ch 24 Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism Overview
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
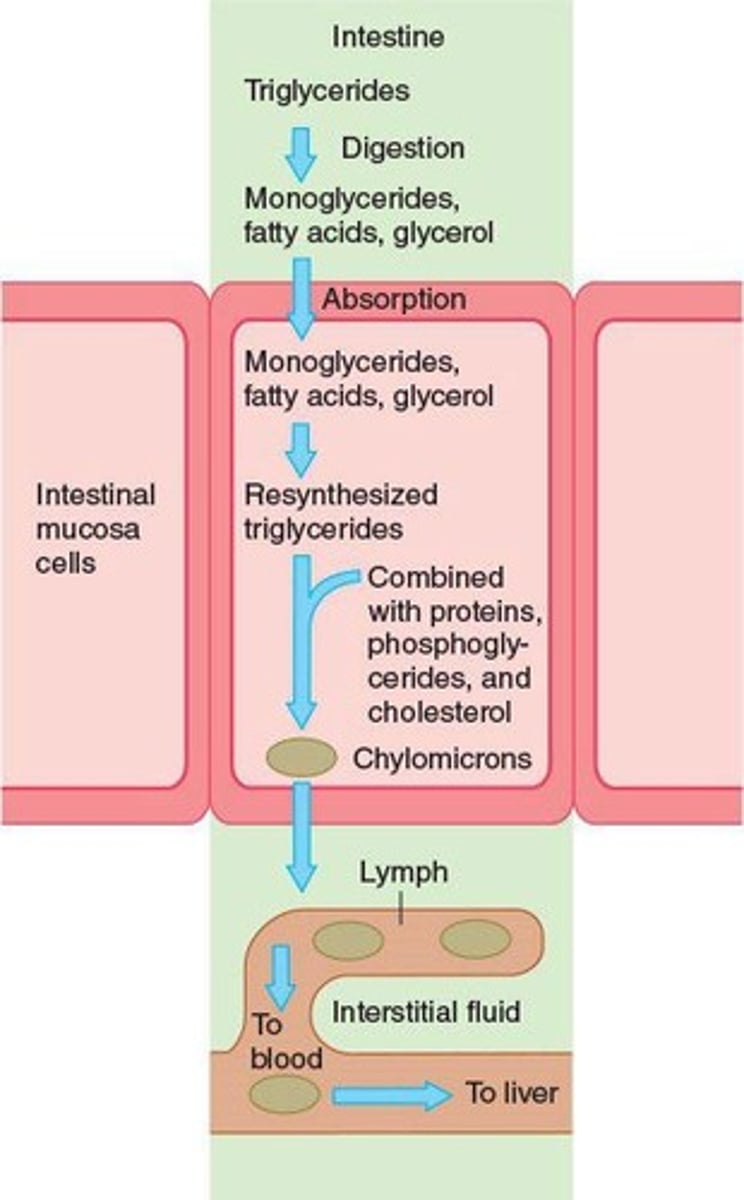
Triglycerides
Hydrolyzed to glycerol and fatty acids during digestion.
Phosphoglycerides
Hydrolyzed to their component substances in digestion.
Chylomicrons
Lipoprotein aggregates formed for lipid transport.
VLDL
Very low density lipoprotein, high lipid concentration.
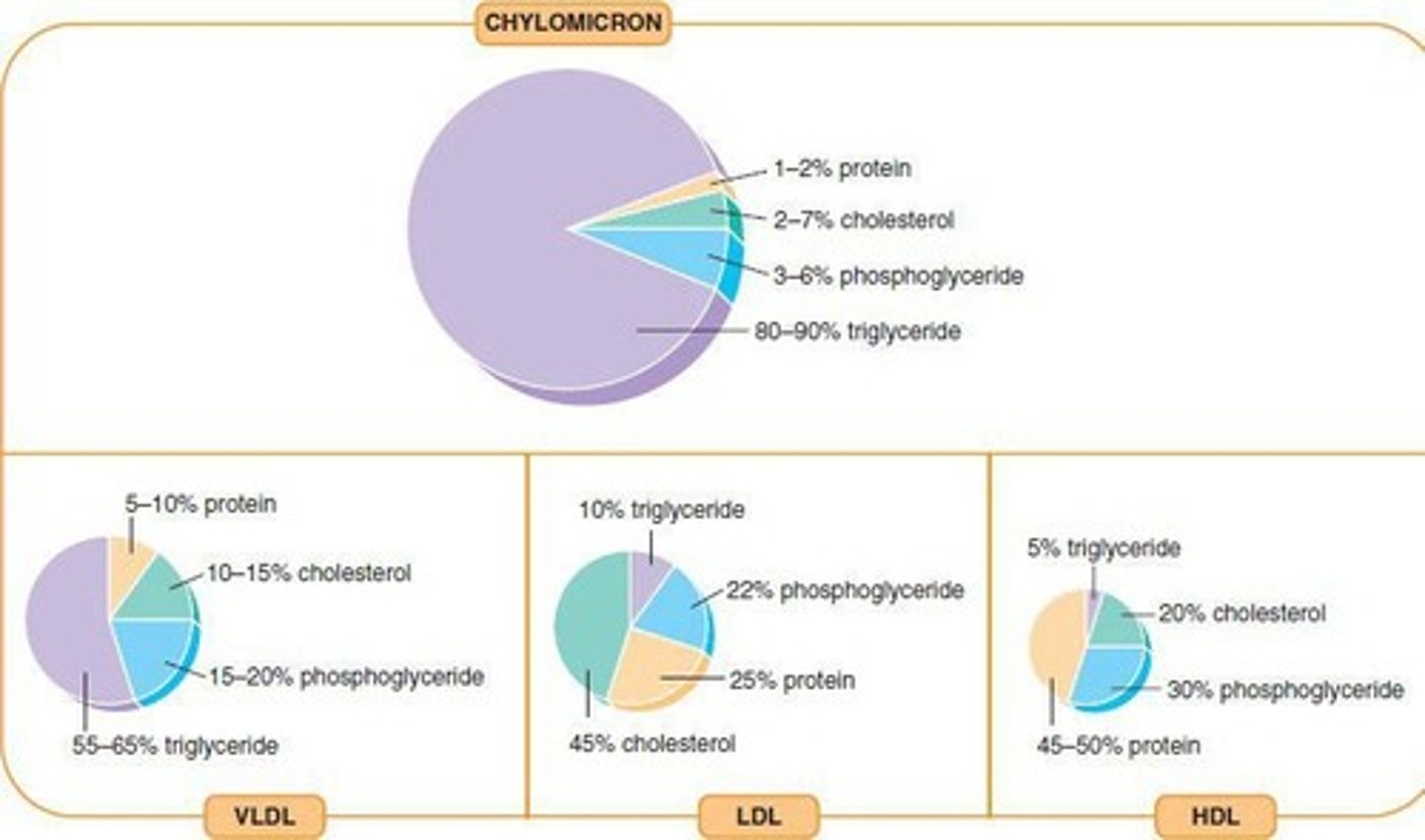
LDL
Low density lipoprotein, associated with cholesterol transport.
HDL
High density lipoprotein, helps remove cholesterol from blood.
Fat Mobilization
Hydrolysis of triglycerides releasing fatty acids into blood.
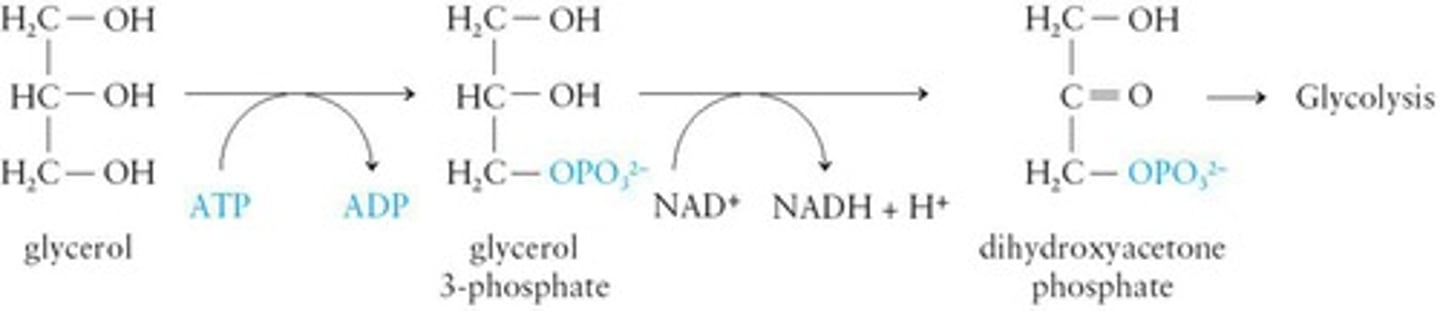
Glycerol Metabolism
Converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate for glycolysis.
Fatty Acyl CoA
Activated form of fatty acids for catabolism.
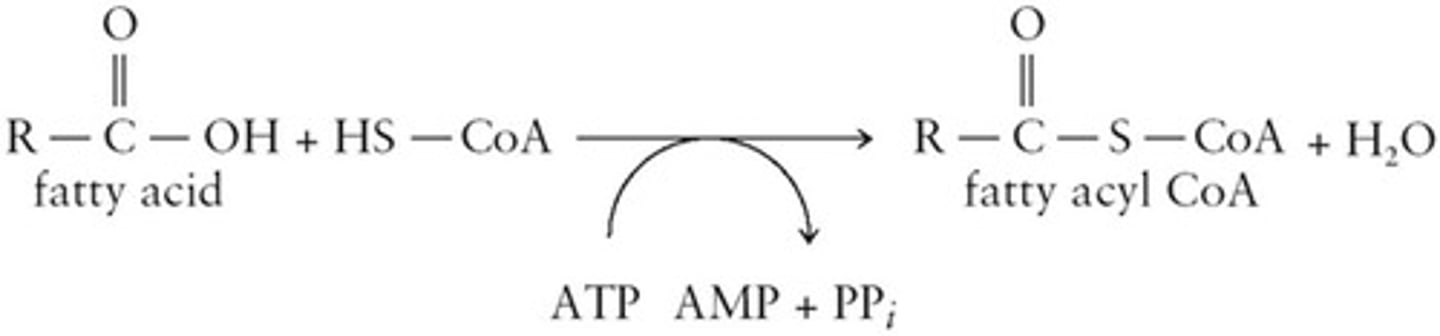
Acyl CoA Synthetase
Enzyme catalyzing fatty acid activation to acyl CoA.
ATP Hydrolysis
Provides energy for fatty acid activation process.
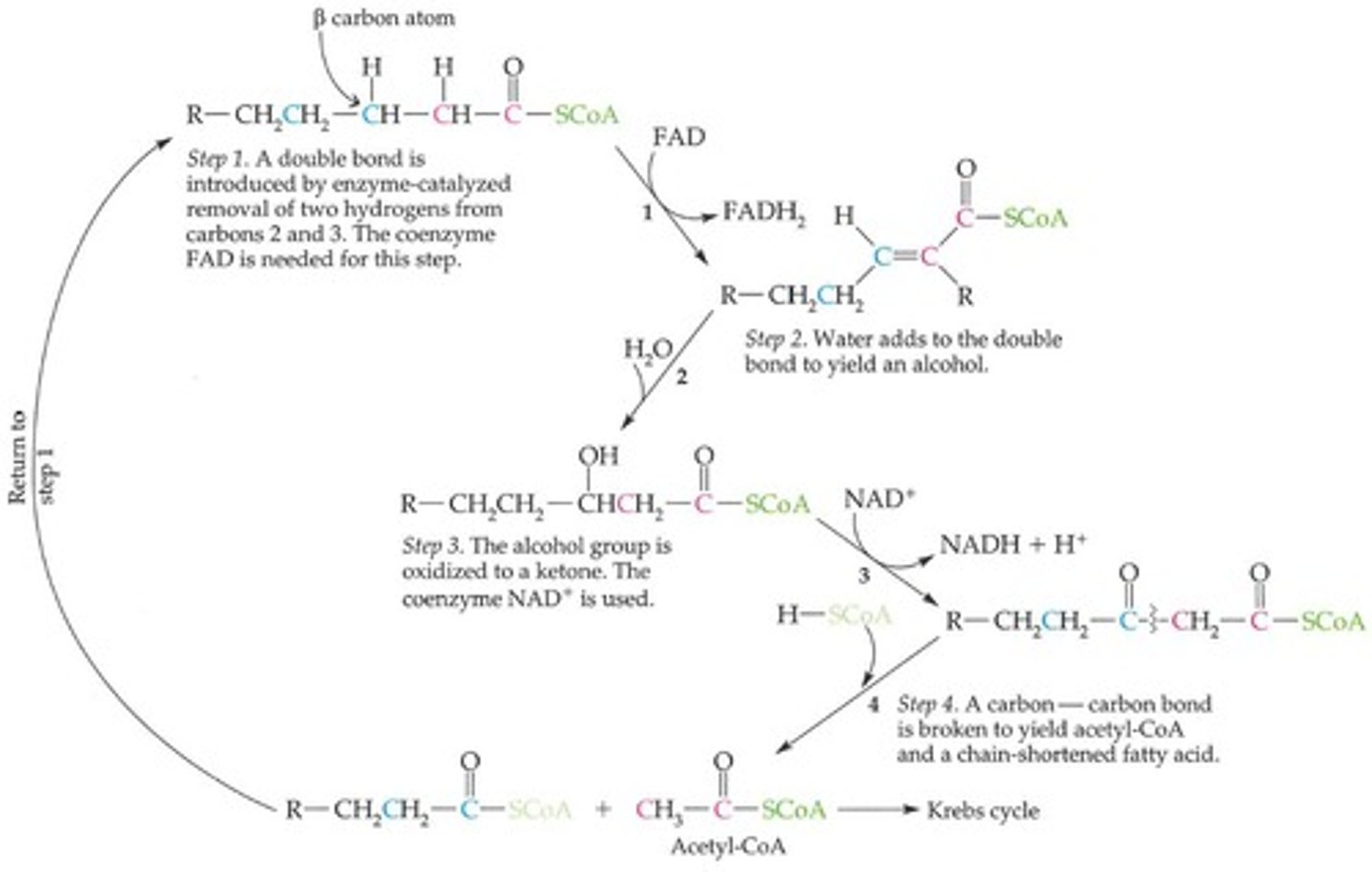
β-Oxidation
Metabolic pathway for fatty acid catabolism.
Ketone Bodies
Produced during fatty acid oxidation, includes acetoacetate.
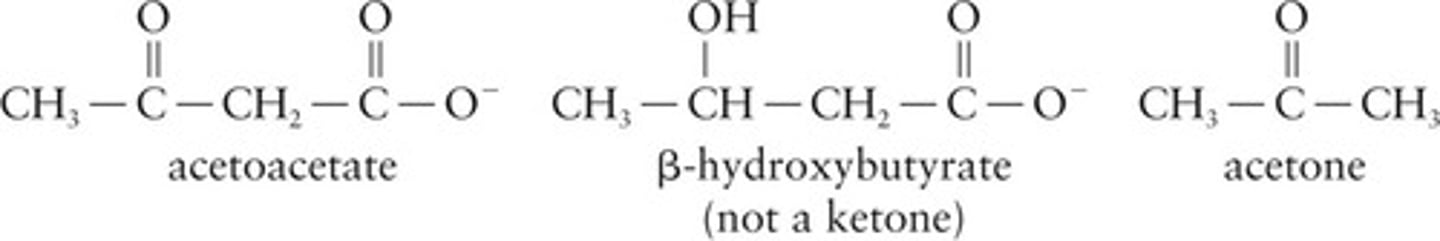
Urea Cycle
Pathway converting ammonia to urea for excretion.
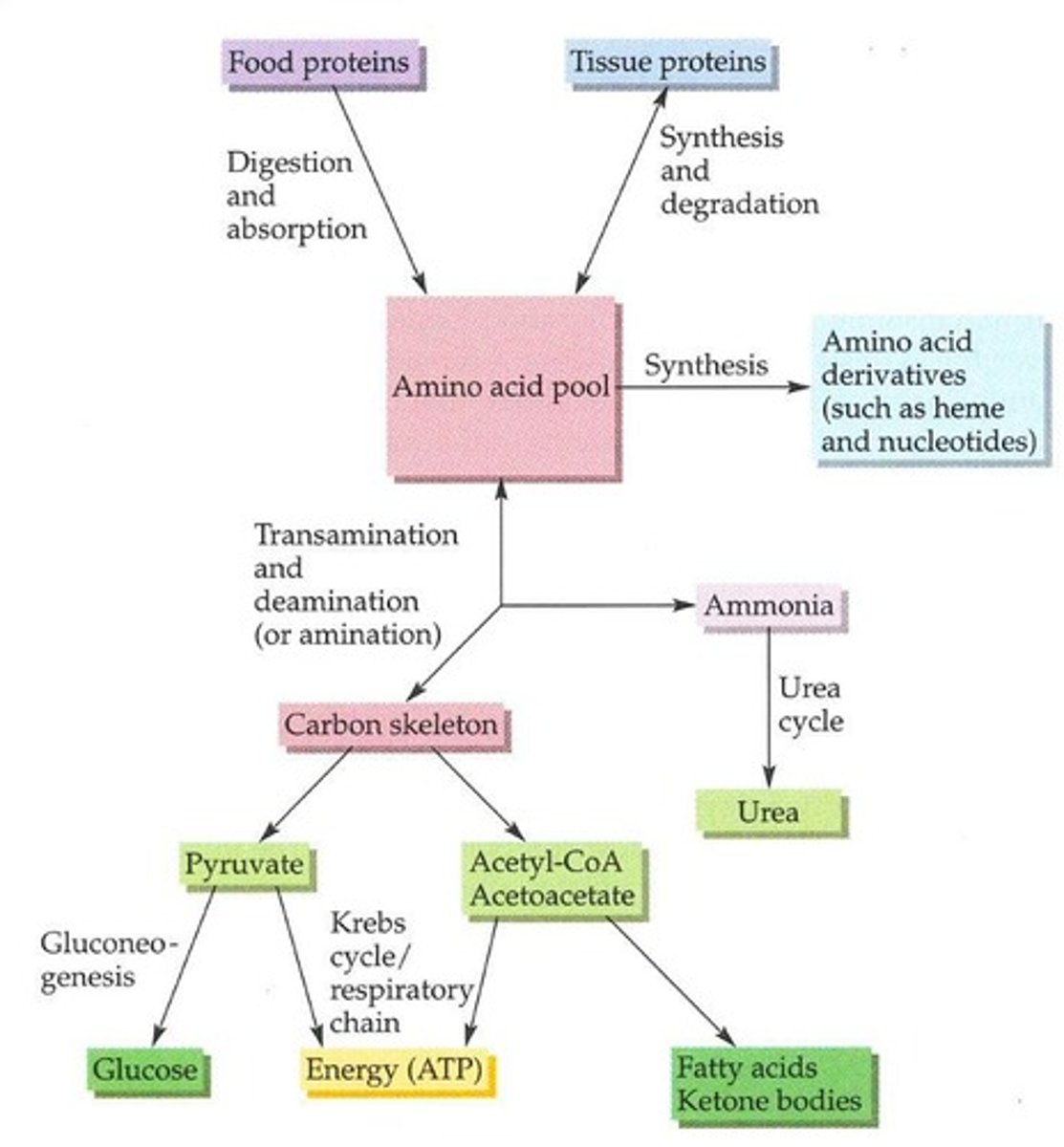
Transamination
Process of transferring amino groups between amino acids.
Deamination
Removal of an amino group from an amino acid.
Amino Acid Pool
Collection of amino acids available for protein synthesis.
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Energy Production
Amino acids can be converted to ATP.
Triglyceride Resynthesis
Occurs in intestinal mucosa after lipid absorption.
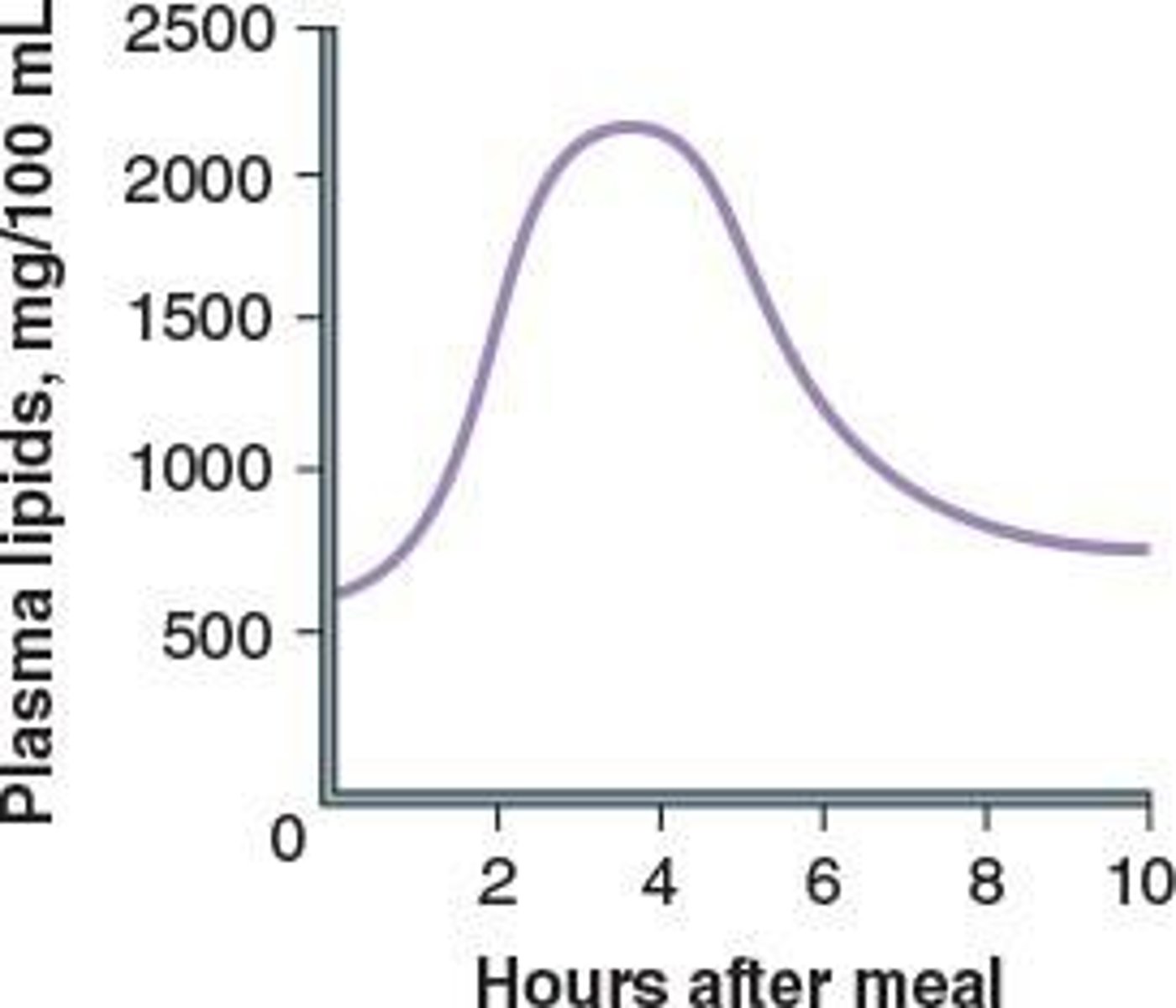
Blood Lipid Behavior
Increases post-meal, normalizes through fat storage.
Fatty Acid Energy Source
Used when glycogen stores are depleted.
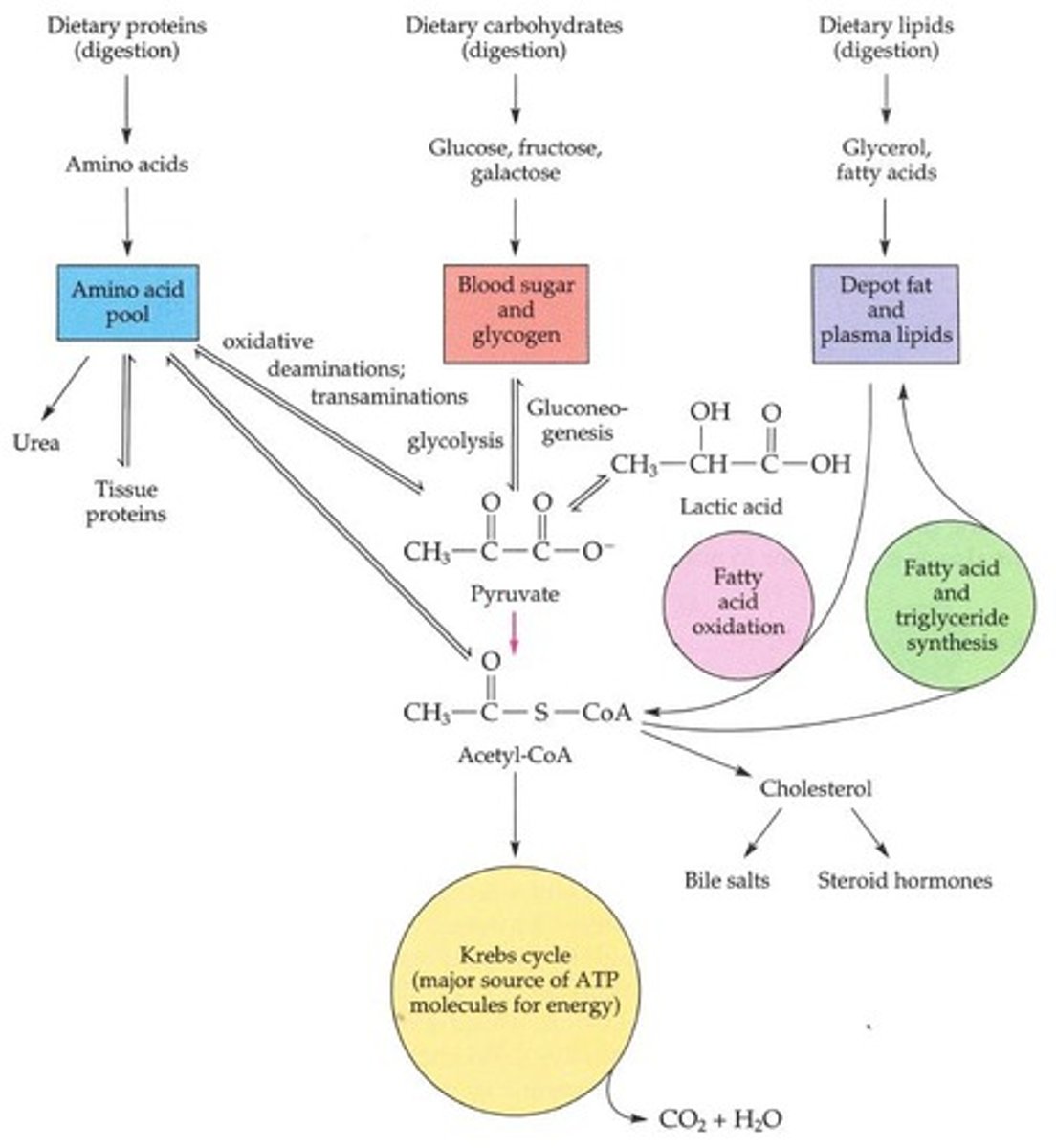
Blood-Brain Barrier
Prevents direct nutrient access to brain cells.
Phosphoglycerides
Hydrolyzed to component substances in lipid digestion.
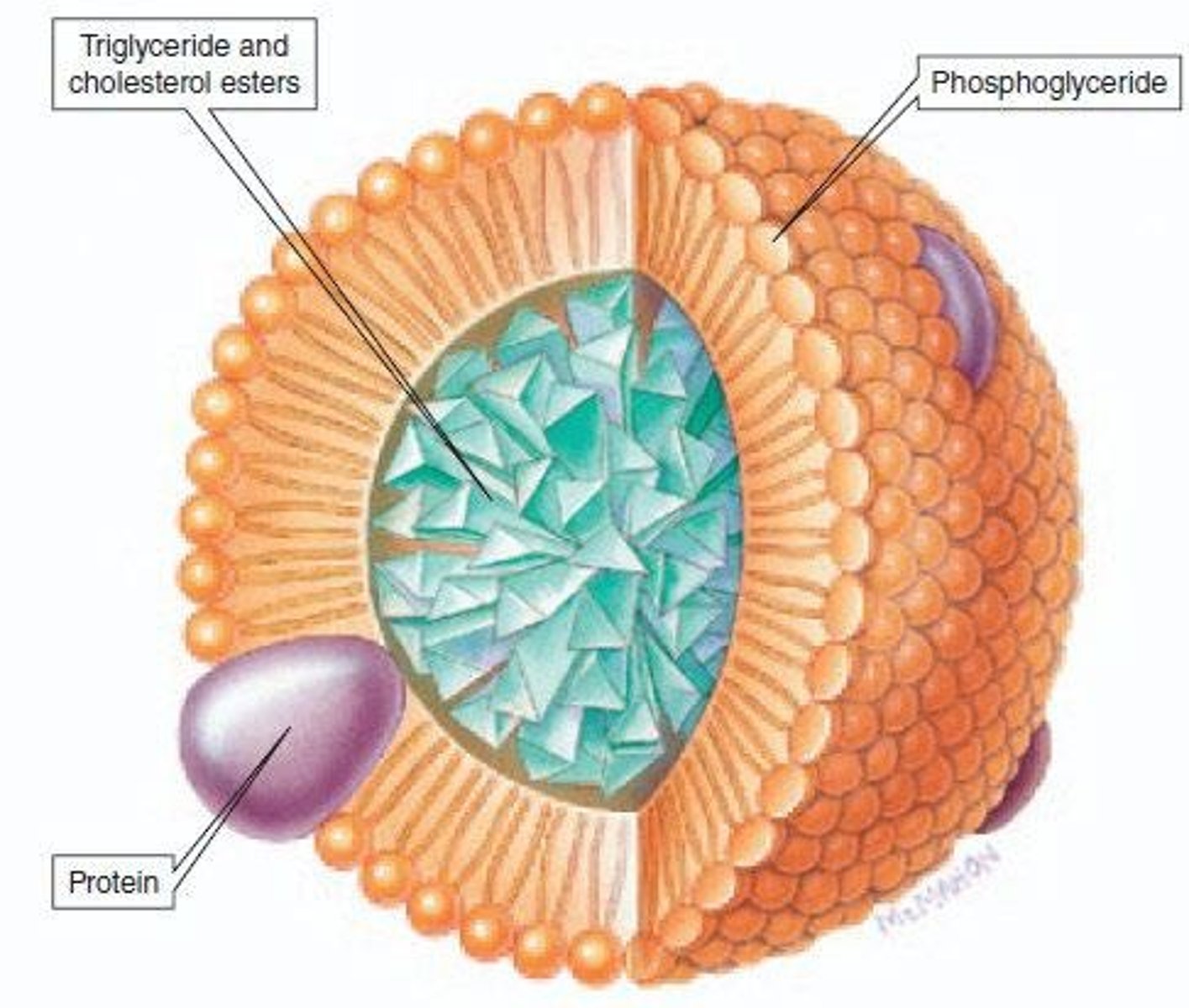
Chylomicrons
Lipoprotein aggregates transporting insoluble lipids.
Lipoproteins
Complexes of lipids and proteins for lipid transport.
LDL
Low density lipoprotein, carries cholesterol to tissues.
HDL
High density lipoprotein, removes cholesterol from tissues.
Fat Mobilization
Hydrolysis of triglycerides for energy production.
Glycerol
Converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate for glycolysis.
Acyl CoA Synthetase
Enzyme converting fatty acids to fatty acyl CoA.
ATP Hydrolysis
Provides energy for fatty acid activation.
β-Oxidation
Pathway for fatty acid catabolism into acetyl-CoA.
Ketone Bodies
Produced during fat metabolism under certain conditions.
Urea Cycle
Process converting ammonia to urea for excretion.
Transamination
Transfer of amino group between amino acids.
Deamination
Removal of amino group, producing ammonia.
Energy Production
Amino acids can be used for ATP synthesis.
Triglyceride Synthesis
Amino acids can synthesize triglycerides for storage.
Gluconeogenesis
Process of synthesizing glucose from non-carbohydrates.
Blood Lipid Behavior
Increases after meals, normalizes through storage.
Plasma Lipid Concentration
Peaks 4-6 hours post meal, then drops.
Amino Acid Pool
Source of amino acids for protein synthesis.
Fatty acyl-CoA
Substrate for the initial β-oxidation step.
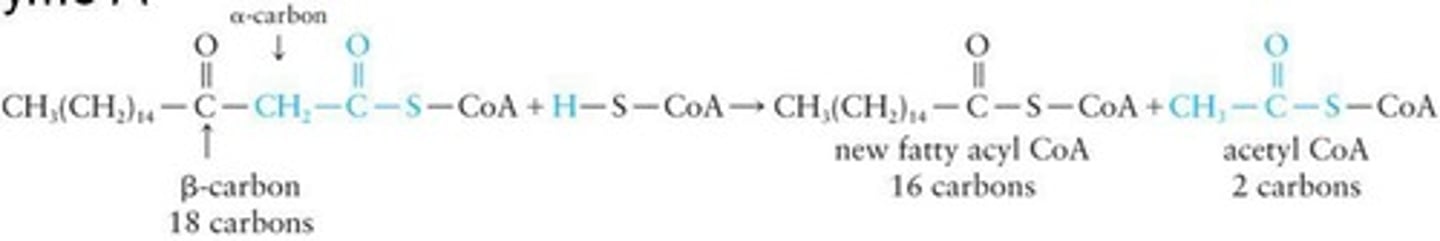
β-Oxidation
Metabolic process breaking down fatty acids.
Substrate
Molecule upon which an enzyme acts.
Final Step
Last phase producing fatty acyl-CoA.
Next Round
Subsequent cycle of β-oxidation process.
β-oxidation
Process of fatty acid degradation in mitochondria.
Acetyl-CoA
Two-carbon molecule produced from fatty acid breakdown.
Fatty Acyl CoA
Activated fatty acid form entering β-oxidation.
NADH
Electron carrier produced during fatty acid oxidation.
FADH2
Another electron carrier generated in β-oxidation.
Fatty Acid Spiral
Pathway for sequential degradation of fatty acids.
Stearic Acid
C18 fatty acid used in oxidation examples.
Activation Step
Conversion of fatty acid to fatty acyl CoA.
ATP Yield from Acetyl-CoA
10 ATP produced per acetyl-CoA in citric acid cycle.
ATP Yield from NADH
2.5 ATP produced per NADH in electron transport.
ATP Yield from FADH2
1.5 ATP produced per FADH2 in electron transport.
Ketonemia
Elevated ketone bodies in blood above 20 mg/100 mL.
Ketonuria
Presence of ketone bodies in urine above 70 mg/100 mL.
Acetone Breath
Detection of acetone in breath indicating ketosis.
Ketosis
Condition with ketonemia, ketonuria, and acetone breath.
Ketoacidosis
Condition with low blood pH due to ketones.
Insulin Treatment
Used to manage diabetes-related ketosis.
Oxaloacetate
Intermediate that combines with acetyl CoA for transport.
Citrate
Formed from acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate in cytoplasm.
Butyryl CoA
Four-carbon chain that undergoes β-oxidation.
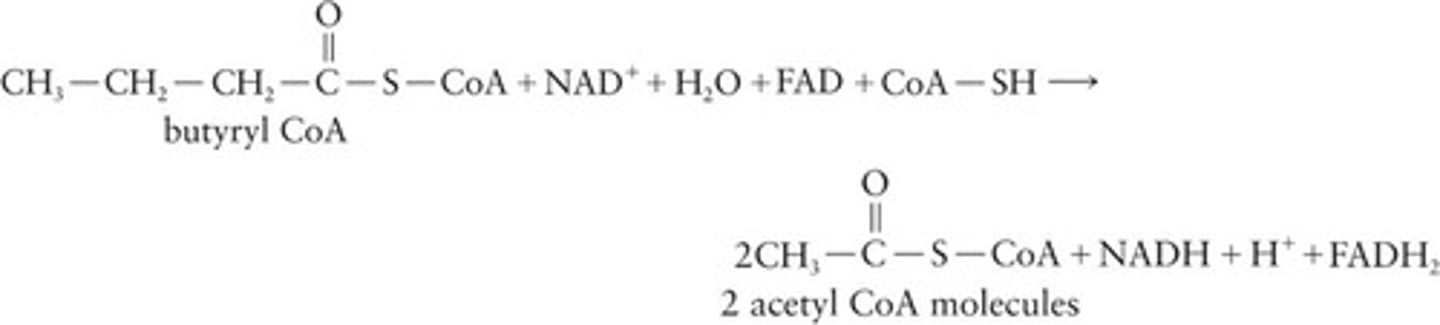
Total ATP from Stearic Acid
120 ATP produced from complete oxidation of stearic acid.
Energy Density of Fatty Acids
Lipids contain more than twice the energy of carbohydrates.
Fatty Acid Synthesis Location
Occurs in the cytoplasm, opposite of degradation.
Fatty Acid Degradation Location
Occurs in mitochondria, opposite of synthesis.
Fatty Acyl-CoA
Substrate for β-oxidation in mitochondria.
β-Oxidation
Process degrading fatty acids into acetyl-CoA.
Acetyl-CoA
End product of fatty acid degradation.
NADH
Electron carrier produced in β-oxidation.
FADH2
Another electron carrier generated during oxidation.
Fatty Acid Spiral
Pathway for sequential fatty acid degradation.
Activation Step
Conversion of fatty acid to fatty acyl-CoA.
Stearic Acid
C18 fatty acid undergoing β-oxidation.
ATP Yield
Total ATP from stearic acid oxidation is 120.
Oxaloacetate
Intermediate that regulates citric acid cycle activity.
Ketonemia
Elevated ketone bodies in blood (>20 mg/100 mL).
Ketonuria
Presence of ketone bodies in urine.
Acetone Breath
Detection of acetone in breath.
Ketoacidosis
Low blood pH due to high ketone levels.
Citrate
Transport form of acetyl CoA to cytoplasm.
ATP Multipliers
10 ATP per acetyl CoA, 2.5 per NADH, 1.5 per FADH2.
Butyryl CoA
Four-carbon chain processed in β-oxidation.
Energy Density
Lipids provide more energy than carbohydrates.
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Occurs in cytoplasm, opposite of degradation.
Hydrolysis of ATP
Provides energy for fatty acid activation.
Total ATP from NADH
20 ATP from 8 NADH produced.
Total ATP from FADH2
12 ATP from 8 FADH2 produced.
Malonyl-ACP
Carries carbon pairs in fatty acid synthesis.
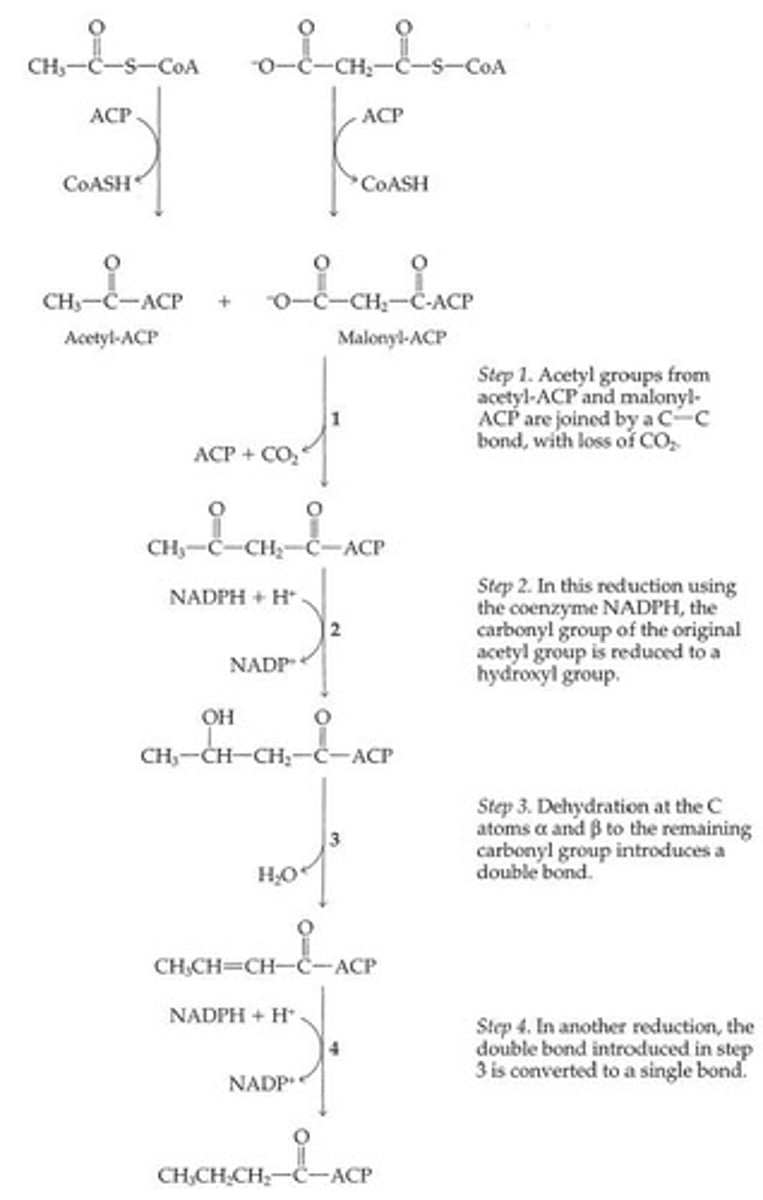
Fatty Acid Synthetase System
Multienzyme complex for fatty acid synthesis.
Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)
Binds fatty acyl chains during synthesis.
Triglycerides
Form of fat stored in adipose tissues.
Adipose Tissues
Body tissue that stores fat.
Liver Role
Modifies body fats through chain alterations.