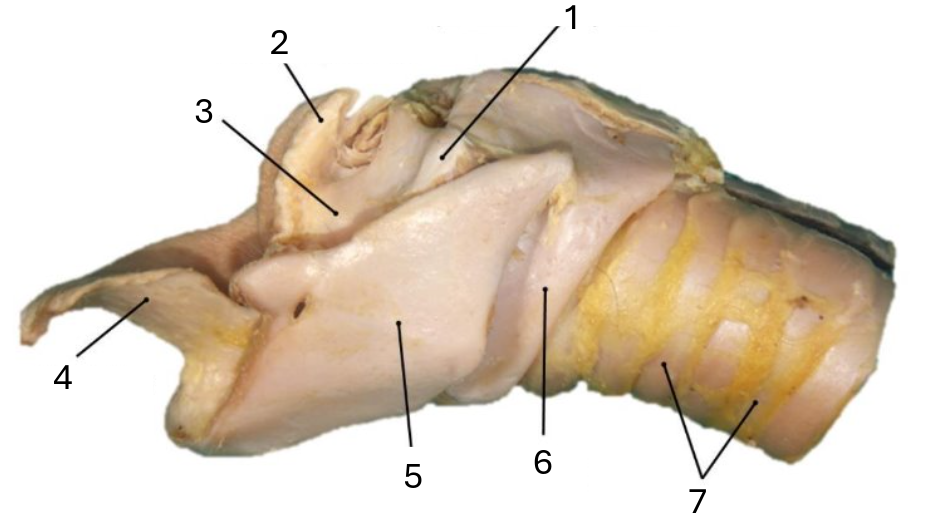
6
cricoid
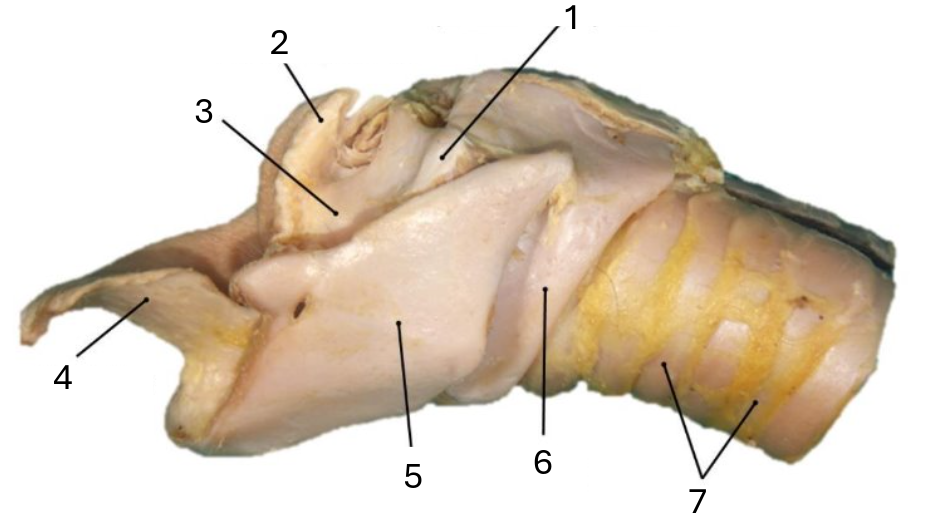
7
tracheal rings
What innervates the cricothyroid?
cranial laryngeal nerve (branch of vagus)
What innervates all laryngeal muscles (except cricothyroid)?
recurrent laryngeal nerve (branch of vagus)
How many lobes does the right lung of a horse have?
3
How many lobes does the left lung of a horse have?
2
What are the 2 lobes of the left lung of a horse?
cranial and caudal
What are the 3 lobes of the right lung of a horse?
cranial, caudal and accessory
How do the lobes of the right lung of a horse differ from that of other species?
no middle lobe
Name the lobes of the left lung of a dog, ruminant and pig
cranial (cranial and caudal) and caudal
Name the lobes of the right lungs of dogs, ruminants and pigs
cranial, caudal, middle and accessory
Which species lungs are lobulated?
pig
Which species are considered obligate nasal breathers?
horses, rabbits, rodents, cats
Define the term respiration
breathing through the lungs involving inhalation and exhalation
What does the pharyngeal and laryngeal anatomy of the horse consist of?
hyoid apparatus, larynx and guttural pouch
What 5 bones is the hyoid apparatus in the horse composed of?
stylohyoid, epihyoid, ceratohyoid basihyoid, thyrohyoid,
What 4 main cartilages does the larynx of the horse consist of?
epiglottis, thyroid, arytenoid and cricoid cartilages
Where is the epiglottis of the horse located
retrovelar (behind the soft palate)
What does the guttural pouch of the horse conssit of?
two air-filled sacs located deep within the head
What features of the pharyngeal and laryngeal anatomy of the horse can be palpated on physical examination?
guttural pouches, larynx, trachea, muscular processes of the cartilage of the arytenoids
Where is the soft palate positioned in dogs, cats and ruminants?
on tongue with free edge rostral to epiglottis
What does the horse’s retrovelar epiglottis block air from entering via?
oropharynx
How is the soft palate positioned in humans and other athletic species?
not in tight contact with epiglottis (allowing air to enter from both nasopharynx and oropharynx)