Biology-Chapter 6-Lipids, Membranes and the first Cells
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
Plasma membrane can also be referred to as what?
cell membrane
Plasma membrane is composed of ( ) and separates life from nonlife
lipids
The lipids in cell membrane serves as ( ) barrier
selective
Lipids in plasma membranes allow entry of ( ) needed by the cell and keeps ( ) out of cell
materials
damaging materials
The lipids in the cell membrane allows for the ( ) of a particular environment inside the cell compared to outside the cell
maintenance
The lipids in the cell membrane ( ) chemical reactions necessary for life, they allow ( ) to occur by sequestering appropriate chemicals
facilitate
chemical reactions
what does sequester mean?
isolate
( ) proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates, most lipids are ( ) polymers
unlike
not
lipid structure ( ) widely
varies
Fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids and steroids are all ( )
lipids
Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
Lipids are hydrophobic compounds due to their high ( ) content
carbon-hydrogen
Why are hydrocarbons hydophobic?
They’re nonpolar, the difference between their electronegativities is small
lipids are ( ) in water
insoluble
Are lipids hydrocarbons?
Mostly yes
Hydrophobic lipids in the fur of aquatic mammals- ( ) them from the elements
protects
Fatty acids are simple lipids made of ( ) chain bonded to polar ( ) function group
hydrocarbon
carboxyl
Fatty acids can be saturated or ( )
unsaturated
Fatty acids are ( ) hydrocarbon chains joined to a ( ) group
unbranched
carboxyl
What is a carboxyl group?
COOH
In ( ) fatty acids kinks may form in hydrocarbon chains
unsaturated
What does saturated mean?
carbons in the long chain are all ‘saturated’ with hydrogens
What does unsaturated mean?
carbons in the long chain are not ‘saturated’ with hydrogens
Unsaturated carbons are caused by what?
double bonds exist between carbons
Name some saturated lipids
butter
beeswax
Name some unsaturated lipids
Safflower
Olive oil
Canola oil
What hydrogenation?
manufacturing process that takes polyunsaturated fats and turns them into saturated fats
Hydrogenation makes ( ) fats
trans
Cis means what?
same side
Trans means what?
opposite side
What are essential Fatty acids?
“essential”- body cannot produce, and one must consume to obtain
Give an example of an essential fatty acid
alpha-linolenic acid, an example of an omega-3 fatty acid
Fats ( ) energy than carbohydrates
store more
Glycerol + fatty acids are joined by
Ester linkages
Fats and oils are polymers
false, they are not
What is another name for triacyclglycerols?
triglycerides
Glycerol + Fatty acids make what?
triacyclglycerol
Glycerol + fatty acids is caused by hydrolysis or dehydration reaction?
condensation reaction
A fatty acid as increased ration of bonds with higher ( ) energy than a carbohydrate
potential
Steroids are in the family of ( )
lipids
Steroids are distinguished by bulky, ( )
four-ring structure
Steroids differ from one another by ( ) attached to carbons in rings
functional groups
cholesterol is a component of ( )
plasma membranes
Give some examples of steroids
estrogen
testosterone
cholesterol
Phospholipids are made of what?
glycerol
two fatty acids
phosphate
charged or polar molecule
phospholipids have a ( ) head and ( ) tail
hydrophilic
hydrophobic
Are phospholipids amphipathic?
yes
What does amphipathic mean?
having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts
Lipid micelles are what?
tiny spherical aggregates of a phospholipid with single fatty acid chain
What is cell aggregation?
binding of cells of the same type
What are lipid bilayers?
from when phospholipids align in paired sheet, have two tails
Lipid micelles and lipid bilayers both form ( )- no energy is needed to occur
spontaneously
Hydrophilic heads of lipid micelles and bilayers interact with ( )
water
Hydrophobic tails of lipid micelles and bilayers interact with ( )
one another
Liposomes are ( ) membrane bound vesicles
artificial
phospholipids form a spherical structure when added to ( ) solution
aqueous
Two phospholipid layers are called what?
phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid bilayer creates a barrier that does what
Separated the outside from inside
Molecules are in constant ( )
motion
Molecules will not move to occupy the space provided
false
molecules in constant motion is an example of what energy?
kinetic energy
What is Brownian motion?
the erratic random movement of microscopic particles in a fluid, as a result of continuous bombardment from molecules of the surrounding medium.
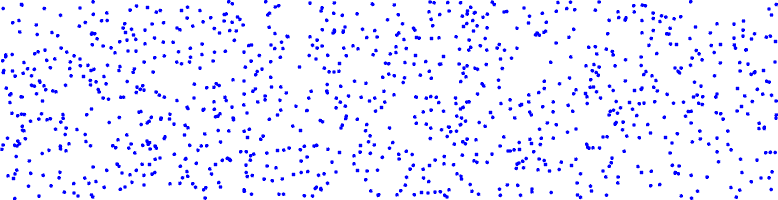
This is an example of what concentration gradient ?
no concentration gradient
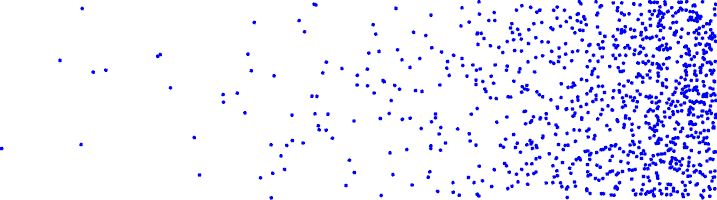
From left to right what is the concentration gradient? Is it a concentration gradient?
low concentration to high concentration
yes its a concentration gradient
When a substance goes from high concentration to an area where it is low concentration, we say it goes ( ) or ( ) its concentration gradient
down
with
When a substances goes from where it is in low concentration to a region where it is in high concentration, we say that it goes ( ) or ( ) its concentration gradient
up
against
What is electrochemical gradients?
occurs when both concentration gradients and electrical gradients are present and drive the movement of ions
Electrochemical gradients do what?
create a difference in charge across the membrane
Electrochemical gradients are another form of ( ) energy
potential
What is diffusion?
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
In diffusion what moves, the solute or solvent?
solute
What is diffusion driven by?
driven by random movement (kinetic energy)
Is diffusion spontaneous or nonspontaneous
A passive process-it is spontaneous-no energy needed
The cell membrane is not dynamic
False it is dynamic
phospholipids are ( ) in place, but are fluid
NOT fixed
Phospholipids are in constant lateral motion, but rarely ( ) to the other side of the bilayer
flip
Phospholipids move ( ) about the bilayer
laterally
Phospholipids bilayers have ( ) permeability
selective
( ) or ( ) molecules move across phospholipid bilayers quickly
small
nonpolar
( ) or ( ) substances cross slowly, if at all
charged
large polar
Oxygen a ( ) molecules moves ( ) across bilayers
small nonpolar
quickly
Glucose a ( ) molecule moves ( ) across bilayer
large polar
slower
Small ions have a ( ) permeability
low
Many factors influence a membranes ( )
permeability
What affects a membranes permeability
-Length of hydrocarbon tails
-Saturation state of hydrocarbon tails
-Temperature
-Presence of cholesterol molecules in membrane
Lipid bilayer with short and unsaturated hydrocarbon tails have ( ) permeability
higher
Lipid bilayer with long and saturated hydrocarbon tails have ( ) permeability
lower
Membrane fluidity ( ) as temperature drops
decreases
As temperature drops molecules in bilayer move more ( ), and hydrophobic tails do what?
slowly
hydrophobic tails pack together more tightly
As temperature drops this causes decrease membrane fluidity which causes ( ) permeability
decreased
The presence of cholesterol embedded in the membrane ( ) fluidity when cold and ( ) fluidity when warm
increases
decreases
What is equilibrium?
occurs when molecules or ions are randomly distributed throughout solution, but there is no more net movement and molecules are still moving randomly
If we added some blue pigment and 20 ml of water what which would be the solvent and which would be the solute? what would it make?
solute= blue pigment
solvent= water
makes solution
Osmosis is the diffusion of ( ) across a selectively permeable membrane
water
Osmosis is a type of ( )
diffusion
Water will move ( ) its own concentration gradient; from where water is in ( ) concentration to where water is in ( ) concentration
down
high
low
Water moves from regions of ( ) solute concentration to regions of ( ) solute concentration
low
high
The amount of ( ) on the opposite side of the membrane will determine what water does
solute
What is tonicity ?
The ability of a solution to attract water into or out of the cell
The concentration of solution outside cell may ( ) from concentration inside cell
differ