econ 12 - chapter 6 (monopoly and imperfect competition)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
perfect competition
a market structure with many sellers and many buyers of standard product
ex: roadside flower stalls, fish market, food stalls on the roadside in Kudat
monopolistic competition
a market structure with many sellers and many buyers of slightly different products.
easy entry and exit to the market. COMMON IRL
ex: restaurants, clothing services
oligopoly
a market structure where there are only a few businesses offering standard/similar products.
entry to the industry is difficult. very common in canada.
ex: banking, telecom, airlines
monopoly
a market structure where there’s only 1 business supplying a product with no similar substitutes and restricted energy to the industry in common regions.
ex: BC Hydro, ICBC (usually government owned entities)
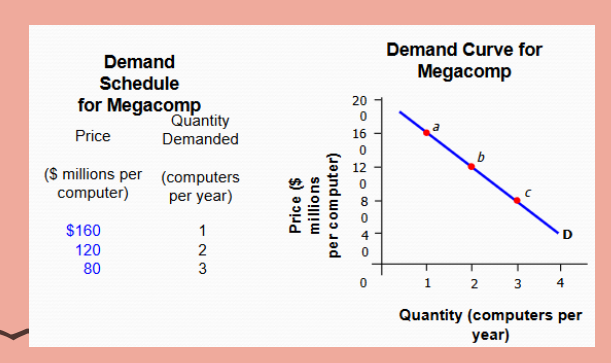
Monopoly Demand Curves
downward sloping. curve represents the entire market.
company has ability to influence price because they’re the only company
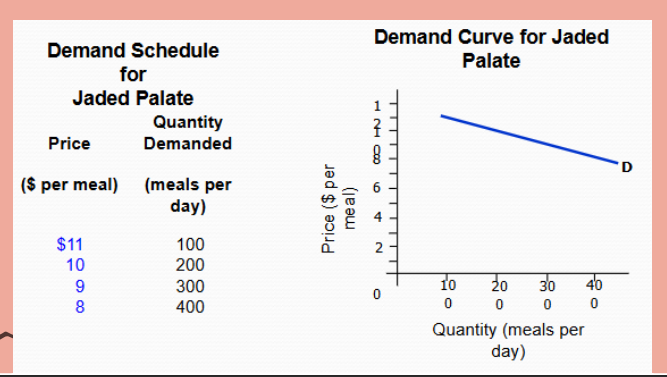
Monopolistic Competition Demand Curve
downward sloping demand curve
demand is elastic because there’s substitutes.
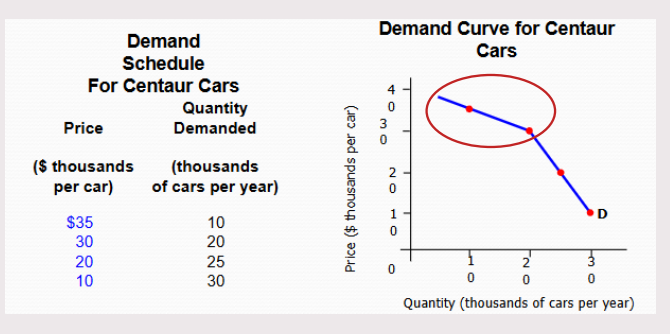
Kinked Demand Curve (Oligopoly)
relies on mutual interdependence (relying on one another to achieve the goals)
each business contributes a lot to the market.
can operate as rivals or fellow players
It is elastic when it’s above the kink — competitors won’t follow price changes as raising price will lose customers (competitors gain customers)
When it’s below the kink, it is inelastic — competitors will follow price changes as lowering prices will gain customers (to make switch less dramatic, prices will lower too)
Oligopoly Rivals
Rivalry comes from wanting to maintain market share. But we must consider the reactions of competitors to price changes and how responses will impact their market share.
Ex: If Air Canada starts charging to bring a carry on, how many people will switch to WestJet? Will WestJet increase their ticket price while maintaining a free carry-on to take advantage of the extra business?
The idea is that companies in an oligopoly are always thinking about what their competitors will do in response to their actions, because it can directly impact their own market share.
Oligopoly: Cooperation
against the interests of consumers: A COLLUSION (secret agreement or cooperation for an illegal or dishonest purpose)
companies work together to have a power like monopoly, minimizing competition
one business acts as the standard (change price) and others follow (change their price too)
it is not dictated by the market but by the business
when businesses agree to this cooperation, it’s called a cartel
competition bureau
independent law enforcement agency
oversees and promotes fair business practices
purpose: encourage innovation and lower pricing, prevents anti-consumer behaviour, protects consumer rights
conspiracy
businesses working together against consumer interest (cooperation?)
bid-rigging
work together to determine winner of bidding price.
predatory pricing
temporarily dropping price to drive out competition
abuse of dominant position
large companies abusing their control over the market
mergers
not bad, but can consolidate too much power
horizontal: former rivals
vertical: business and supplier
conglomerate: businesses in unrelated industries