A&P 1 - Muscular System
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Also joints because even though it was part of our skeletal system unit it got pushed to muscular system exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Name the three types of Muscular Tissue.
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
List four characteristics of skeletal muscle.
Striated, multinucleate, voluntary, attached to bone
List four characteristics of cardiac muscle.
Striated, uninucleate, involuntary, found in heart
List four characteristics of smooth muscle.
Non-striated, uninucleate, involuntary, found in walls of hollow organs

This image represents what type of muscle tissue?
Skeletal
This image represents what type of muscle tissue?
Cardiac

This image represents what type of muscle tissue?
Smooth
What are the seven functions of the muscular system?
Movement of the body
Maintenance of posture
Respiration
Production of body heat
Communication
Constriction of organs and vessels
Contraction of the heart
How does the muscular system maintain posture?
Muscles push against each other
How does the muscular system allow for respiration?
The diaphragm is made of skeletal muscle tissue
The diaphragm (contracts/expands) when breathing in.
contracts
The diaphragm (contracts/expands) when breathing out.
expands
How does the muscular system produce body heat?
Shivering; movement generates heat
How is the muscular system used in communication?
Moving the mouth & tongue
Why is constriction of organs and vessels essential for the muscular system to perform?
Contraction of uterus & extremities require constriction of skeletal muscle to pump blood back to heart
What are the four general properties of muscle tissue?
Contractility, excitability, extensibility, elasticity
What is contractility?
Ability to contract
What is excitability?
Ability to respond to stimuli
What is extensibility?
Ability to stretch/extend/elongate
What is elasticity?
Ability to recoil (return to original shape)
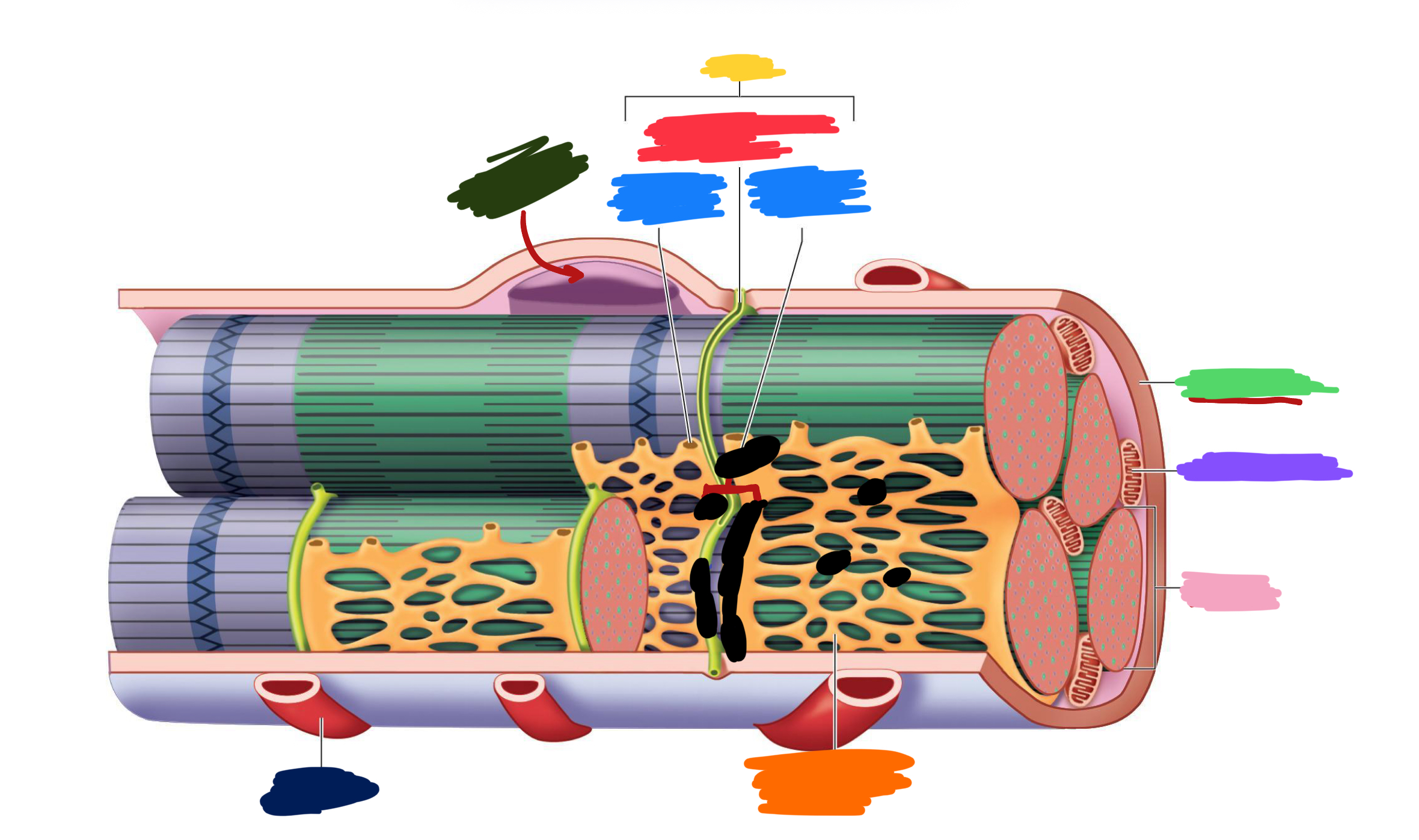
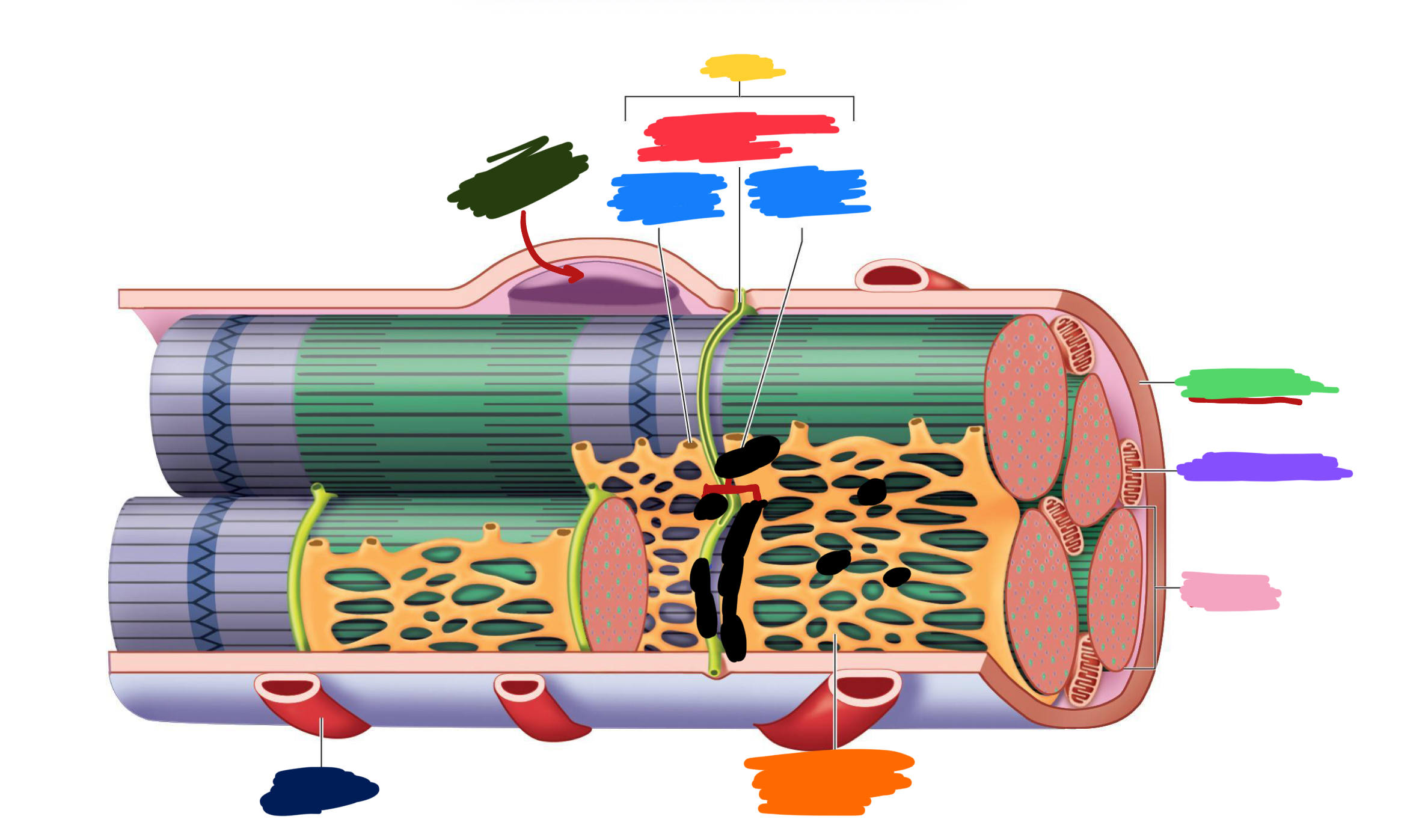
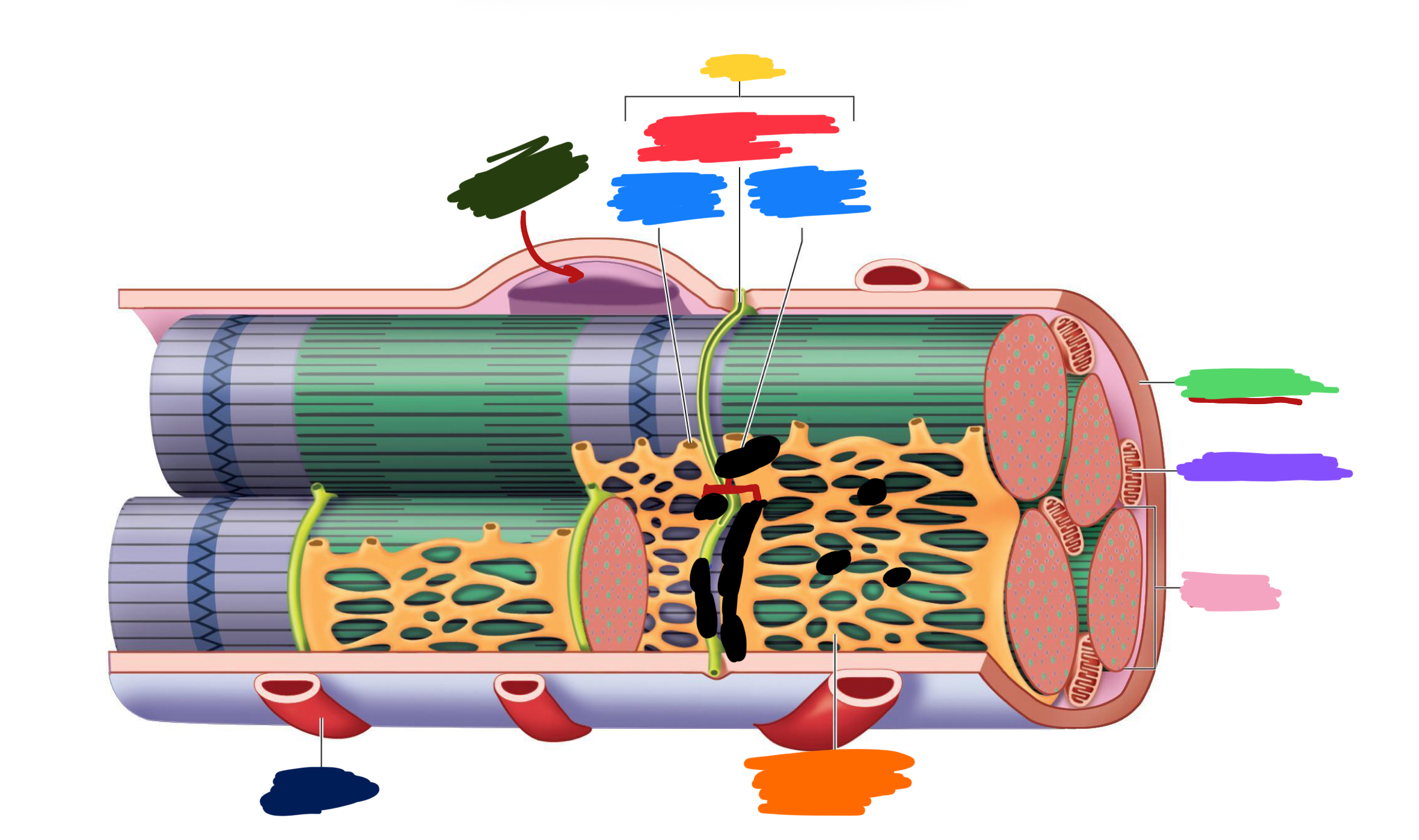
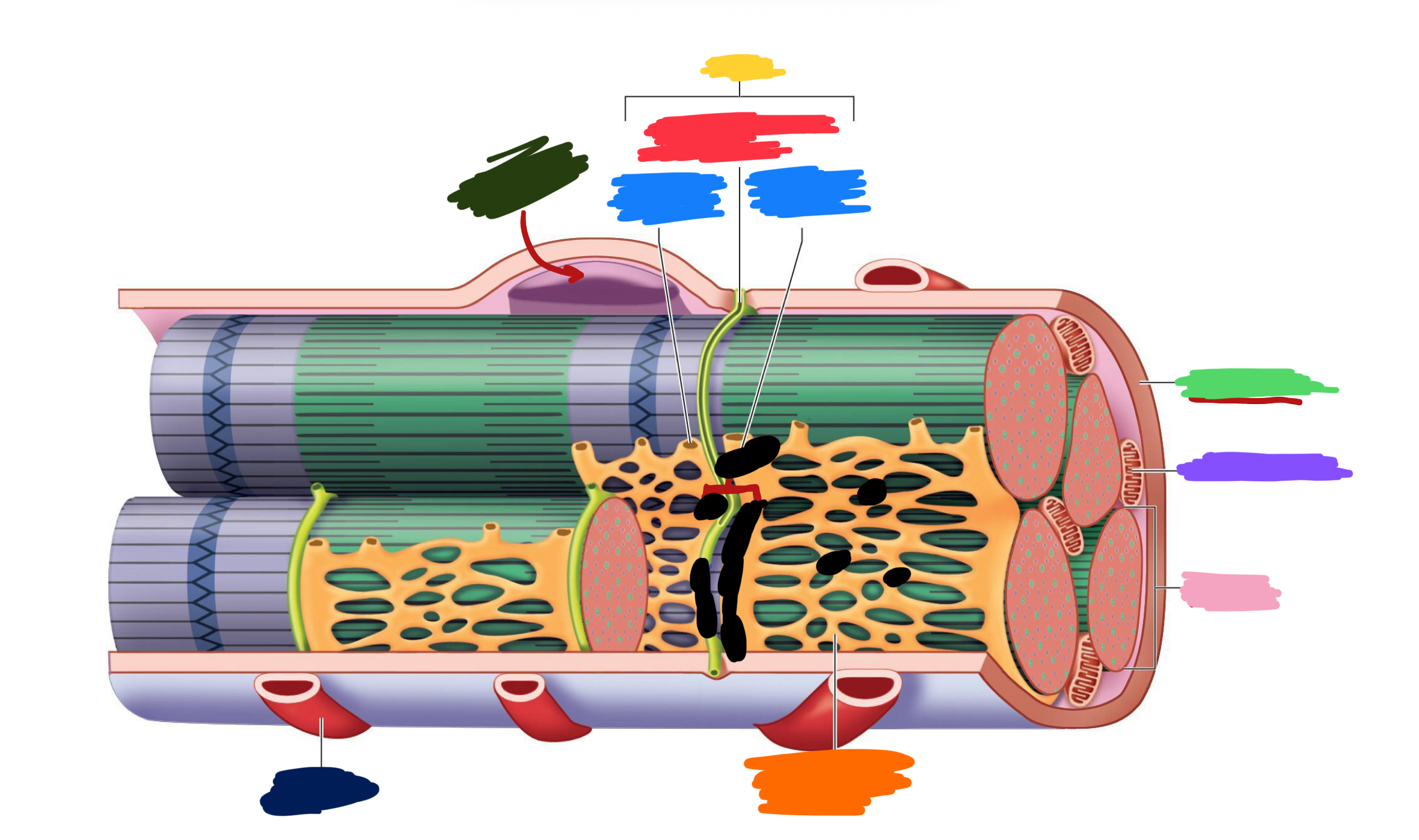
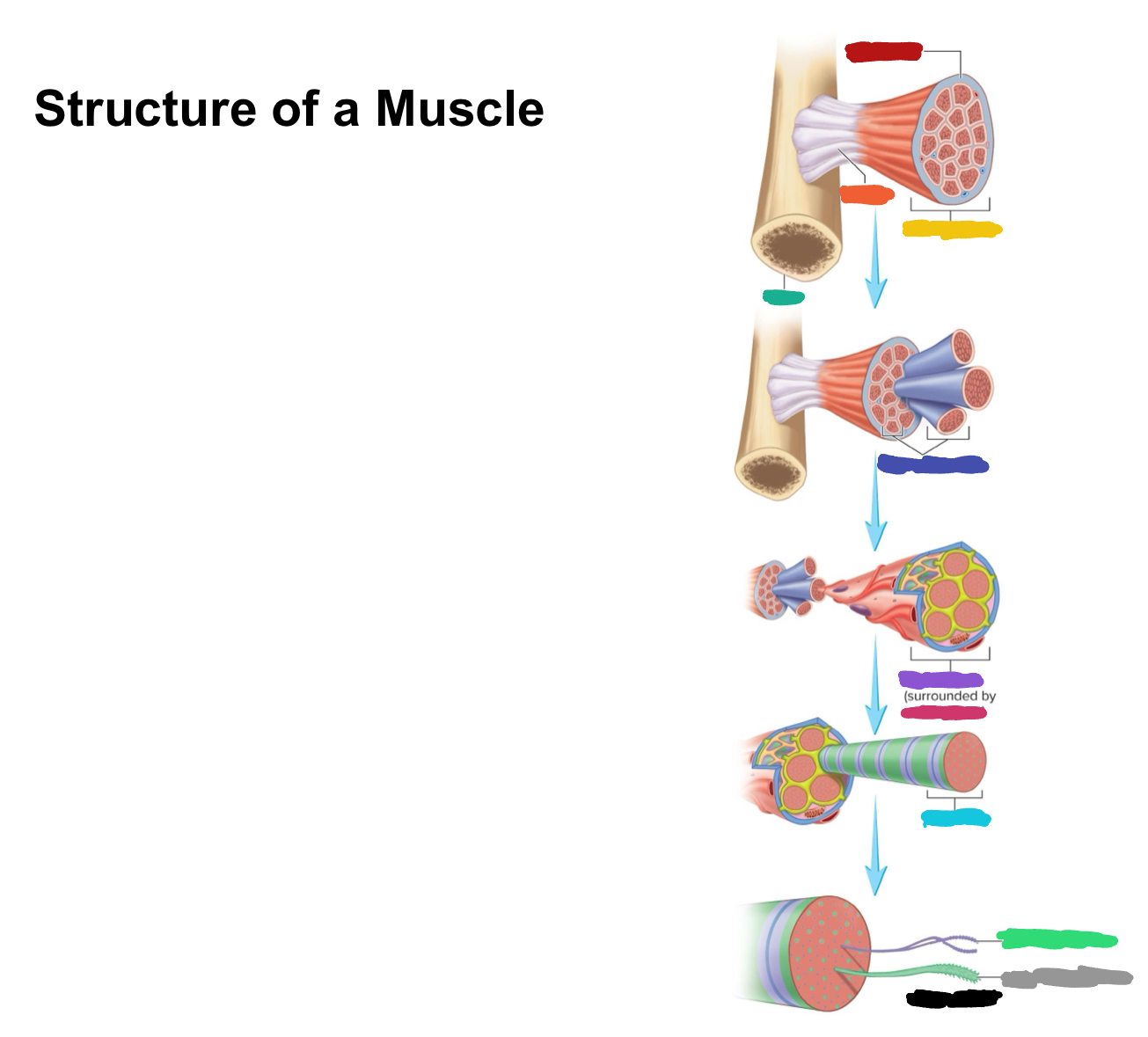
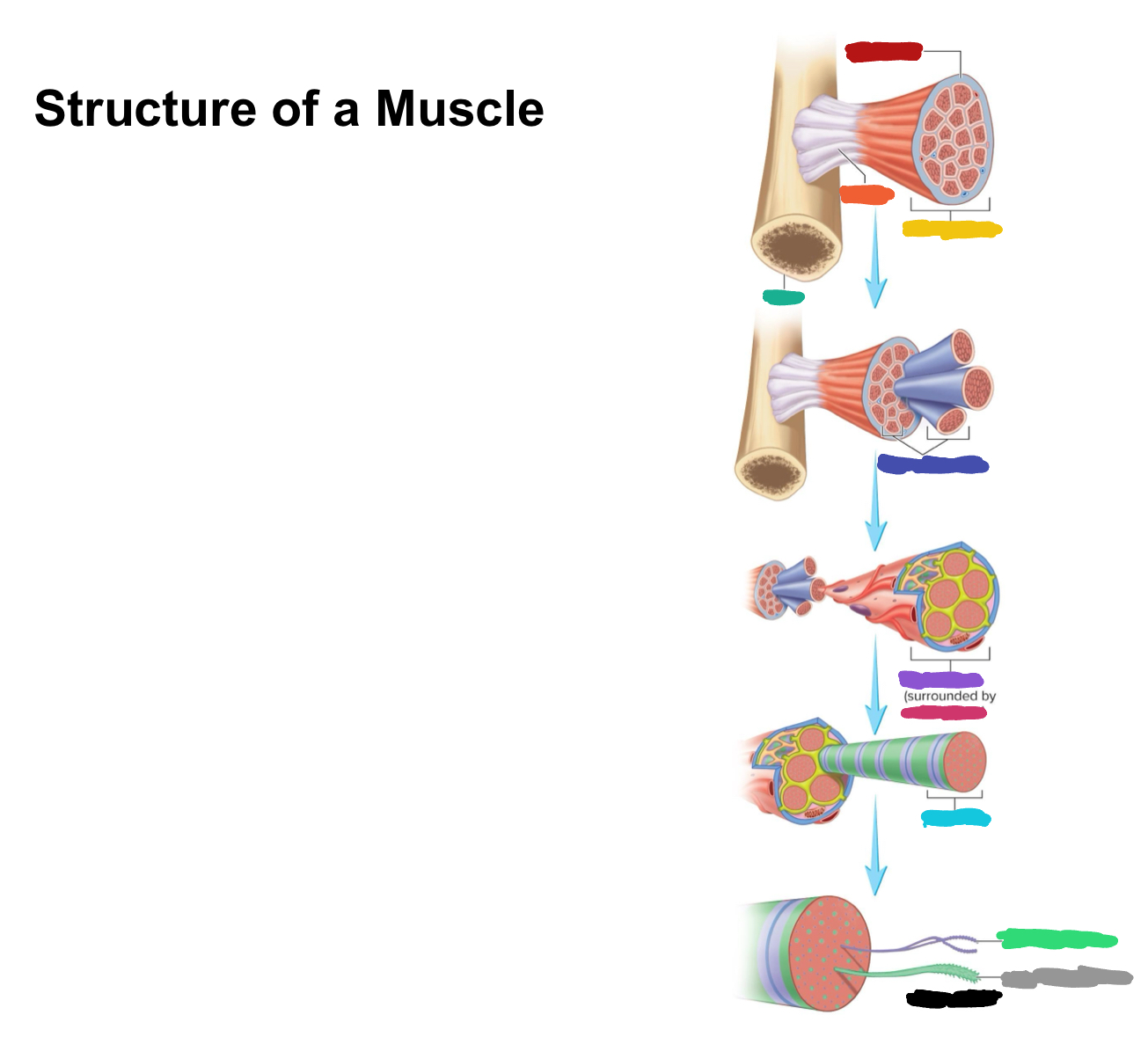
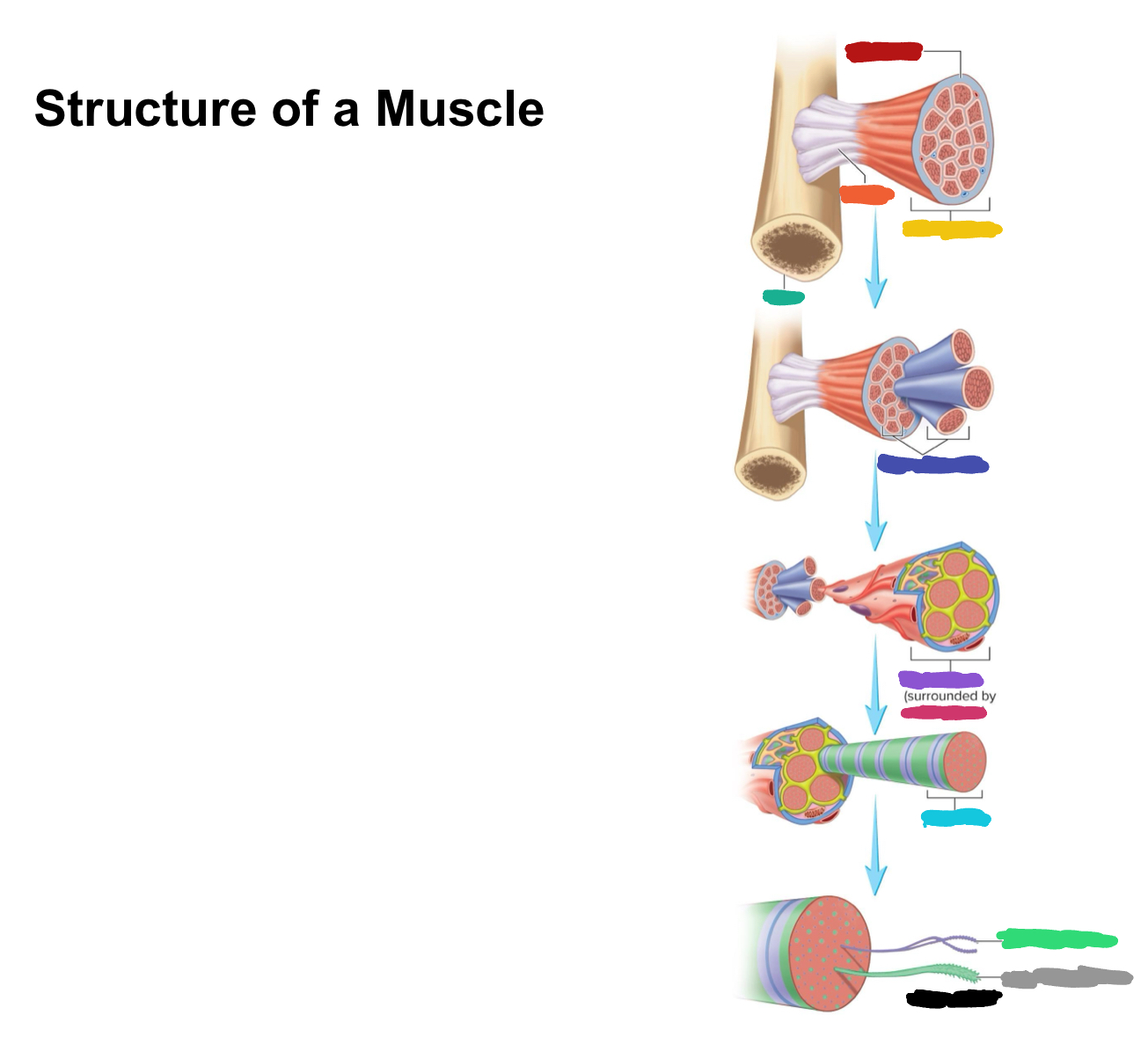
What connective tissue covering covers the whole muscle (organ)
Epimysium
What does muscular fascia do
connects muscle to surrounding tissues
What connective tissue covering surrounds the fascicle?
Perimysium
What are fascicles?
Bundles of fibers
What connective tissue covering surrounds fibers?
Endomysium
Collagen from CT layers merge to form ___ or ___ which attach muscle to bone
tendons; aponeurosis
Which (tendons/aponeurosis) are “rope-like”?
tendons
Which (tendons/aponeurosis) are “sheet-like”?
aponeurosis
What do motor neurons do?
Stimulate skeletal muscle contraction
What are axon terminals connected to?
Muscle fibers
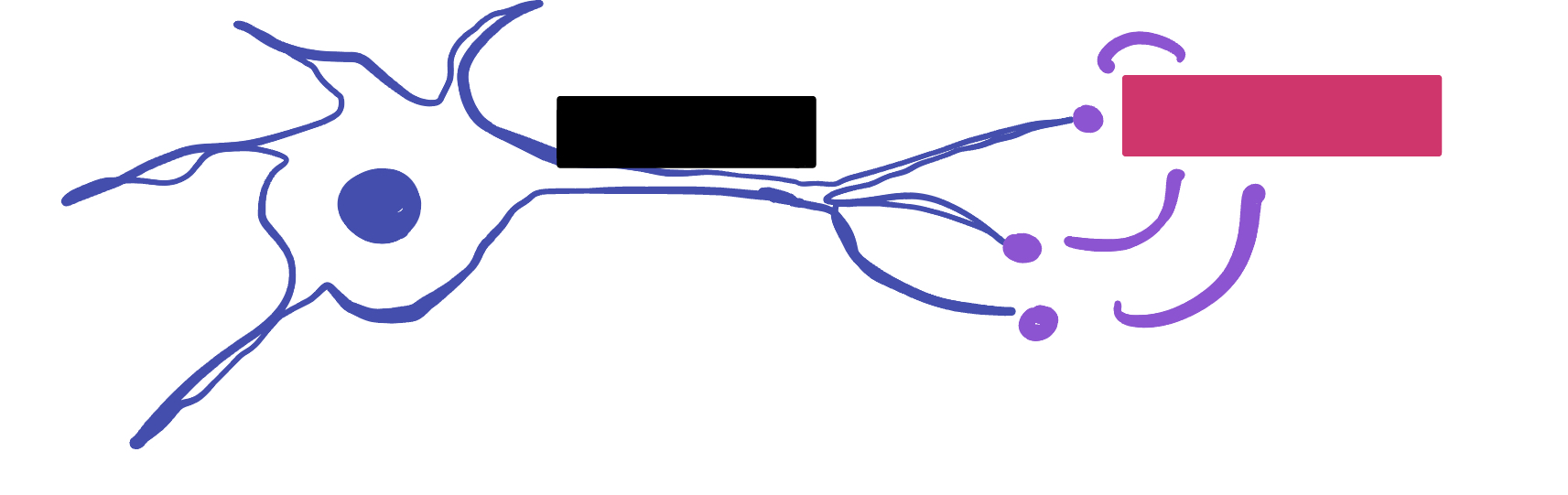
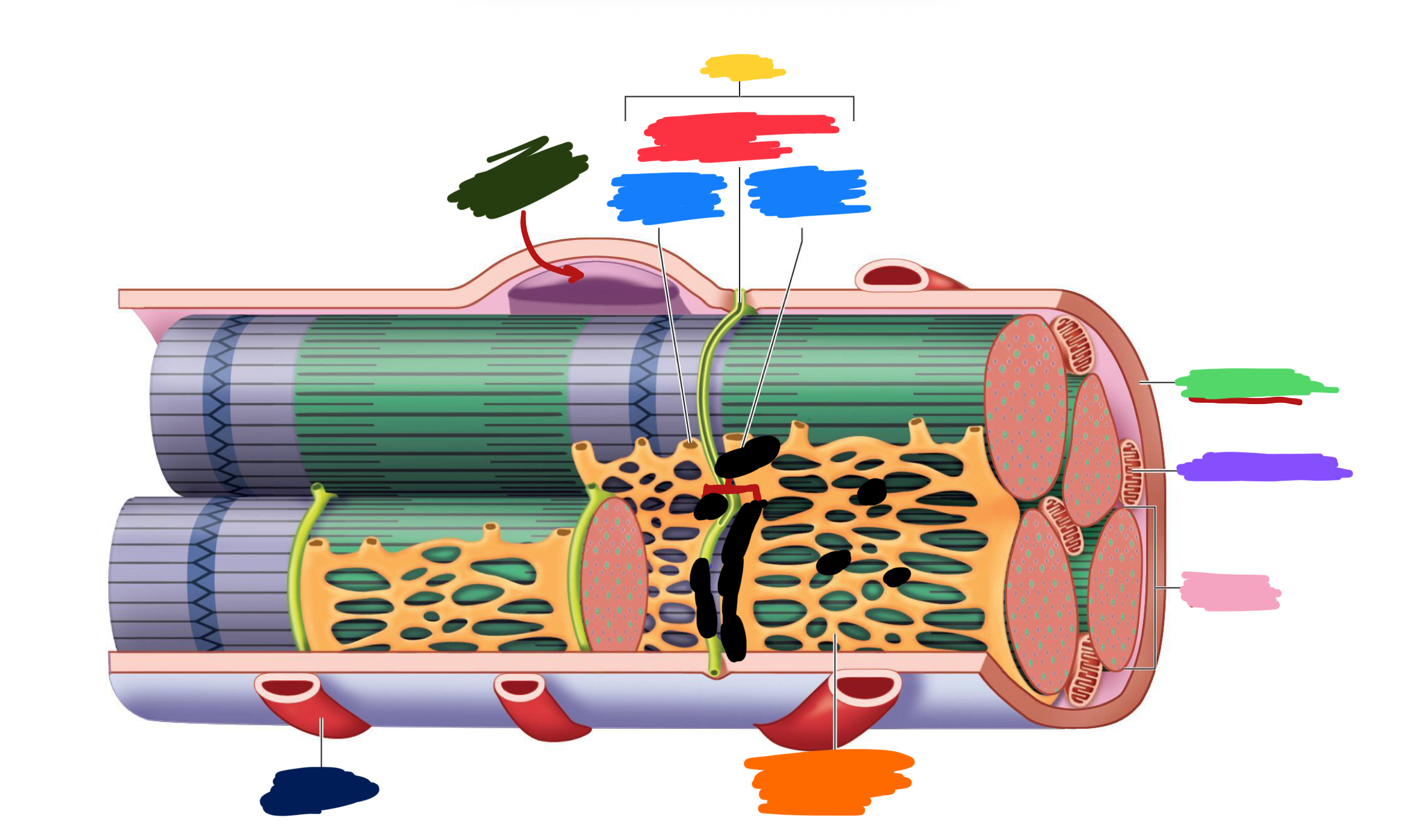
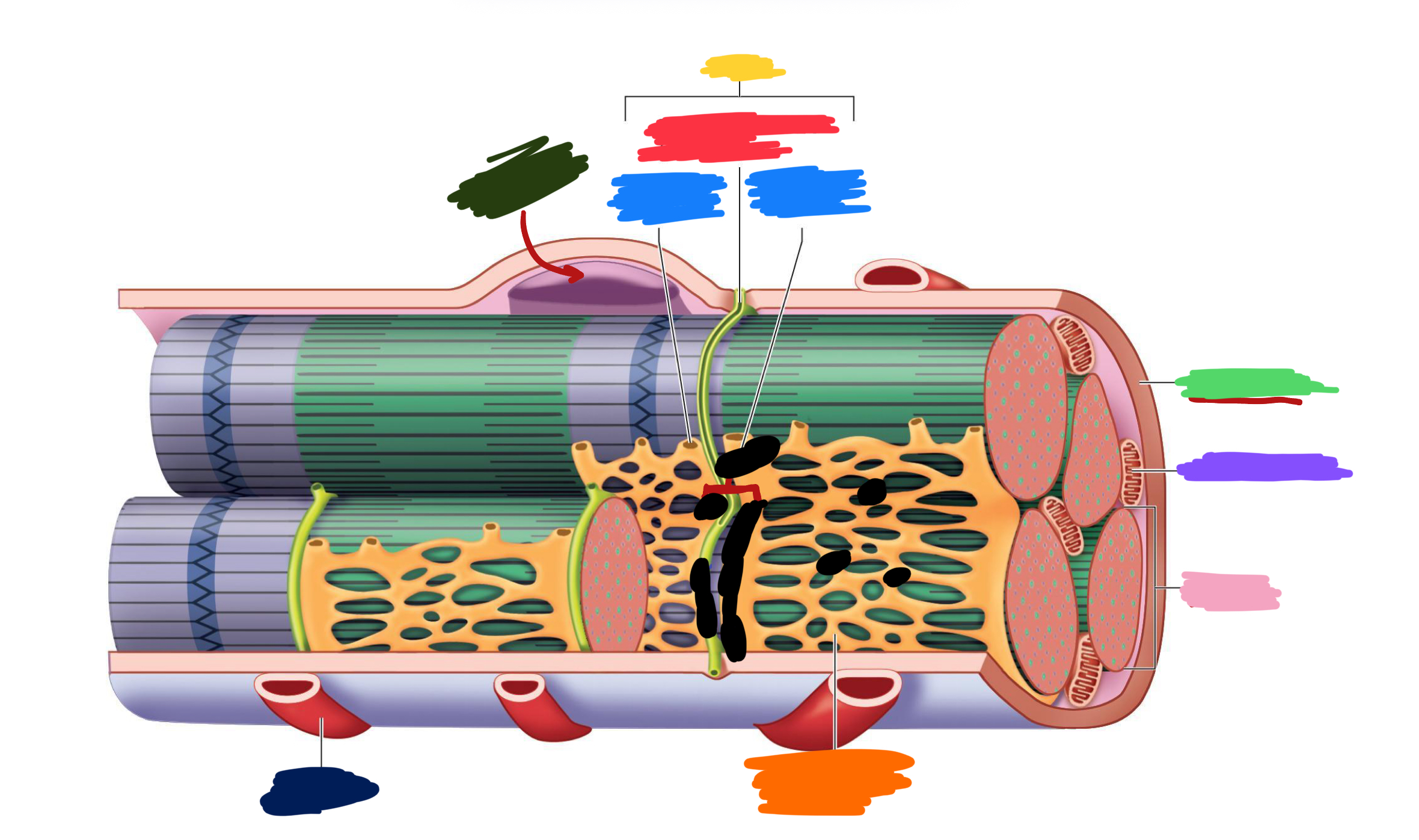
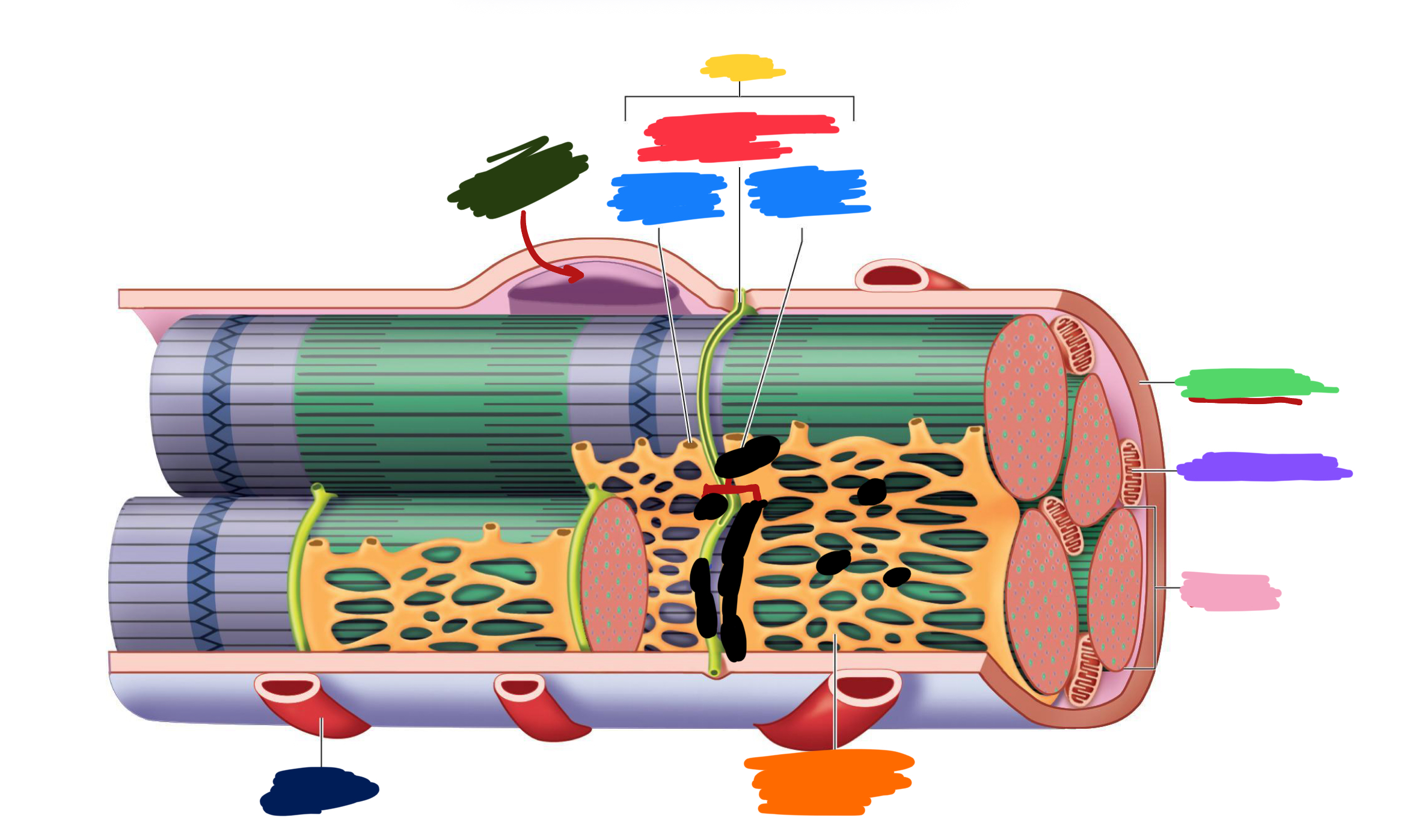
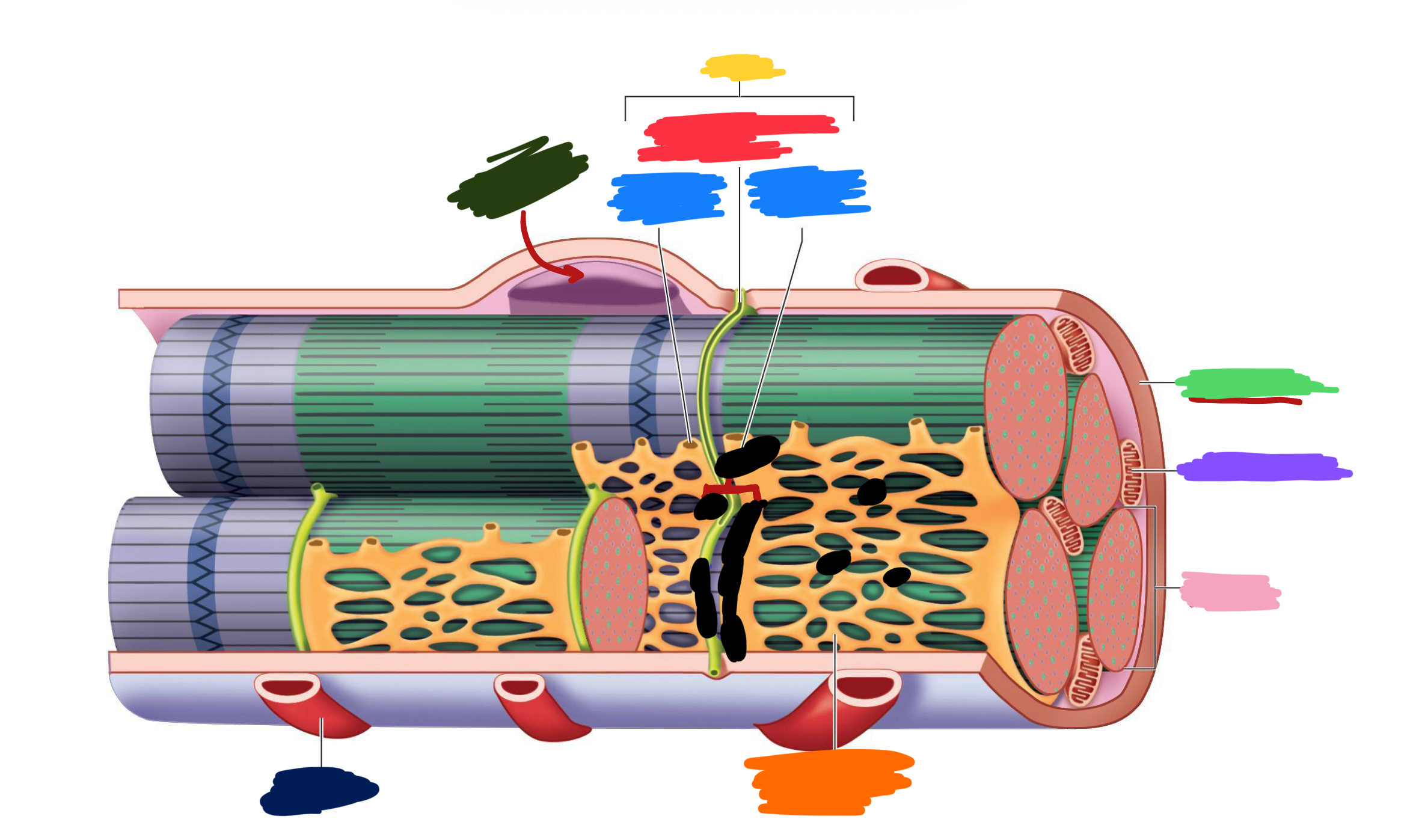
Which color is likely covering the label for “axon”?
Black
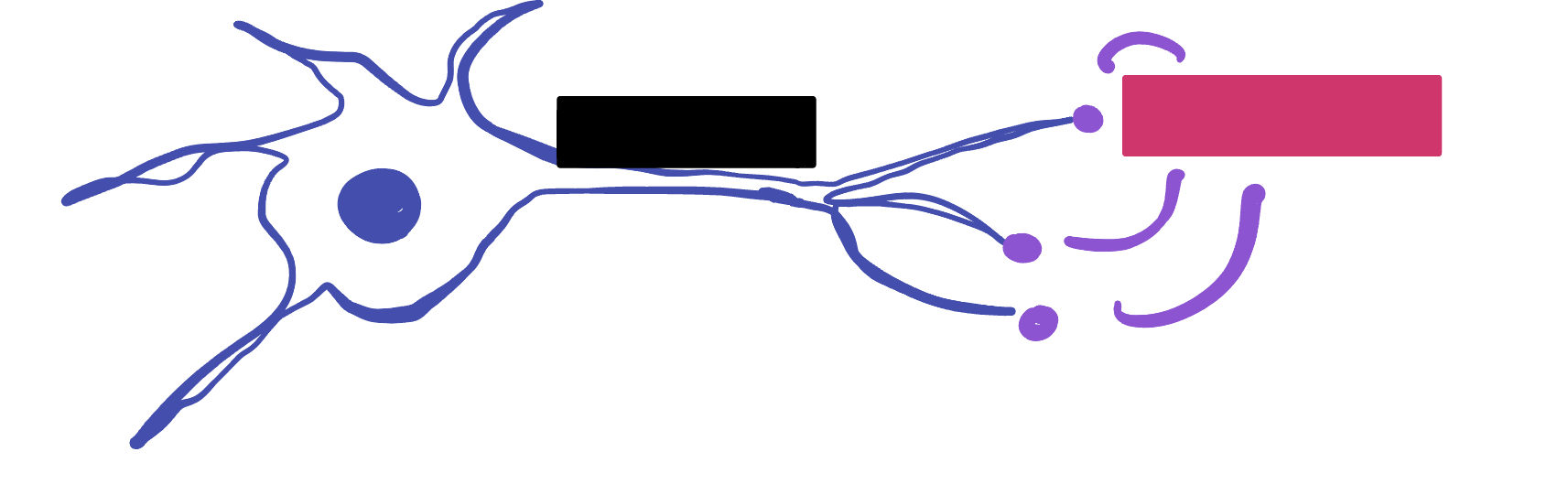
Which color is likely covering the label for “terminal”?
Pink
What 2-3 things extend with a nerve through the CT layers?
Artery and 1-2 veins
Extensive ___ beds surround muscle fibers
capillary
Which color is likely covering the label “terminals”?
Black
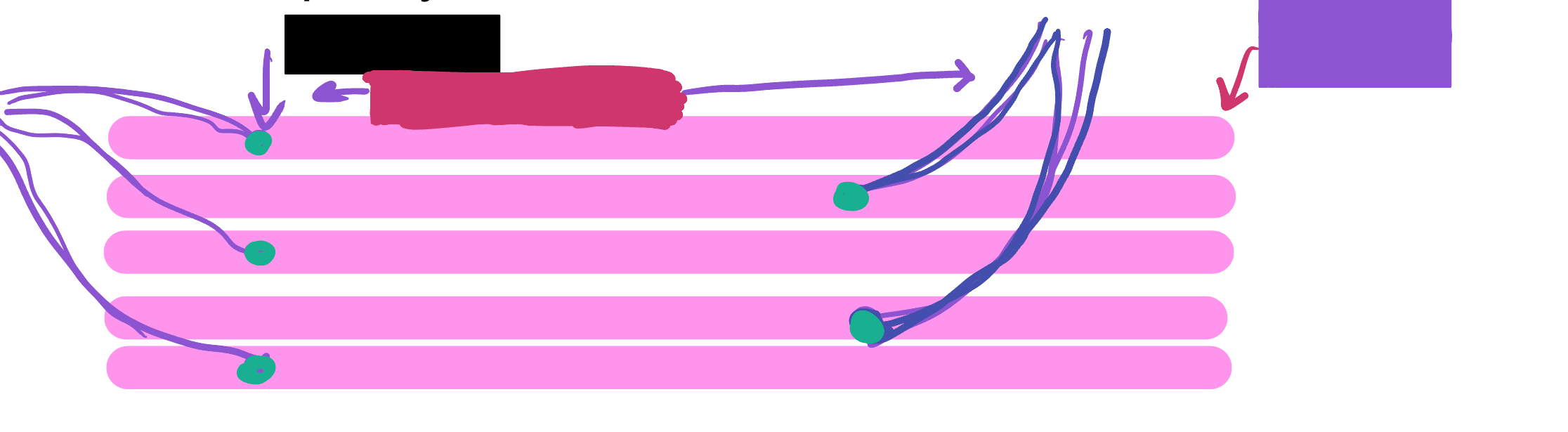
Which color is likely covering the label “motor units”?
Pink
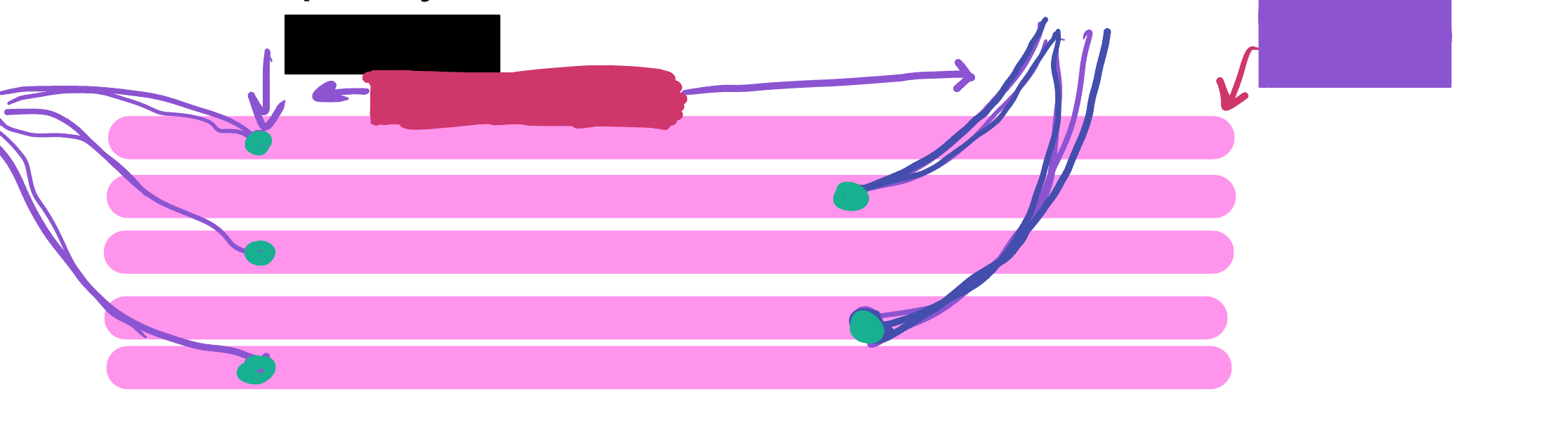
Which color is likely covering the label “muscle fibers”?
Purple
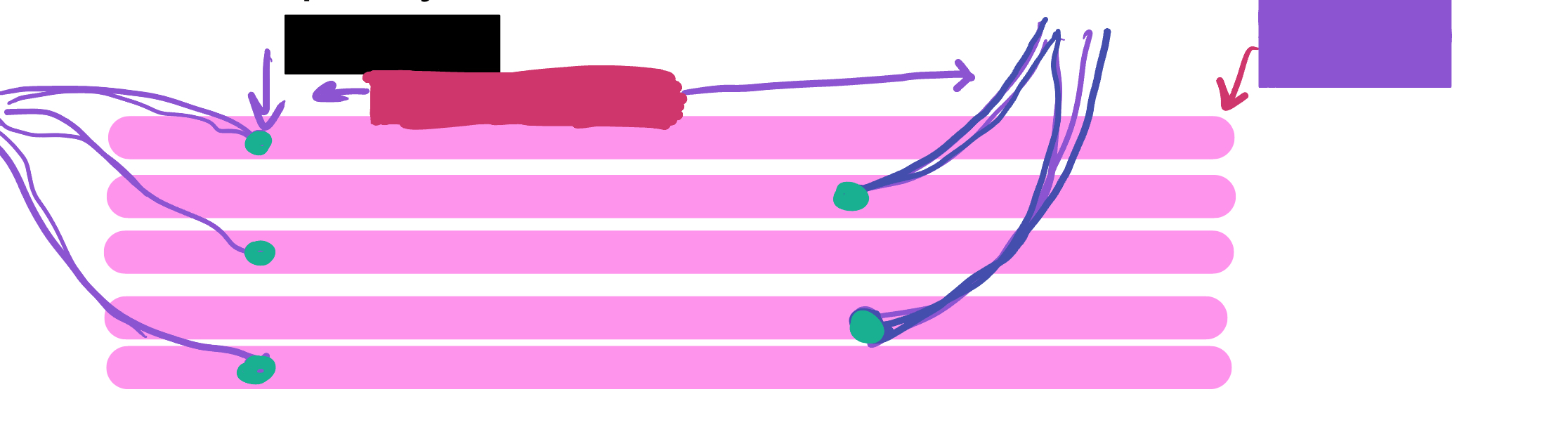
What is the green likely representing?
Perimysium
What is the red likely representing?
Endomysium
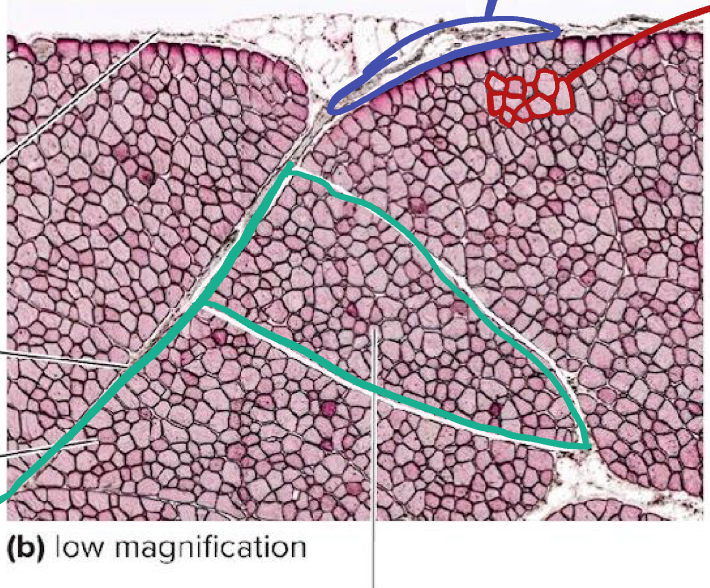
What is the blue likely representing?
Epimysium
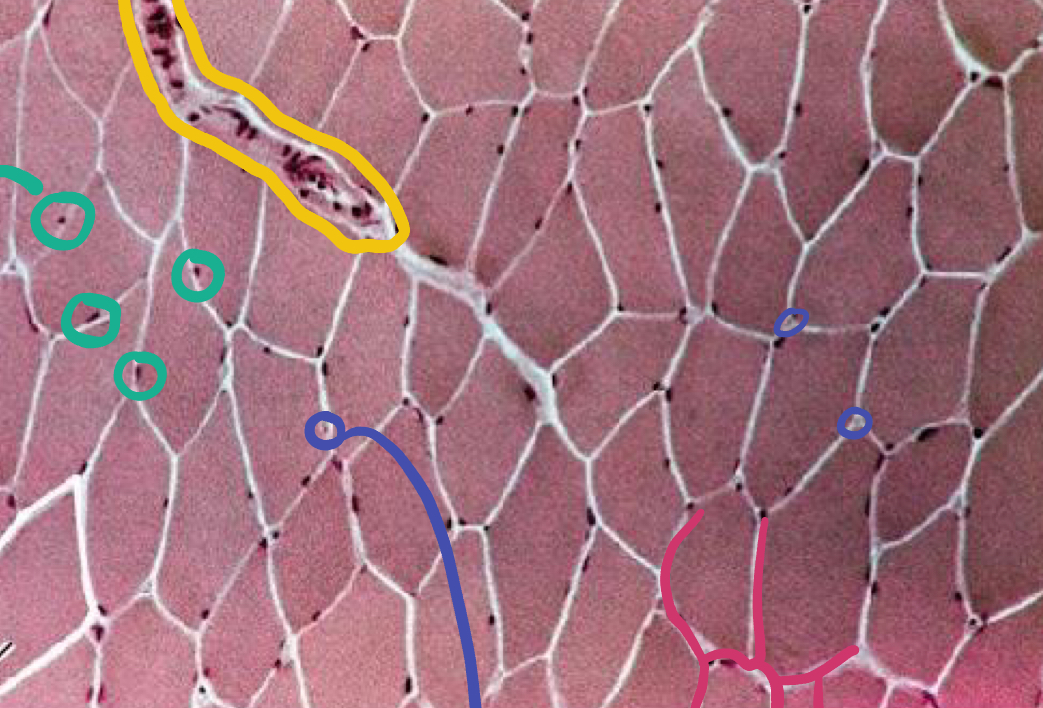

What is the yellow likely representing?
Blood vessel
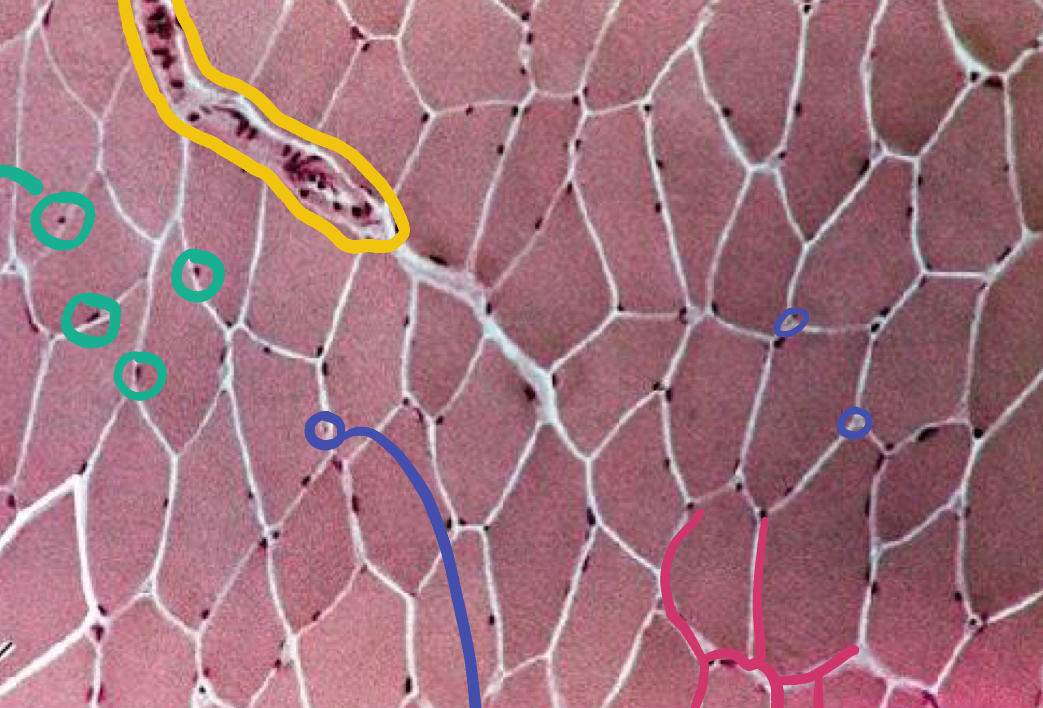

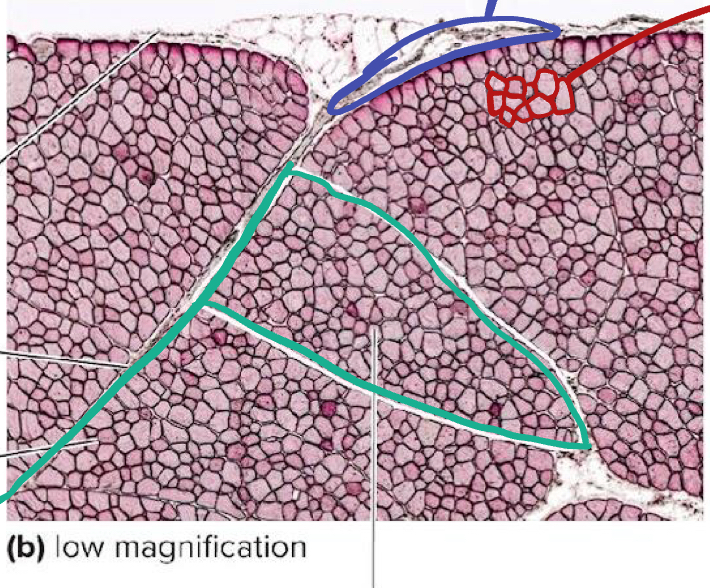
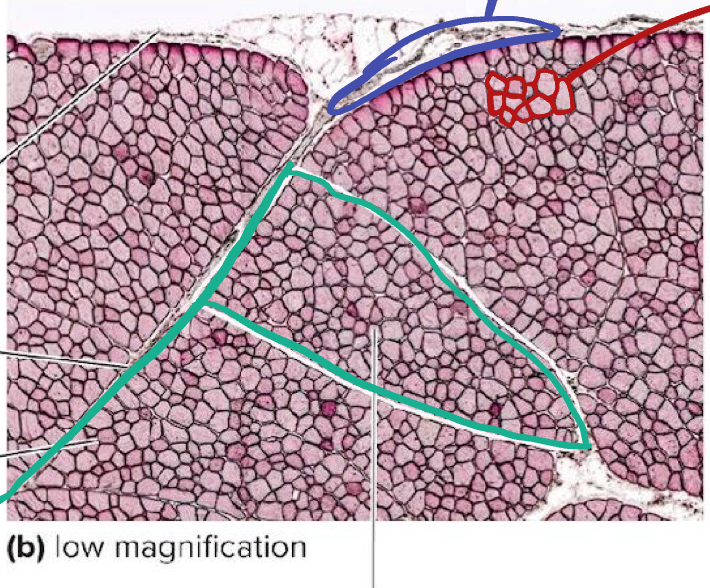
What is the green likely representing?
Nucleus
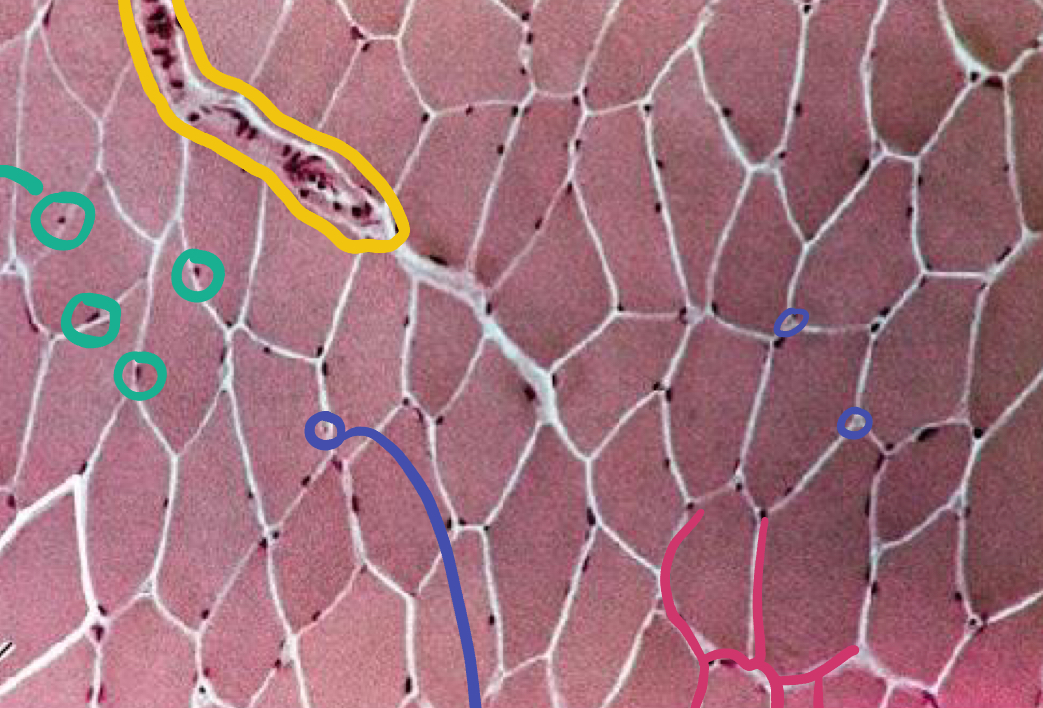

What is the blue likely representing?
Capillaries
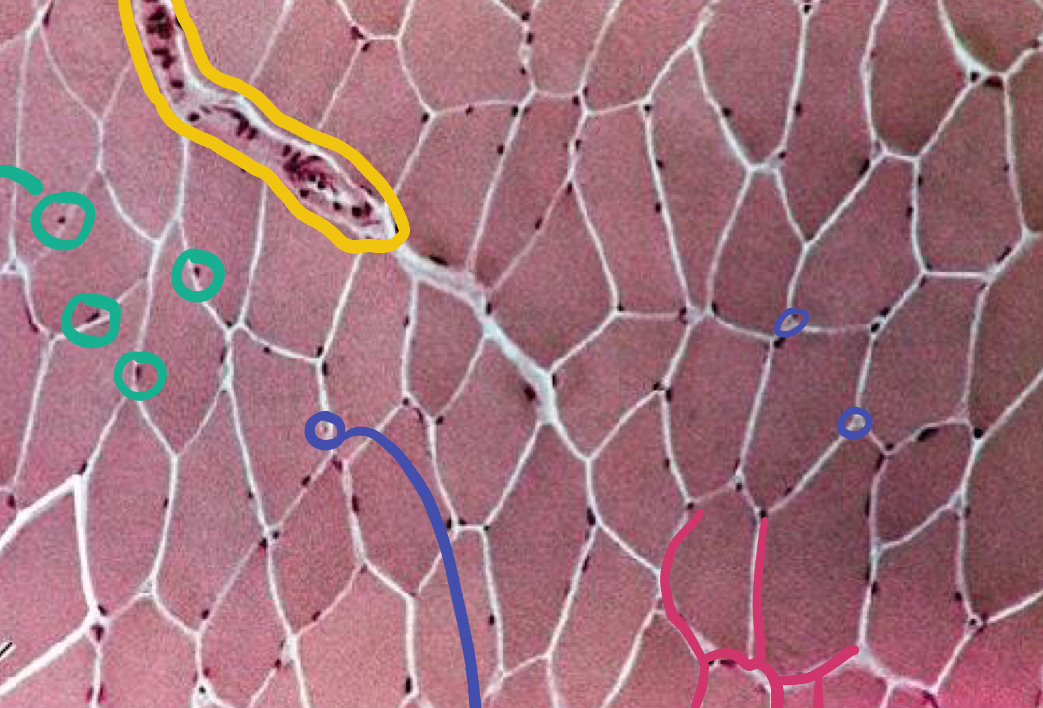

What is the pink likely representing?
Endomysium
What two prefixes relate to “muscle”?
myo- and sarco-
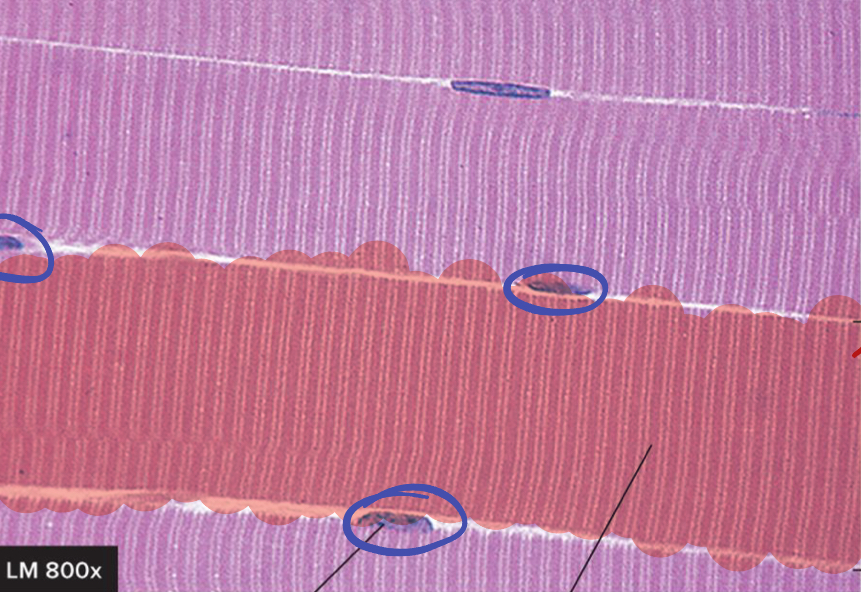
What is circled in blue?
Nucleus
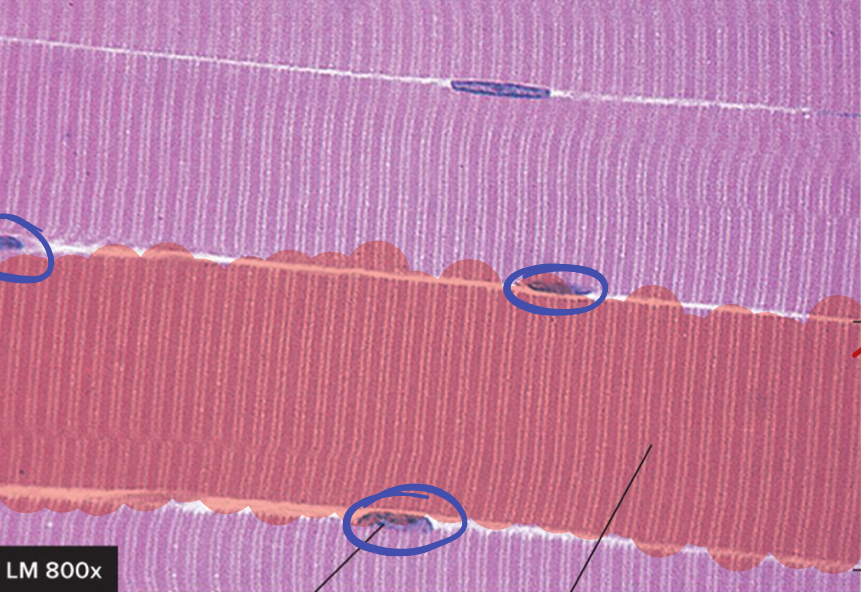
How many muscle fibers are in the red highlighted section?
1
Muscle Fibers develop from the fusion of what?
Myoblasts
What is the average length of a muscle fiber?
1 - 4 mm
T/F muscle fibers can grow up to 1 foot long
True
What is the average diameter of a skeletal muscle fiber?
10 to 100 microns
Number of fibers (increases/decreases/remains constant) after birth
remains constant
Muscles get larger due to ___ of muscle fibers
hypertrophy
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of muscle fiber
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of muscle fiber
Transverse tubules (T tubules)
folds of sarcolemma that go down into muscle fiber
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - specifically for storing calcium
Enlarged portions called _____ lie adjacent to T tubules
terminal cisternae
Terminal cisternae
at end of SR; holds/stores calcium
Two terminal cisternae and their associated T tubules form a ___
triad
What label is covered by yellow
Triad
What label is covered by red?
Transverse tubule (T tubule)
What label is covered by blue?
Terminal cisterna
What label is covered by dark green?
Nucleus
What label is covered by bright green?
Sarcolemma
What label is covered by purple?
Mitochondrion
What label is covered by pink?
Myofibril
What label is covered by orange?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
What label is covered by dark blue?
Capillary
Mechanical component structures allow muscles to contract; due to what two things?
Myofibrils & Myofilaments
What are Myofibrils?
bundle of proteins; contain the myofilaments that contract
What are the two types of myofilaments
Actin and Myosin
(Actin/Myosin) is the thin myofilament
Actin
(Actin/Myosin) is the thick myofilament
Myosin
Myofilaments arrange into orderly units called ___
Sarcomeres
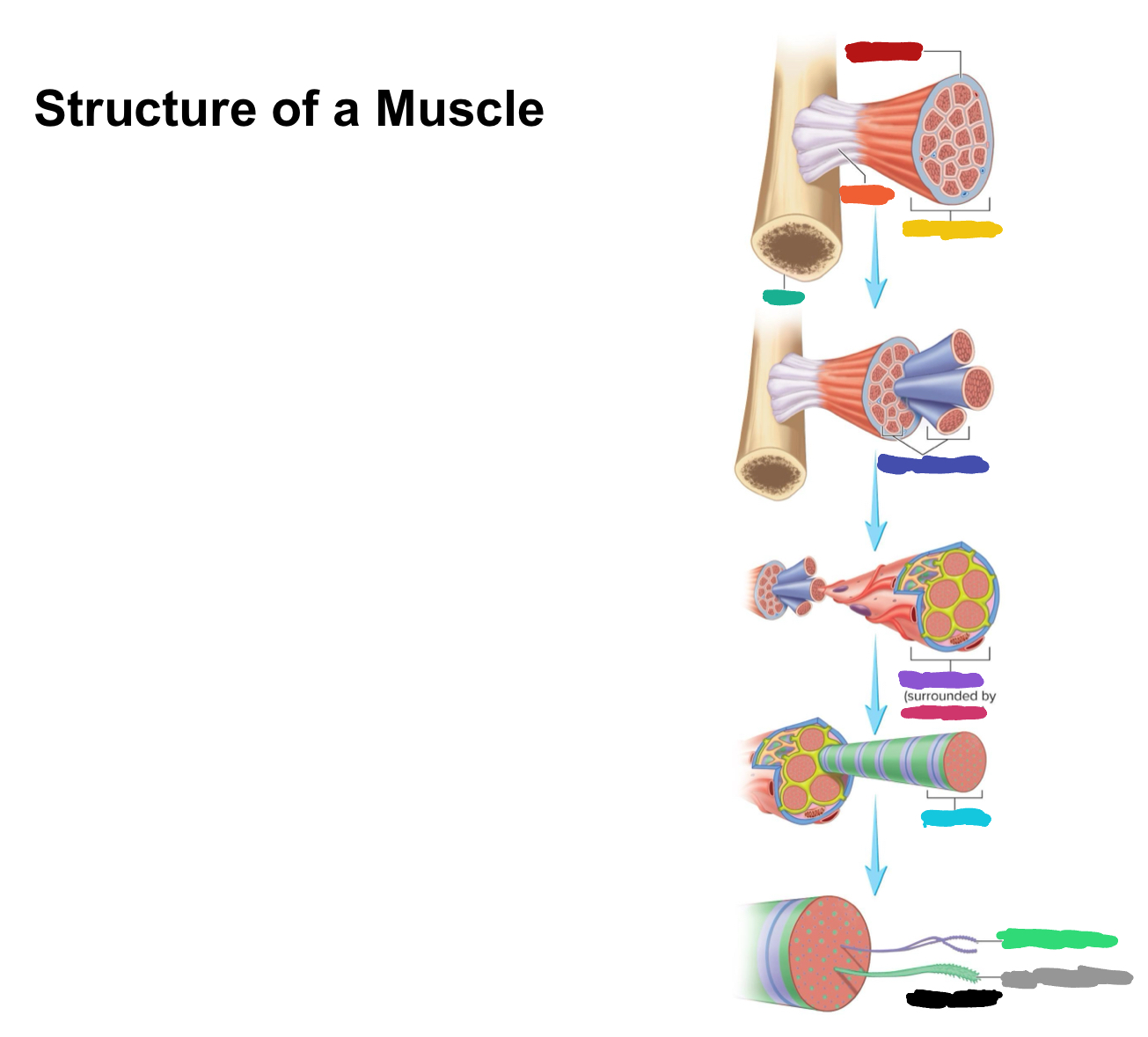
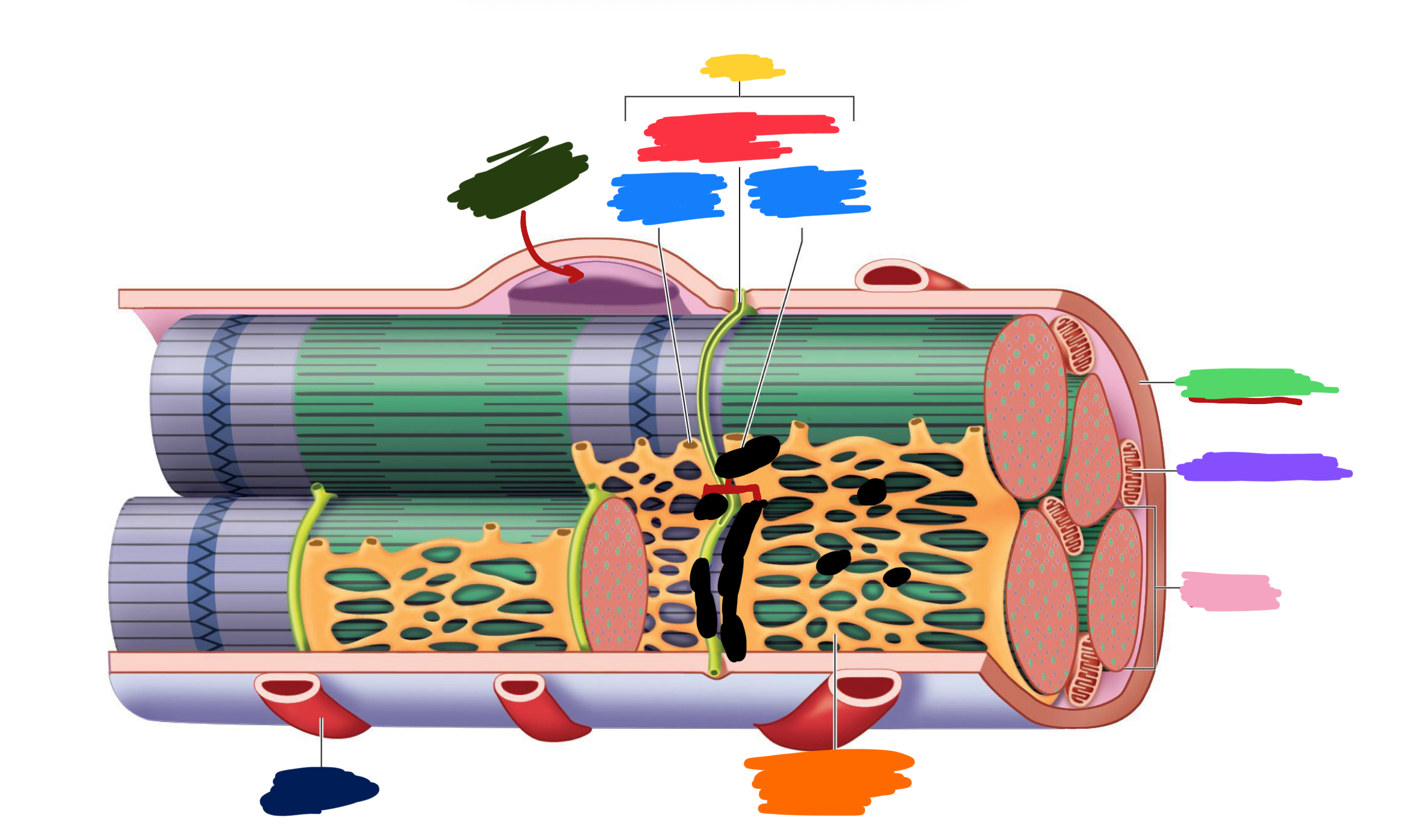
What label is covered by red?
Epimysium
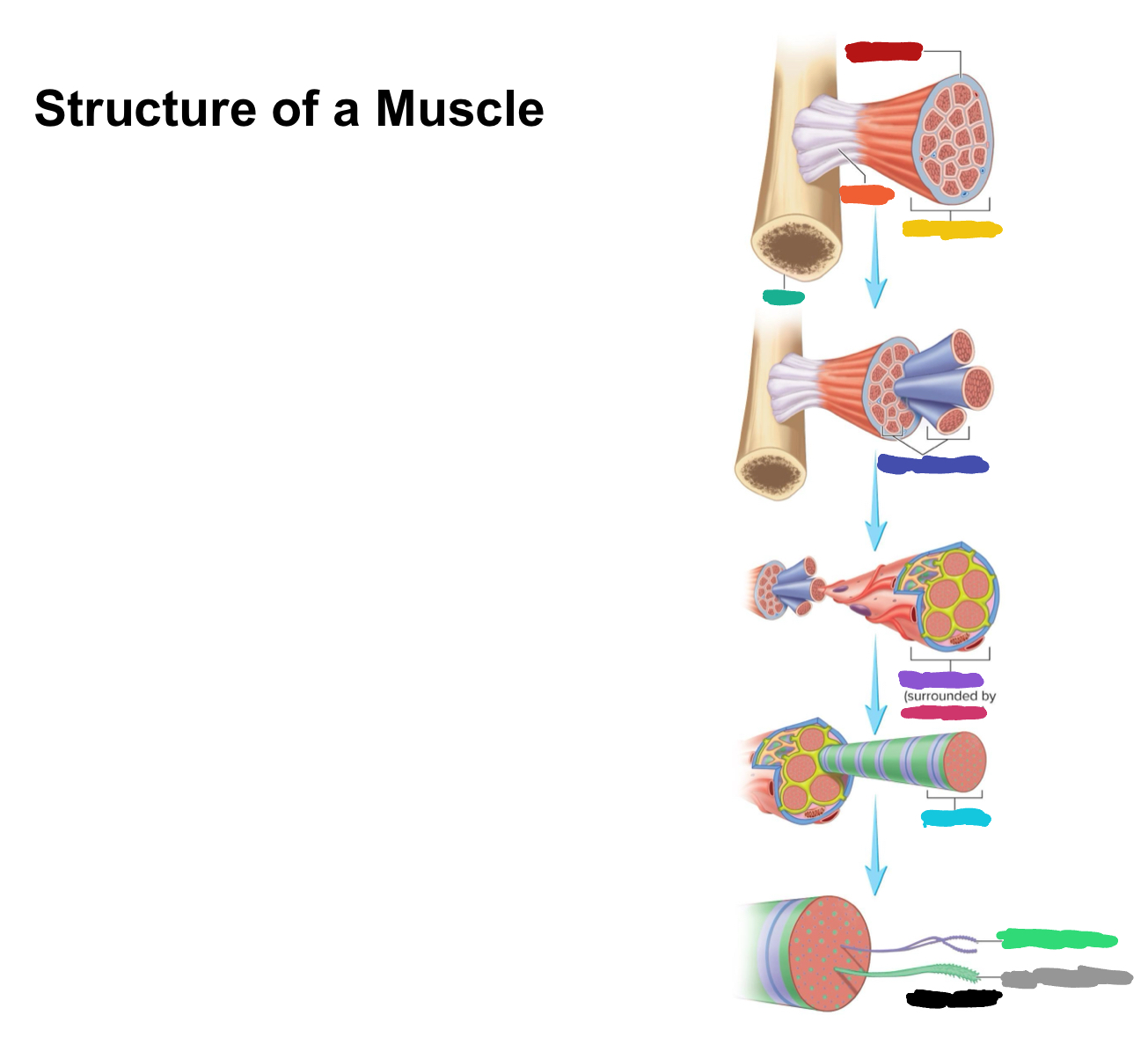
What label is covered by orange?
Tendon
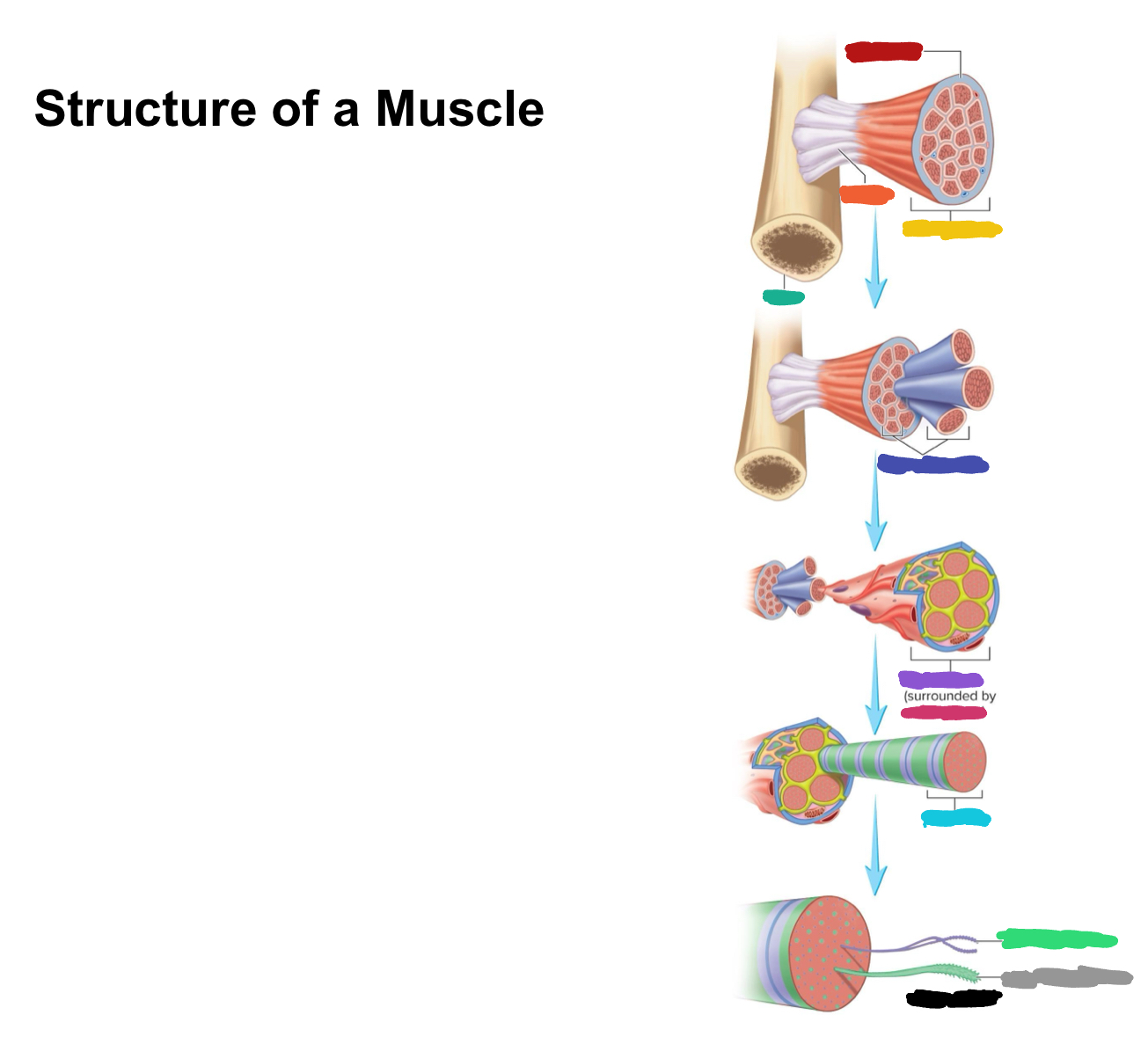
What label is covered by yellow?
Whole muscle
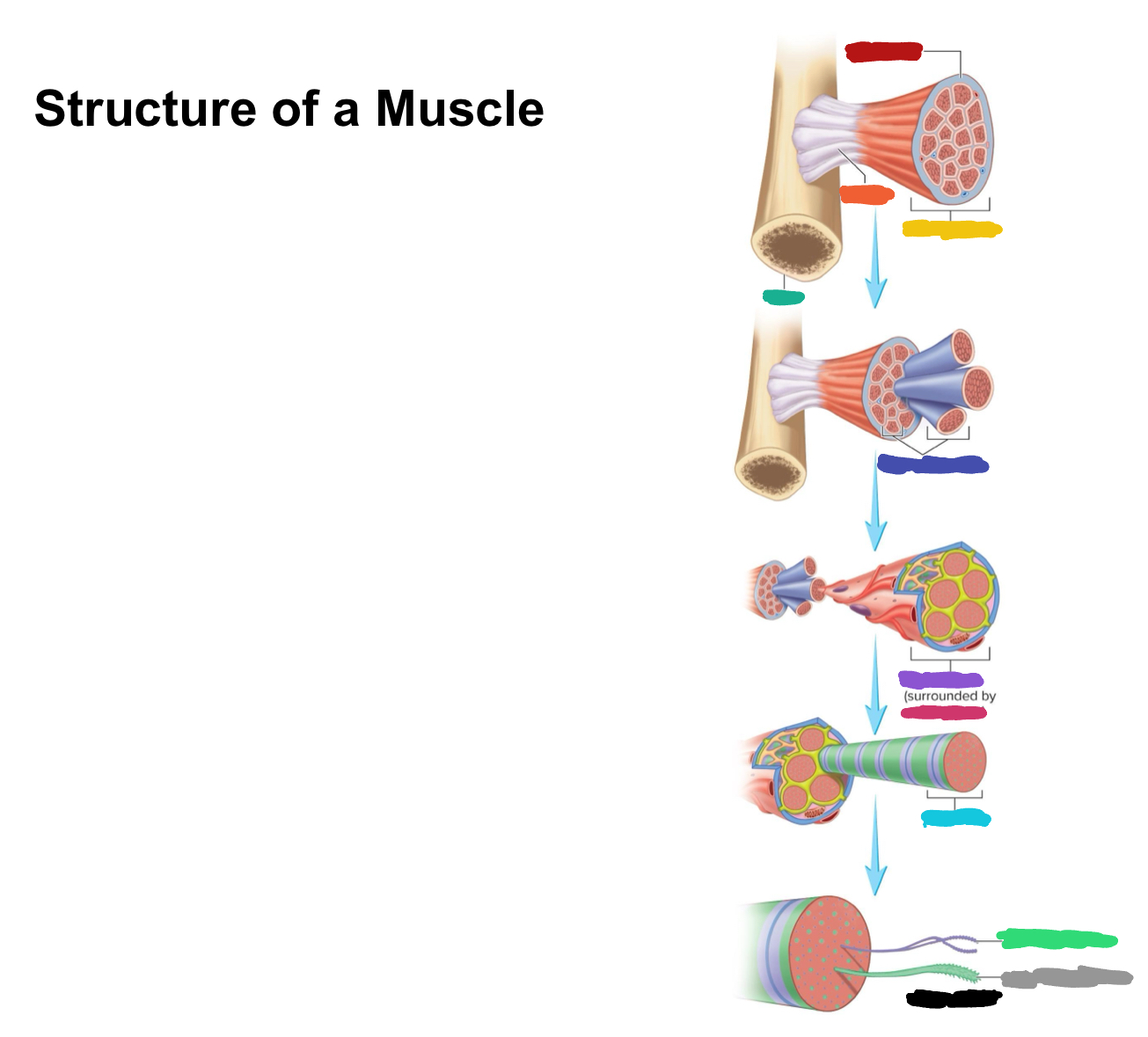
What label is covered by dark green?
Bone
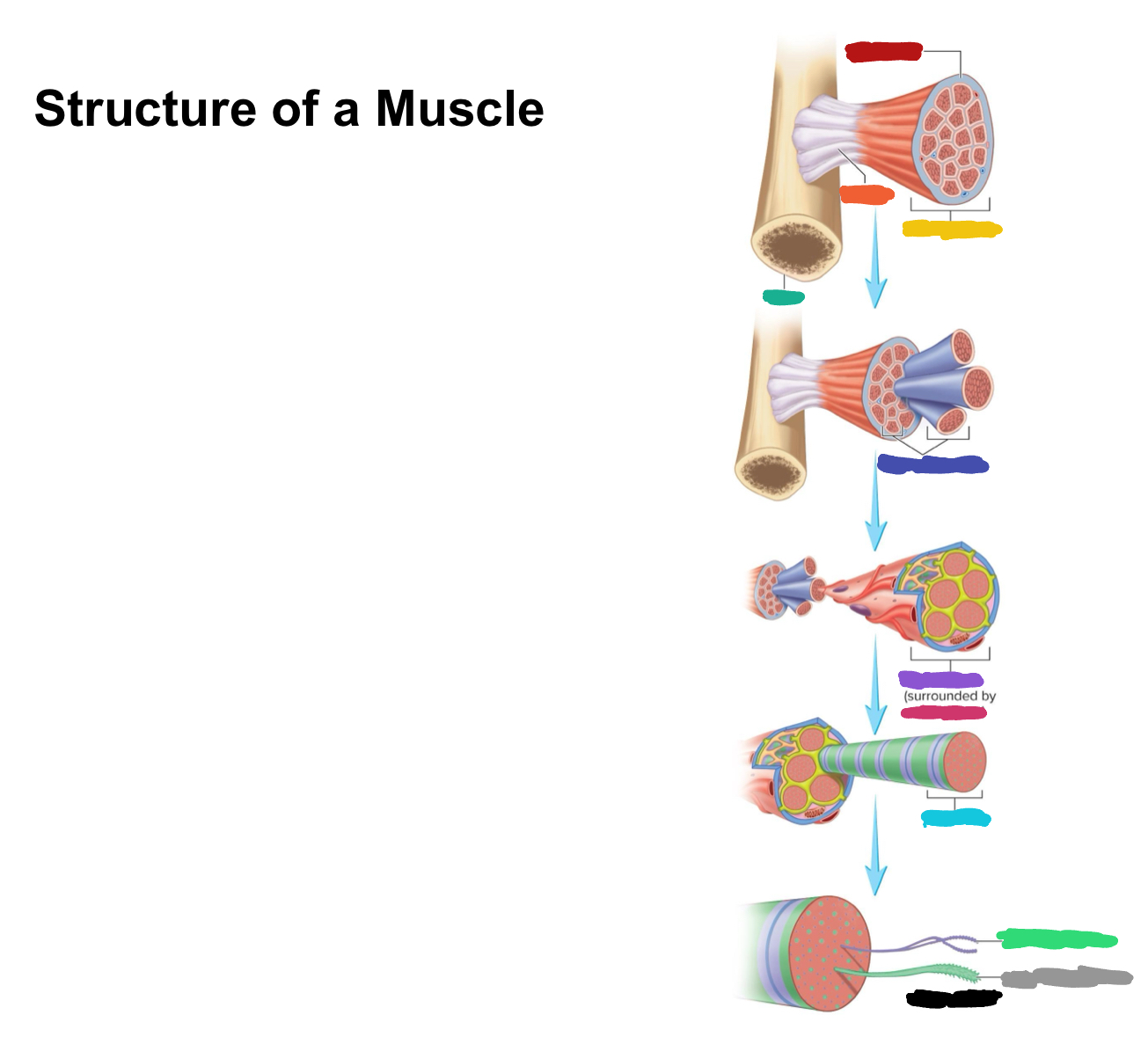
What label is covered by dark blue?
Muscle fascicles
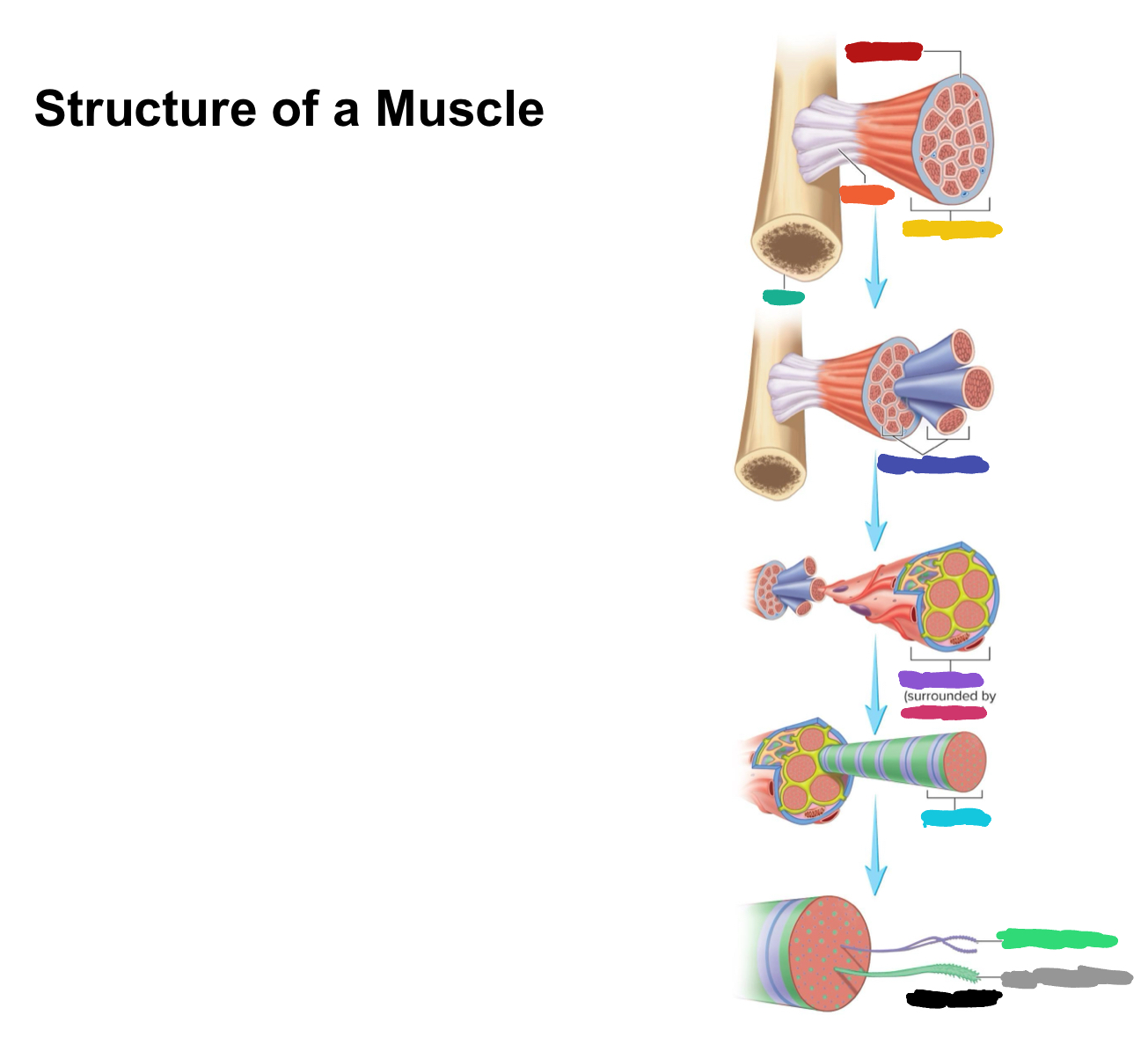
What label is covered by purple?
Muscle fiber
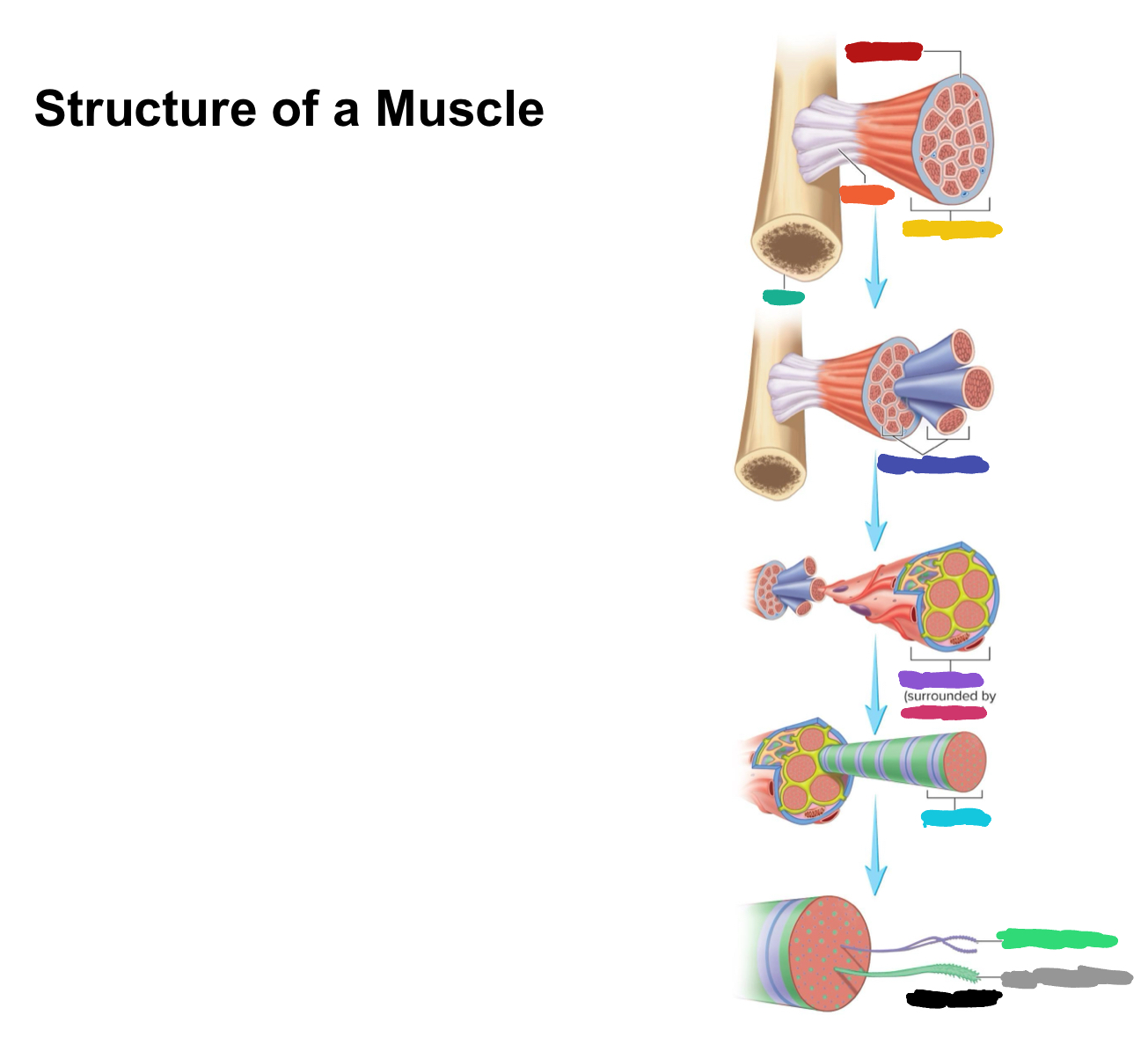
What label is covered by pink?
Endomysium
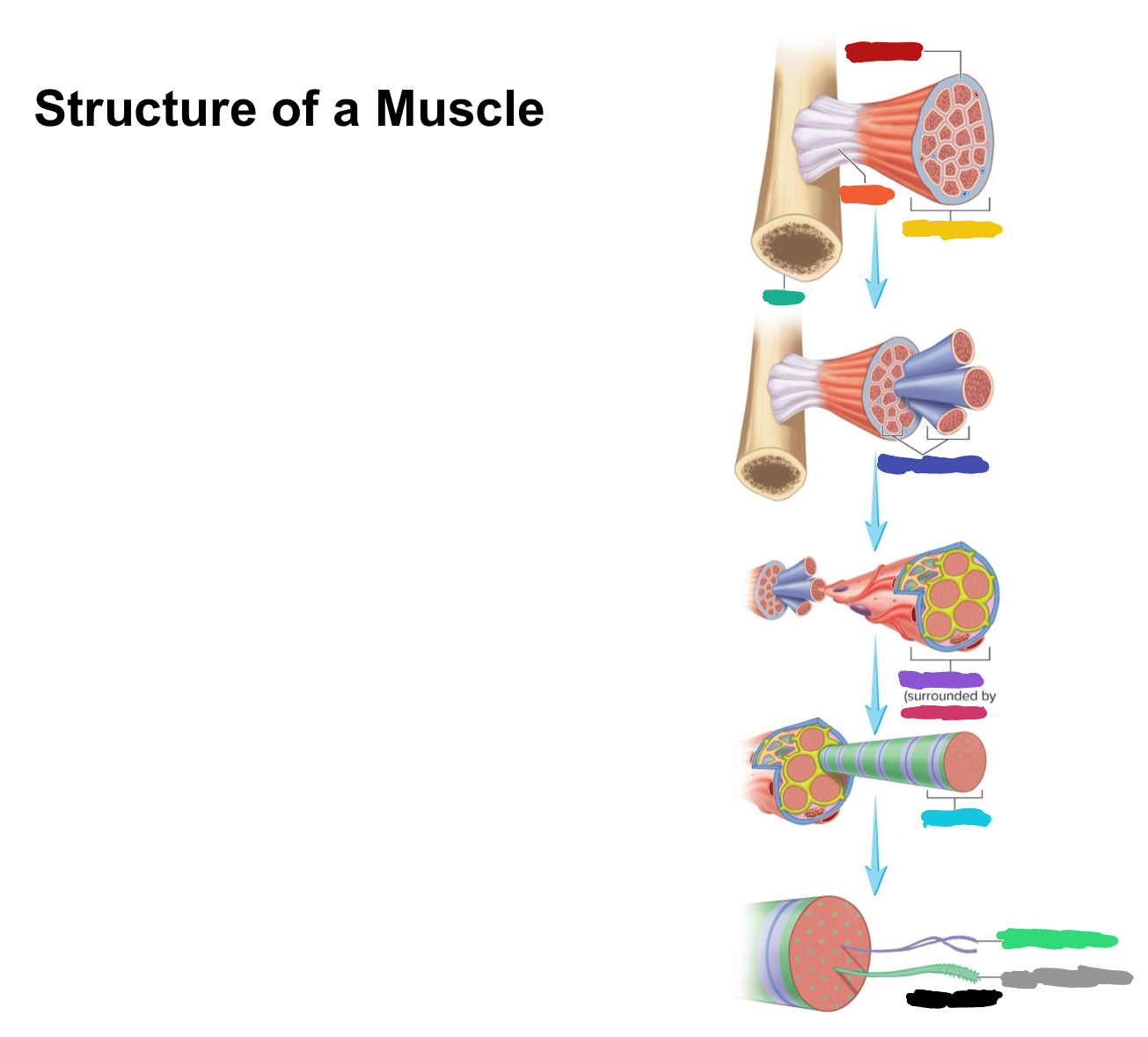
What label is covered by Miku Blue?
Myofibril
What label is covered by bright green?
Actin Myofilament
What label is covered by gray?
Myosin myofilament
What label is covered by black (hint: its referring to both bright green and gray)
Myofilaments
What are sarcomeres?
basic functional unit of a fiber
What is the smallest part that can contract?
Sarcomere
What is the Z disk?
Filamentous proteins
Z disks are the attachment point for what?
Actin
What are the four regions of the sarcomere?
I bands, A bands, H zone, M line
How to distinguish the I band?
lighter region
How to distinguish the A band?
Darker region
How to distinguish the H zone?
lighter area within A band
How to distinguish the M line?
Dark line down middle of H zone
What makes the striated appearance of skeletal muscle?
A and I bands of parallel myofibrils are aligned
Titin filaments
elastic chains of amino acids; make muscles extensible and elastic
Define Fast-Oxidative
contract fast to produce a great force
Fast glycolytic fibers
produce a strong contraction, that fatigue quickly and are white in colour
Slow oxidative fibers -
fatigue slowly