Topic 3.4 - Alkenes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is an alkene?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons with a C=C
double bond
What is the general formula
of an alkene?
C n H 2n
Why is there no rotation
about the C=C double
bond?
Due to the π (pi) orbital - electron density above
and below the single bond, which holds the
carbon atoms in place
Are they more or less
reactive than alkanes?
Why?
More reactive, due to high electron density of
double bond and the fact the pi-bond is slightly
easier to break
What intermolecular forces
of attraction do they have?
Only van der Waals due to non-polar bonds
Are they soluble in water?
Why?
No, non-polar bonds (van der Waals’ < hydrogen
bonding)
Name and describe the
three kinds of isomers
alkenes can have
Chain isomers (branched chains)
Position isomers (C=C on different carbon atom)
Geometric E-Z isomers (Z is when 2 highest atomic number
chains are on the same side of the double bond; E is when
they're on opposite sides)
Write an equation for the
complete combustion of
pent-2-ene.
CH 3
CH=CHCH 2
CH 3 + 7½O 2 → 5CO 2 + 5H 2
O
What is an electrophile?
Electron deficient atoms/ions which accept a pair
of electrons (here, from the C=C double bond)
What is the most stable type
of carbocation intermediate?
why?
Alkyl groups have a positive inductive effect, so the most
stable carbonation is the one bonded to the most other
carbon atoms i.e. A tertiary carbocation
Major products will be
formed from which kinds of
carbocations?
Tertiary (or the most stable avaliable)
What conditions are needed
for the electrophilic addition
of H 2 O to an alkene?
Acid catalyst, usually phosphoric acid
What are the product(s) of
the reaction?
An alcohol
Draw a mechanism for the
addition of water to ethene
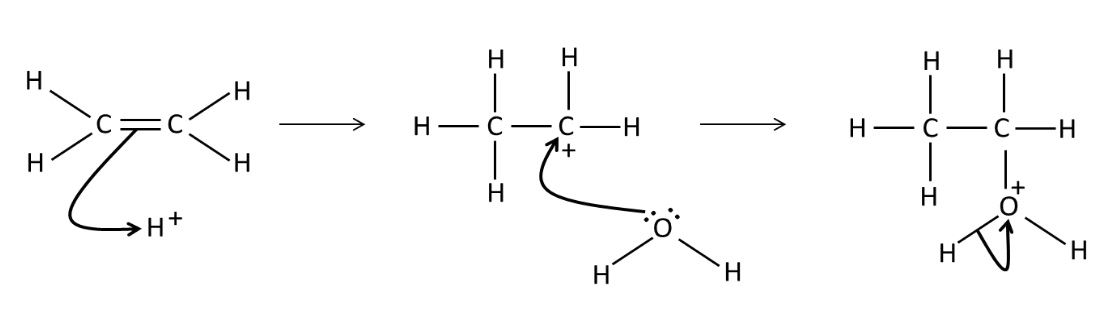
What conditions are needed
for the electrophilic addition
of a hydrogen halide to an
alkene?
Room temperature
Draw a mechanism for the
reaction of HBr and ethene.
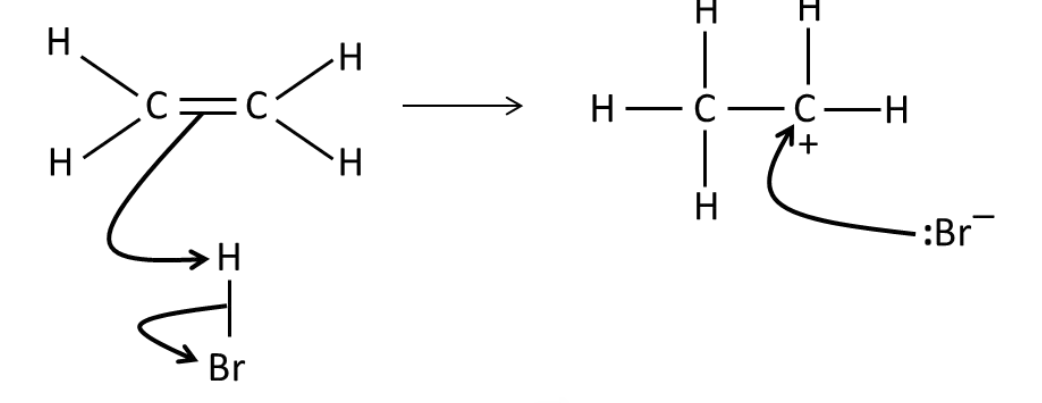
What conditions are needed
for the electrophilic addition
of a halogen molecule to an
alkene?
Room temperature and organic solvent
How does a molecule with a
non-polar bond react as if it
is an electrophile?
C=C double bond with a high electron density
induces a temporary dipole in the halogen
molecule → δ+ atom attracted to double bond
Draw a mechanism for the
reaction between bromine
and ethene
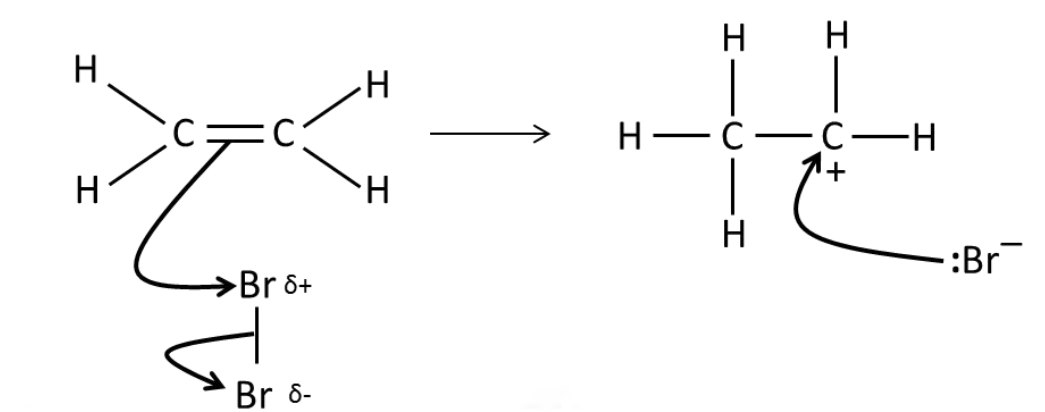
Draw a mechanism for the
reaction of sulfuric acid with
ethene.
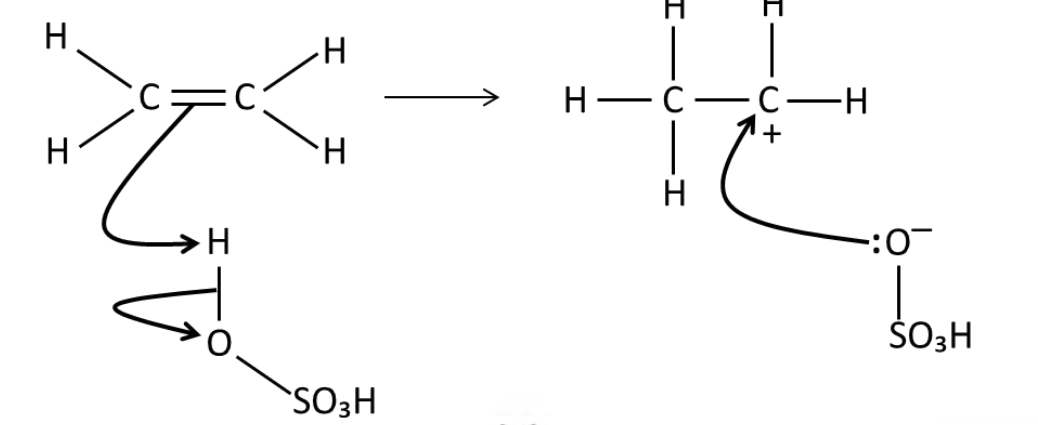
How would you turn the product (from
sulfuric acid + ethene) into an alcohol
and how does this show that sulfuric acid
catalyses the addition of water to an
alkene?
Add water
H₂SO₄ reforms, showing it catalyses the
hydration of alkenes
What is an addition
polymer?
many monomers bonded together via
rearrangement of bonds without the loss of any
atom or molecule
What are monomers? What
form do they usually take?
Molecules which combine to form a polymer
Usually have a C=C bond which breaks to leave
a repeating pattern
Draw how you would
represent the polymerisation
of ethene.
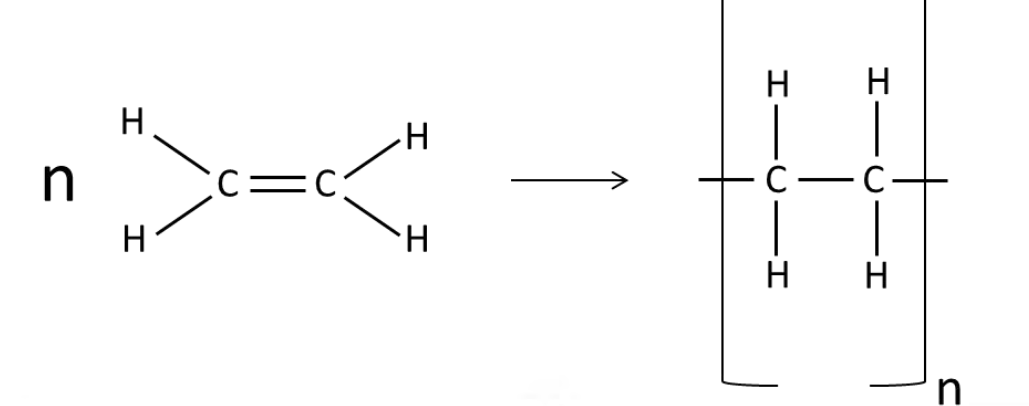
Give 3 uses of
poly(chloroethene) / PVC
Drainpipes
Vinyl
Aprons
Give two examples of
plasticisers
esters and phthalates
What are plasticisers?
Small molecules that get between polymer
chains to force them apart and allow them to
slide over one another
How do the physical properties
of PVC change due to a
plasticiser? What applications
does this lead to?
PVC with a plasticiser become flexible, used for
aprons
Without a plasticiser, PVC is rigid, used for
drainpipes
Why do things containing
mainly C-C and C-H bonds
not decompose easily?
Bonds are non-polar so are not attacked by
enzymes
Why is a lack of
biodegradability in
compounds with C-C or C-H
bonds a problem?
Disposal is very problematic
What is mechanical
recycling?
Where plastics are separated into different types,
washed, ground down, melted and re-moulded
What is mechanical
recycling used for?
Soft drinks bottles → fleeces
What is feedstock
recycling?
Plastics heated to a temperature which break
polymer bonds, leaving original monomers that
can be made into new plastics
What is feedstock recycling
used for?
Making totally new plastics
What is a problem with
recycling?
Each time thermosoftening plastics are melted
and remoulded, their properties degrade, so they
can only be remoulded a limited number of times