2.5 - Legislation
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Who are business laws put in place by?
The government in the form of Acts of Parliament
Why are business laws put in place?
To stop bsuinesses from mistreating and exploiting their workers and consumers
What are the 3 types of law that apply to businesses?q
- Consumer law
- Employment law
What are the advnatages of employment law on a business?
- Greater productibity
- Lass absenteeism (employees being absent)
- Fewer mistakes
- Fewer accidents
- Higher quality products
- Improved reputation
- Higher sales and revenues
What is the disadvantage of employment law on a business?
Increases the costs of production
What is the national minimum wage? (description)
The wage varies according to the age of the worker
What is the National Living Wage?
The 25+ rate for the National Minimum Wage
What are the advantages to a business of the National Minimum Wage?
- Workers are more motivated to work for higher wages
What are the disadvantages to a business of the National Minimum Wage?
- Can't afford to employ as many people (have to make people redundant)
- If they break the law, they have to pay back their owed money and susbtantial fines
What does the Equality Act 2010 do?
Legally protects peopel from discimination in the woorkplace and in wider society
What is discrimination?
The illegal tratement of any individual/group of individuals who are termed to be different
In the UK , it is unacceptable for...
An employer to discriminate against an employee on this basis
What is legislation?
A set of rues that governs the way society operates (antoher term for 'laws')
What is the National Living Wage?
Alll employees above a certain age must receive at least this rate of pay
What is the aim of legislation?
Aim is to allow employers to use labour efficiently while preventing the unfair tratement of employees
What does consumer protection law do?
Provents businesses treating their customers unfairly, while allowing them to sell goods and services profitably
What is an Act of Parliament?
When a law comes into operation
What is discrimination? (define)
Treating one person differently from another without having good reasons to do so
What is a part-time employee?
Works for a proportion of the working week (eg. 3/5 days a week)
What is a trade union?
A group of workers who act together to imrpove their pay and working conditions
What is a contract of employemnt?
A legal document stating the hours, rates of pay, duties and other conditions under which a person is emplyoed
What is motivation?
Refers to the range of factors which influence the way a person behaves at work
What are consumer laws?
Laws that have been introduced to prevent businesses from treating their customers unfairly
The Equality Act 2010 says that employees can't be treated differently in the workplace on the basis of any of the following factors?
- Disability
- Race
- Gender reassignment
- Marraige and civil partnership
- Religion/belief
- Pregnancy/maternity
- Gender
- Sexual orientation
In 2010, the Equality act brought together all legislation...
intended to stop discrimination
What are the types of discrimination?
- Disability
- Race
- Trade union members
- Gender reassignment
- Marriage/civil partnership
- Religion/belief
- Pregnancy/maternity
- Gender
- Sexual orientation
- Fixed-term/part-time worker
What are the ways in which businesses discriminate?
- Recruitment
- Employee contract
- Promotions & transfers
- Providing training
- Providign benefits
- Employee dismissal
What are the advantages and disadvantages of maternity/paternity leave on a business?
- Avoiding legal fees
- Have to pay 2 full wages (1 for the maternity leave, 1 for the person to cover their shifts)
- Potential legal fees if they break the legislation
What are some other employment laws?
- All employees have a legal right to a paid holiday (5.6 weeks)
- Working hours are subject to legal limits
- Employees have a right to choose whether or not to join a trade union
- Employees must have a contract of employment - state amount they need to be paid
- Time off for a range of reasons (trade union activities and bc a dependent person is ill)
What does the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 cover?
- installation and maintenance of safety equipment
- maintenance of workplace temperature
- sufficient breaks
- protection against dangerous substances
- safety policy
- employees follow all H&S procedures"
How can businesses treat their customers unfairly?
- By selling unsafe products
- Selling products that don't work properly/unfair prices
- Selling info abt consumers to other businesses without permission
Why are consumer laws passed by the government?
To protect customers by preventing unfair practices taking place (consumer protection laws)
What does the consumer rights act 2015 cover?
- Returning goods (protects against products ""going missing"" before delivery, late delivery)
- Repairs/replacements
- Delivery rights
- unfair terms in contracts between businesses and customers (eg. hidden fees and charges)"
Diagram of consumer laws
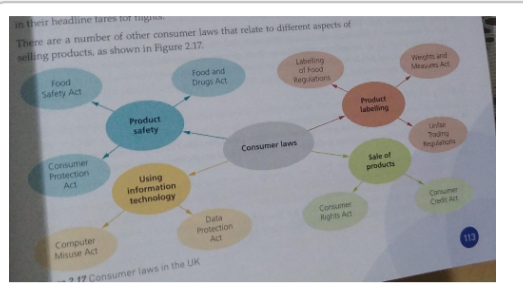
What is the legislation concerning the labelling of products?
- Weight and measures act
- consumer protection from unfair trading regulations act (illegal to give consumers incorrect information on packaging and labels + agressive selling tactics)
What is the legislation of buying products using laws?
- Allows consumers a week during which they have the right to change their minds about agreeing to a loan
What acts concern using information incorrectly?
- Data protection act (controls the ues of consumers' information - prevents theft/loss/selling/giving without consent of data)
Which legilsation concerns the safety of products?
- Consumer protection act (law prevents firms from selling dangerous products to consumers - liability if they do)
- Food safety act (illegal to sell food that's unsafe and may cause illness)
What are the advnatages and disadvnatages of consumer laws to a business?
- Consumers more willing to make decisions to buy expensive products
- Not as concerned to buy products about which they know little (and rely on the business) - higher sales
- Encourage businesses to produce safe, fit for purpose, as described foods - rivals are limited in smae ways (level playing field)
Disadvnatages
- Increased costs of production
- Prevents businesses from finding extra sources of revenue (eg. thorough selling customer data)
What are the Consequences of meeting legal obligations?
"- Business gains a good reputation for reliable and trustworthy products. As this reputation grows, sales are likely to increase, as more customers are attracted.
- Staff will feel more confident that they will be safe at work and that their employer takes its responsibilities seriously. This can bring a number of benefits:

What are the consequences of not meeting legal obligations?

Explain one example of how a business would meet he requirements of consumer law to provide safe goods/services
1 mark for identifying the requirements of consumer law in relation to providing safe goods or services.
1 mark for giving an example or how it would be achieved.
Possible answers may include:
• goods must be as described
• labelling of products
• products must work properly
• products must be safe to use/consume
Examples of developed answers
Consumer law states goods must be labelled correctly, (1) for example businesses need to state what ingredients are in food products (1).
Business must make sure that products are safe to use (1) for example any electrical products must be tested (1).

Equality act
Health and safety act
Minimum wage, holiday pay, maternity pay, safety equipment, recruitment costs

D

Okay 😋