BIOM 3010 Midterm 3 Cardiovascular & Urogenital System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/233
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
1
New cards
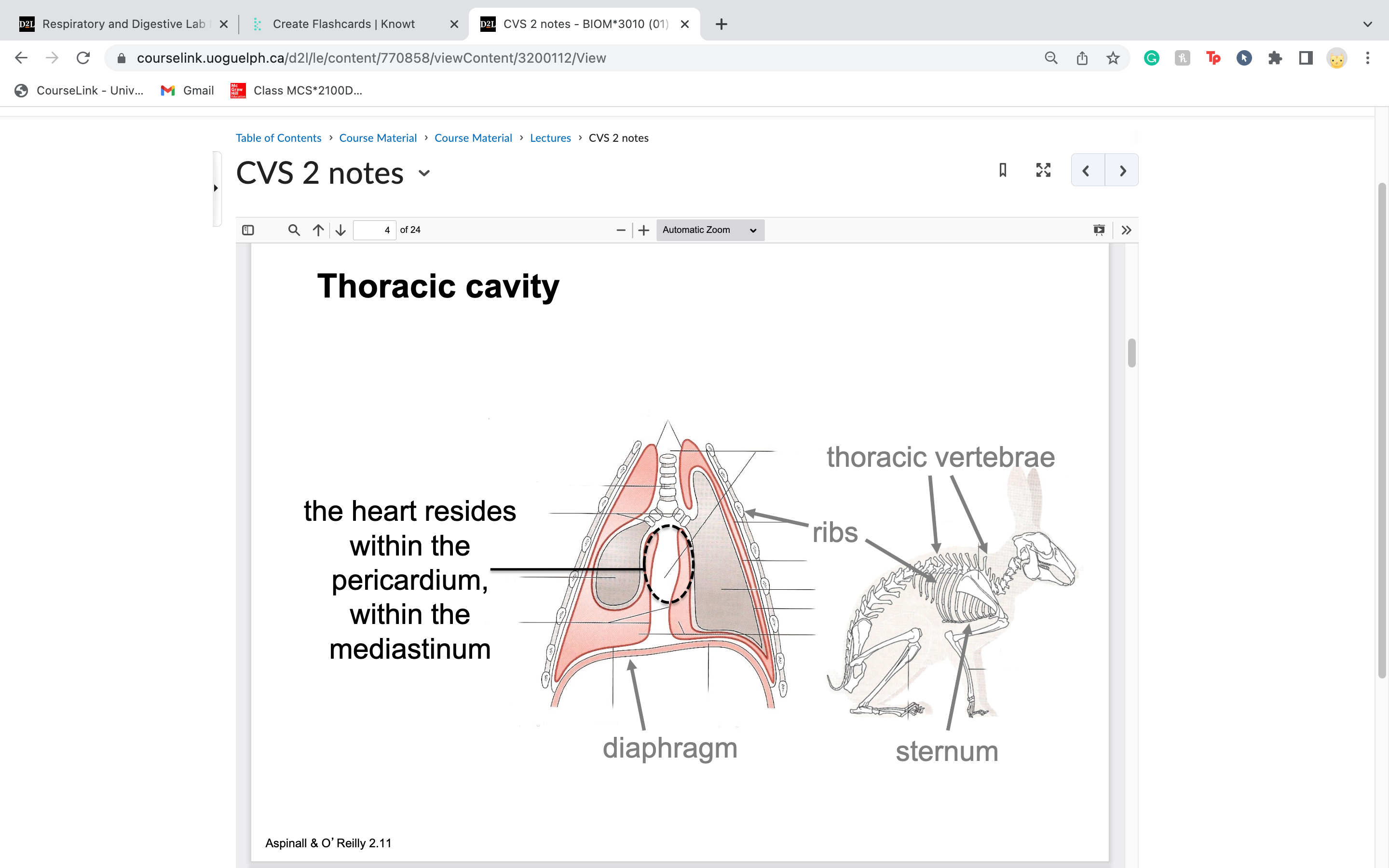
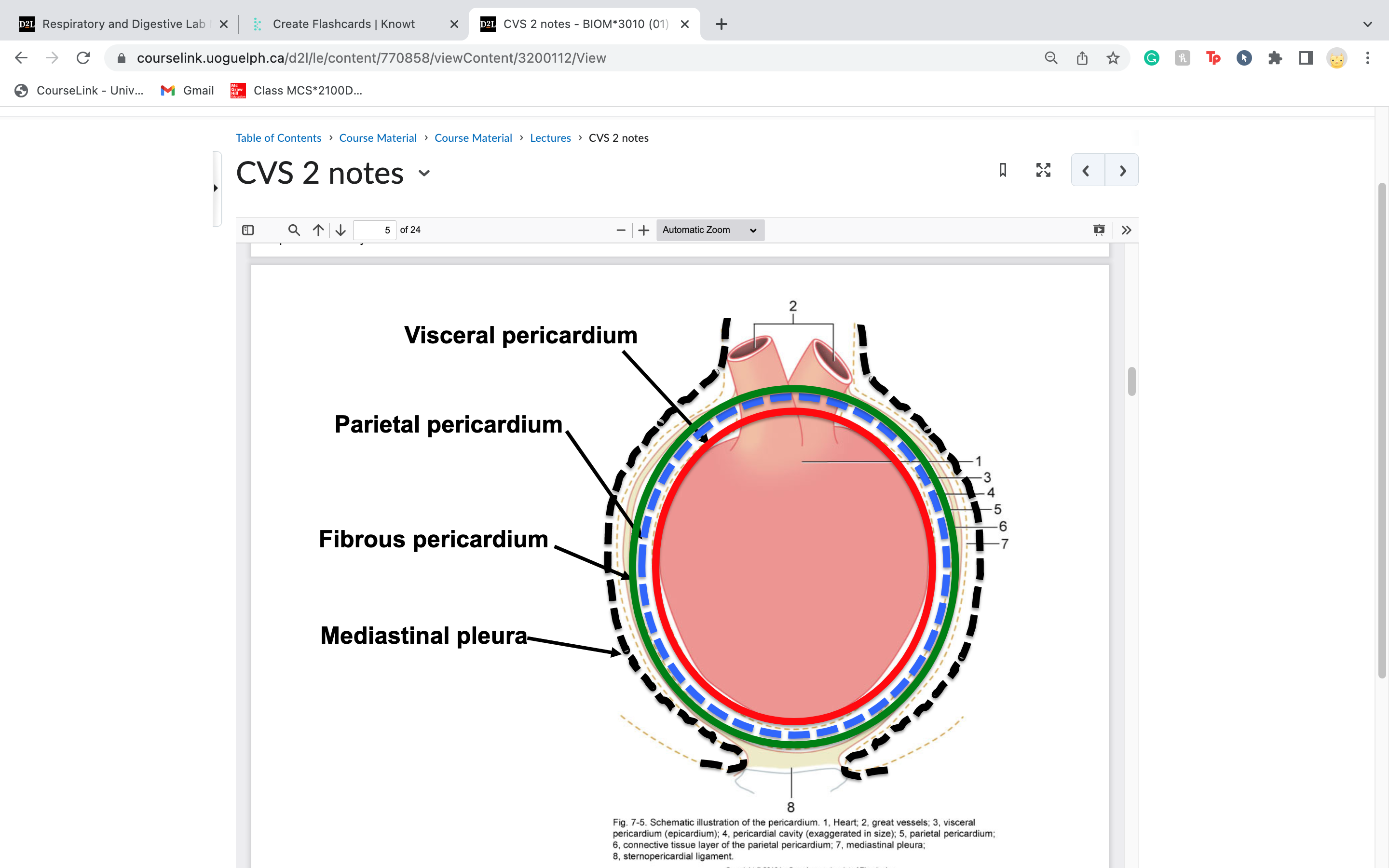
the heart resides within the pericardium, within the mediastinum... the heart is made of 3 layers:
Visceral pericardium
Parietal pericardium
Fibrous pericardium
2
New cards
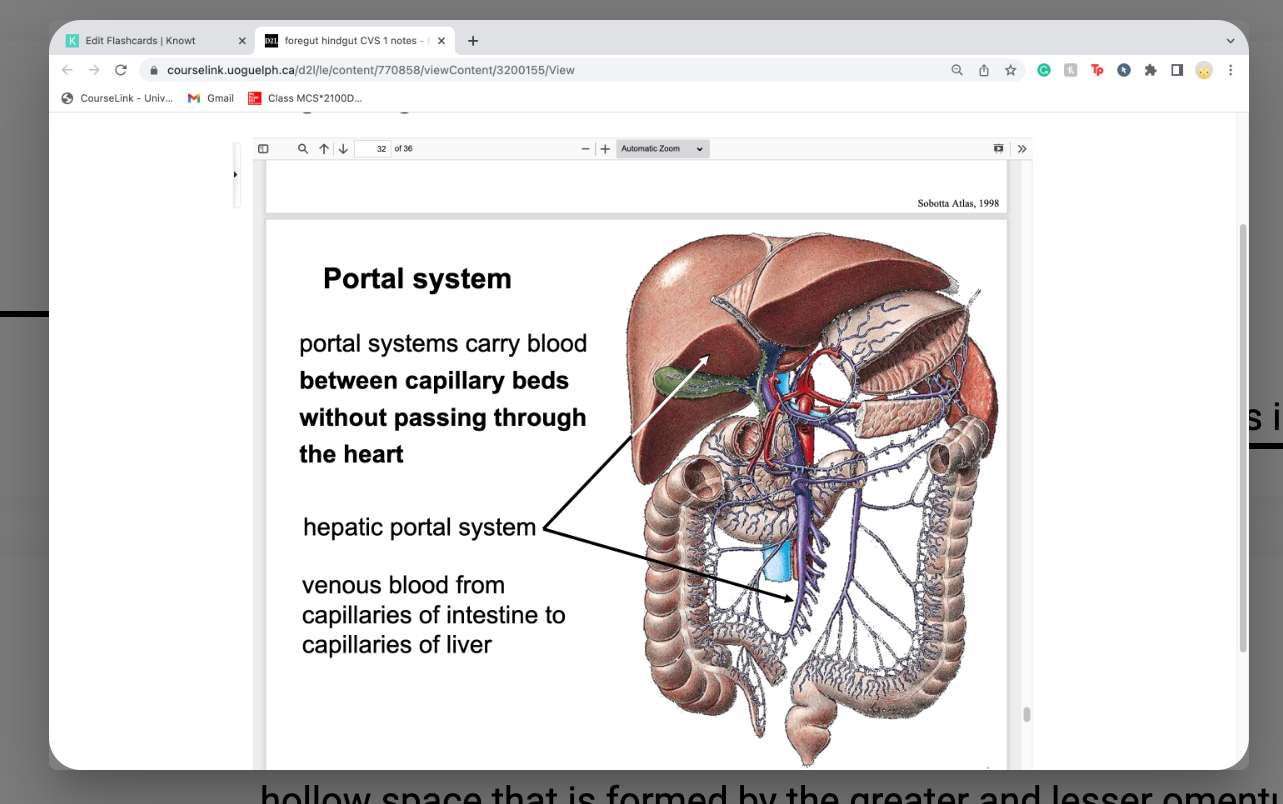
portal system
portal systems carry blood between capillary beds
without passing through the heart
-hepatic - capillary bed in digestive system to capillary beds in liver itself
without passing through the heart
-hepatic - capillary bed in digestive system to capillary beds in liver itself
3
New cards
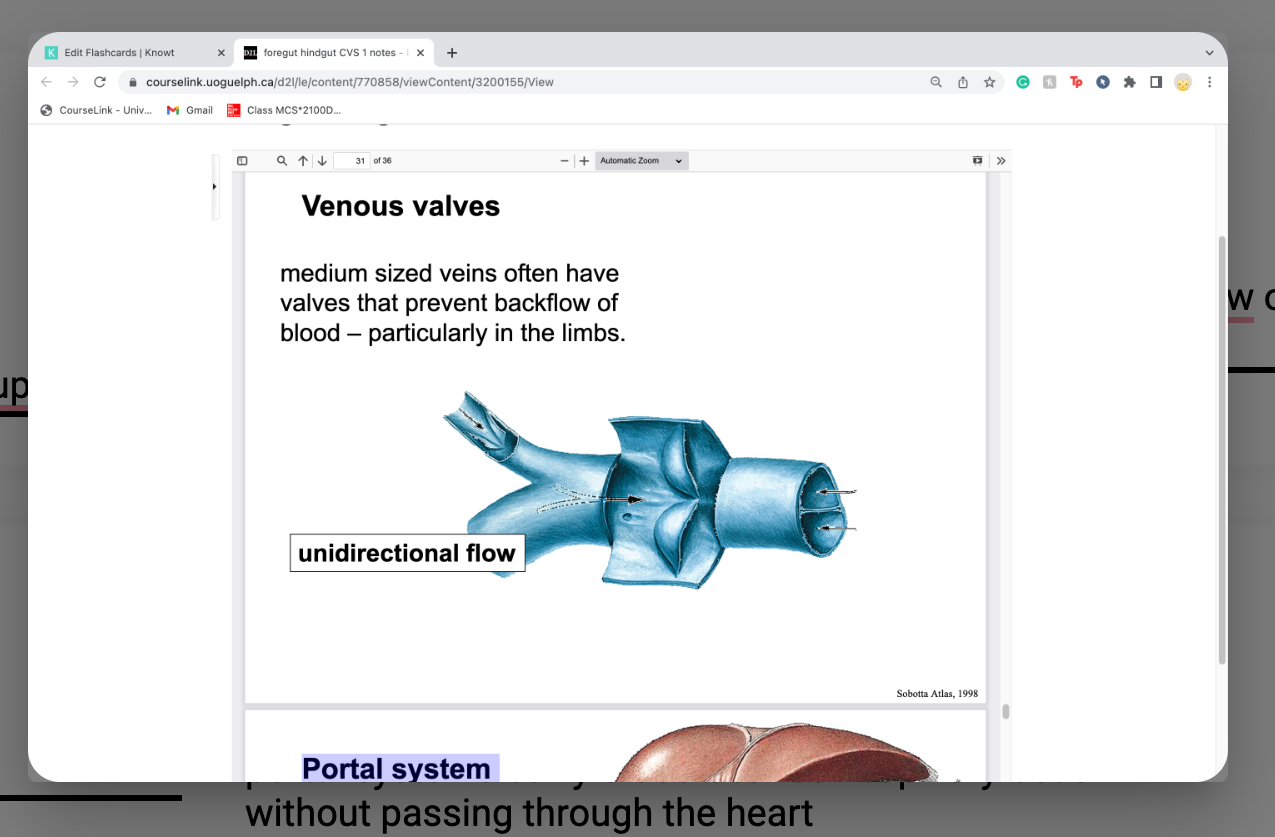
Venous valves create __________________ flow
*semilunar valve - makes cup
*semilunar valve - makes cup
unidirectional
medium sized veins often have valves that prevent backflow of
blood – particularly in the limbs.
medium sized veins often have valves that prevent backflow of
blood – particularly in the limbs.
4
New cards
anastomosis
direct connections between two different arteries and/or an artery and vein
represent alternative routes of blood flow when a vessel becomes constricted or blocked
represent alternative routes of blood flow when a vessel becomes constricted or blocked
5
New cards
visceral pericardium
directly on the heart
6
New cards
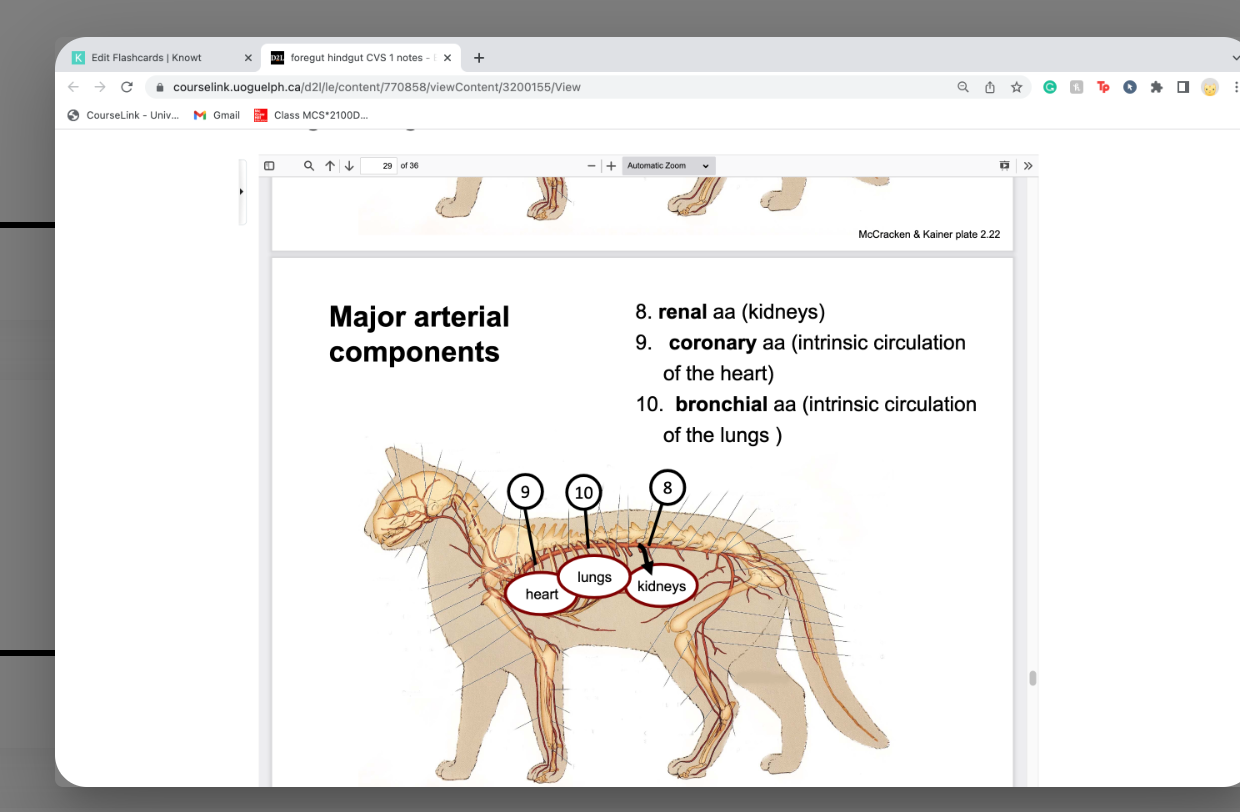
providing blood to lung tissue itself **NOT for oxygenation**
-intrinsic circulation of lungs
-intrinsic circulation of lungs
bronchiole arteries
7
New cards
functions of the cardiovascular system
1. transport (O2, CO2, nutrients, wastes, hormones)
2. regulation (pH, temperature, osmotic pressure)
3. protection (e.g., foreign material, diseases, clotting)
2. regulation (pH, temperature, osmotic pressure)
3. protection (e.g., foreign material, diseases, clotting)
8
New cards
99% are red blood cells (___________)
1% are
white blood cells (_________)
1% are
white blood cells (_________)
erythrocytes
leukocytes
leukocytes
9
New cards
what are platelets and what do they do
platelets: cell fragments (control bleeding)
10
New cards
arteries take blood _________ from the heart, and they are:
away
thick, elastic & muscular
– arterioles (10-100μm)
thick, elastic & muscular
– arterioles (10-100μm)
11
New cards
capillaries (4-10μm) are very thin (only ____________)
epithelium
12
New cards
veins take blood _________ the heart and they are:
towards
thin, less elastic, & less muscular
– valves
– venules (10-100μm)
-most carry deoxygenated blood
thin, less elastic, & less muscular
– valves
– venules (10-100μm)
-most carry deoxygenated blood
13
New cards
pulmonary circulatory system
carries *deoxygenated* blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood
back to the heart
back to the heart
14
New cards
systemic circulatory system
supplies blood to all regions of the body including the lungs.
15
New cards
arteries carry blood to capillary beds in organs
• veins drain capillary beds
• veins drain capillary beds
capillary bed is an interwoven network of capillaries that supplies an organ.
16
New cards
digestive track and ______ require the most % of blood in body
kidney
17
New cards
common carotid and vertebral arteries
have a left and right
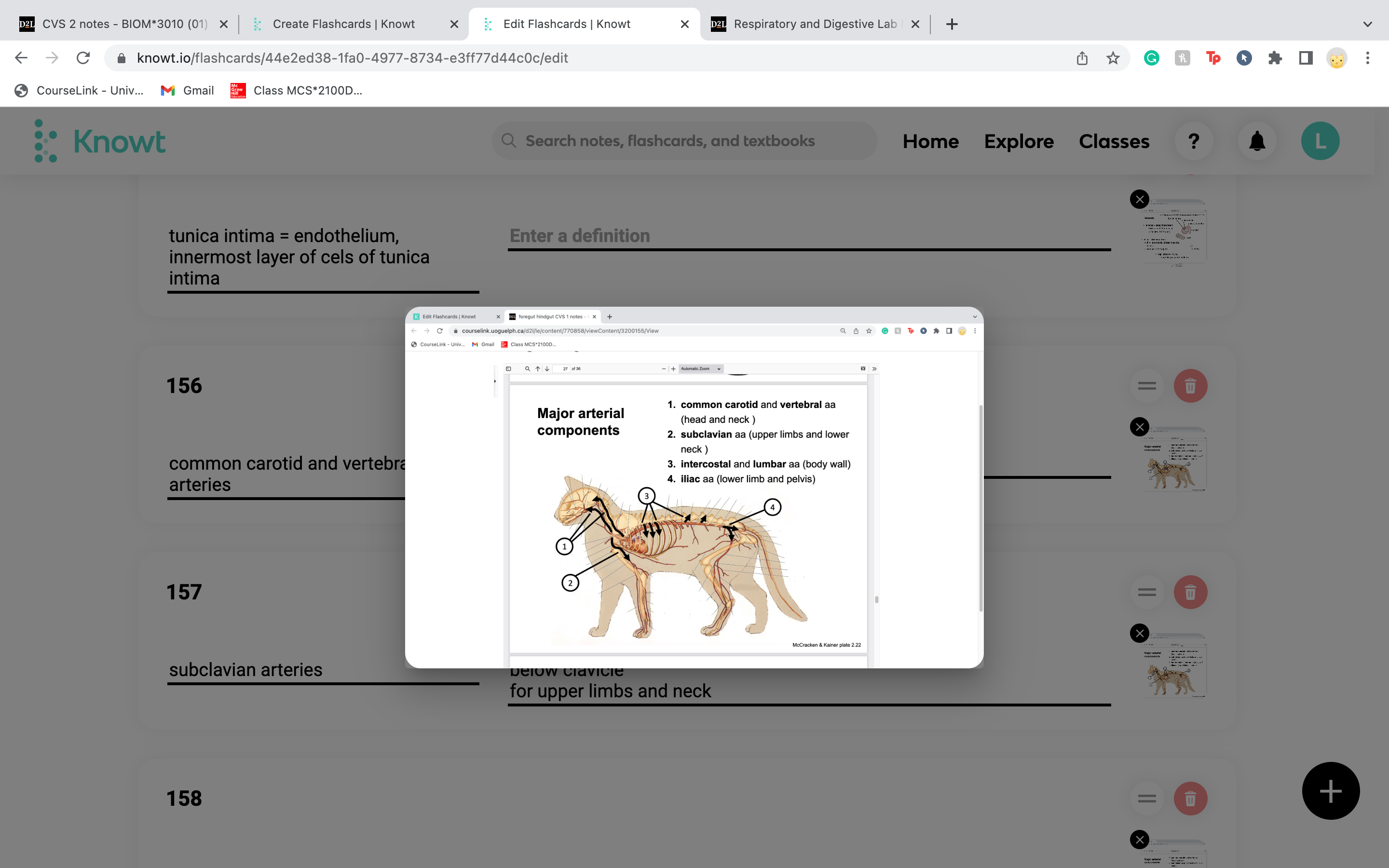
18
New cards
below clavicle
for upper limbs and neck
for upper limbs and neck
subclavian arteries
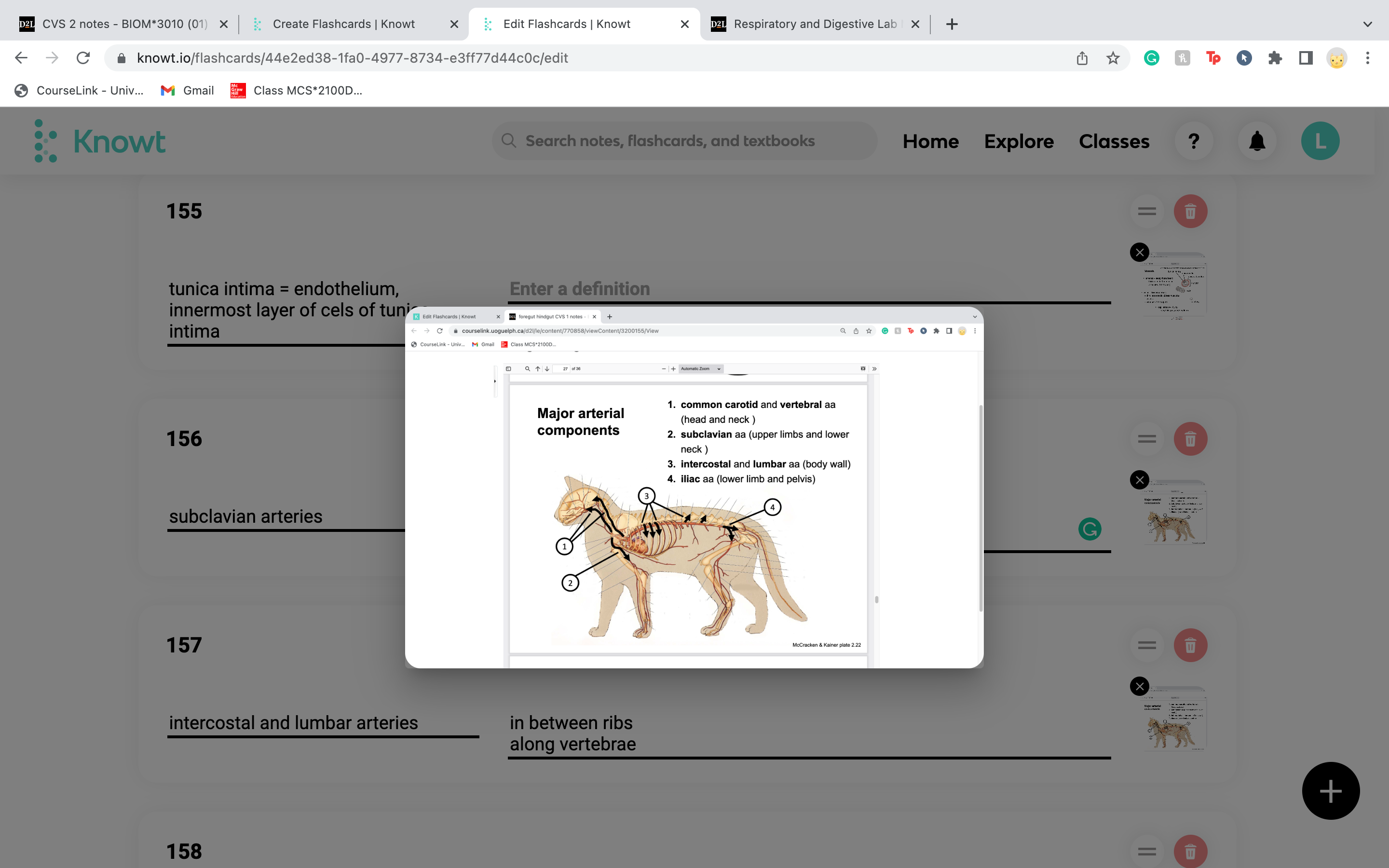
19
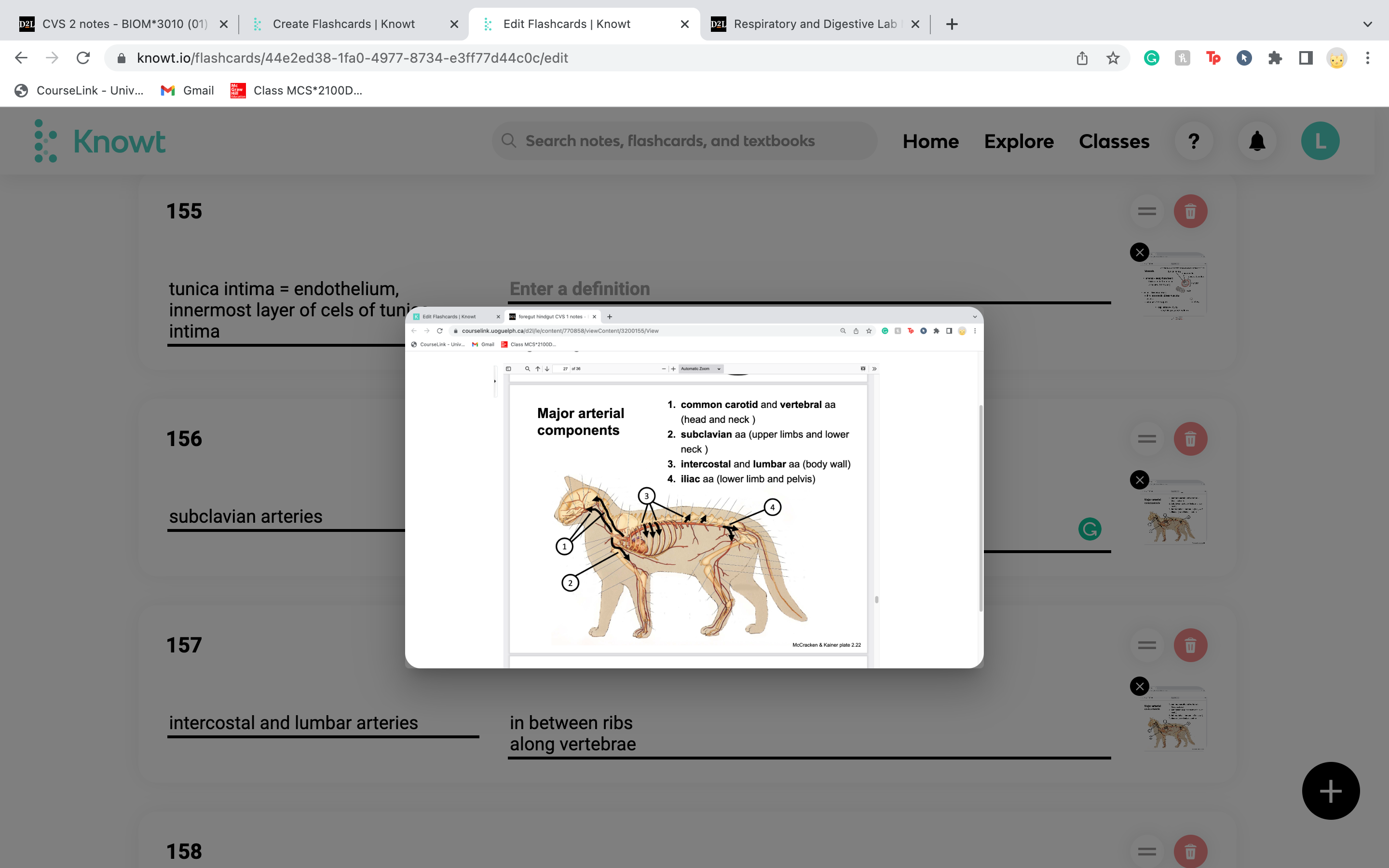
New cards
intercostal and lumbar arteries
in between ribs
along vertebrae
along vertebrae
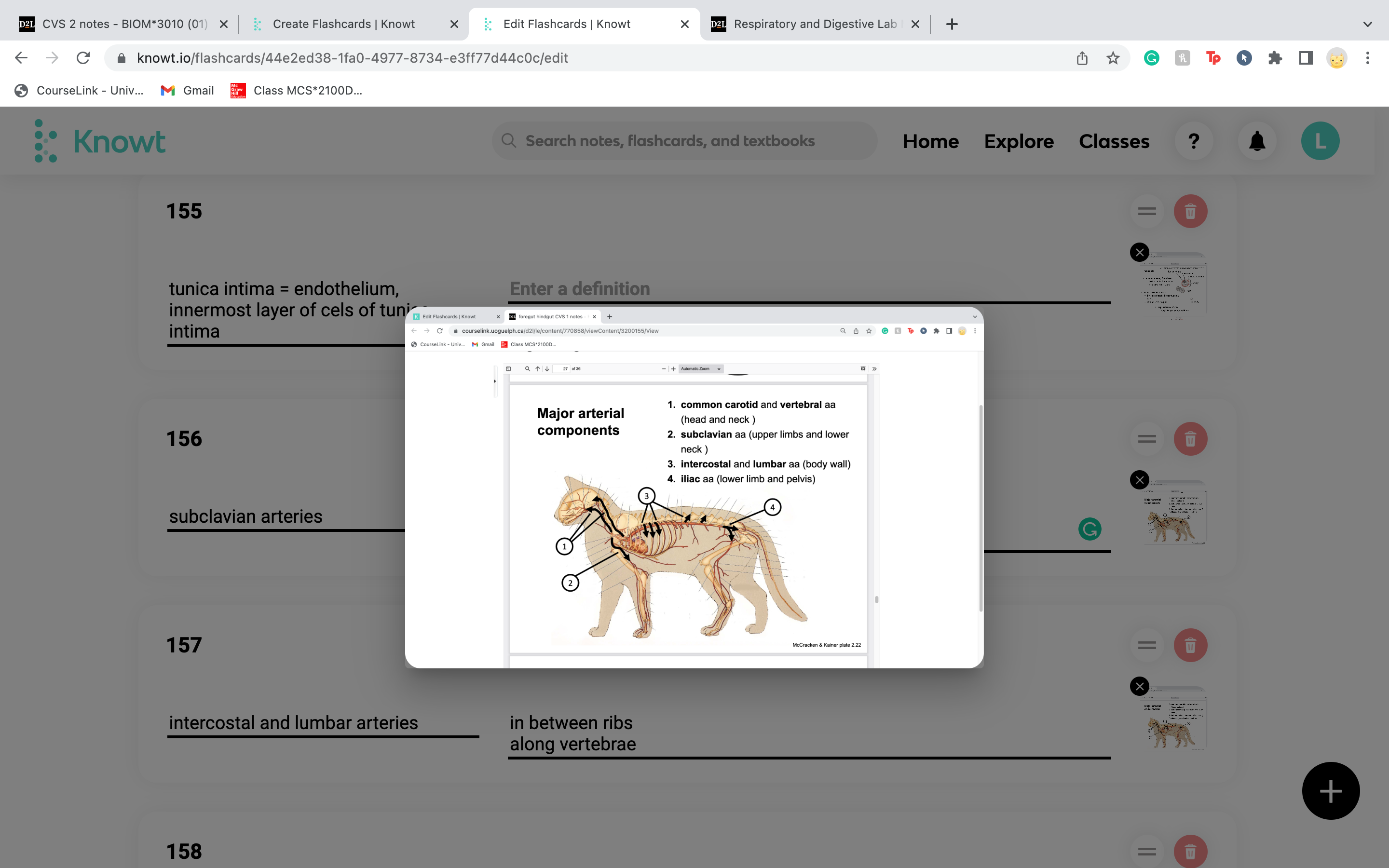
20
New cards
apex is associated w left ventricle
-caudal most part
-caudal most part
21
New cards
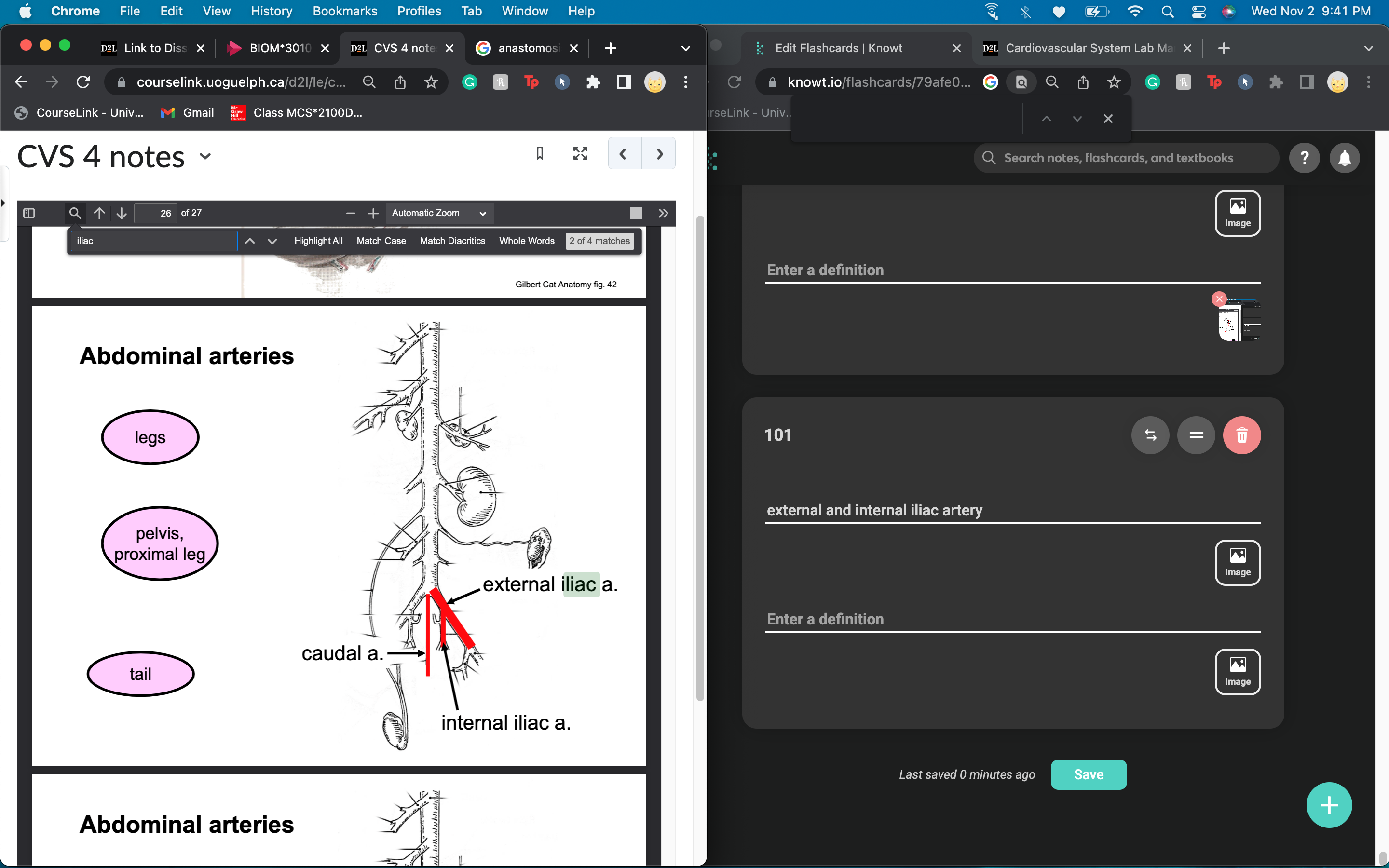
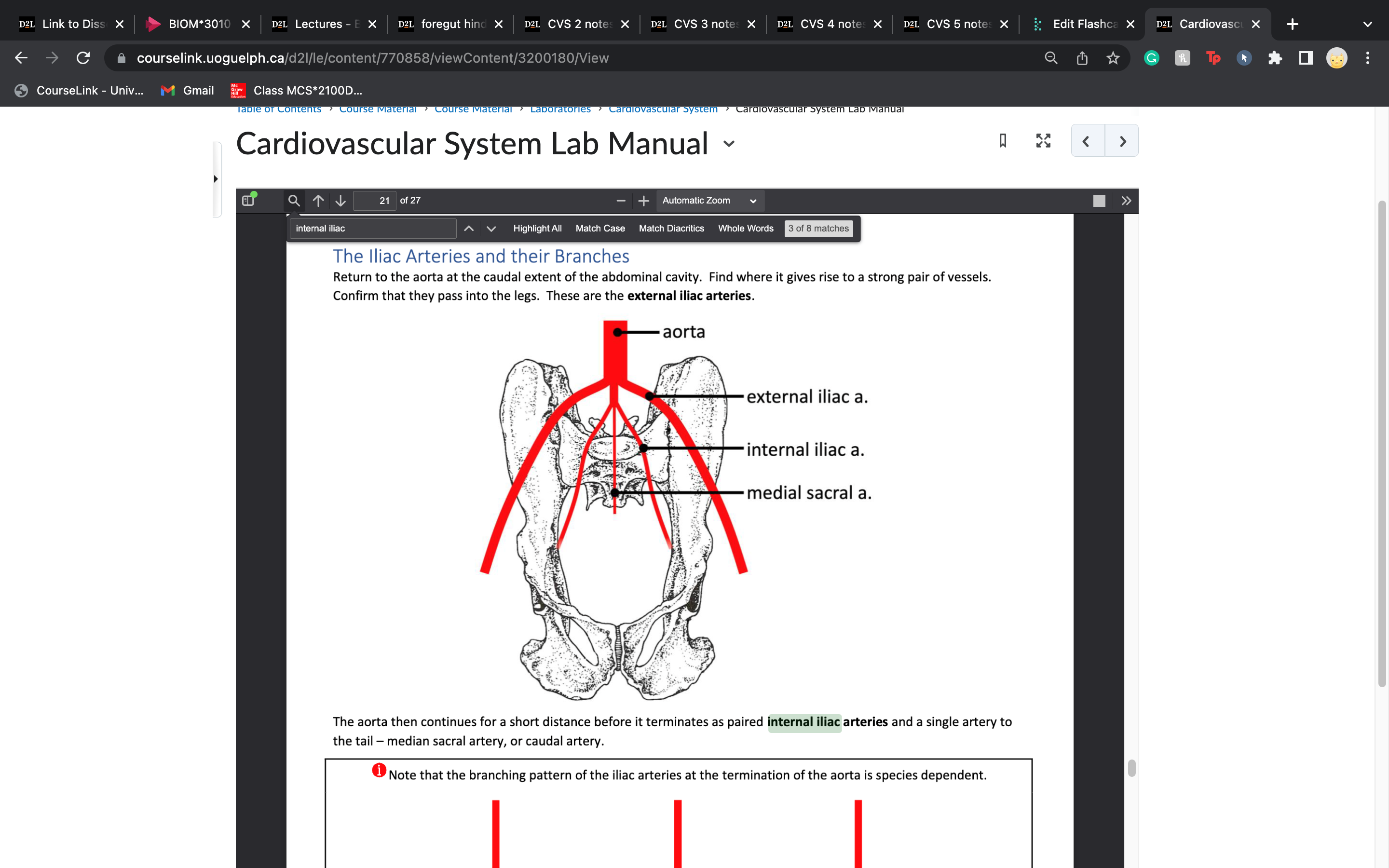
iliac arteries
lower limb and pelvis
22
New cards
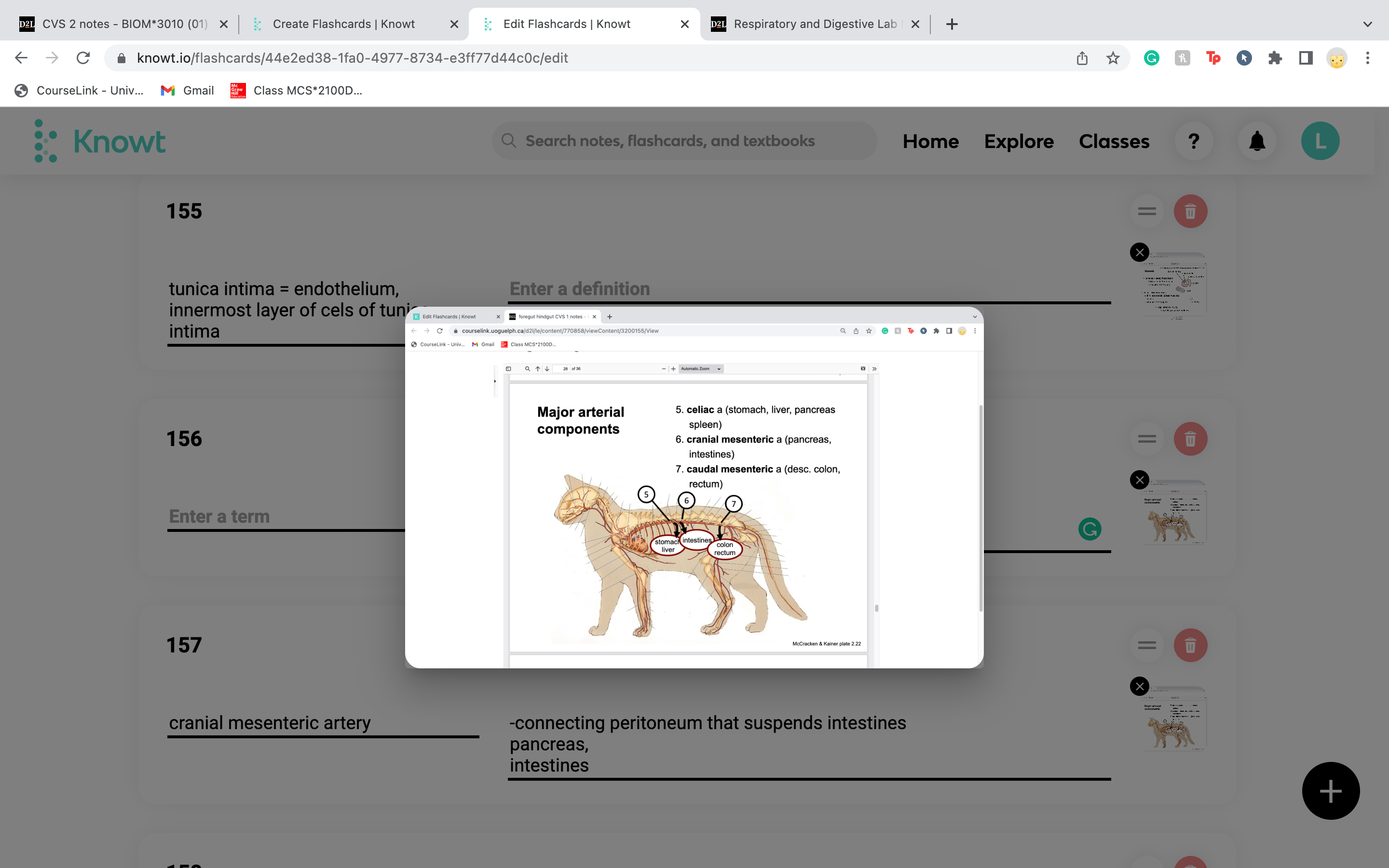
stomach, liver, pancreas
spleen are given blood by the __________ artery
spleen are given blood by the __________ artery
celiac artery
23
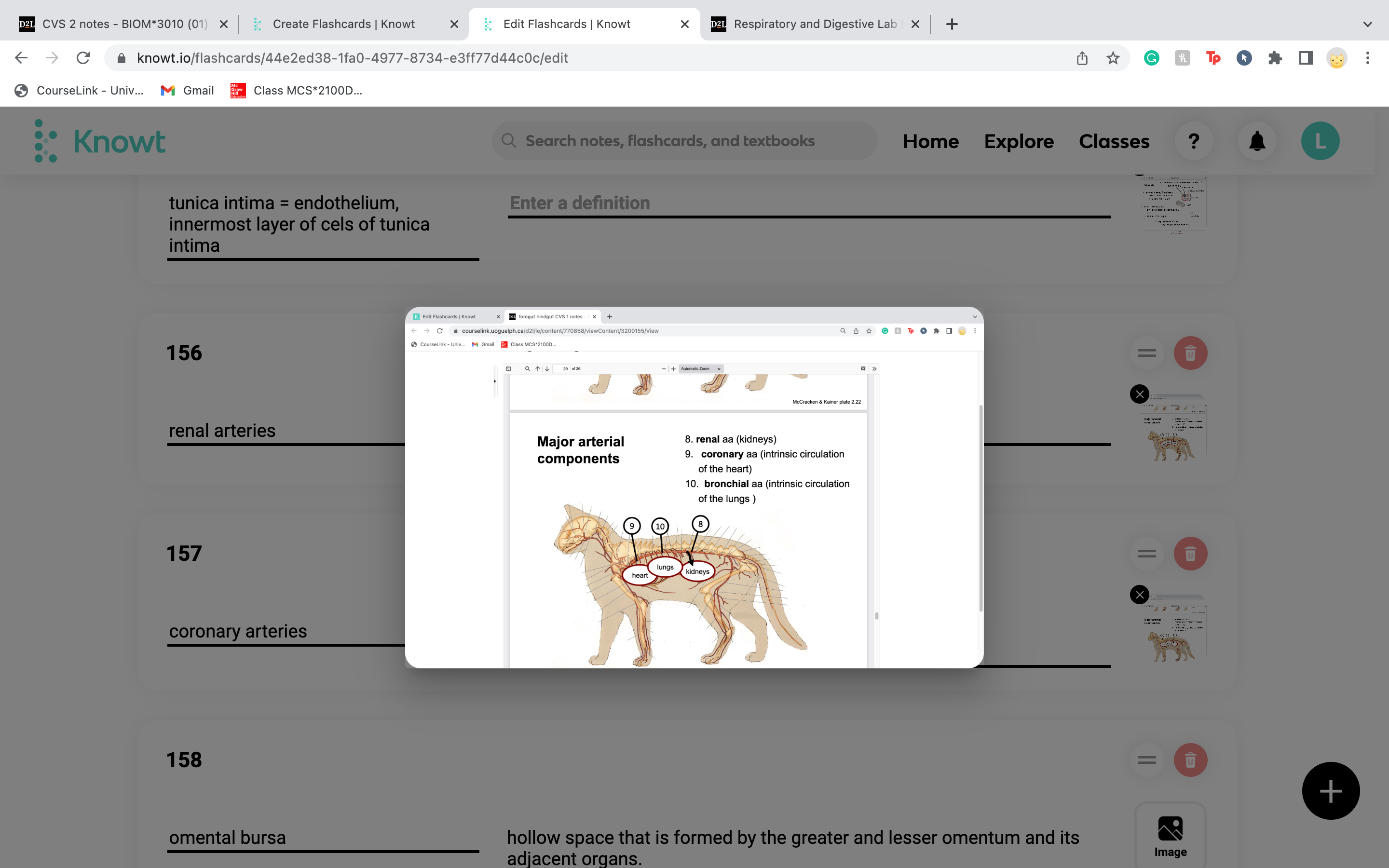
New cards
coronary arteries
intrinsic--- in heart tissue itself
-intrinsic circulation of the heart
-intrinsic circulation of the heart
24
New cards
mediastinal pleura is the outermost layer of membranes around the heart.. what are the three inner ones
-mediastinal pleura
-fibrous pericardium *the two below prevent points of attachment*
-parietal pericardium
- visceral pericardium
-fibrous pericardium *the two below prevent points of attachment*
-parietal pericardium
- visceral pericardium
25
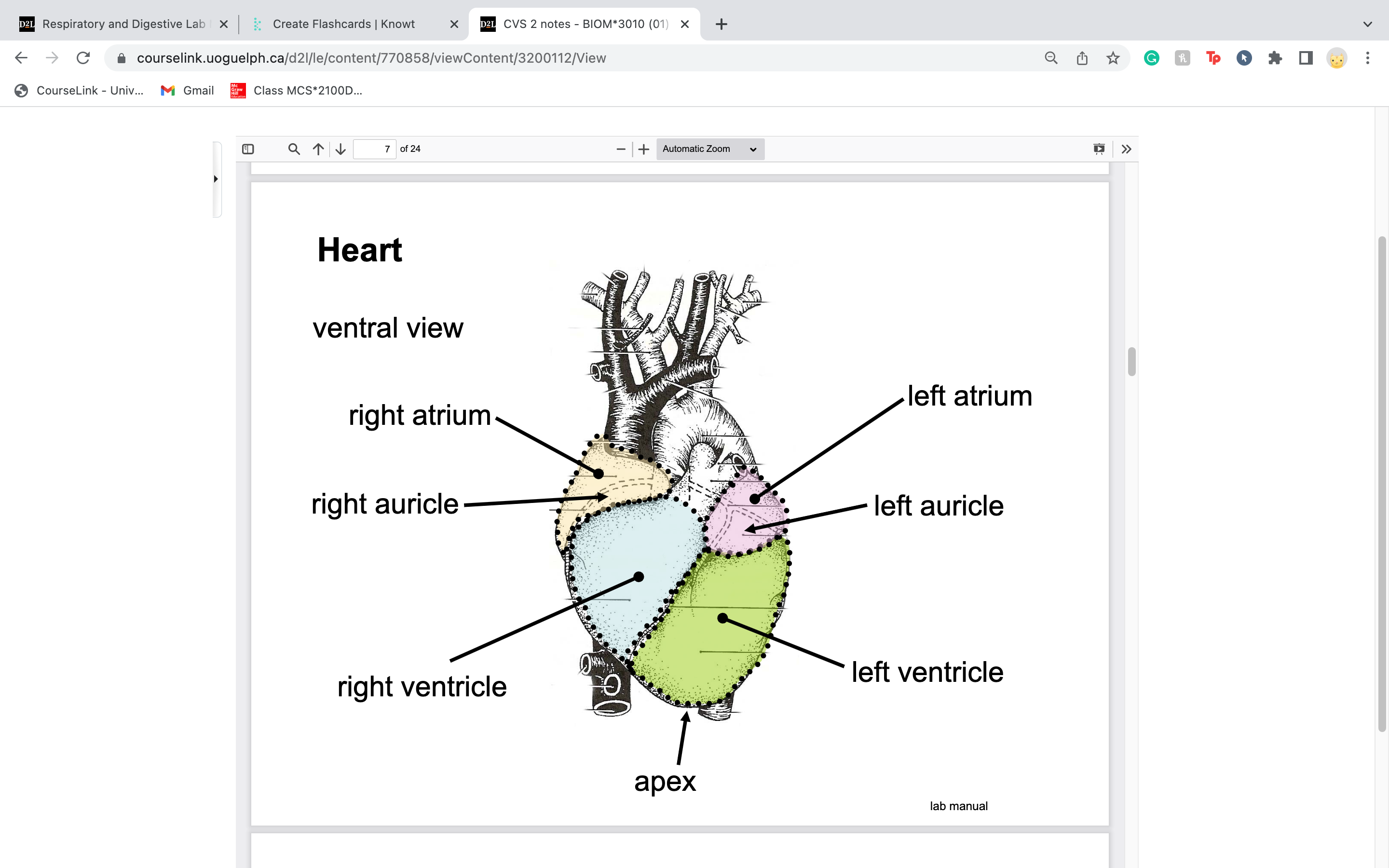
New cards
label atrium, auricles, ventricles
26
New cards
atrioventricular valves are under high pressure, so they are reinforced with 2 structures.. what are they
chordae tendineae
papillary muscles
-make sure valves are held in place when heart contracts
papillary muscles
-make sure valves are held in place when heart contracts
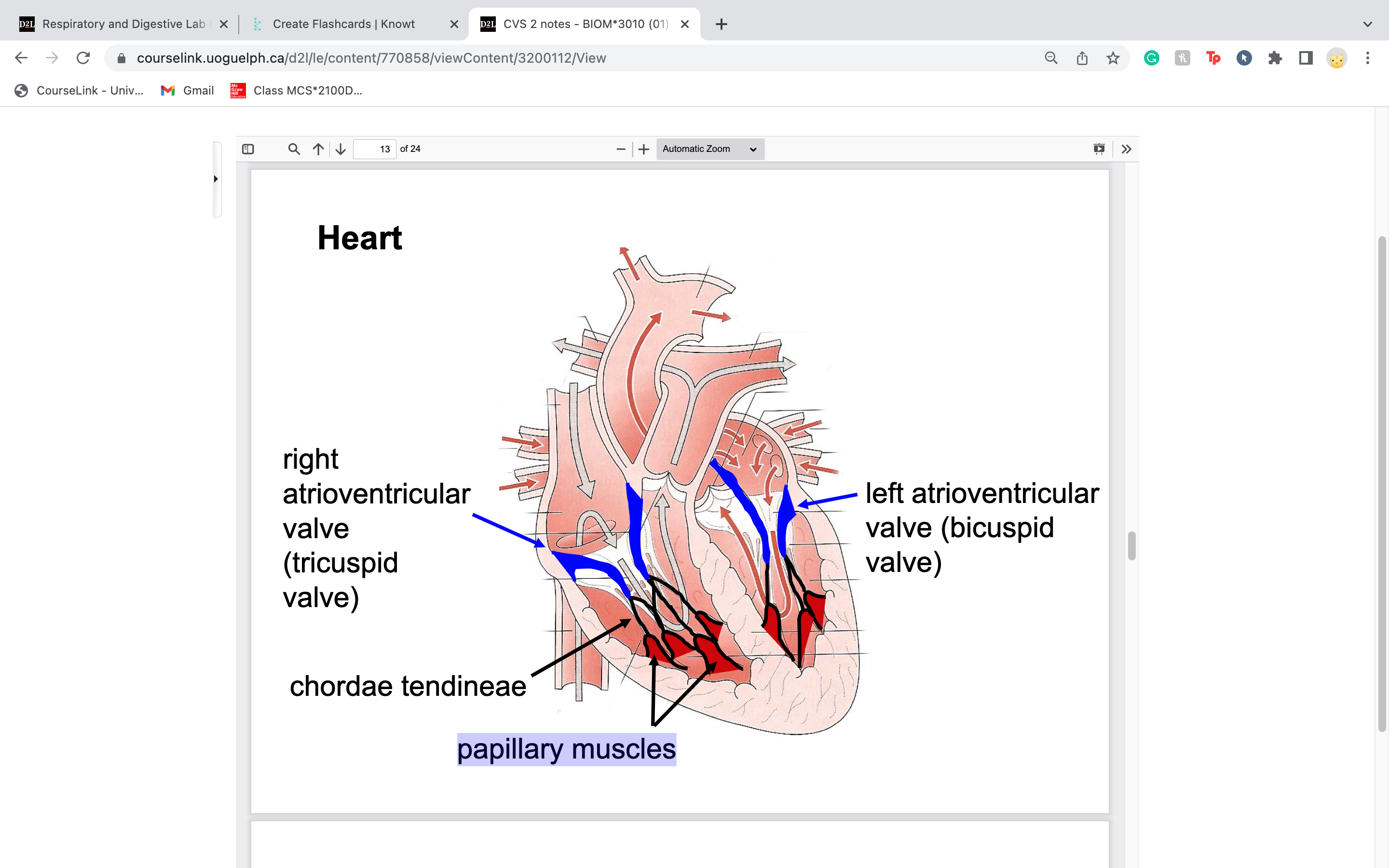
27
New cards
label right and left atrioventricular valve
blood goes right before left... (deoxy, then oxy)
divides atrium and ventricle
divides atrium and ventricle
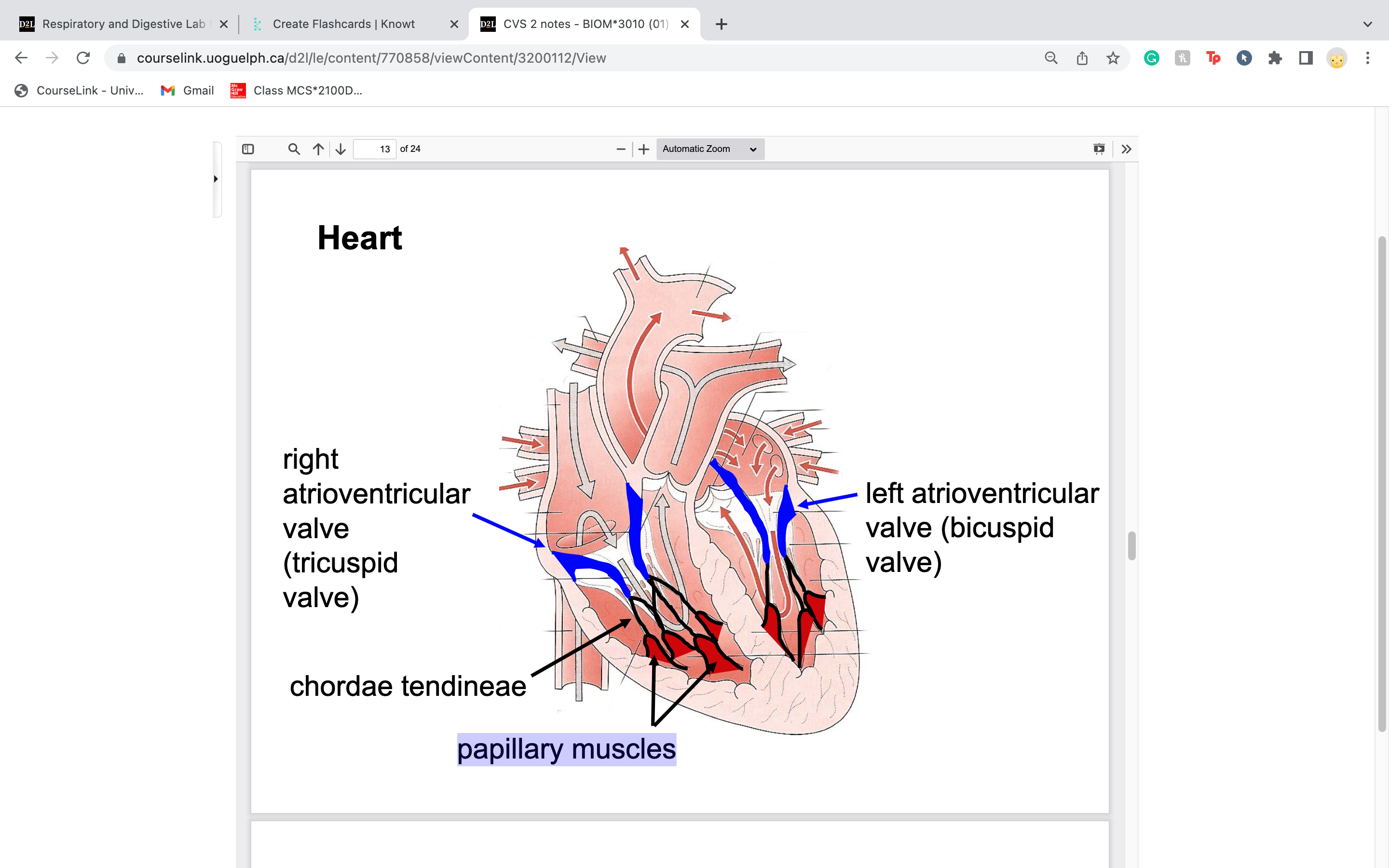
28
New cards
label pulmonary (semilunar) valve
on route towards the lungs
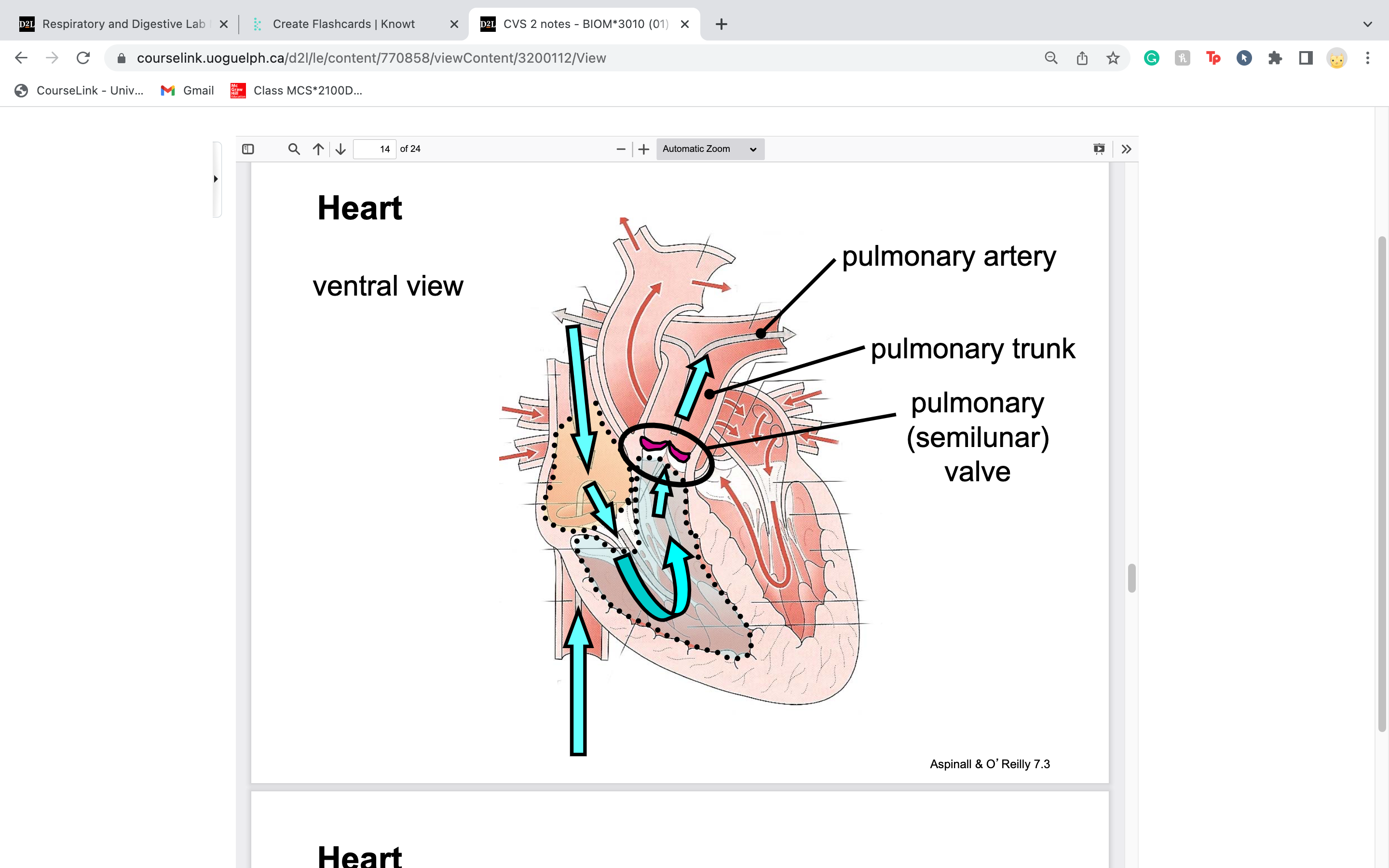
29
New cards
label pulmonary trunk and pulmonary artery..
trunk rapidly divided into 2 to make L and R side
trunk rapidly divided into 2 to make L and R side
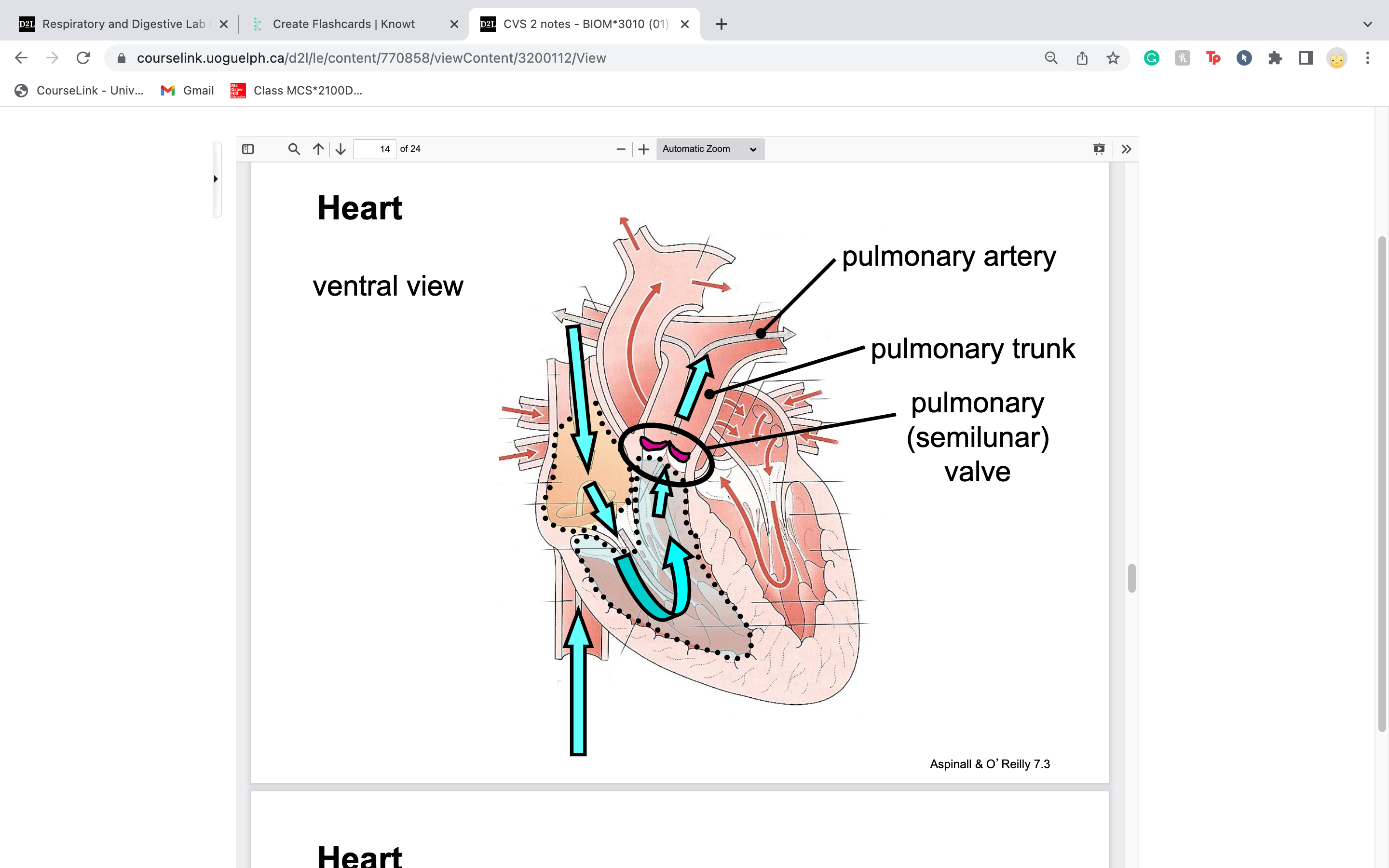
30
New cards
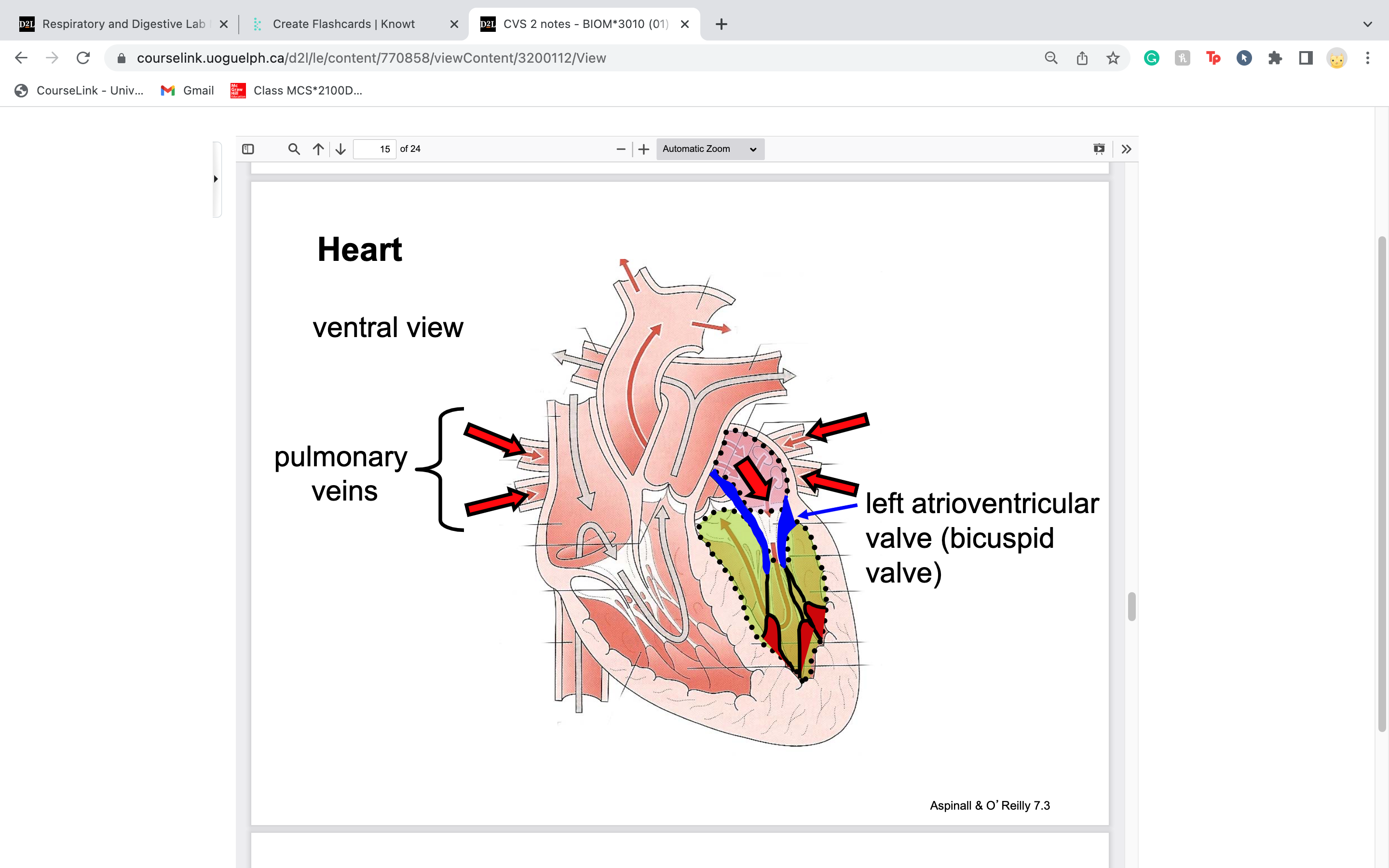
newly oxygenated blood from lungs come into the ________ veins.. then travels into left atrium then to left ventricle though left atrioventricular valve
pulmonary veins
31
New cards
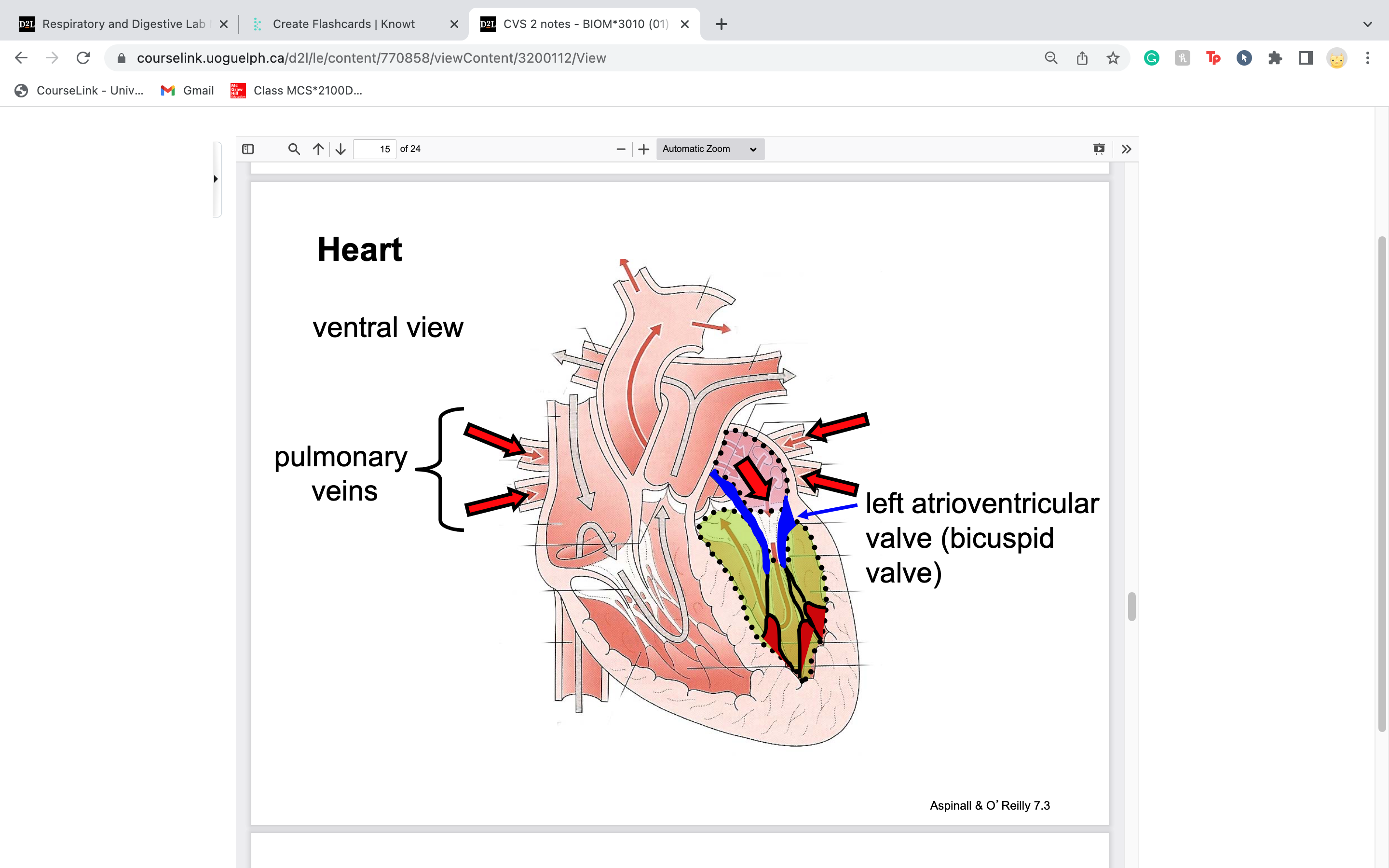
blood leaves left ventricle and passes by the ____________________ valve
aortic semilunar valve
32
New cards
ductus
arteriosus
arteriosus
-no longer has a lumen as baby develops
33
New cards
34
New cards
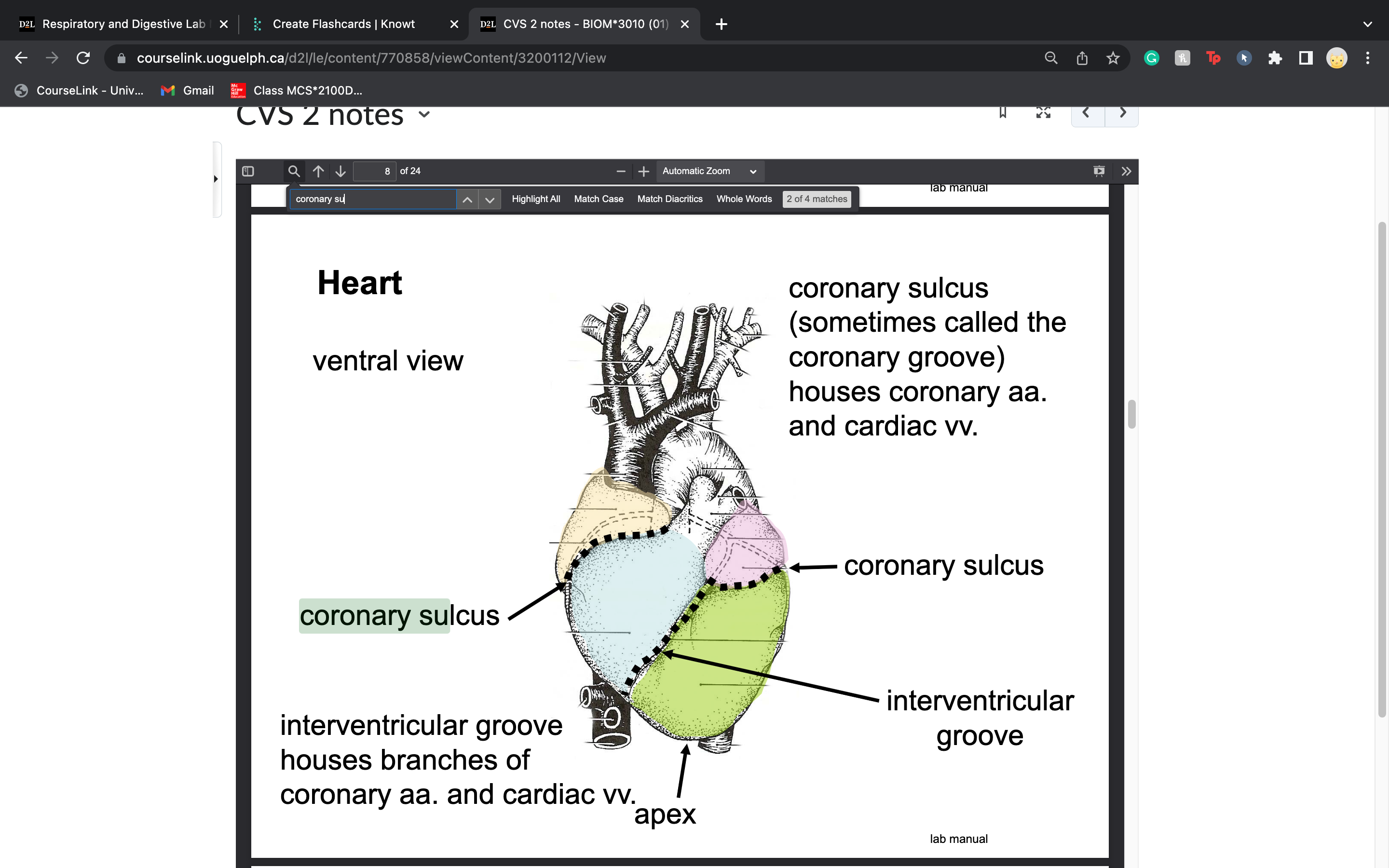
label coronary sulcus
sometimes called the
coronary groove)
houses coronary aa.
and cardiac vv.
coronary groove)
houses coronary aa.
and cardiac vv.
35
New cards
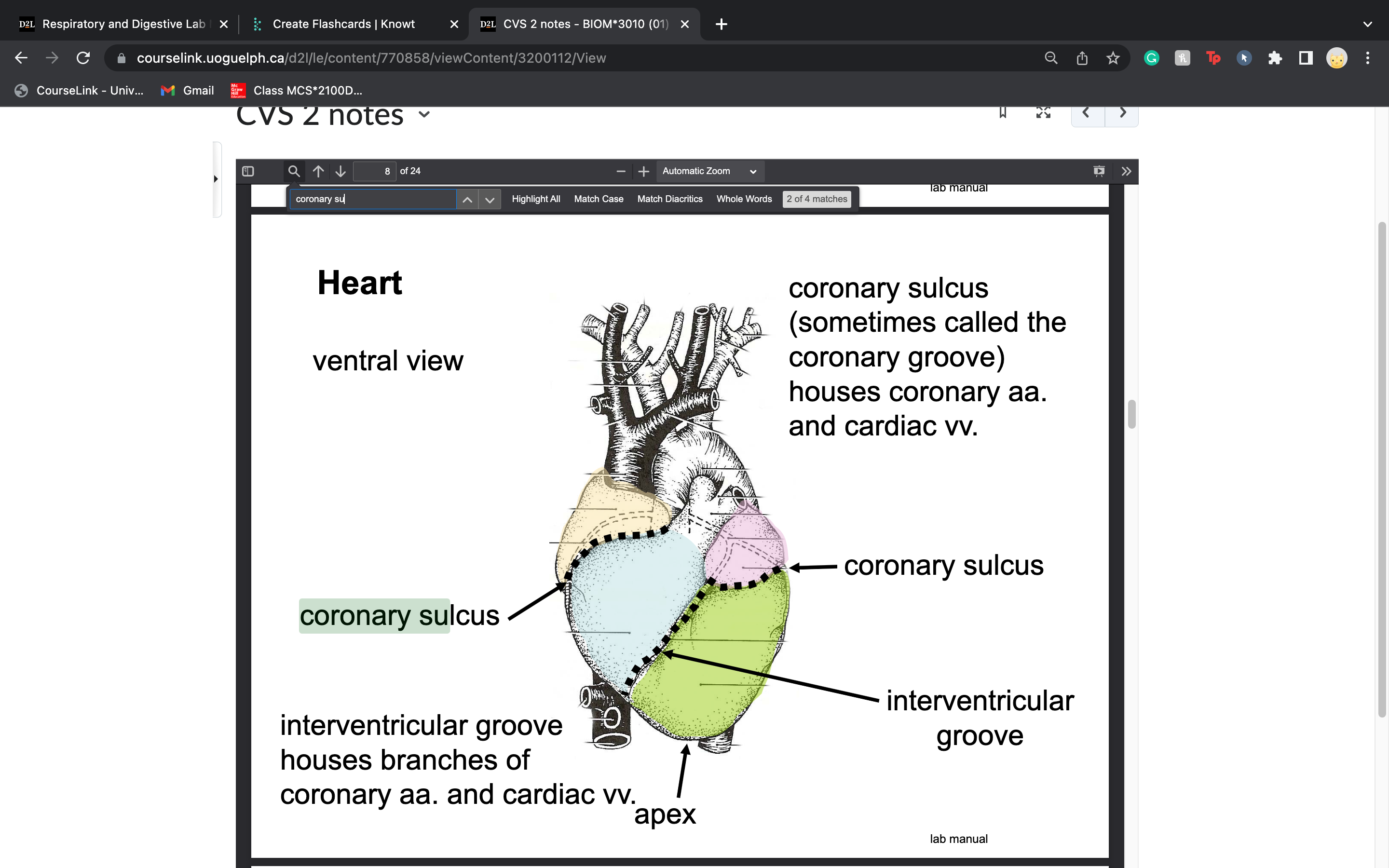
label interventricular groove... what arteries and veins does it house
houses branches of
coronary aa. and cardiac vv
coronary aa. and cardiac vv
36
New cards
label interventricular septum
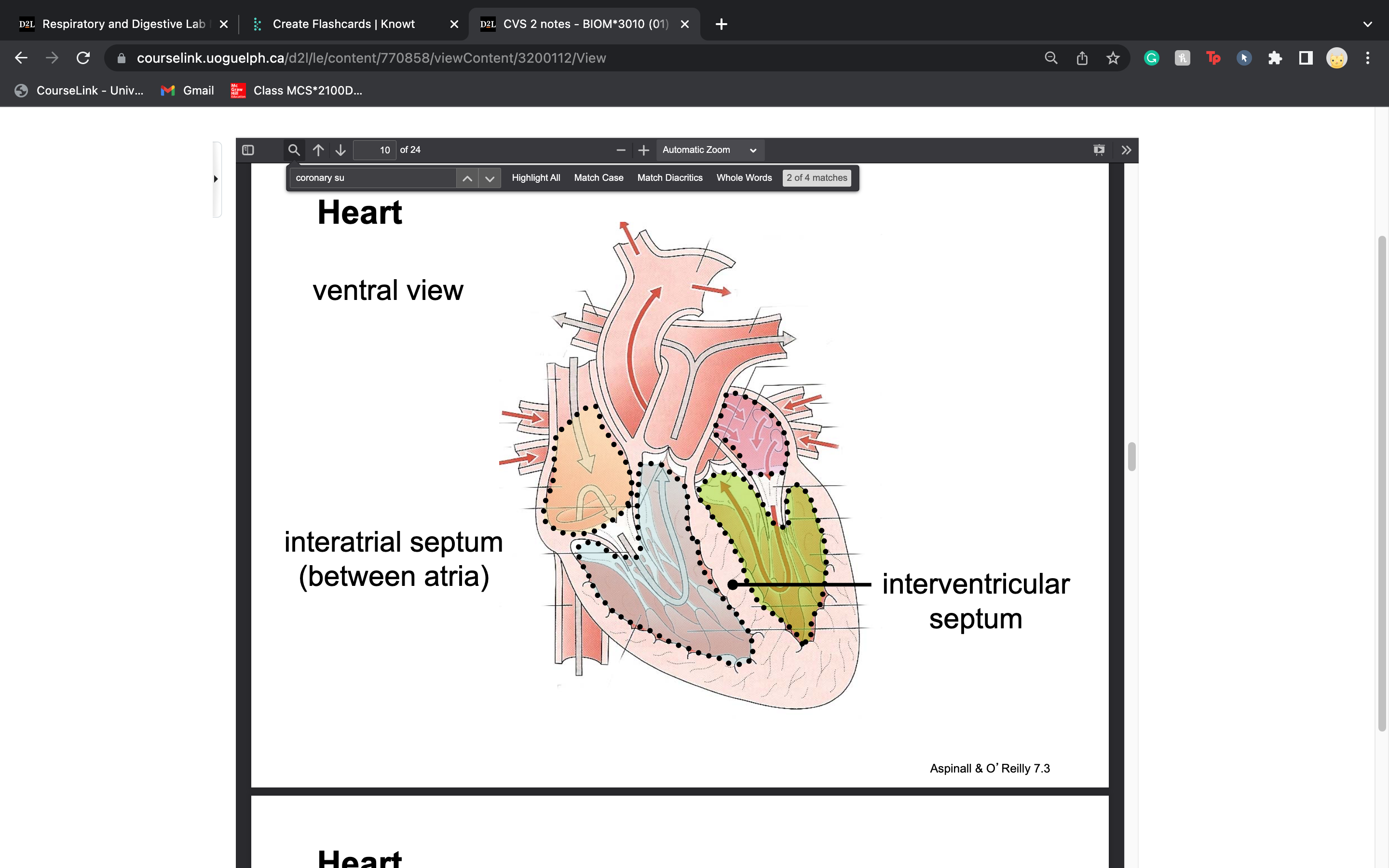
37
New cards
label cranial and caudal vena cava
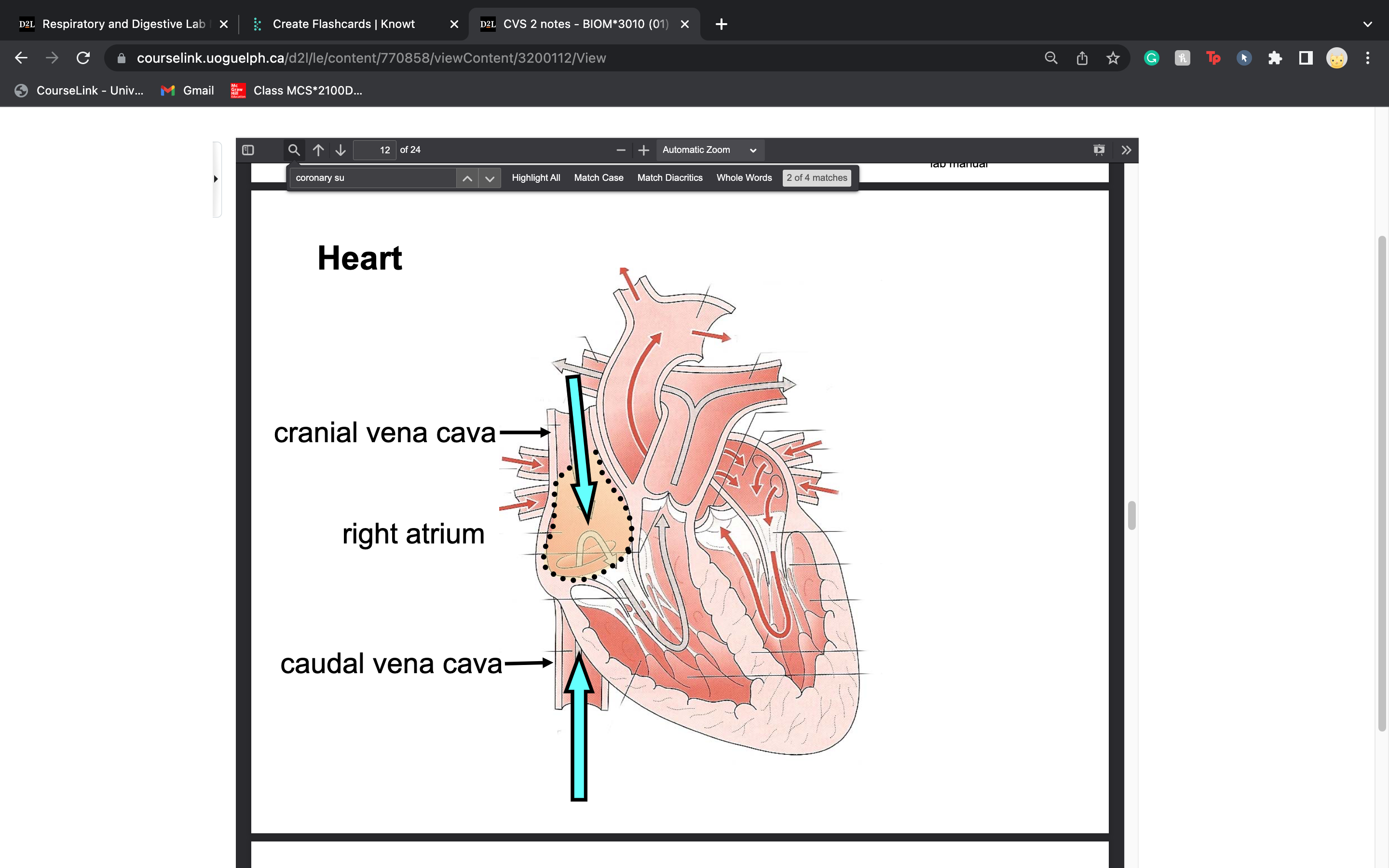
38
New cards
label aortic valve and ascending aorta
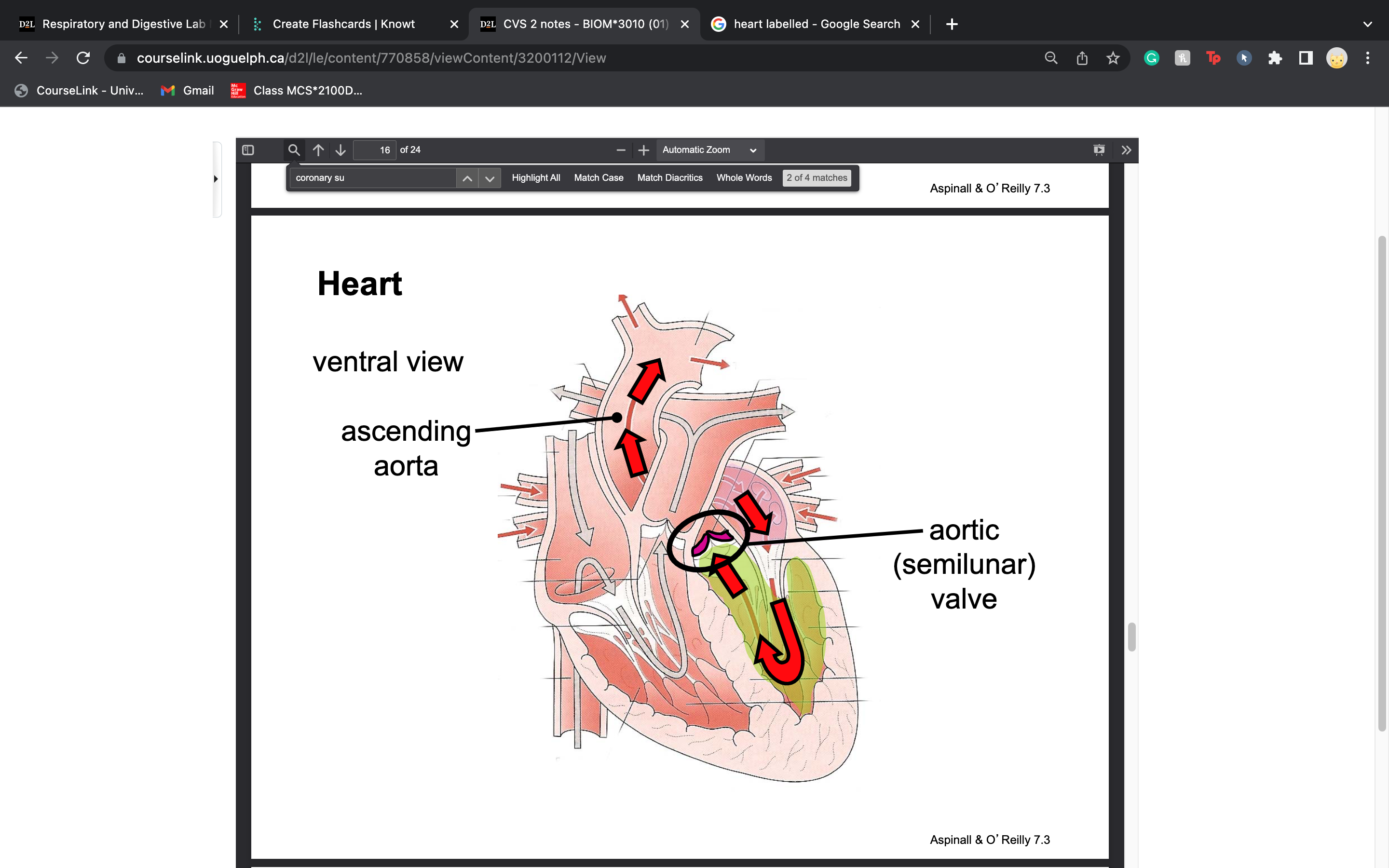
39
New cards
label aortic arch
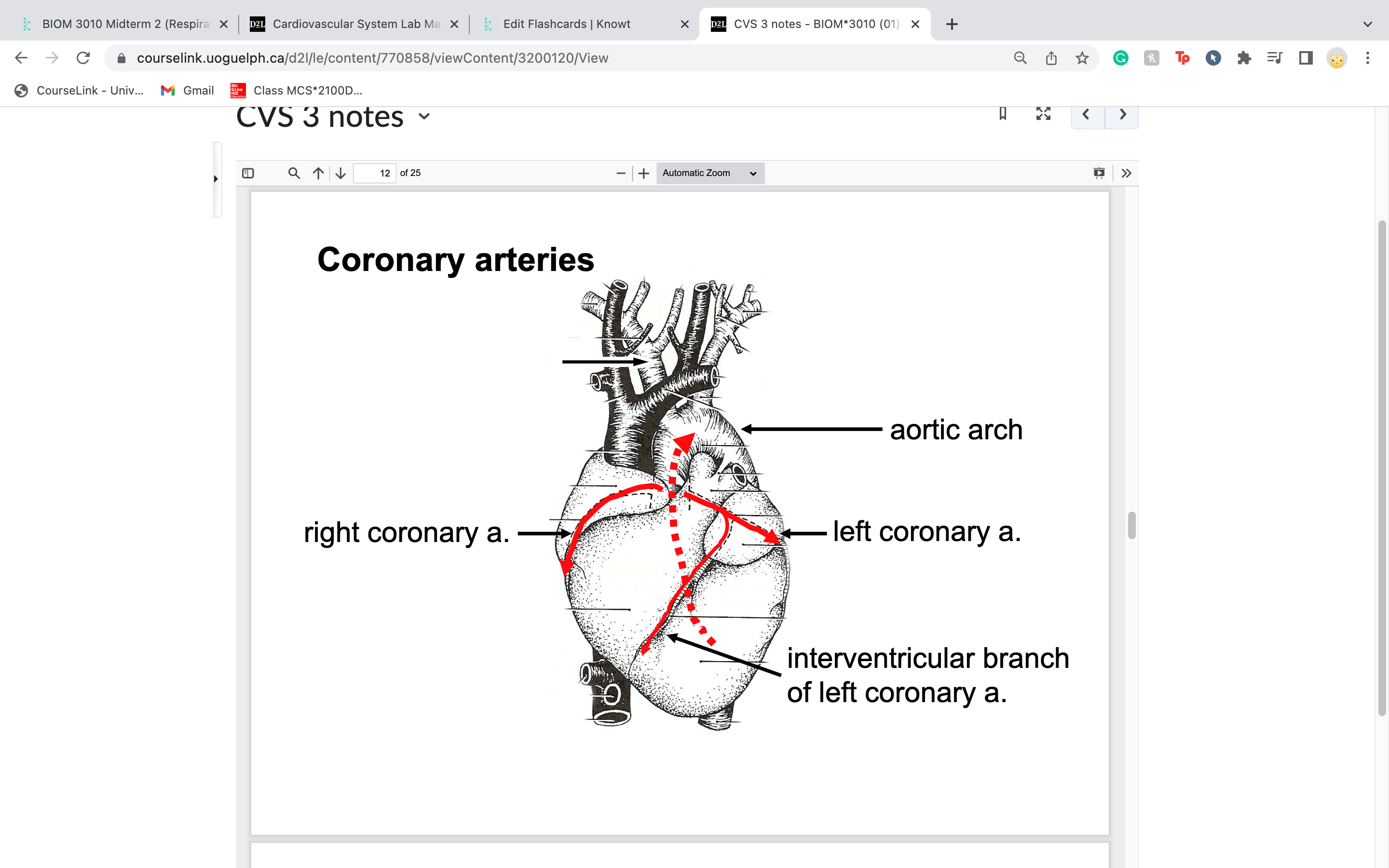
40
New cards
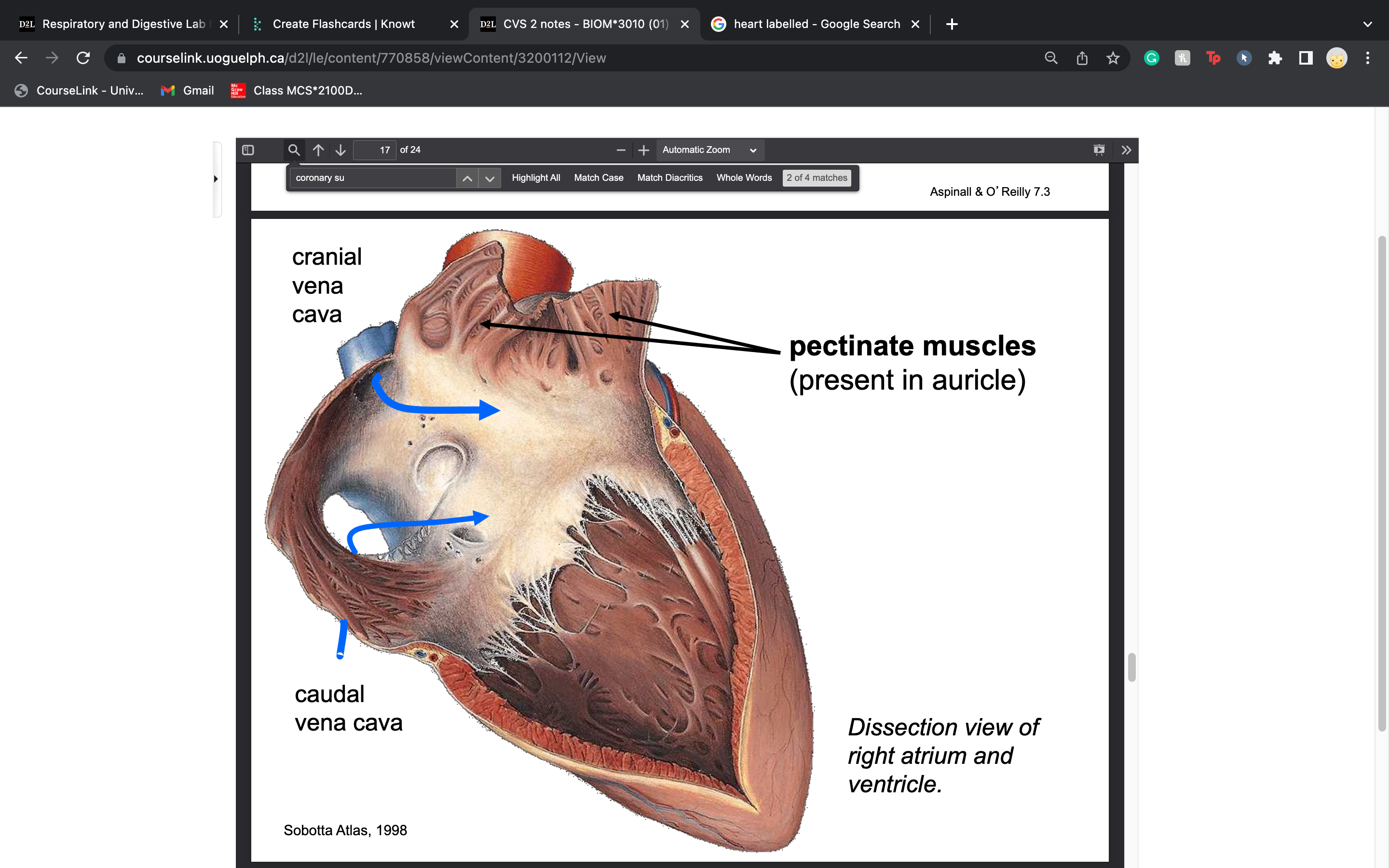
label pectinate muscles (look like a comb)
... they are present in ________
... they are present in ________
auricle of right atrium
41
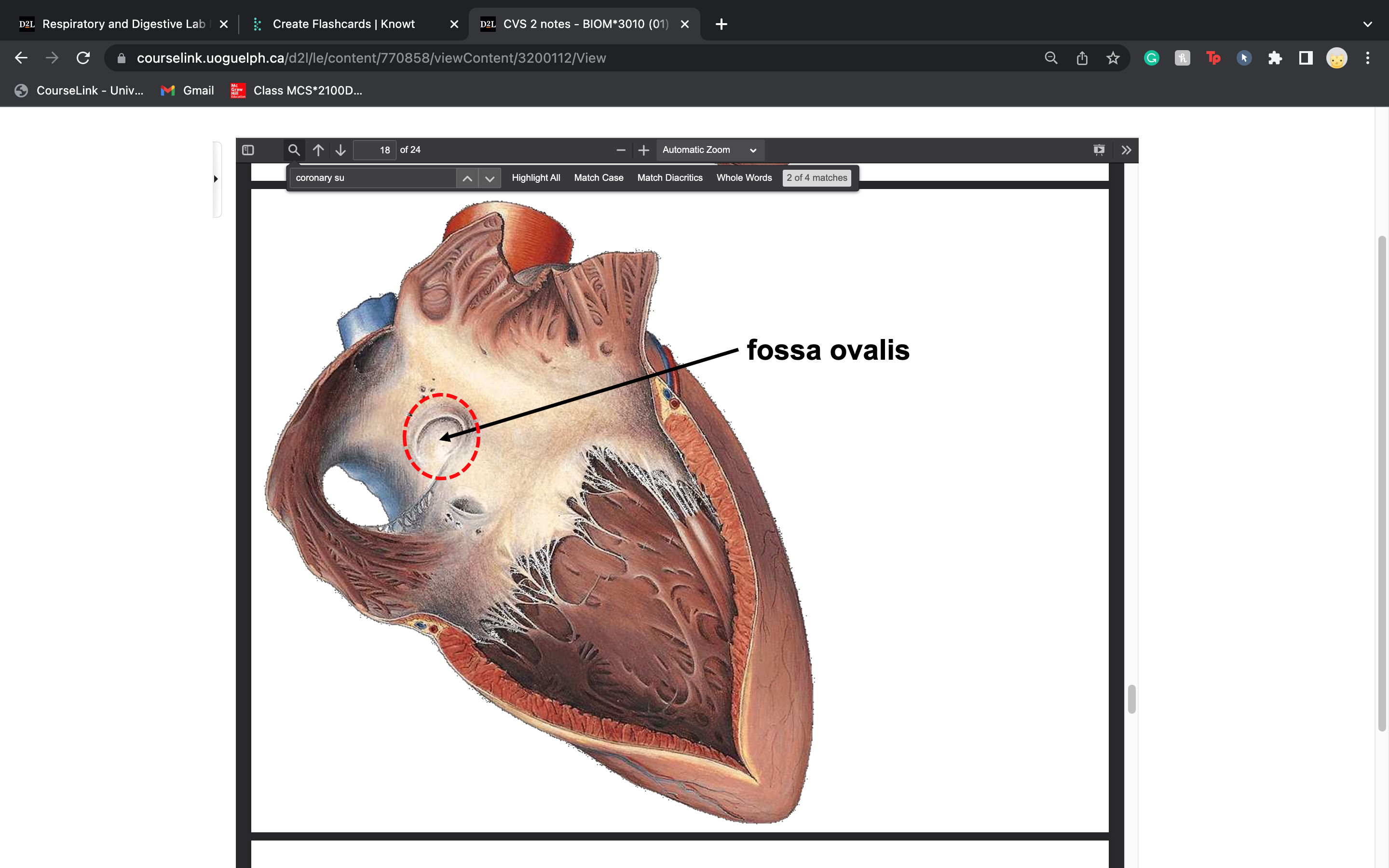
New cards
fossa ovalis location
right atrium
a thin region
of the wall between right and left atria
a thin region
of the wall between right and left atria
42
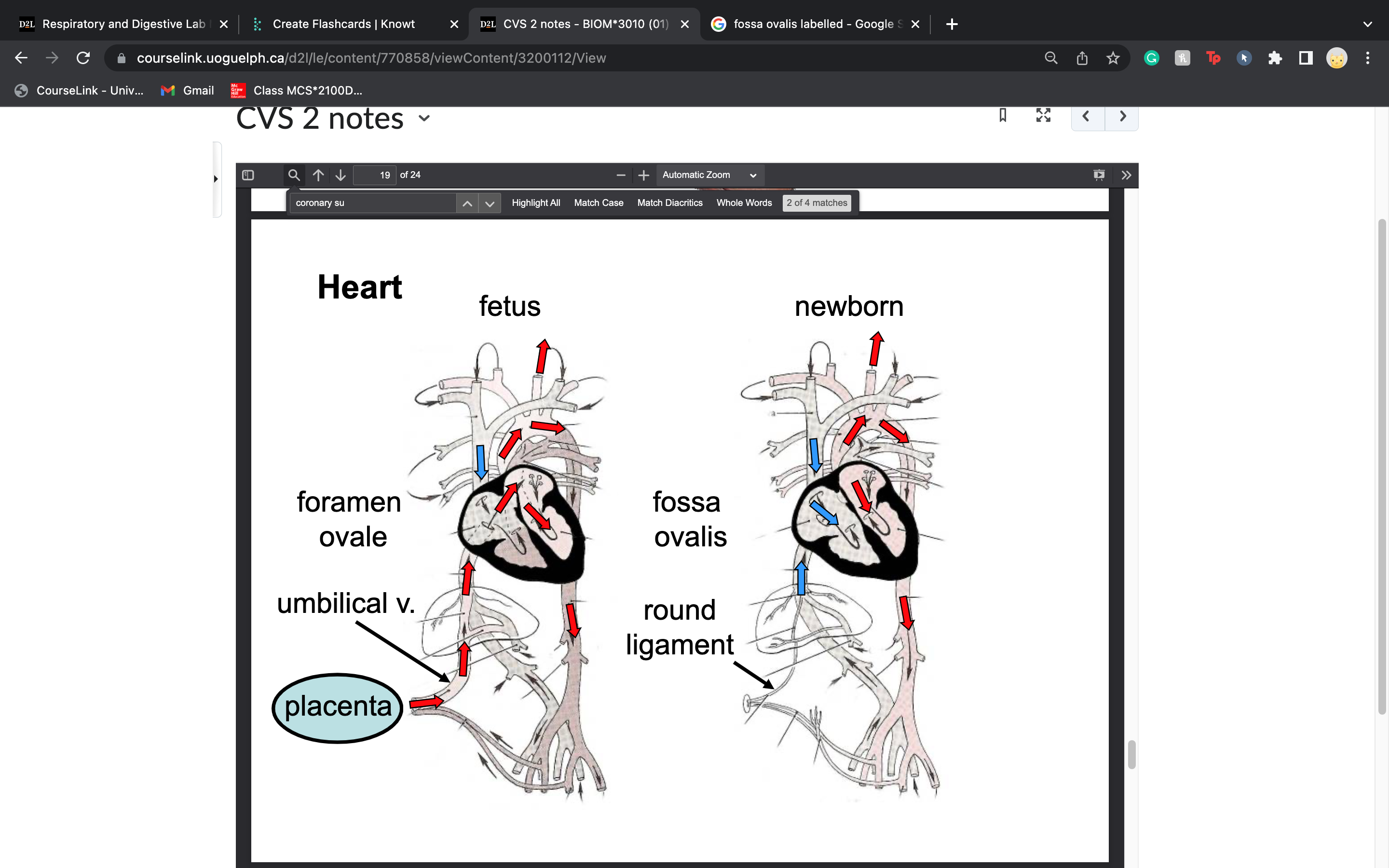
New cards
what is the foramen ovale
a hole between the left and right atria (upper chambers) of the heart. This hole exists in everyone before birth, but most often closes shortly after being born
43
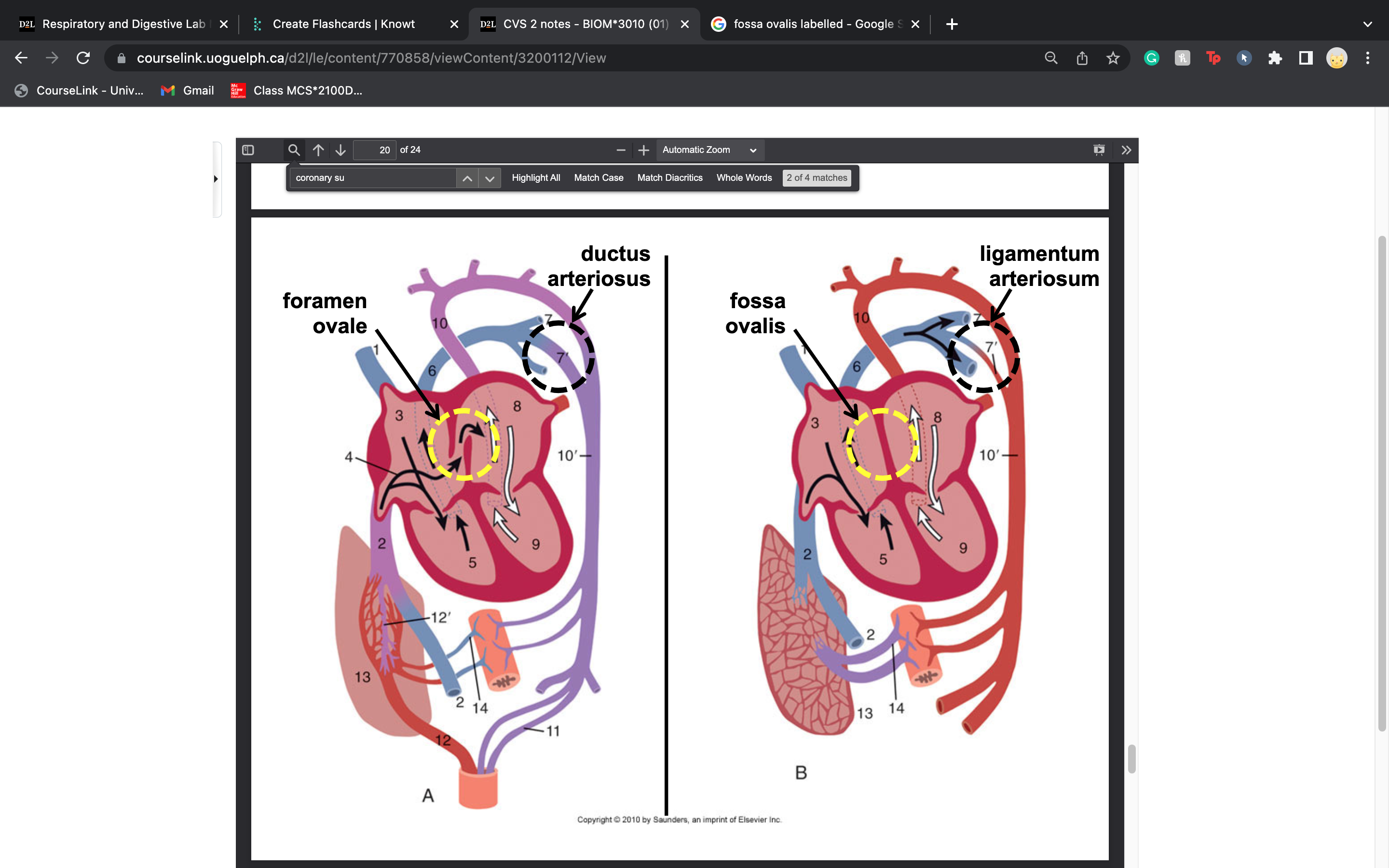
New cards
whats the deal w ductus arteriosus and ligamentum arteriosum
ductus arteriosus is a normal fetal artery connecting the main body artery (aorta) and the main lung artery (pulmonary artery)
CLOSES UP IN THE MONTHS AFTER BIRTH to become the ligamentum arteriosum
CLOSES UP IN THE MONTHS AFTER BIRTH to become the ligamentum arteriosum
44
New cards
trabeculae carneae
strengthen walls and
increase force of contraction
meaty tendrils!
increase force of contraction
meaty tendrils!
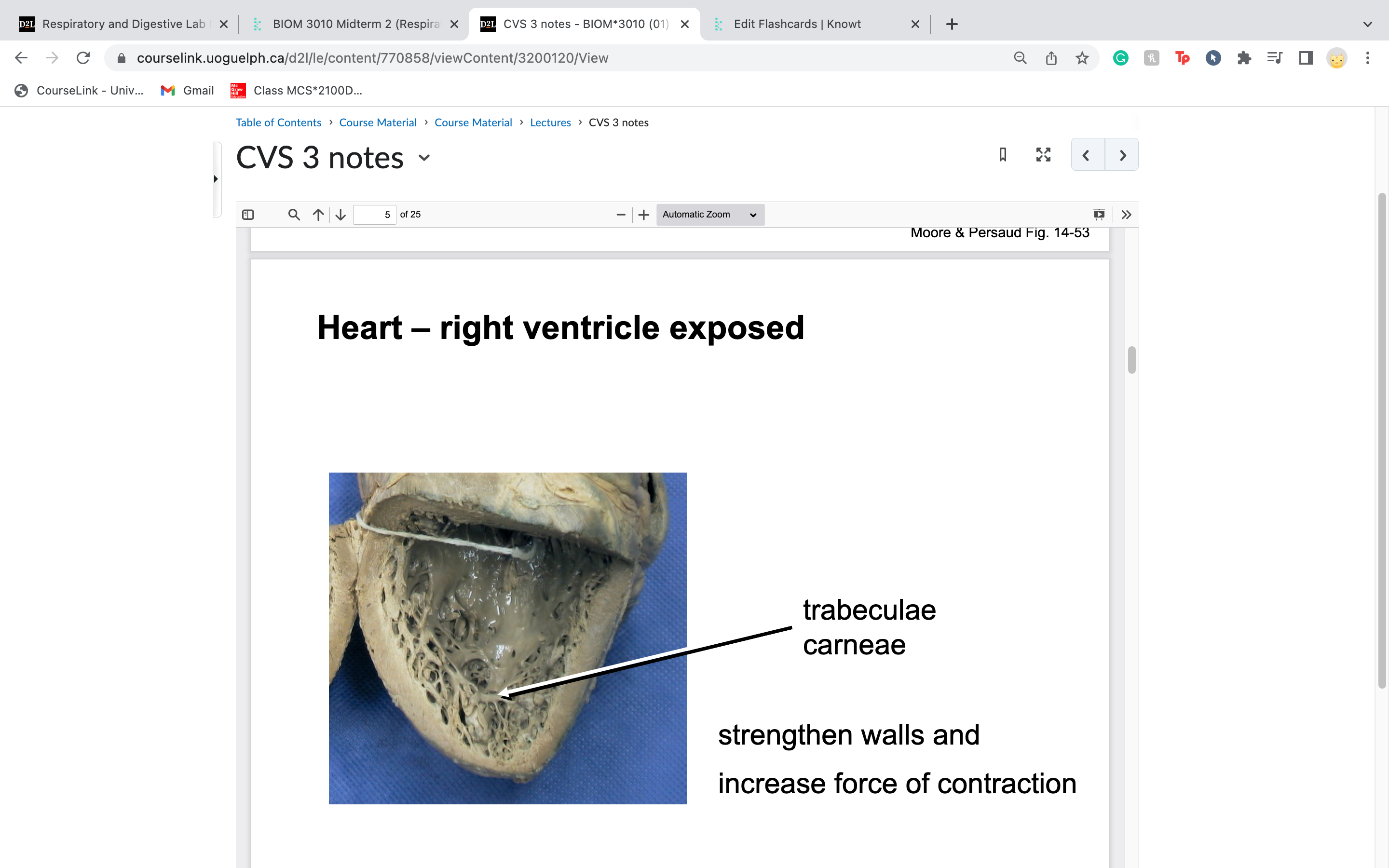
45
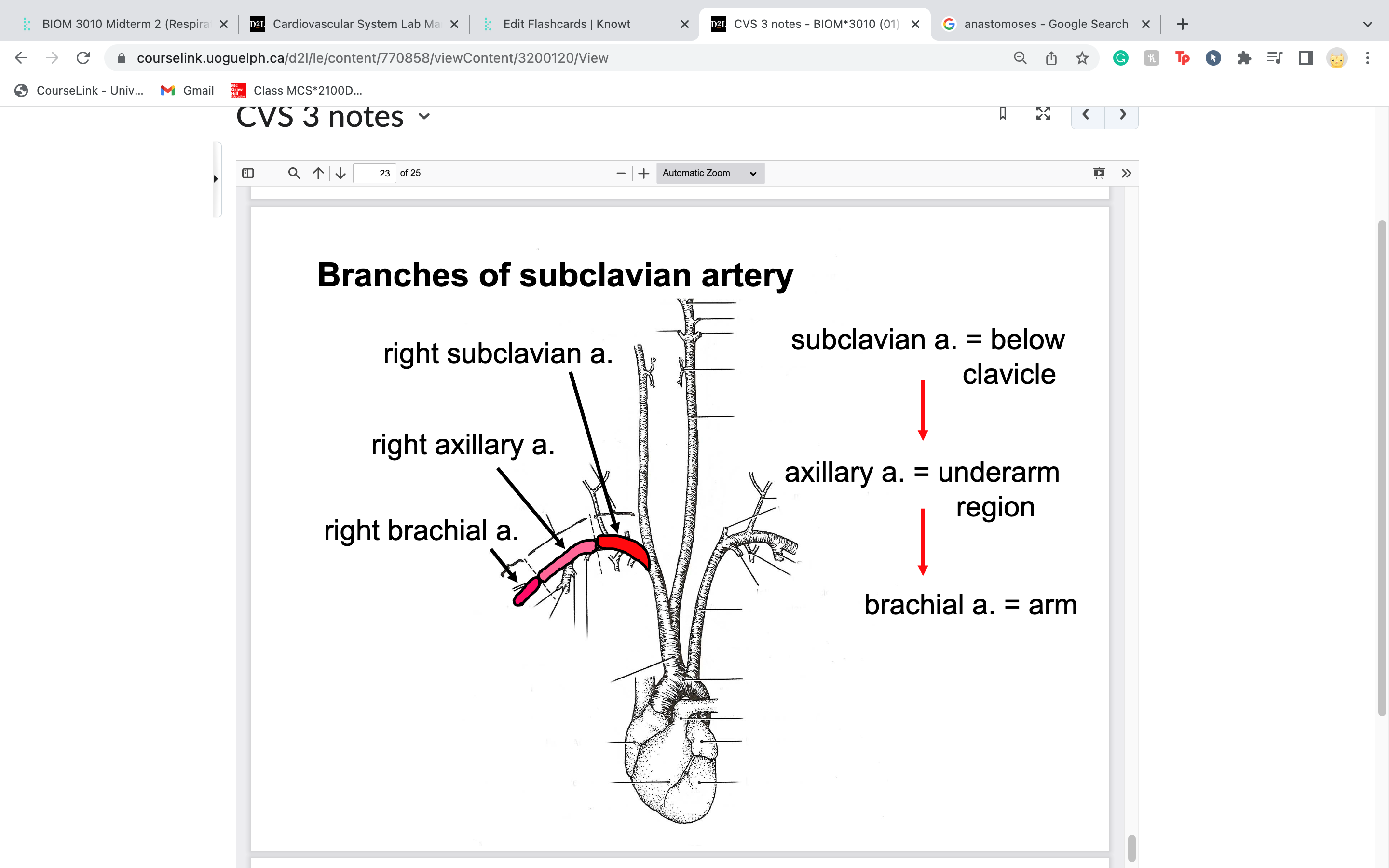
New cards
axillary artery is part of the _____________ artery
subclavian artery
once it extends cranial to the first rib and exits the thorax, it becomes the axillary artery in theunderarm region
axilla = armpit
once it extends cranial to the first rib and exits the thorax, it becomes the axillary artery in theunderarm region
axilla = armpit
46
New cards
brachial artery is part of what artery and what does it supply blood to
part of right subclavian artery
once it reaches humerus its considered brachial artery, and runs parallel to the humerus
once it reaches humerus its considered brachial artery, and runs parallel to the humerus
47
New cards
carotid artery and branches
go to head
48
New cards
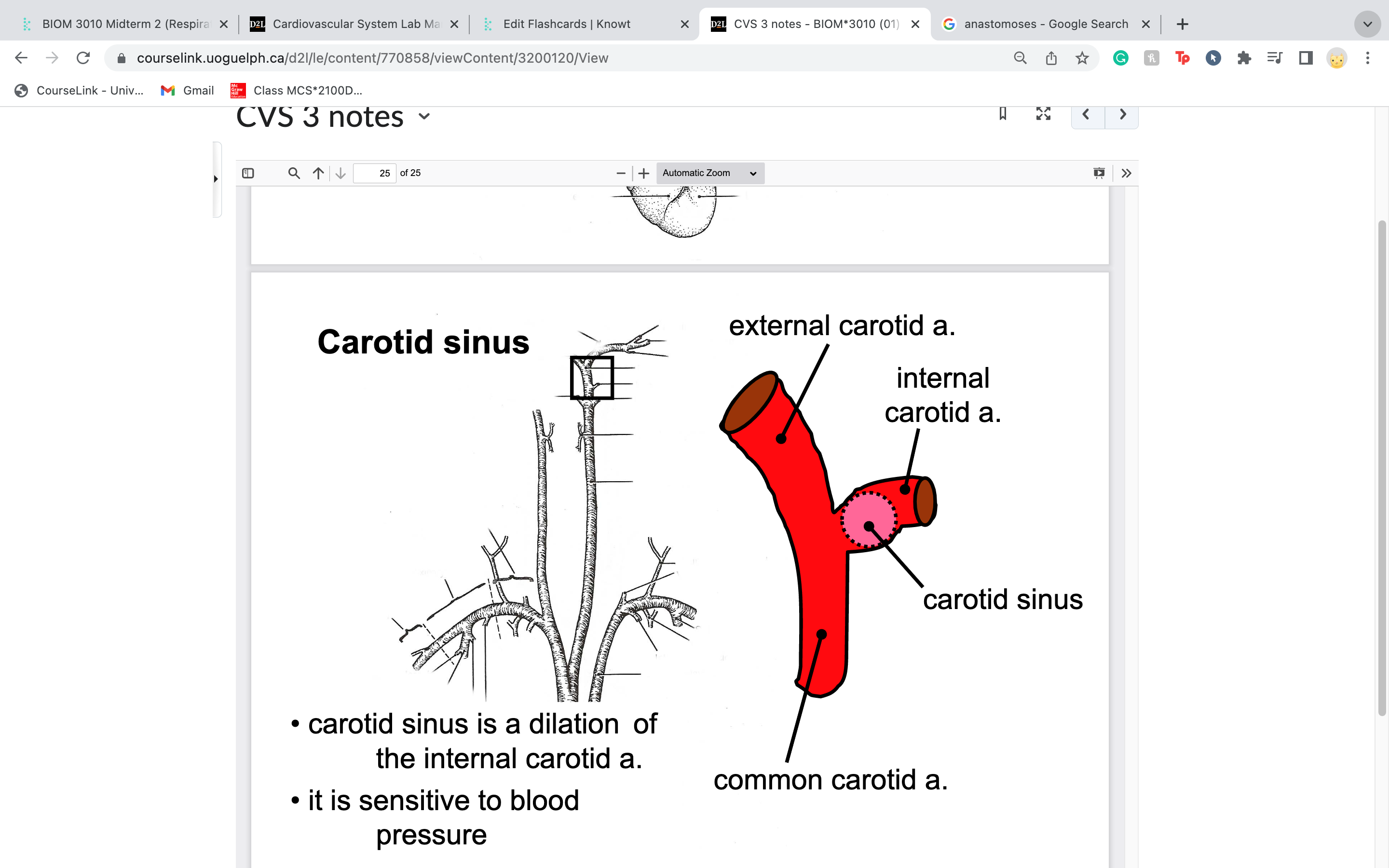
carotid sinus
• dilation of the internal carotid artery
• it is sensitive to blood pressure
-body does blood pressure assessment here .. don't want rly high pressure blood going to brain
• it is sensitive to blood pressure
-body does blood pressure assessment here .. don't want rly high pressure blood going to brain
49
New cards
left ventricle .. blood to the entire body therefore needs thick ass muscle
50
New cards
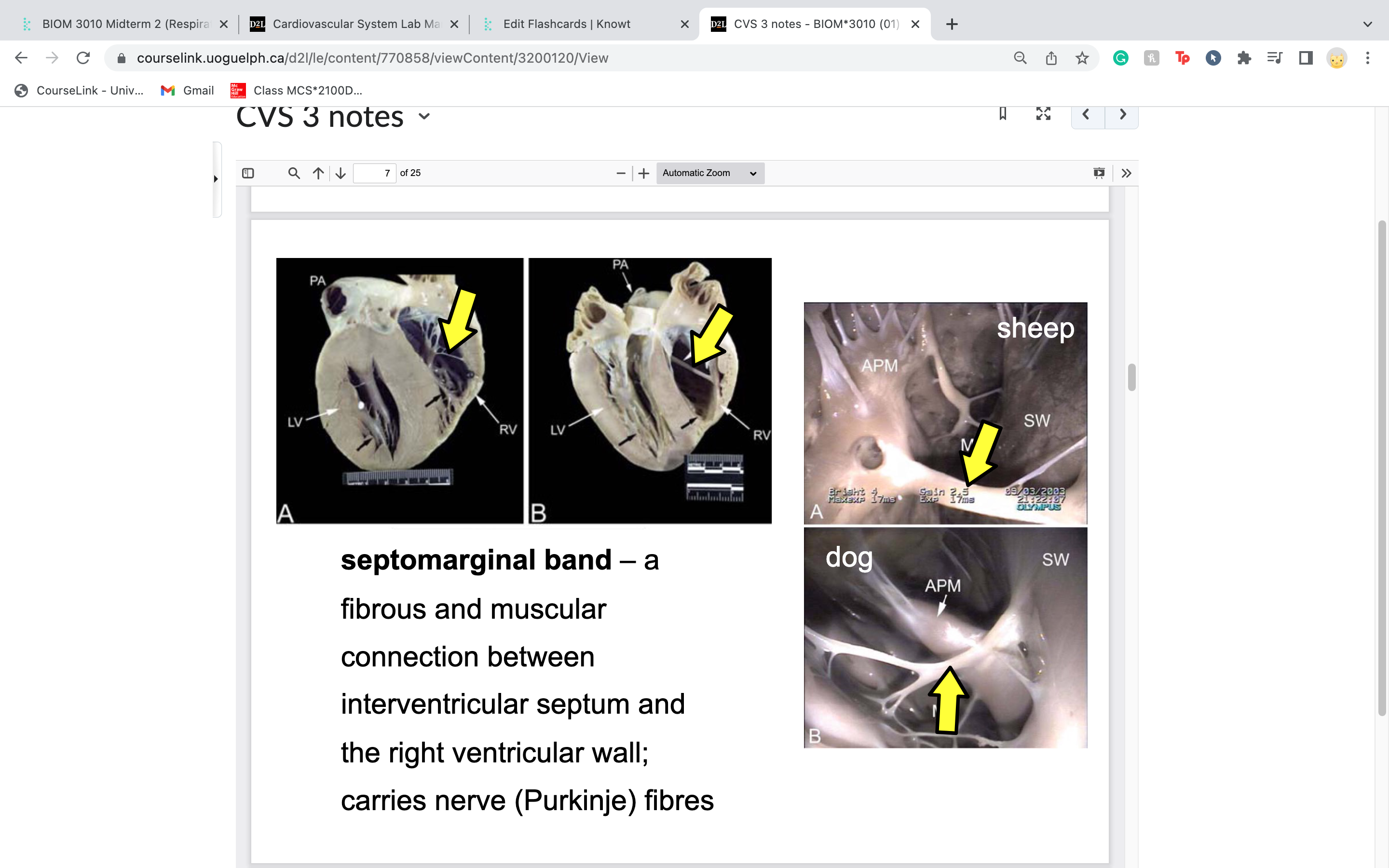
septomarginal band
fibrous and muscular
connection between
interventricular septum and
the right ventricular wall;
carries nerve (Purkinje) fibres
only on right side!
connection between
interventricular septum and
the right ventricular wall;
carries nerve (Purkinje) fibres
only on right side!
51
New cards
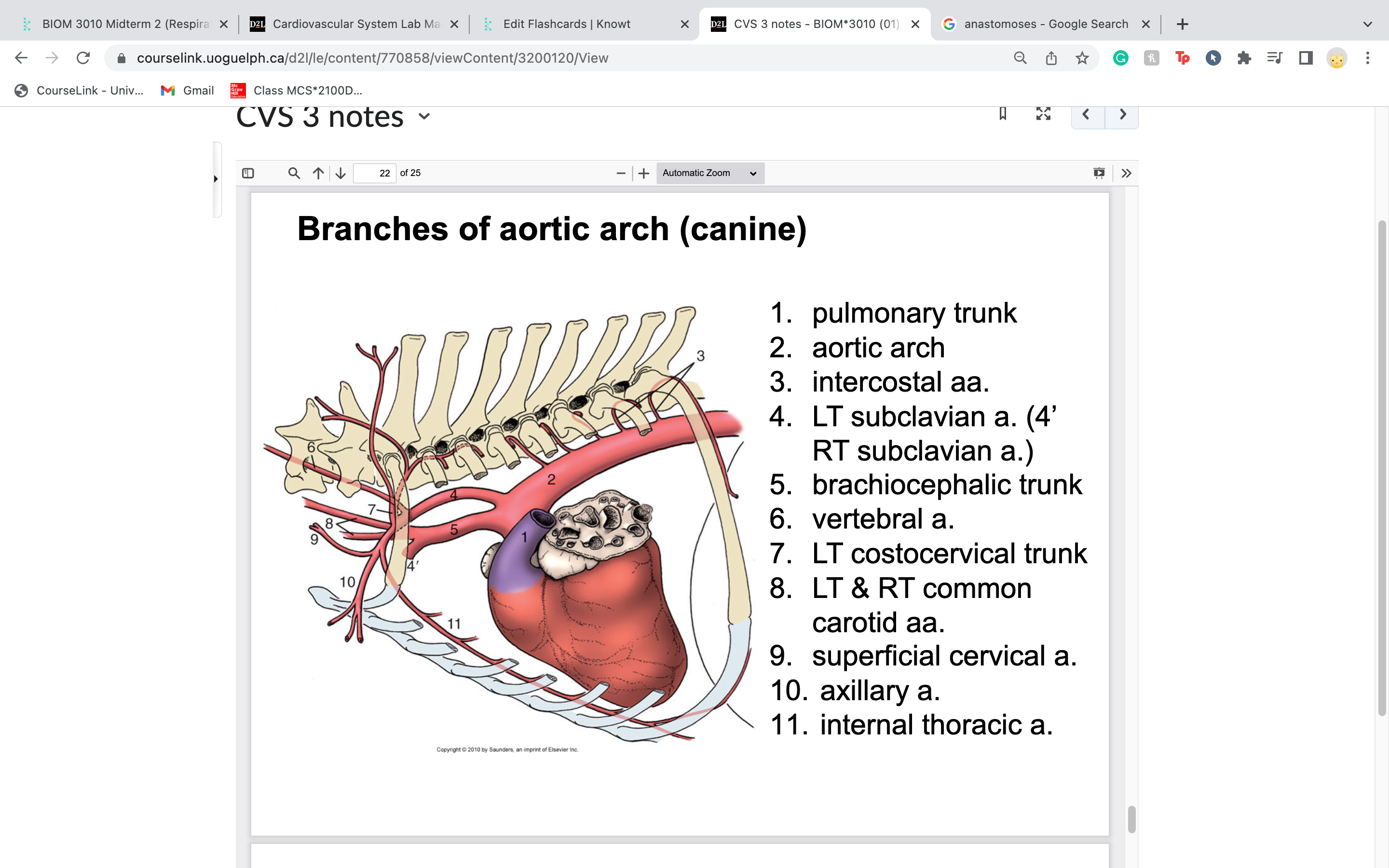
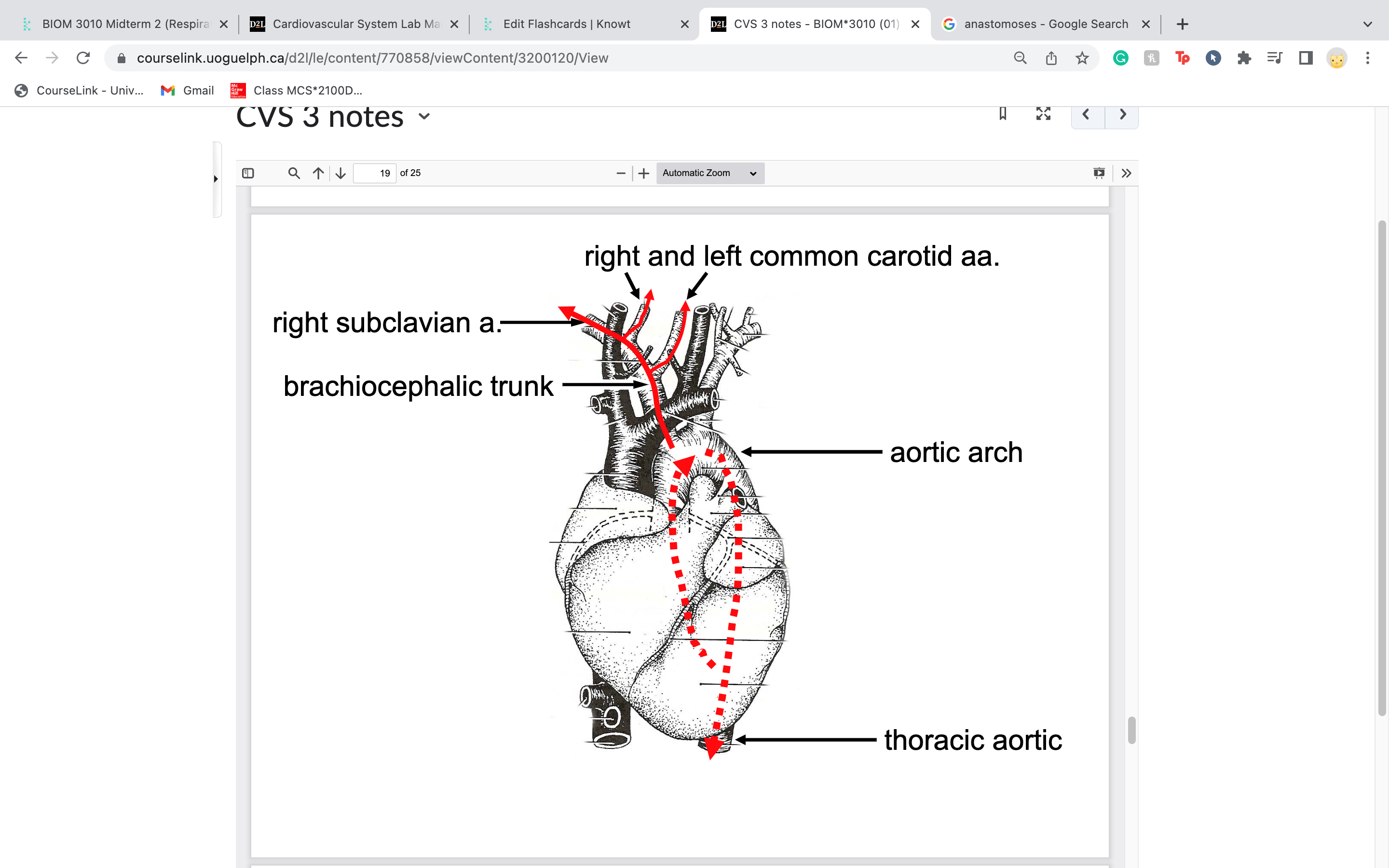
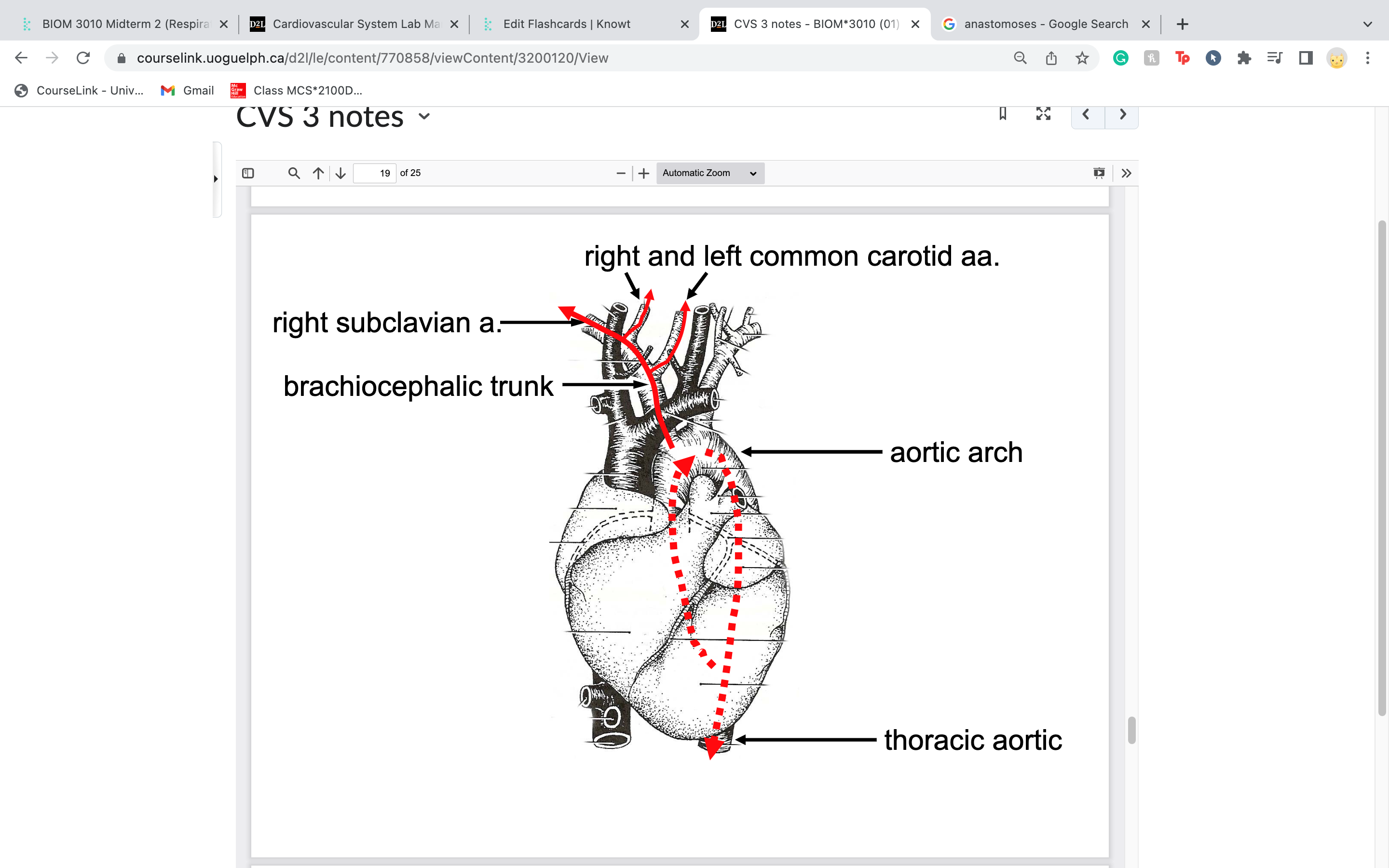
brachiocephalic trunk
right arm and head
-gives rise to 2 arteries: right subclavian = arm
L and R common carotid = head
-gives rise to 2 arteries: right subclavian = arm
L and R common carotid = head
52
New cards
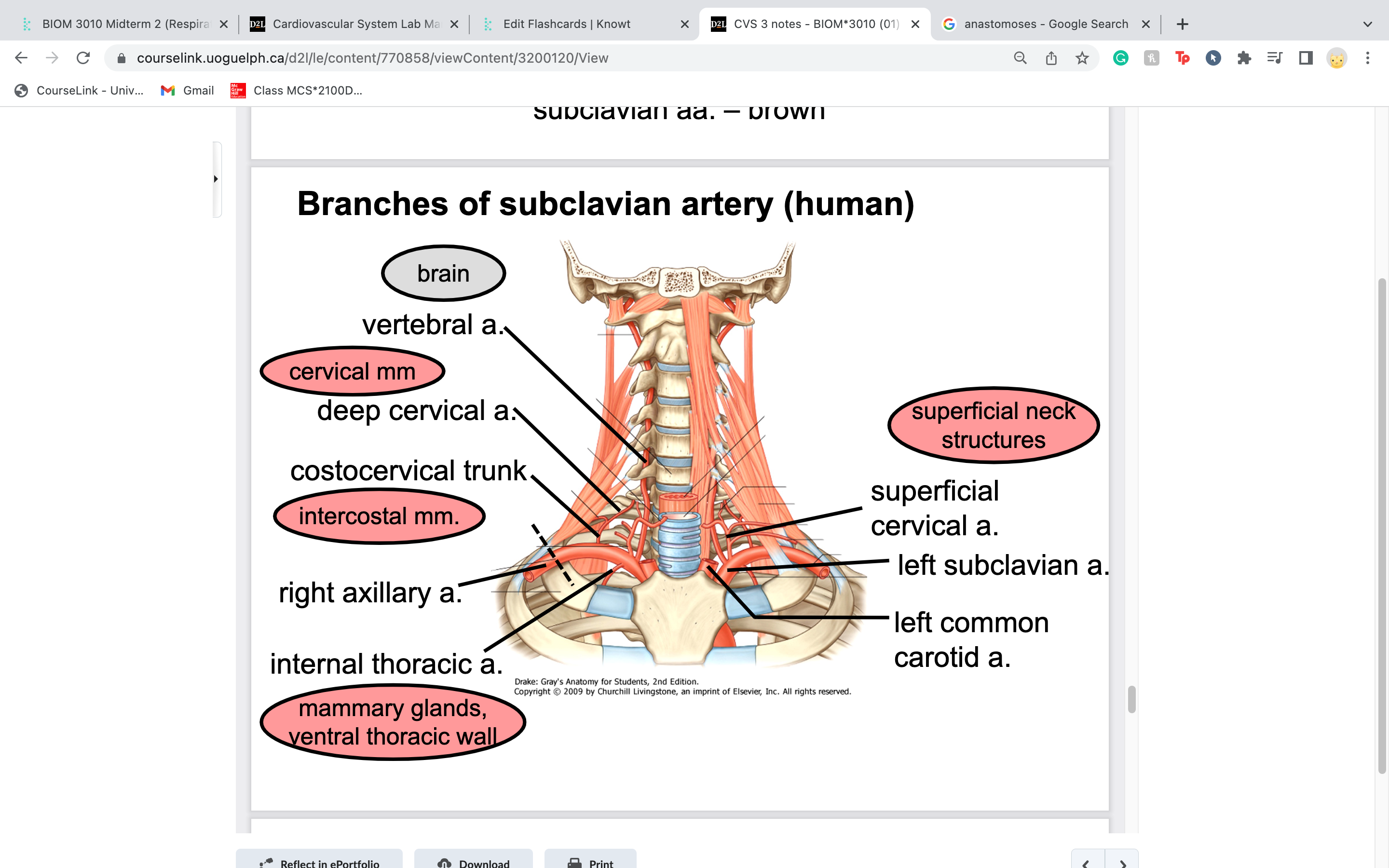
vertebral artery
=towards head/brain
travel in between transverse foramen of vertebrae
travel in between transverse foramen of vertebrae
53
New cards
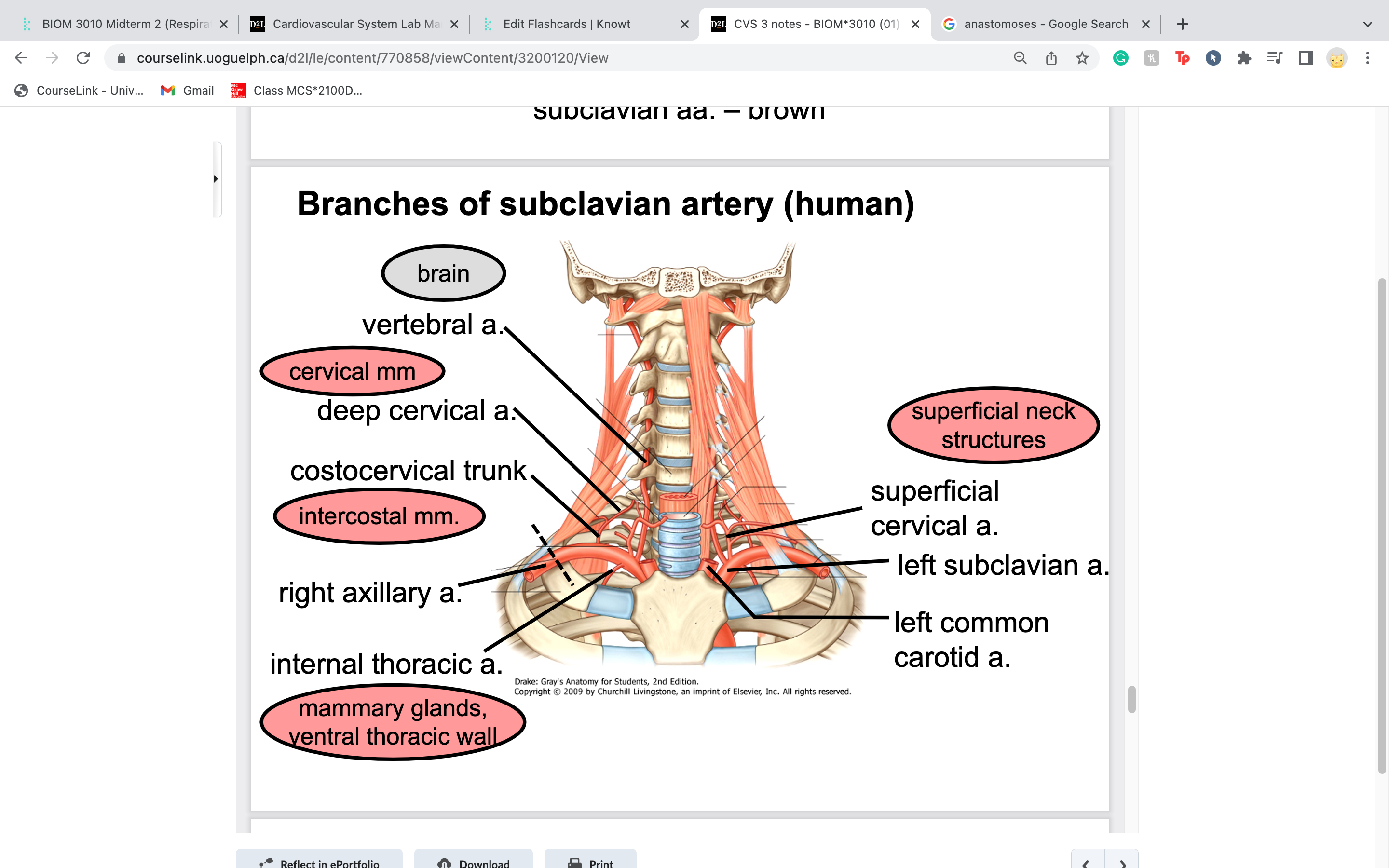
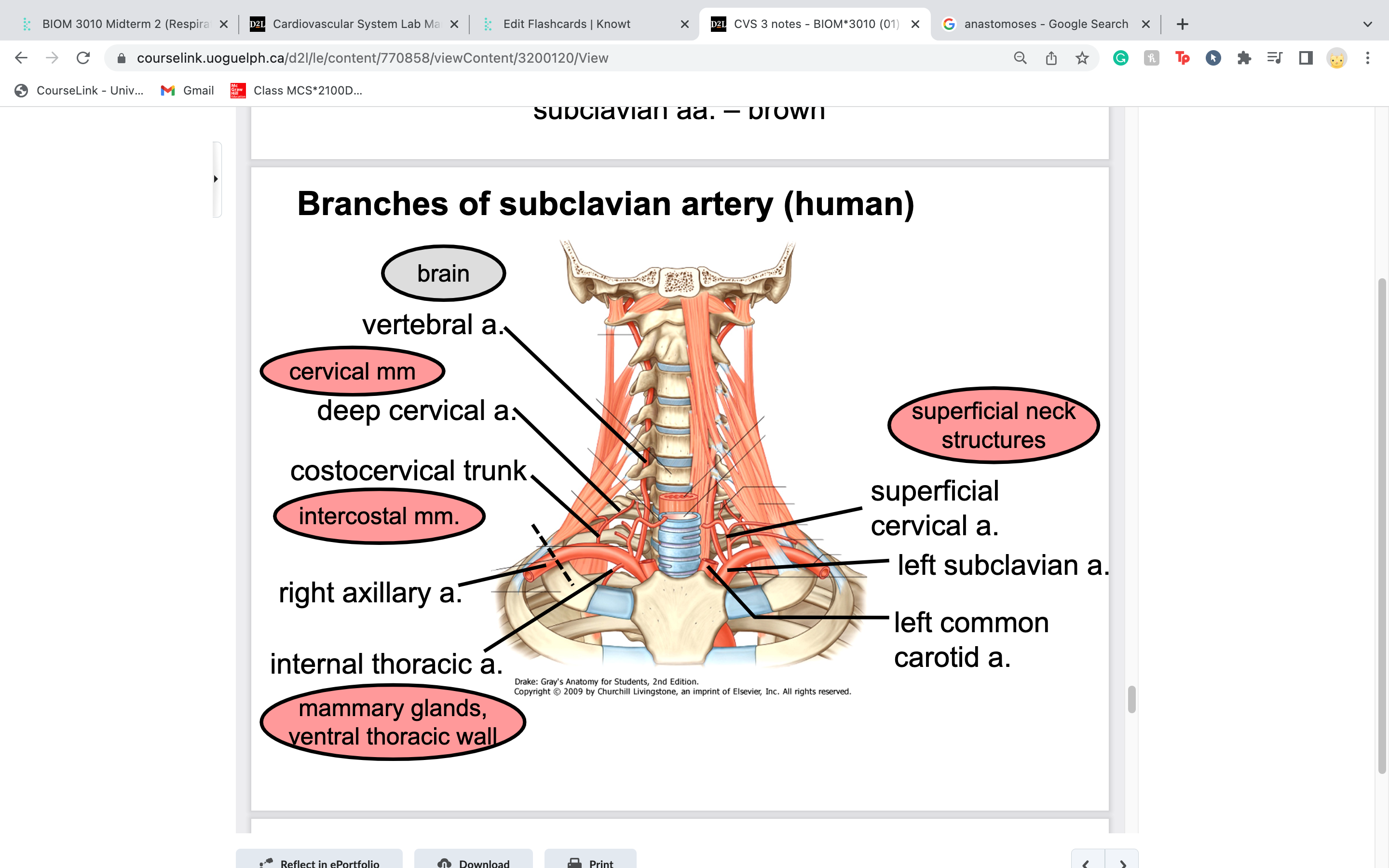
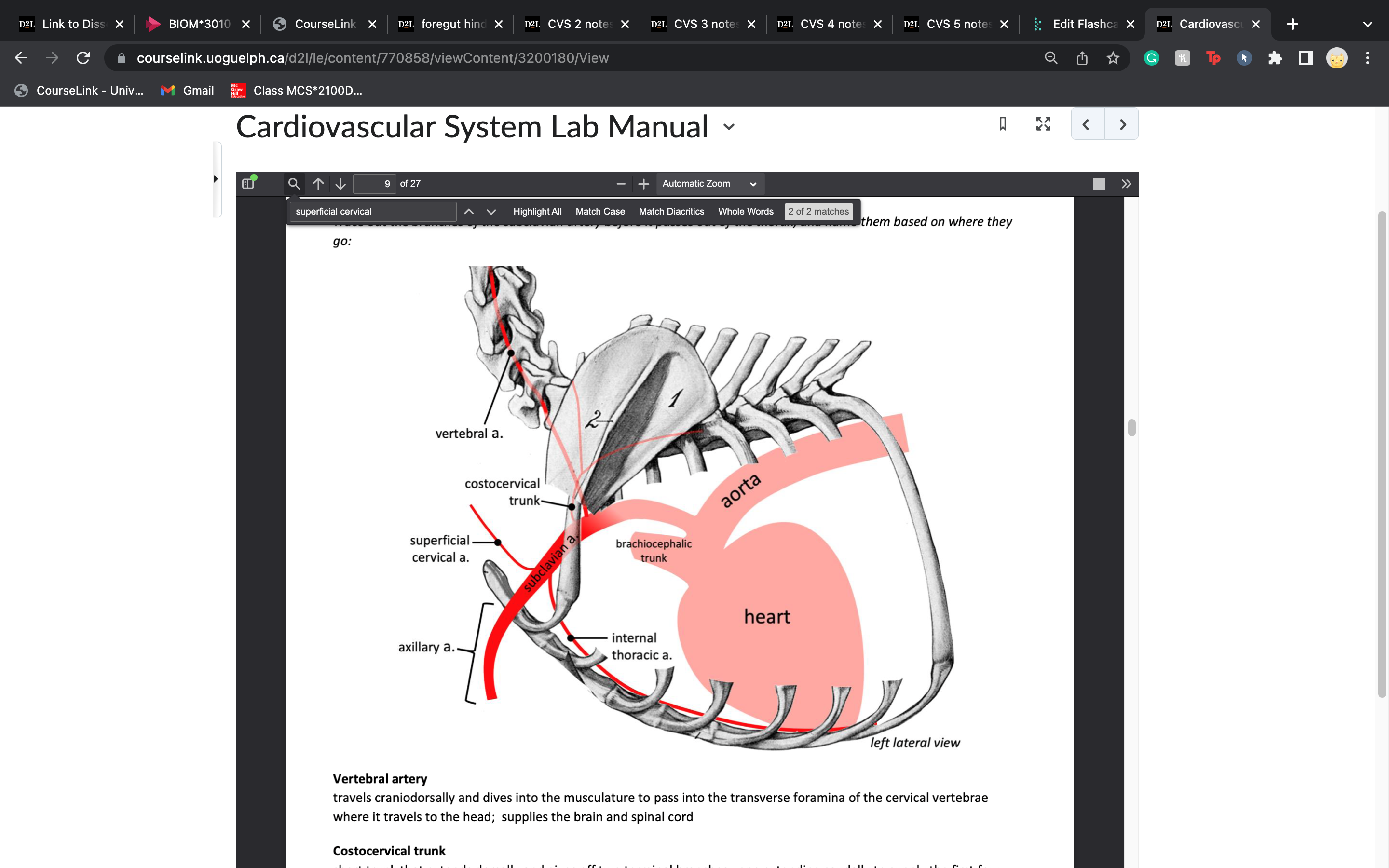
costocervical trunk
in part to intercostal muscles next to ribs
-short trunk that extends dorsally and gives off two terminal branches: one extending caudally to supply the first few
intercostal spaces, the second traveling dorsally to supply the deep musculature of the neck
-short trunk that extends dorsally and gives off two terminal branches: one extending caudally to supply the first few
intercostal spaces, the second traveling dorsally to supply the deep musculature of the neck
54
New cards
internal thoracic artery supplies blood to
travels caudoventrally along the ventral thoracic wall on either side of the sternum to supply the thoracic wall, cranial
abdominal wall and mammary glands in the female (cranial epigastric arteries); was likely removed with the sternum
travel just underneath sternum
abdominal wall and mammary glands in the female (cranial epigastric arteries); was likely removed with the sternum
travel just underneath sternum
55
New cards
superficial cervical artery
extends cranially and laterally to supply the ventral muscles of the neck and the adjacent shoulder region
56
New cards
subclavian artery becomes axillary artery when you pass over ______________..then changes again to ___________ artery when it becomes parallel with humerus
the first rib
brachial
brachial
57
New cards
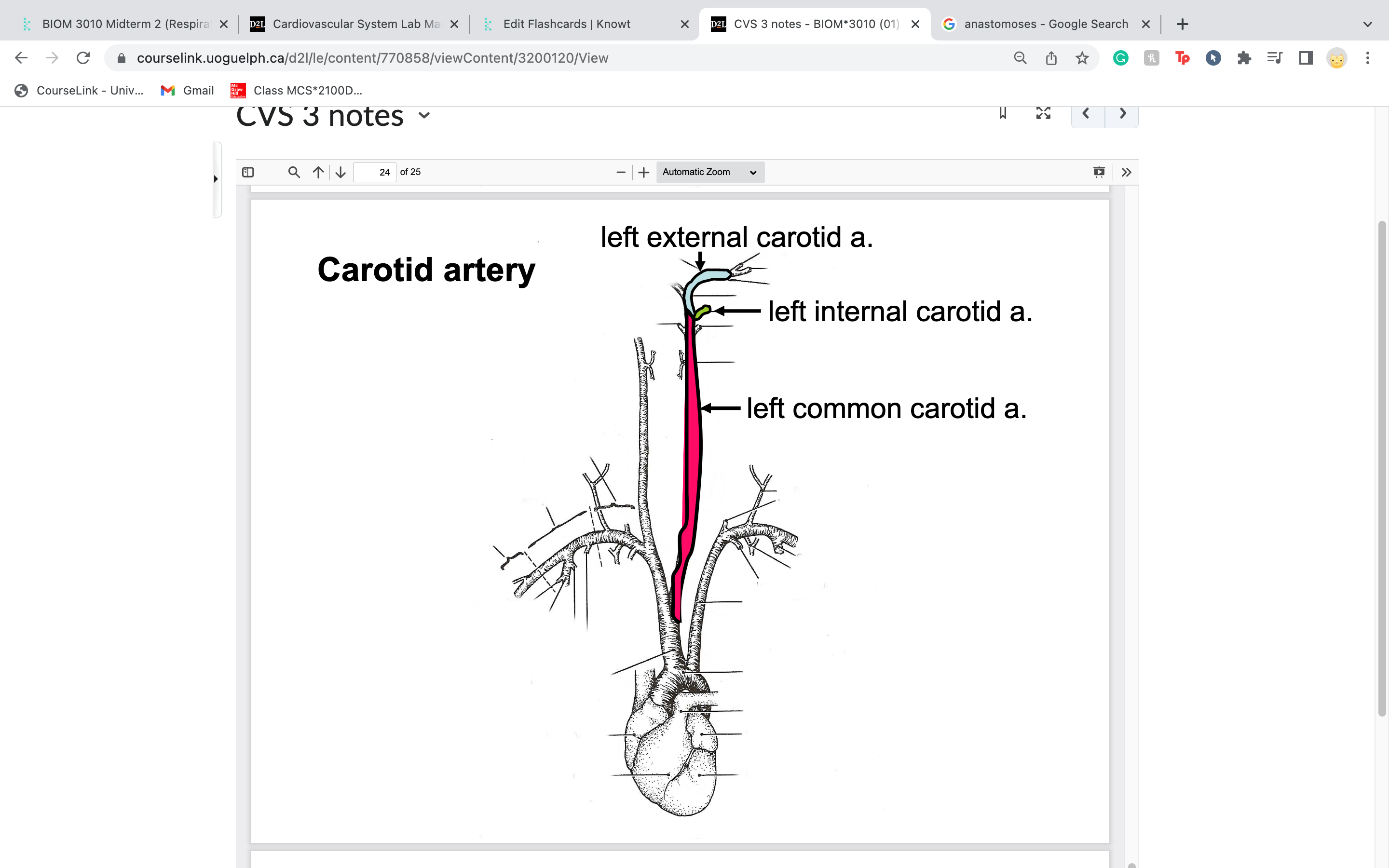
common carotid artery... and internal and external carotid artery....
common splits off to become internal and external
58
New cards
tunica intima = 1 layer of endothelial cells, where is it
innermost layer of cels of tunica intima of an artery or vein
59
New cards
laryngeal artery provides blood to the :
larynx
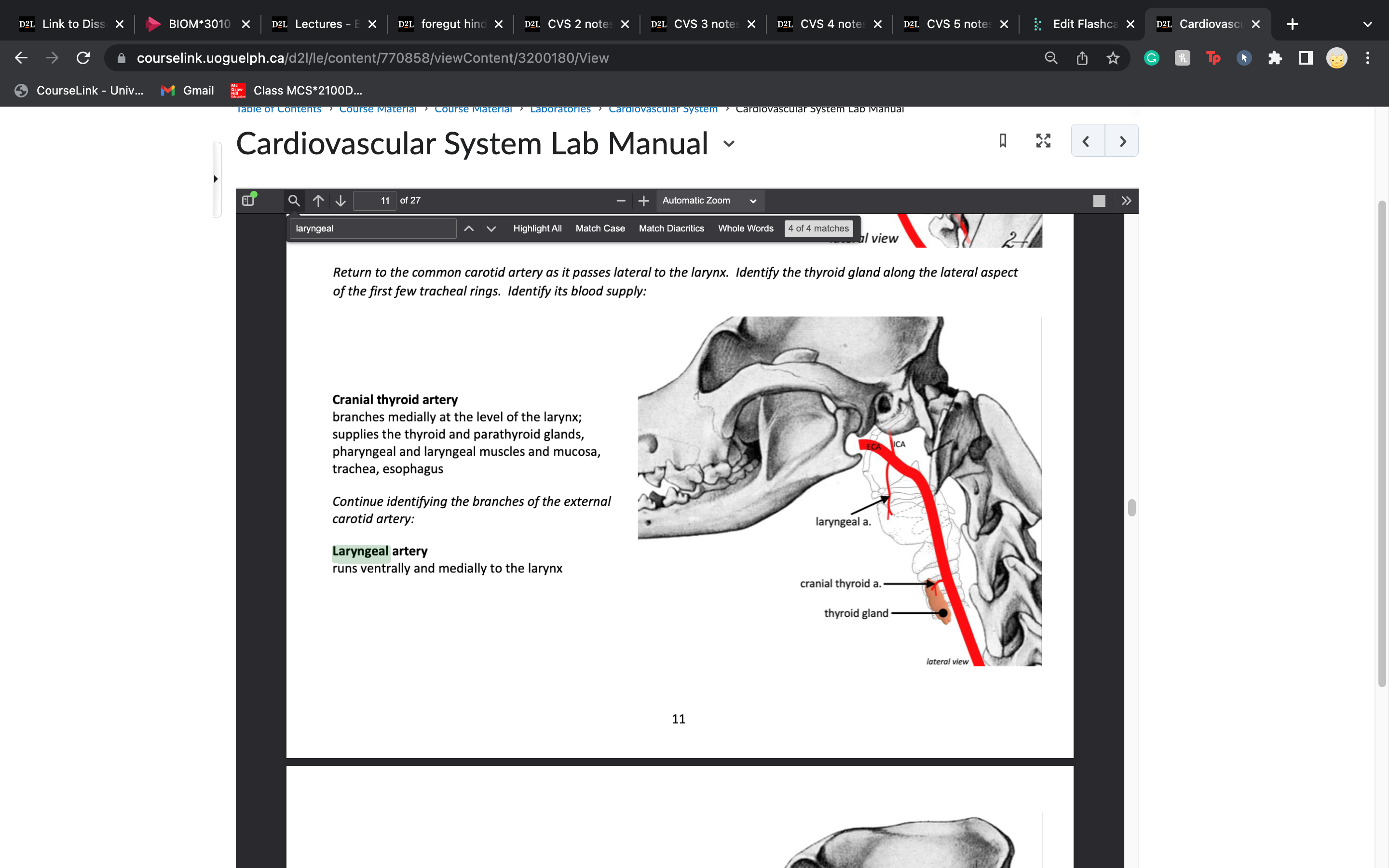
60
New cards
common carotid artery becomes what at the first 3 branches in the head
internal carotid artery
external carotid artery
laryngeal artery
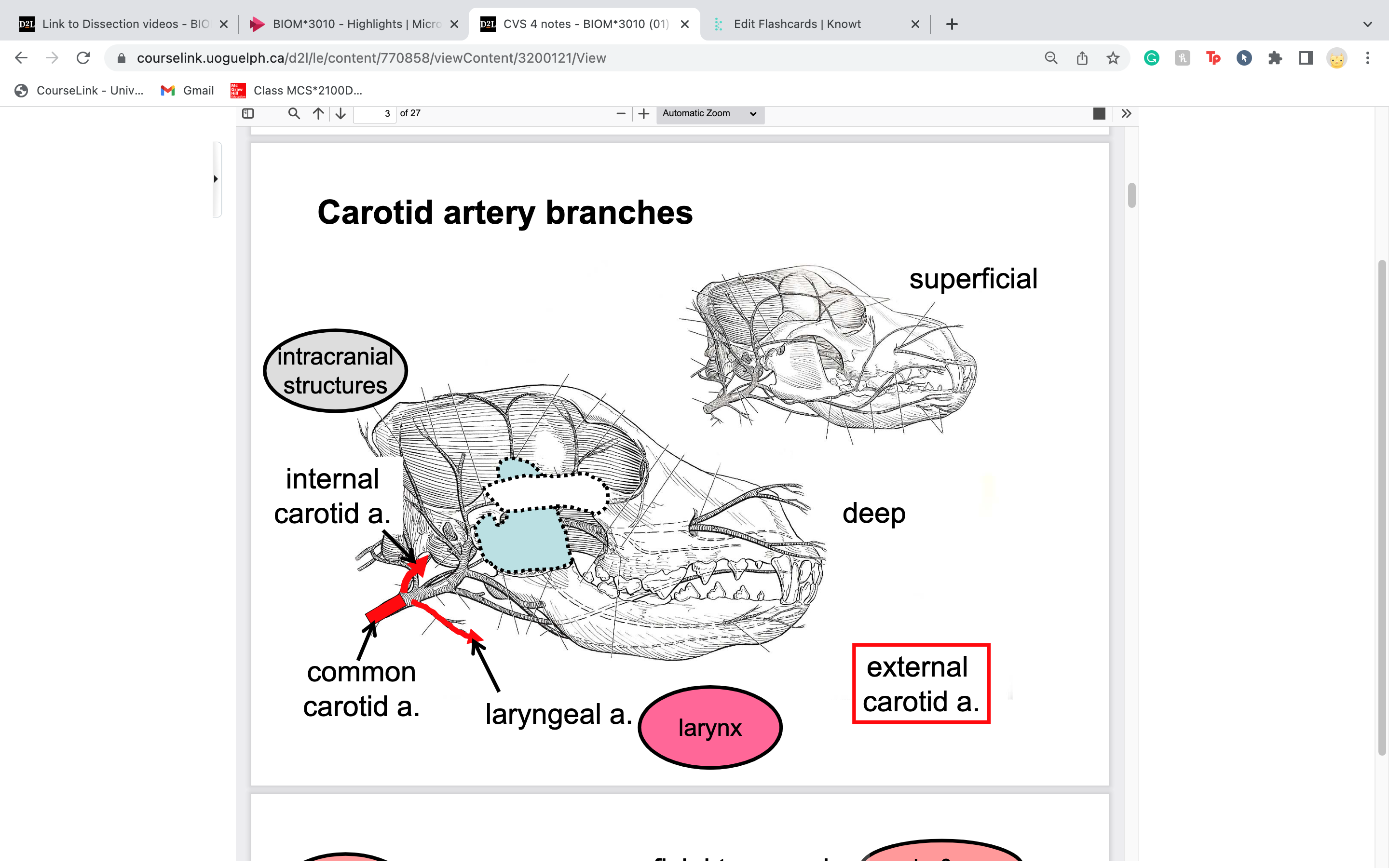
61
New cards
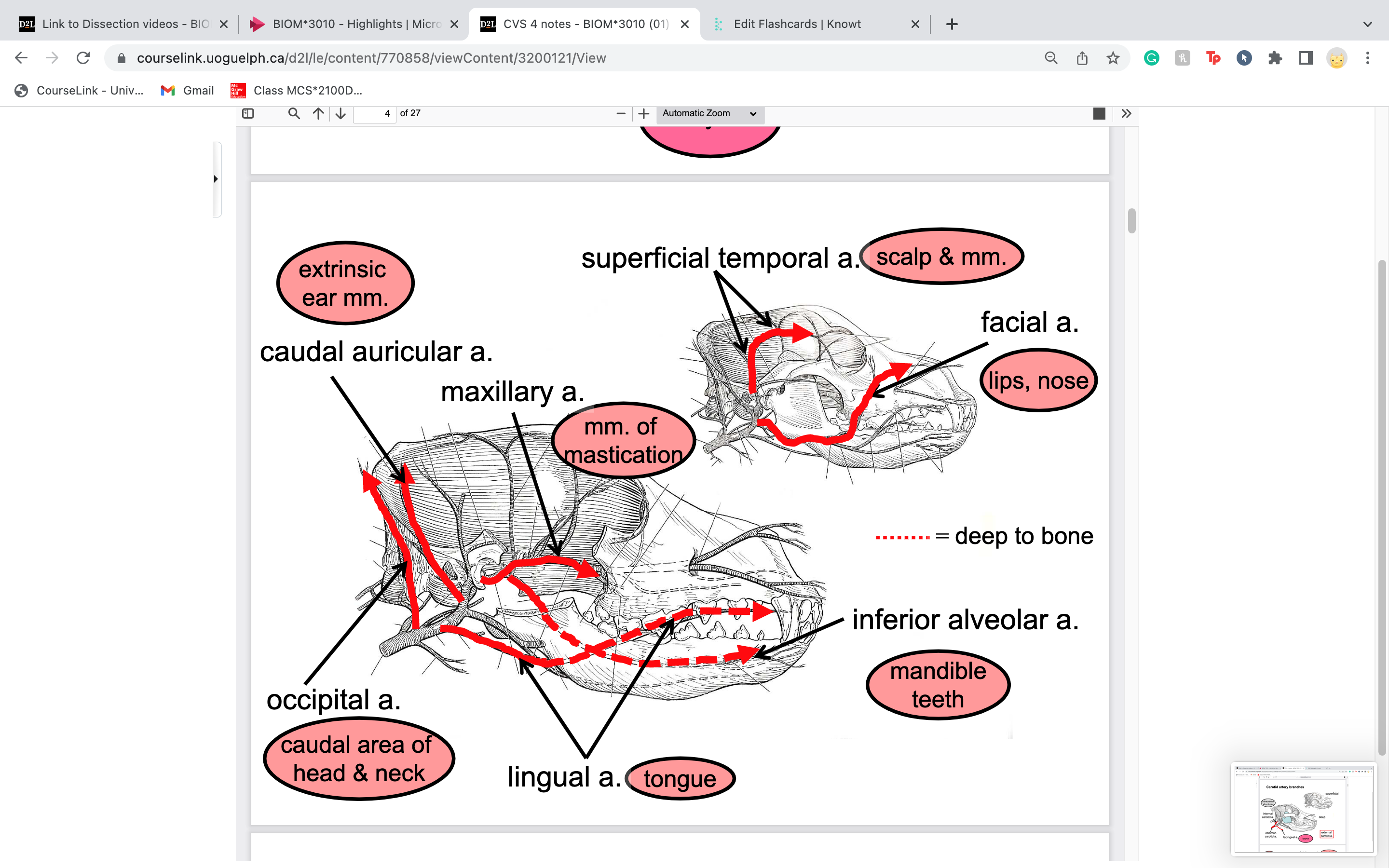
occipital artery runs right along where the occipital bone is
caudal area of the head and neck
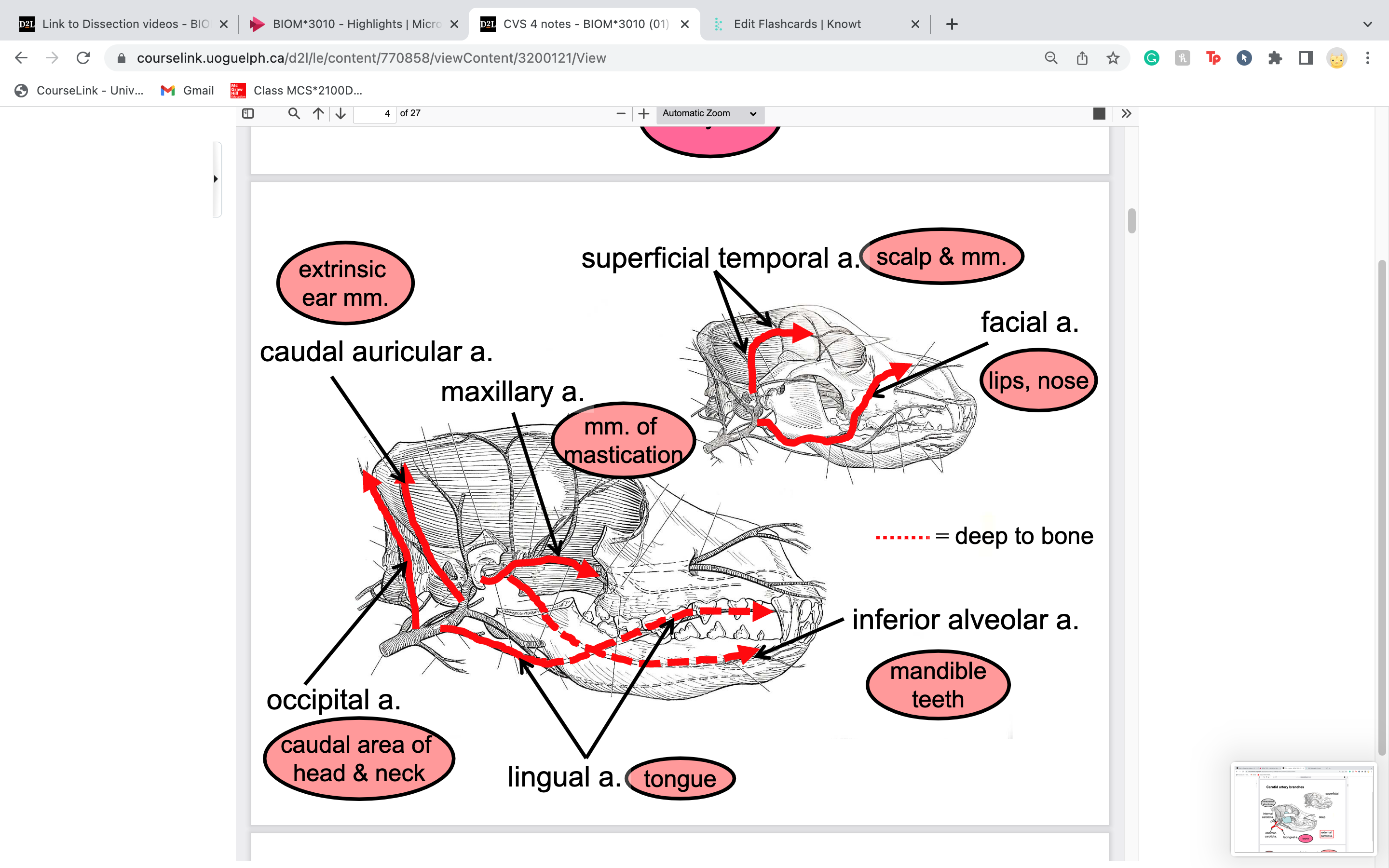
62
New cards
lingual artery provides blood to
tongue
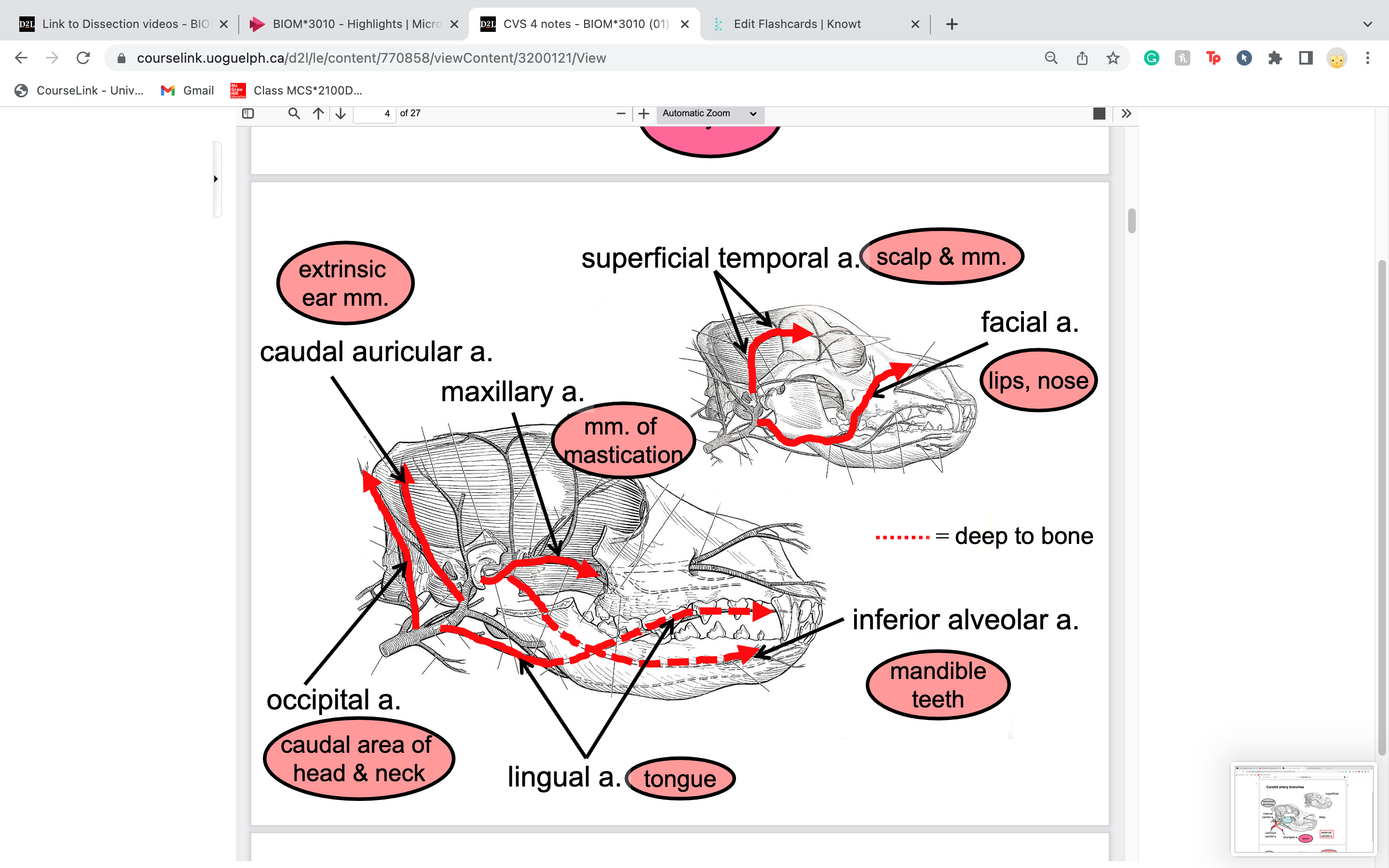
63
New cards
facial artery
lateral to mandible
lateral to mandible
blood to lips, nose
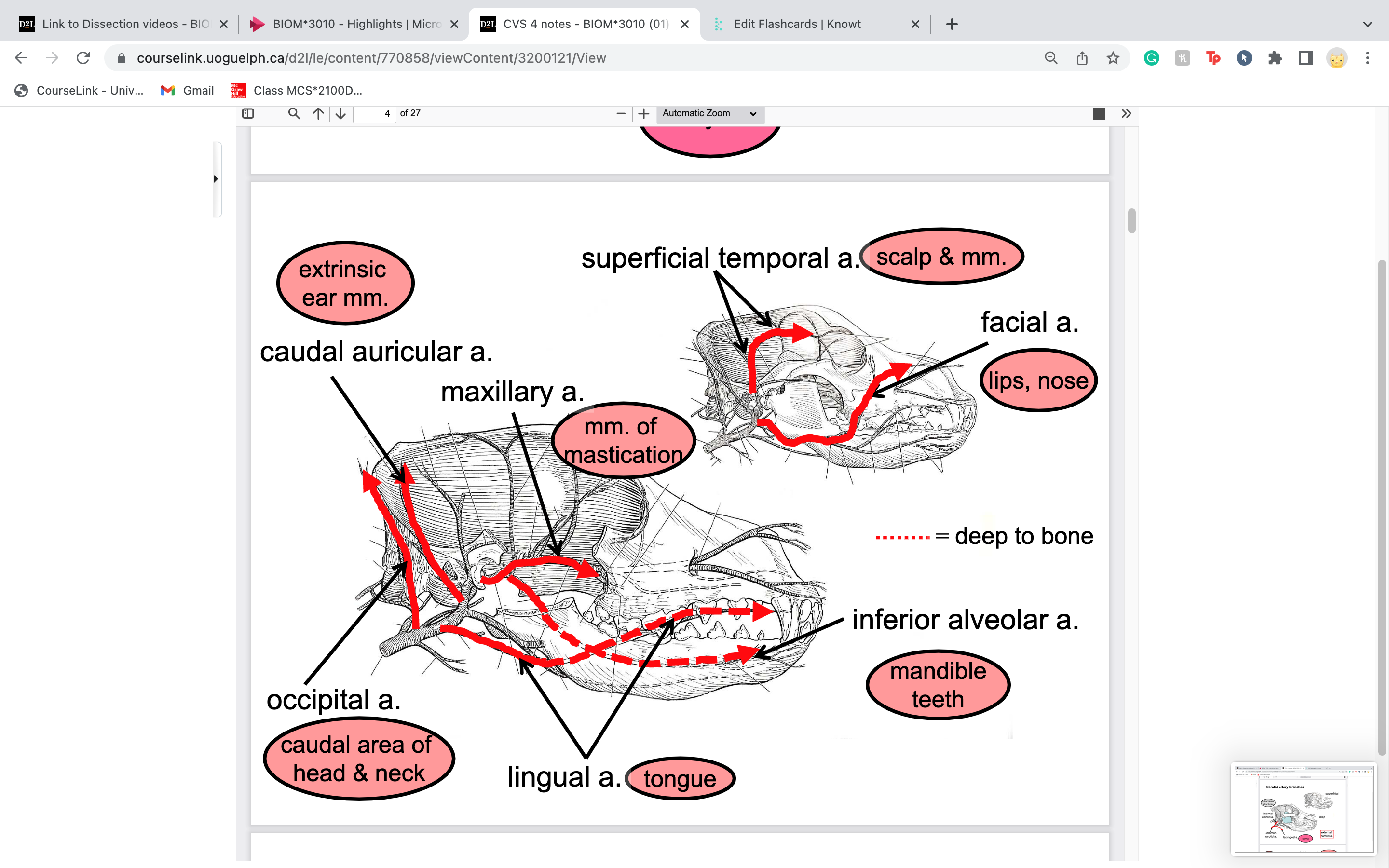
64
New cards
caudal auricular artery provides blood to
ear
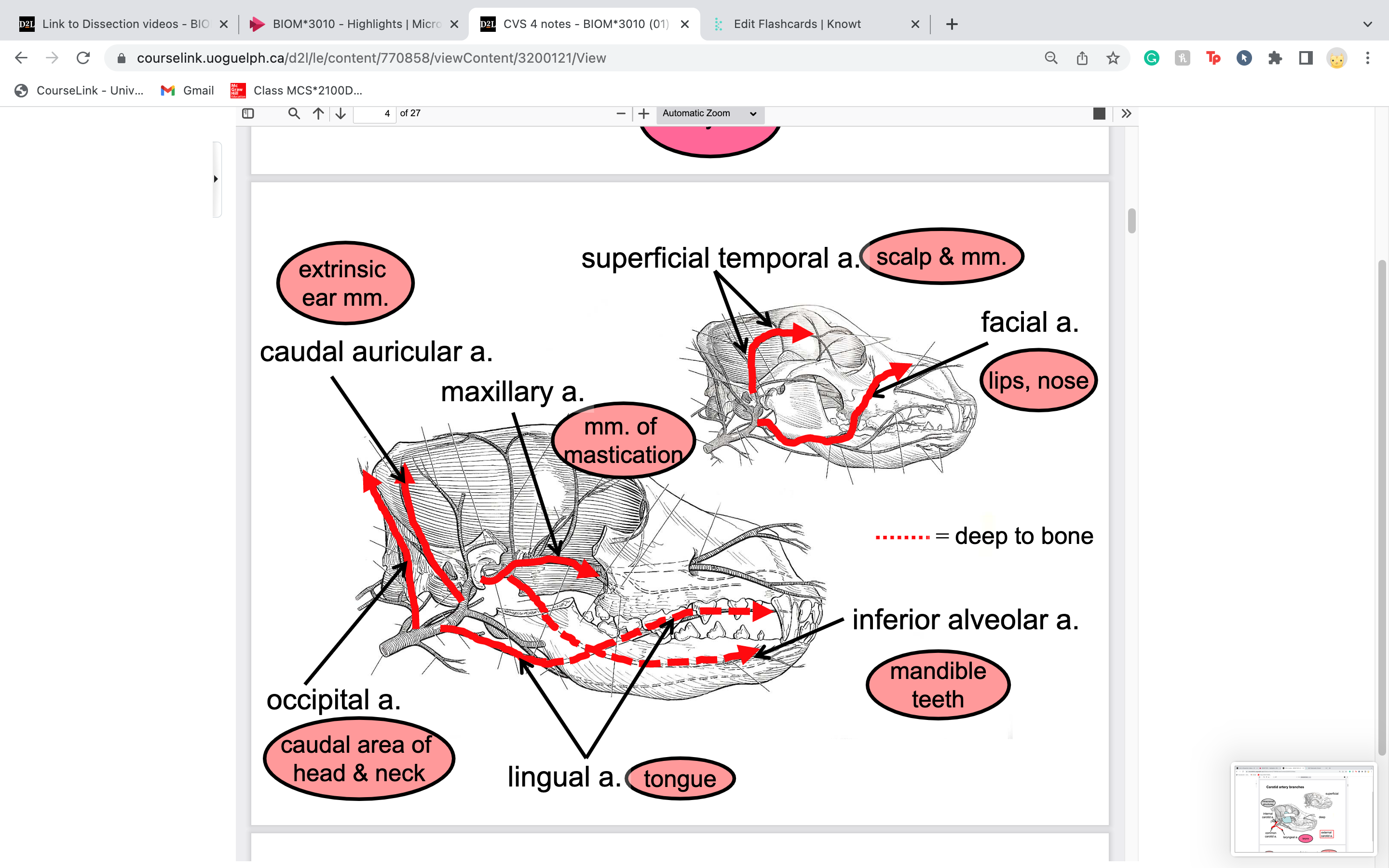
65
New cards
superficial temporal artery
in temporal fossa, where temporalis muscle sits in
courses dorsally and supplies the masseter,
parotid gland, muscles and scalp of the
temporal regio
courses dorsally and supplies the masseter,
parotid gland, muscles and scalp of the
temporal regio
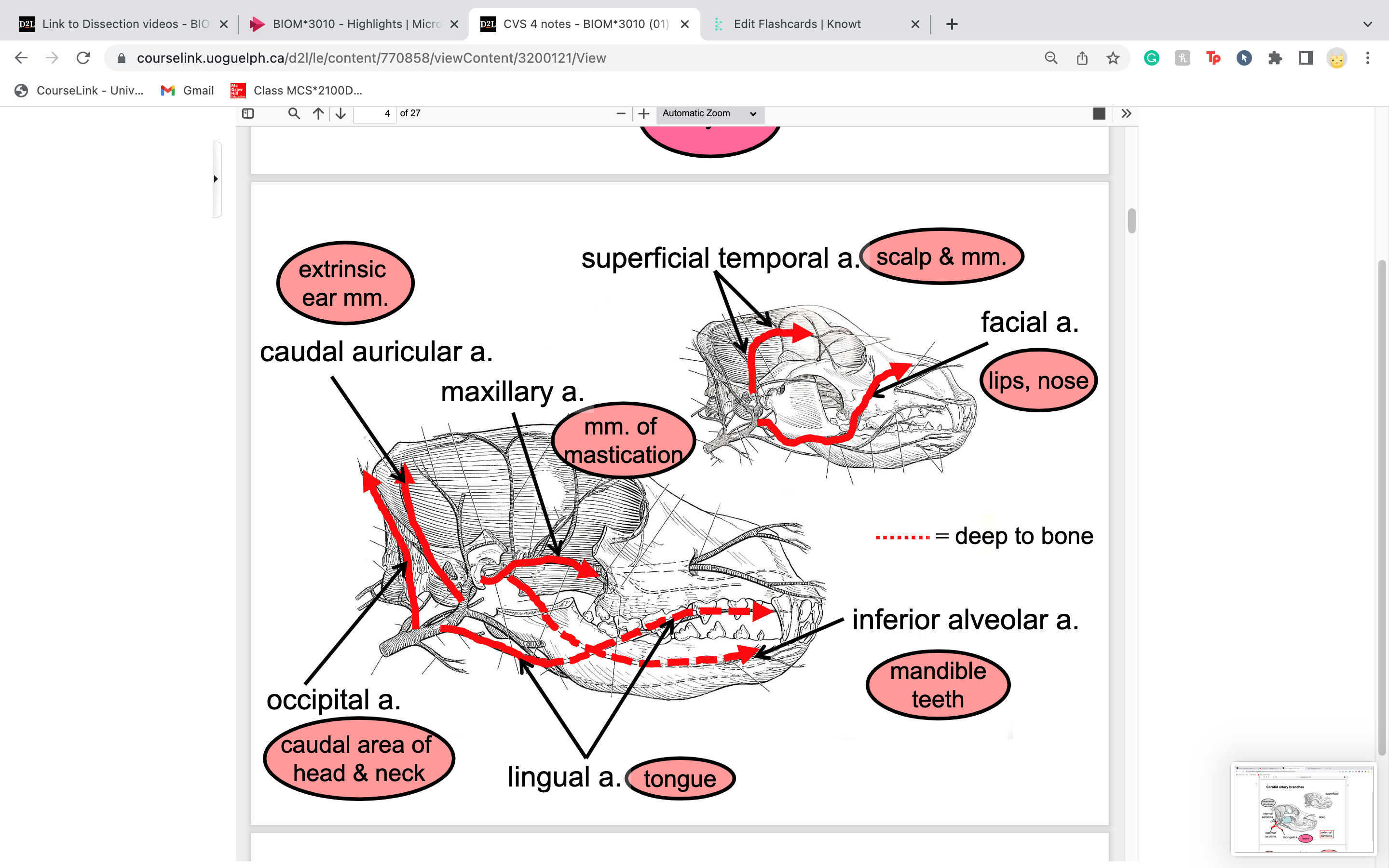
66
New cards
maxillary artery is terminal branch of carotid artery . provides blood for .....
temporalis snd masseter (chewing)
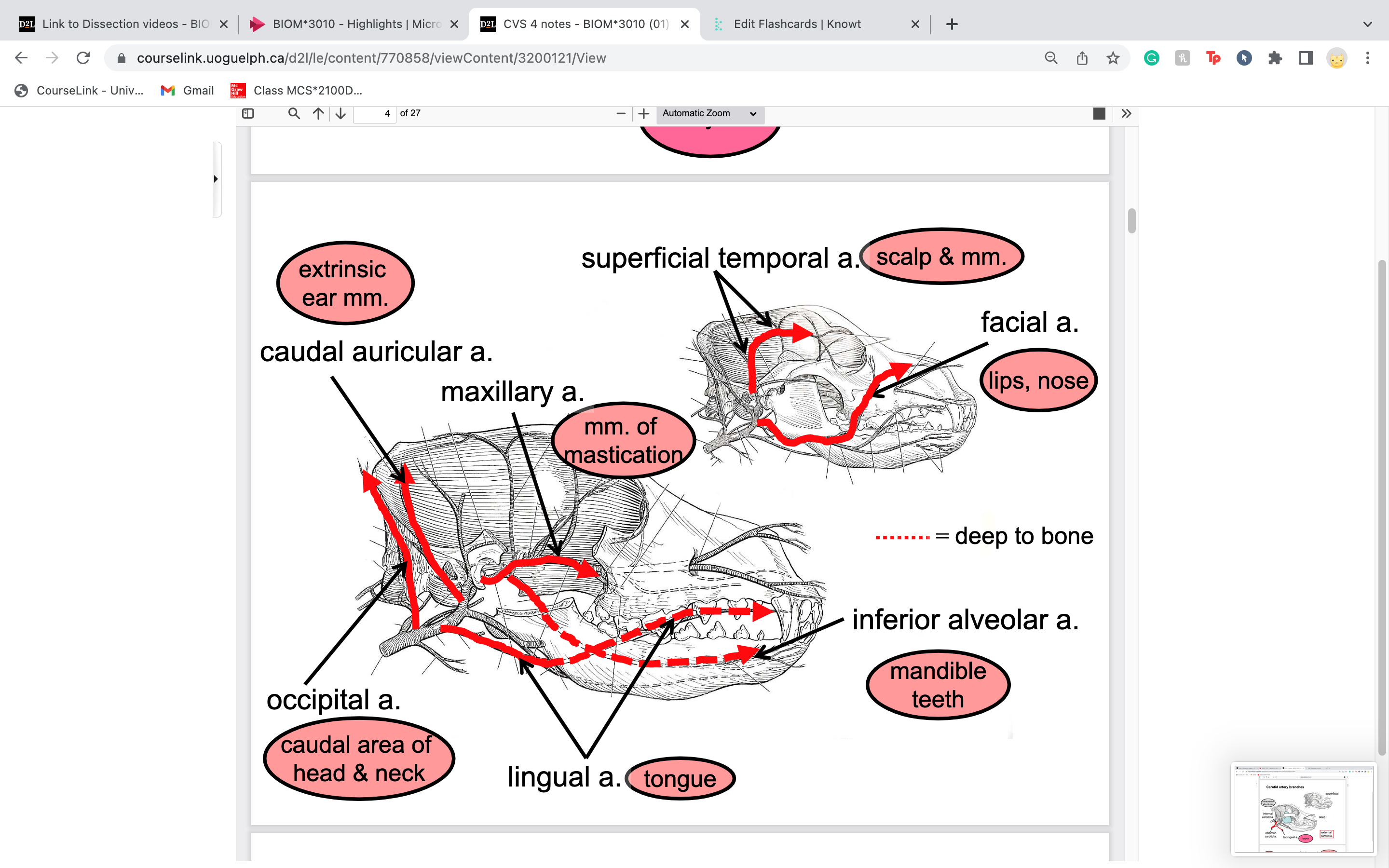
67
New cards
inferior alveolar artery
TOOTH sockets* alveolus is also a term for where tooth roots fit
supplying mandible and teeth
supplying mandible and teeth
68
New cards
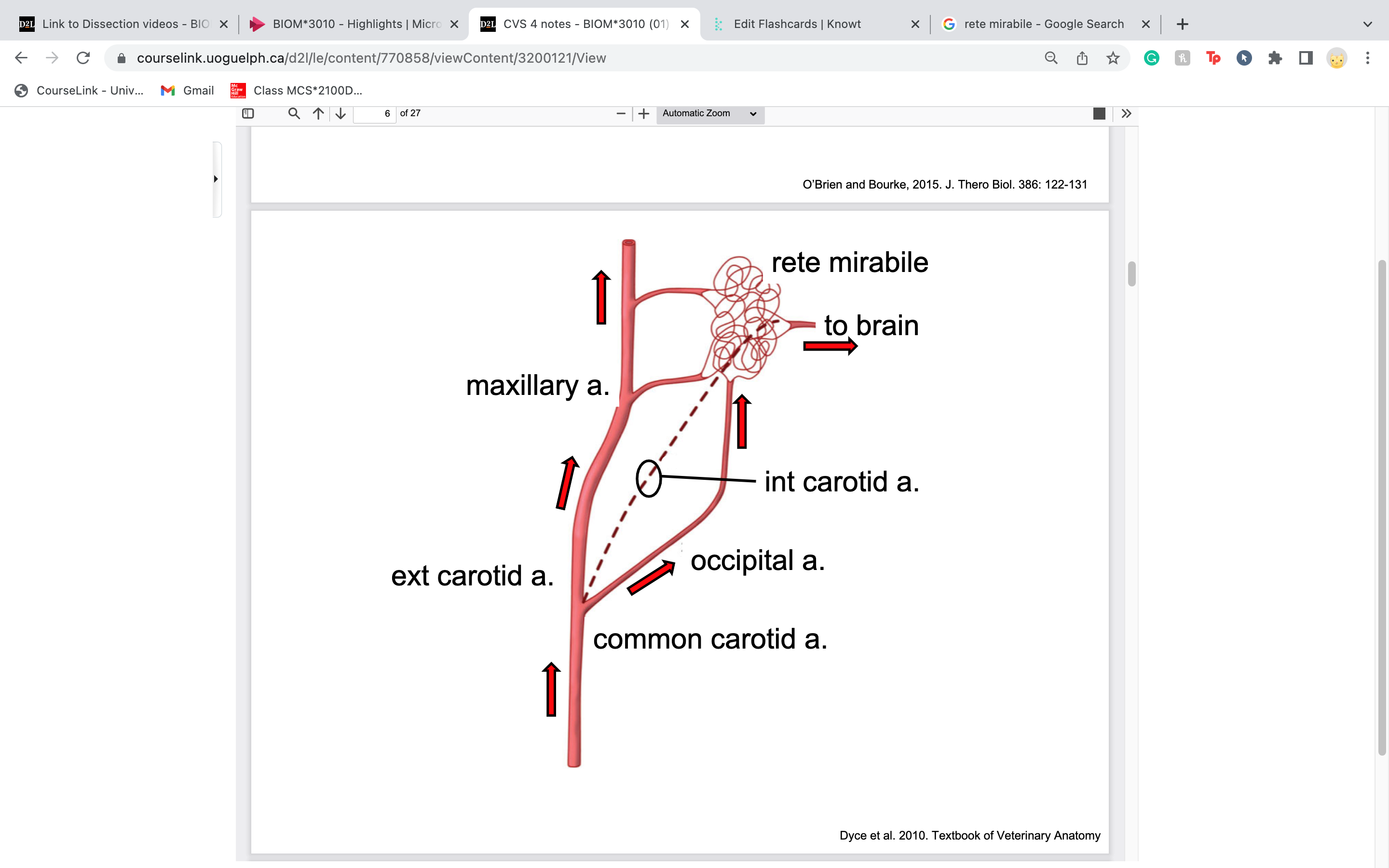
rete mirabile
cooling brain
big jumble of veins, lets it cool
big jumble of veins, lets it cool
69
New cards
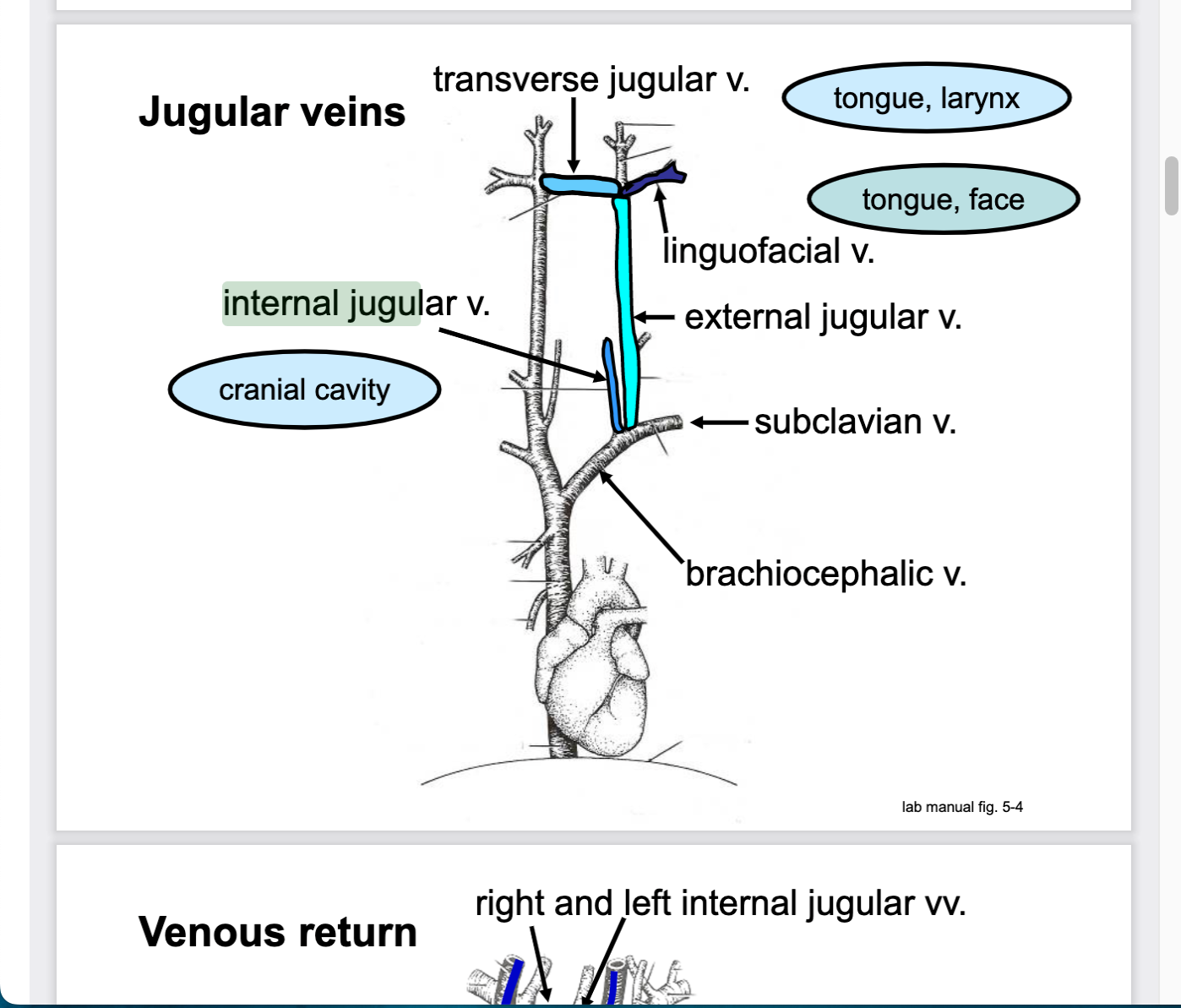
transverse jugular drains blood from _________
tongue, larynx
70
New cards
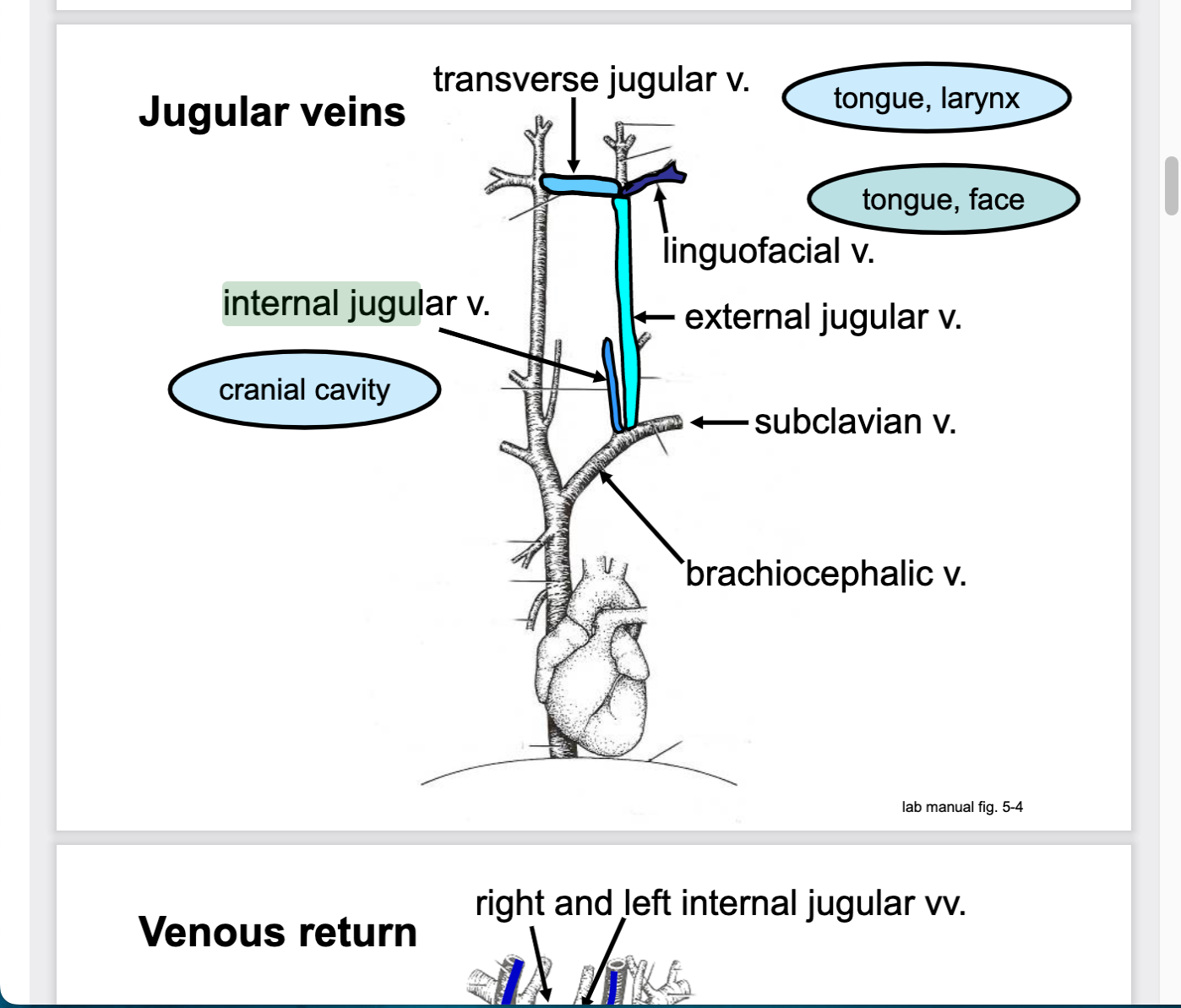
linguofacial vein drains blood from ______
tongue and face
71
New cards
cranial vena cava from cranial to the heart
72
New cards
axillary artery bc its over the first ___
rib
73
New cards
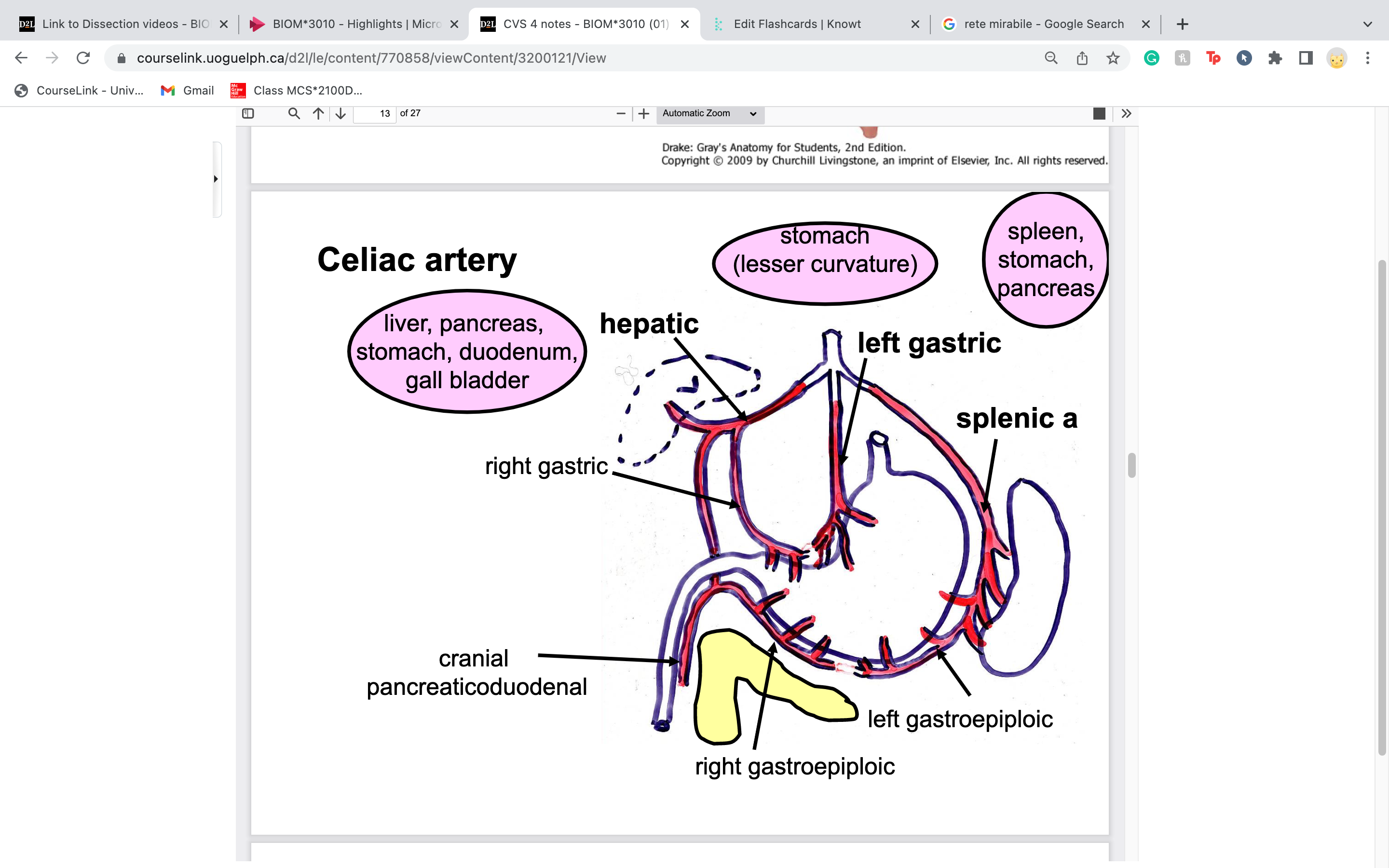
celiac artery gives blood to
foregut
stomach, duodenum, liver, gall bladder, pancreas and spleen
stomach, duodenum, liver, gall bladder, pancreas and spleen
74
New cards
cranial mesenteric artery gives blood to
small intestine, pancreas, cecum colon
*branches before kidneys off abdominal aorta
*branches before kidneys off abdominal aorta
75
New cards
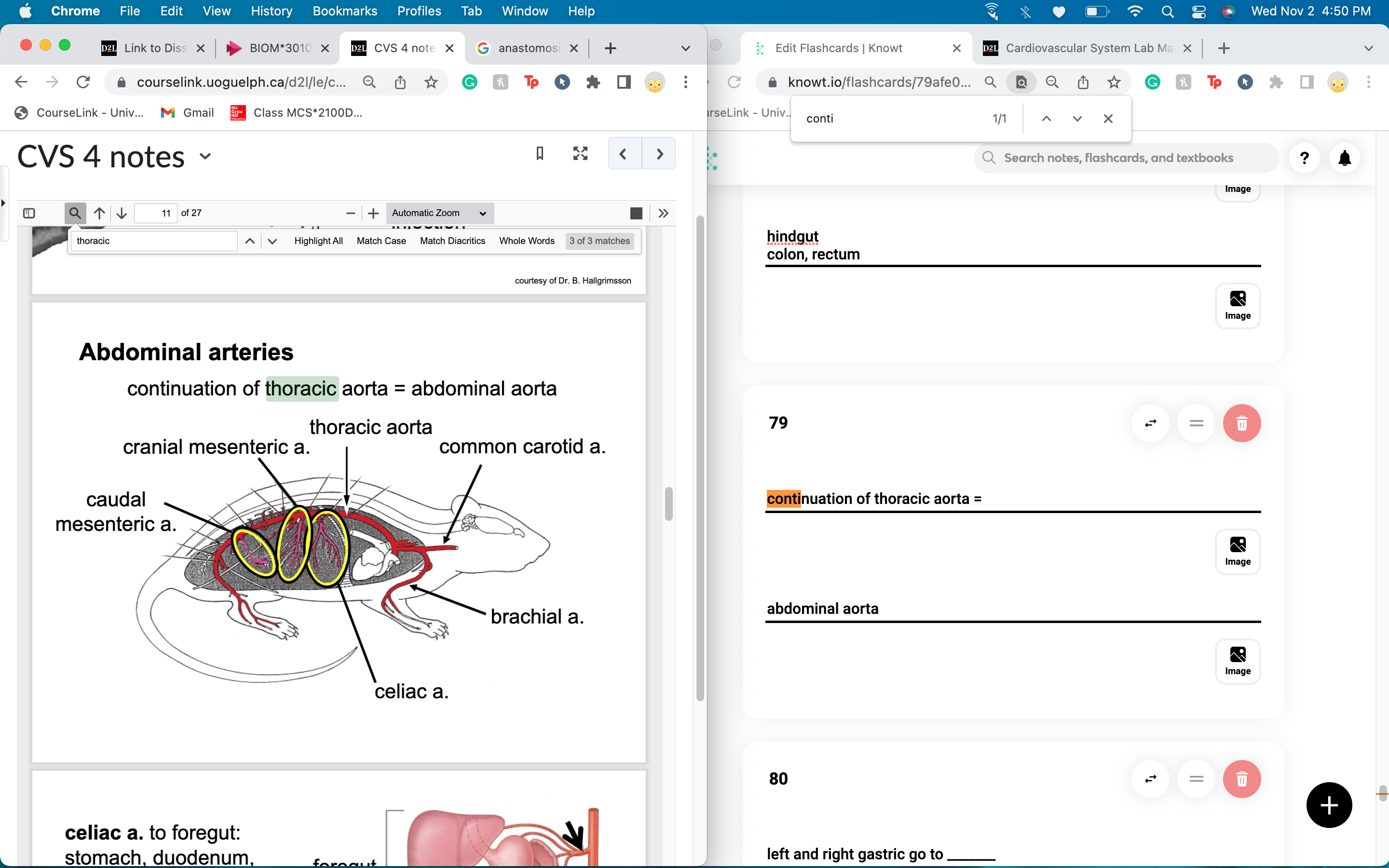
continuation of thoracic aorta =
abdominal aorta
76
New cards
left and right gastric artery go to _______
greater curvature of the stomach
77
New cards
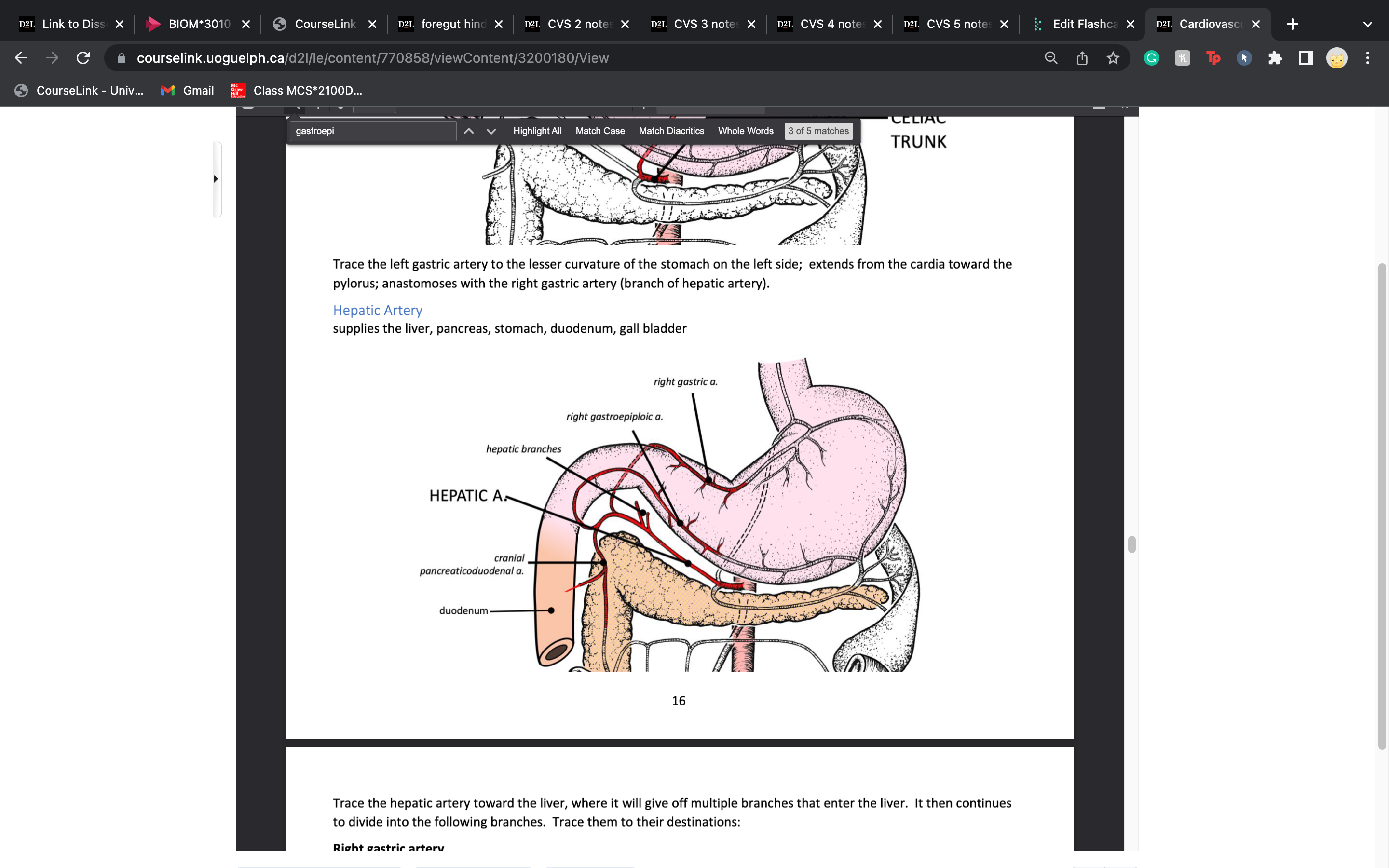
right gastroepiploic arteries
78
New cards
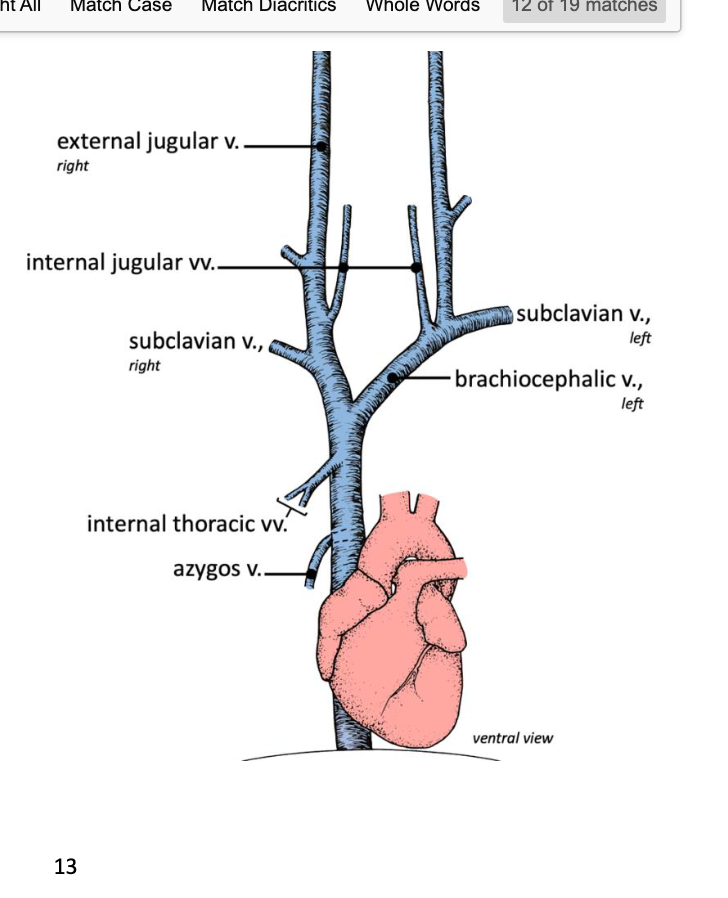
internal thoracic vein
either side of the sternum, fuse before entering the
cranial vena cava as one vessel
cranial vena cava as one vessel
79
New cards
external jugular vein drains blood from..
head and neck
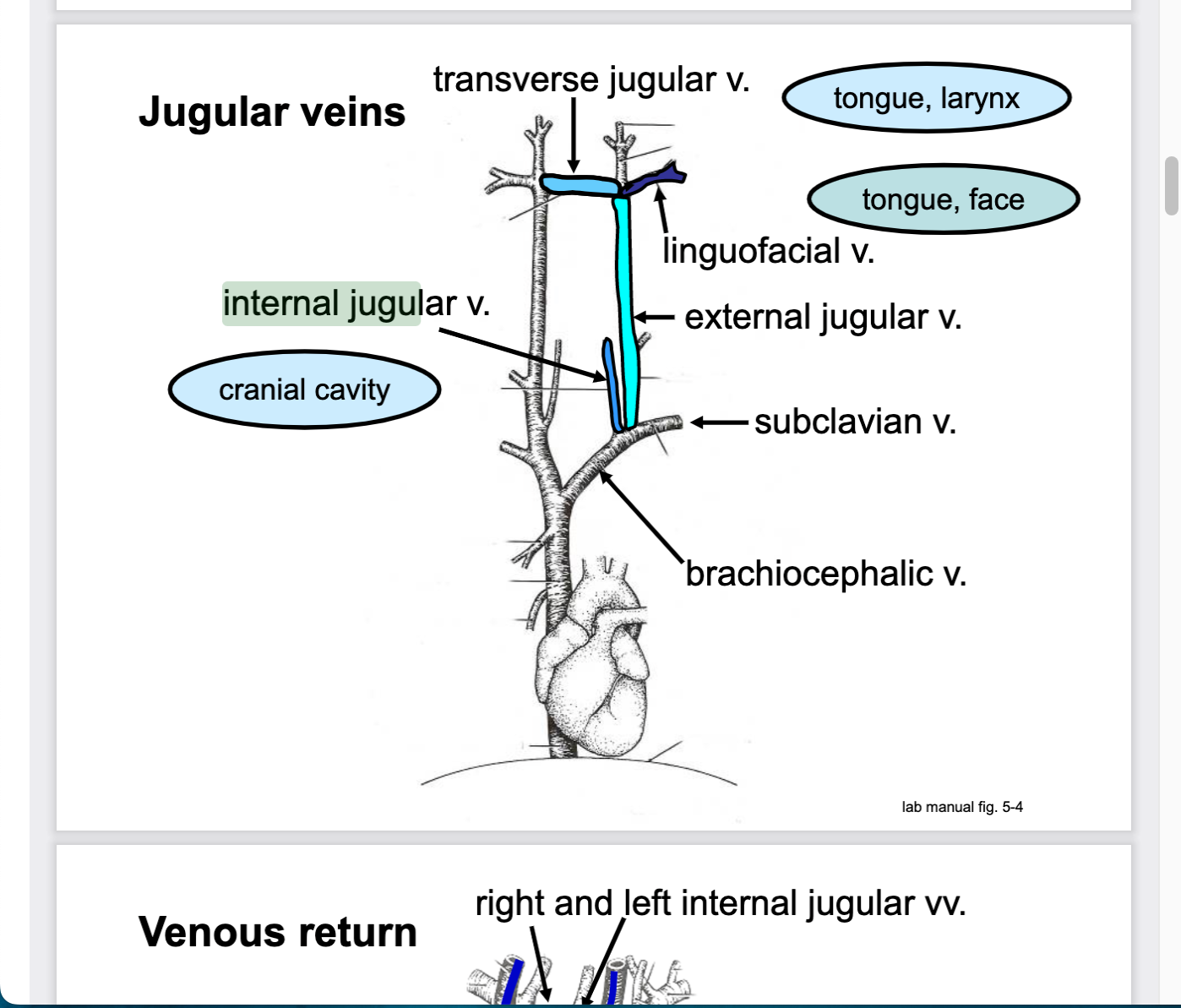
80
New cards
internal jugular vein drains blood from..
head and neck
cranial cavity
cranial cavity
81
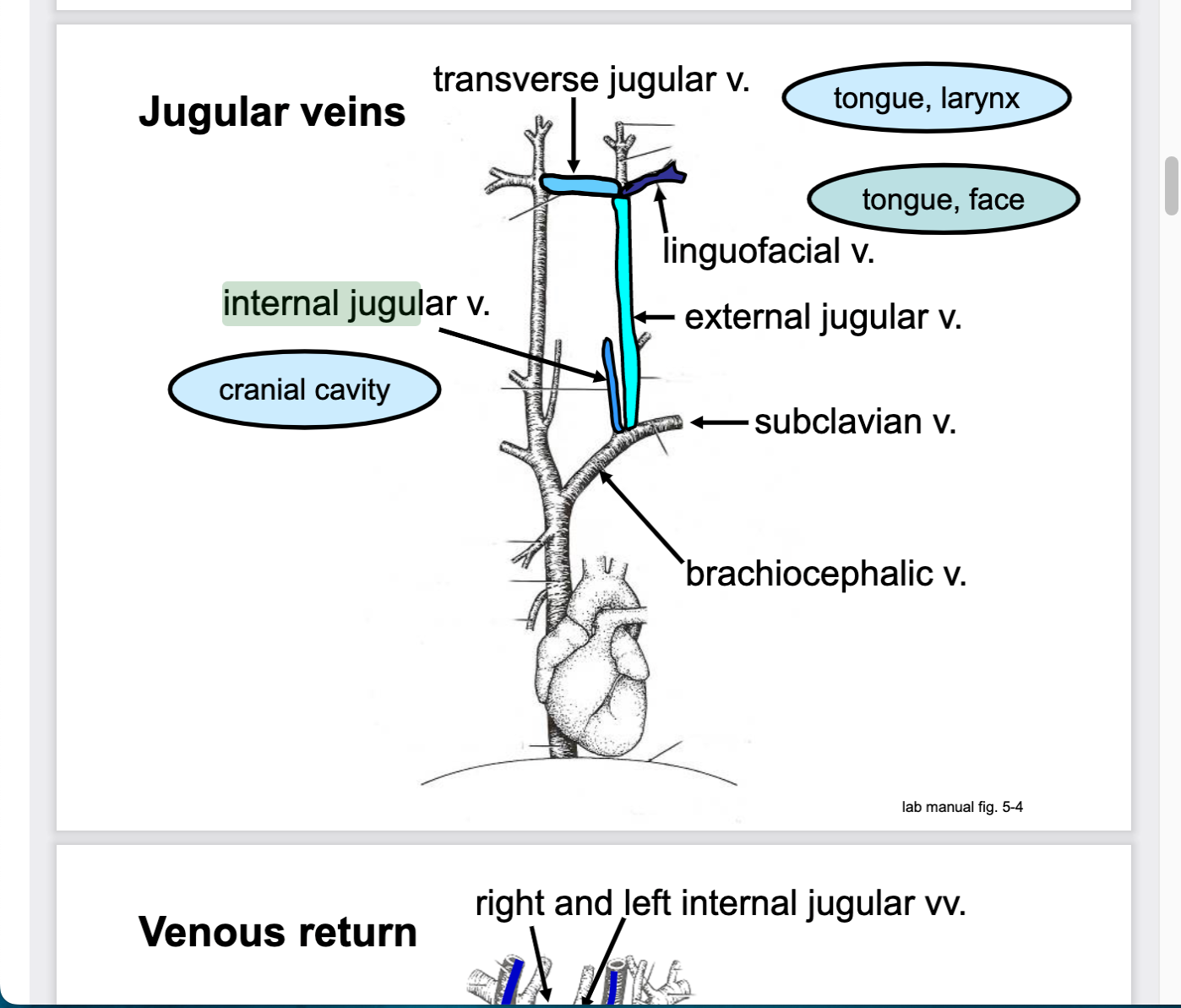
New cards
left and right brachiocephalic veins converge to form what
Left and right brachiocephalic veins
converge to form the cranial vena cava
converge to form the cranial vena cava
82
New cards
abdominal aorta
83
New cards
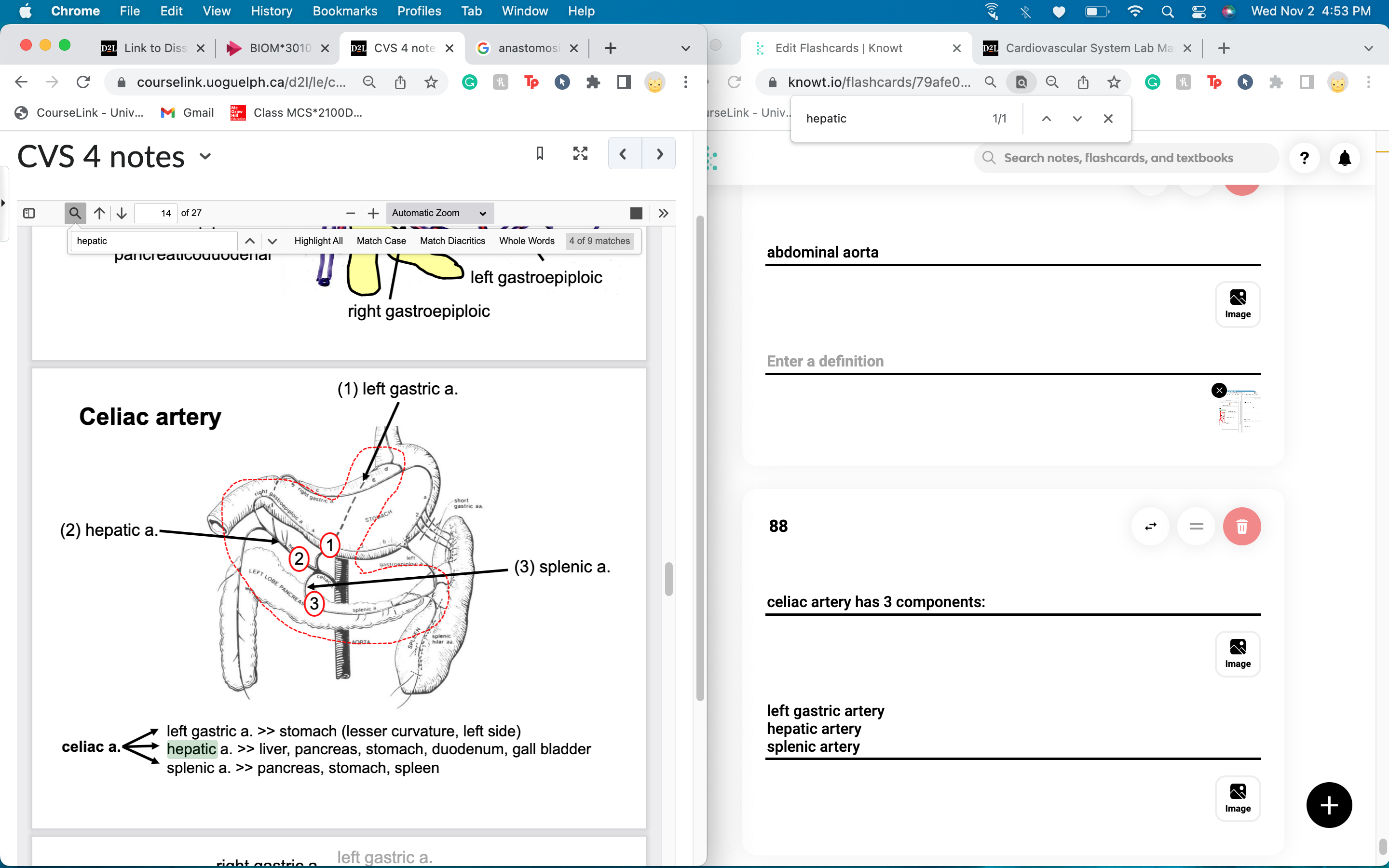
celiac artery has 3 components:
left gastric artery
hepatic artery
splenic artery
hepatic artery
splenic artery
84
New cards
right gastric artery gives blood to
lesser curvature of the stomach
supplies the lesser curvature of the stomach on the right side; extends from the pylorus toward the cardia; anastomoses with the left gastric artery
supplies the lesser curvature of the stomach on the right side; extends from the pylorus toward the cardia; anastomoses with the left gastric artery
85
New cards
splenic artery supplies blood to
pancreas, stomach, spleen
86
New cards
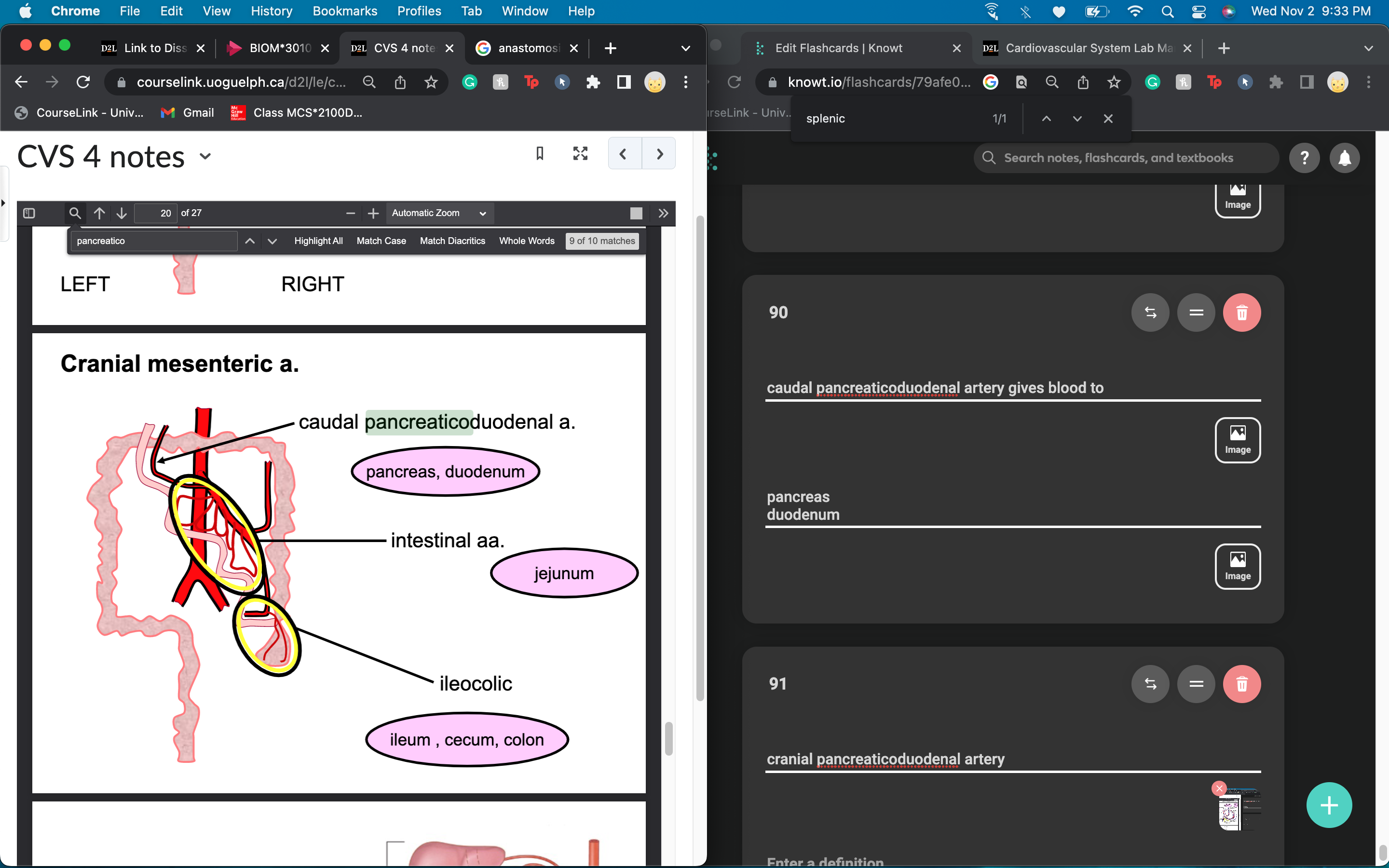
caudal pancreaticoduodenal artery gives blood to
pancreas
duodenum
duodenum
87
New cards
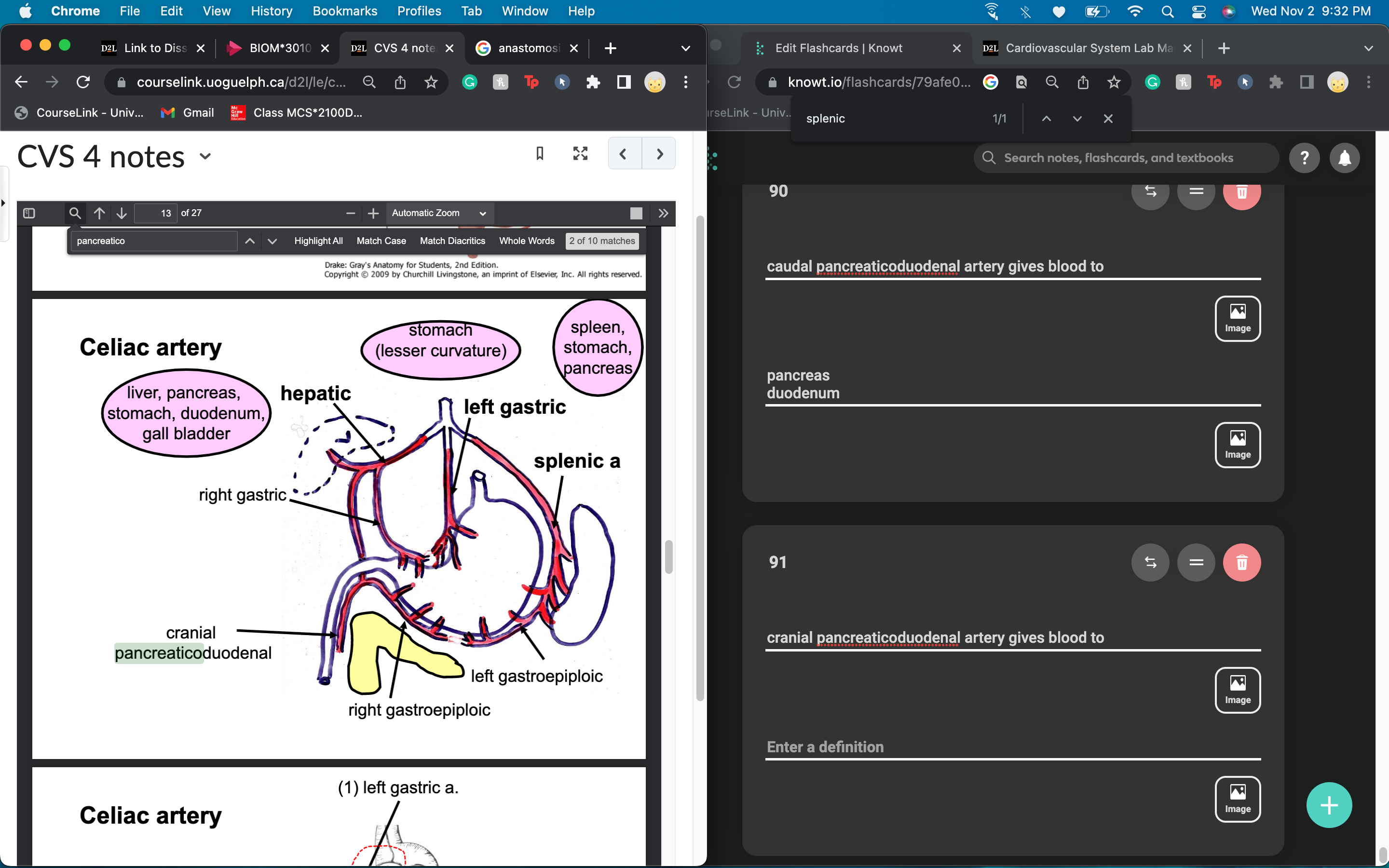
cranial pancreaticoduodenal artery
88
New cards
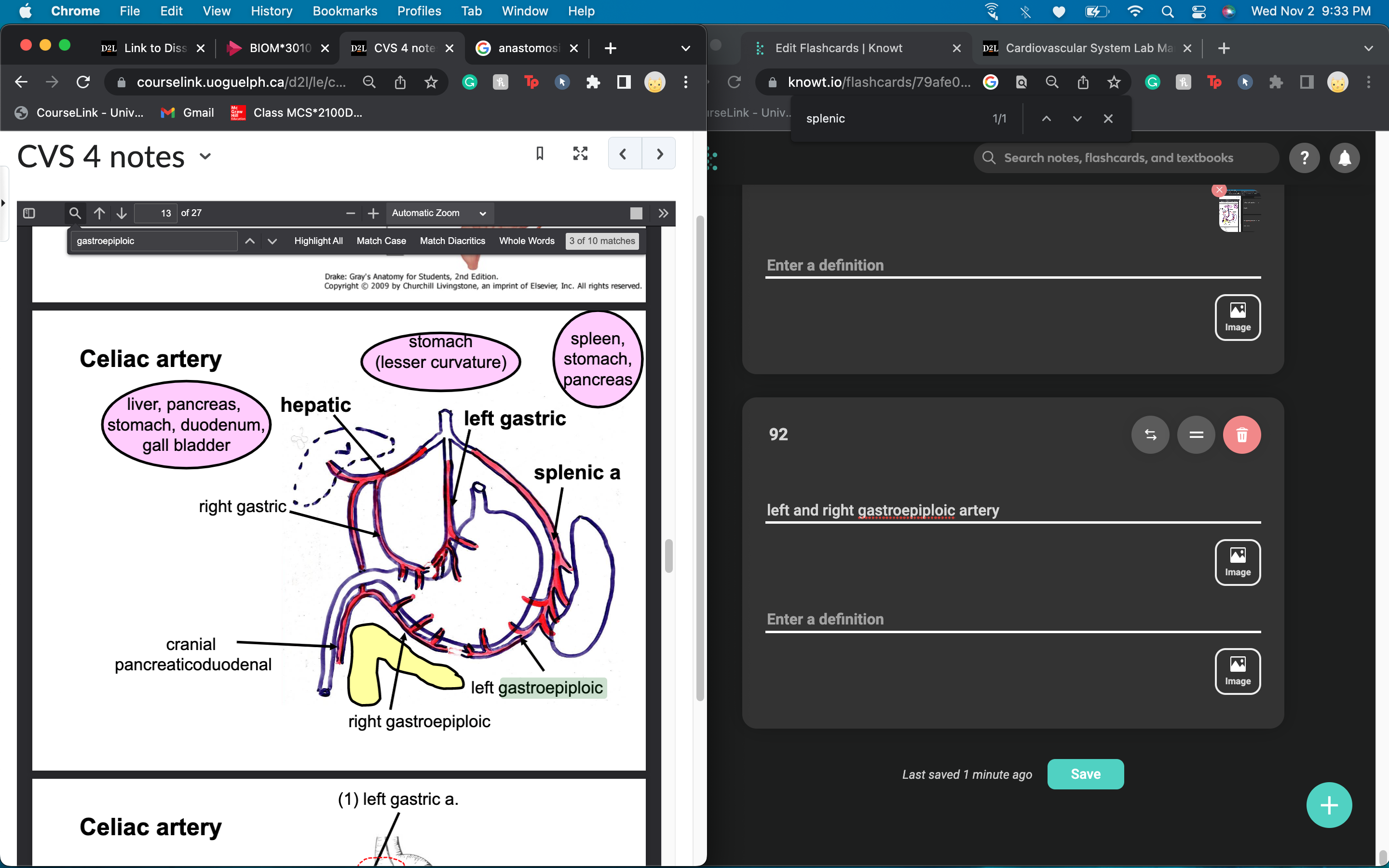
left and right gastroepiploic artery give blood to
greater curvature of the stomach on both sides
89
New cards
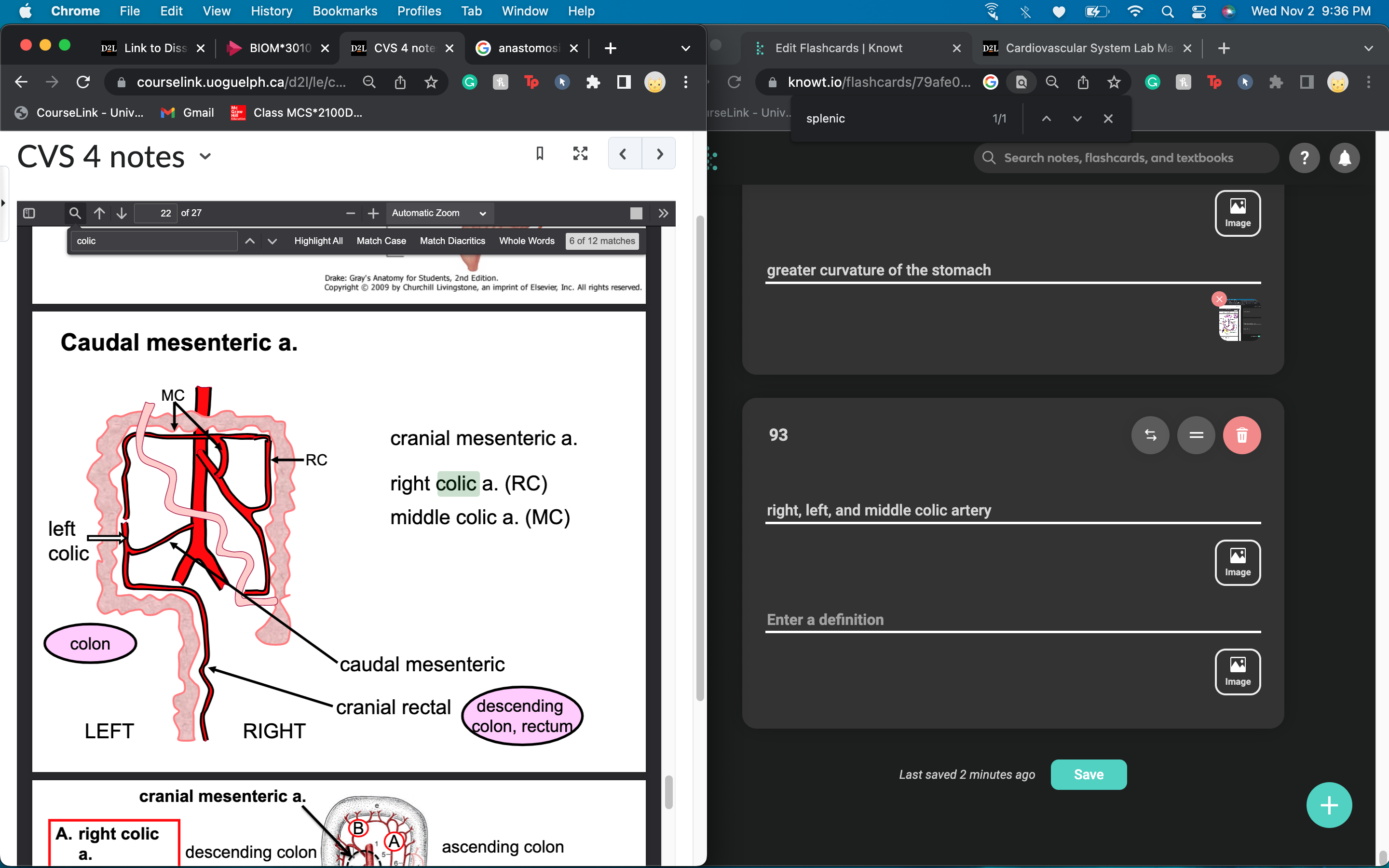
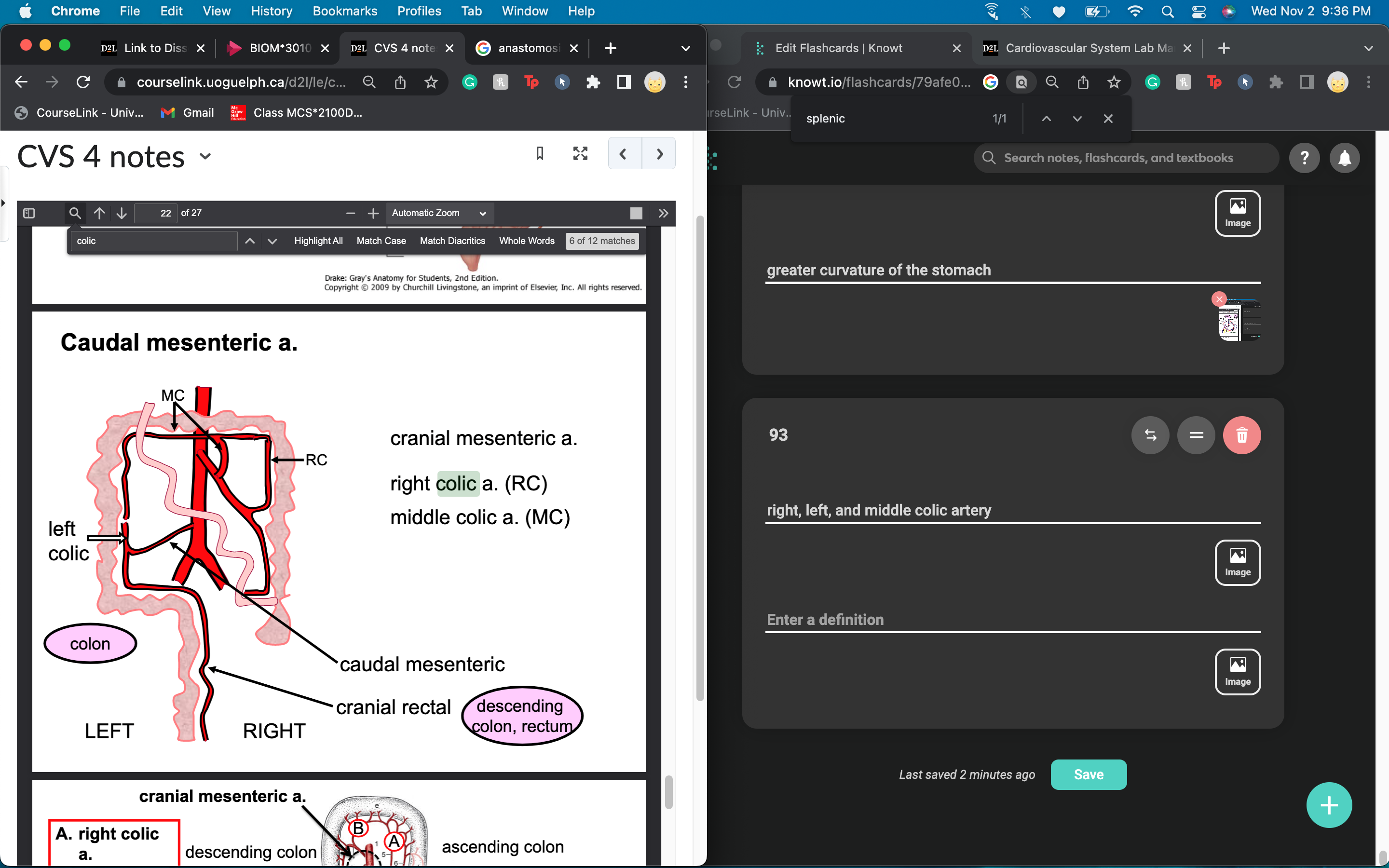
caudal mesenteric artery separates into right, left, and middle colic artery
90
New cards
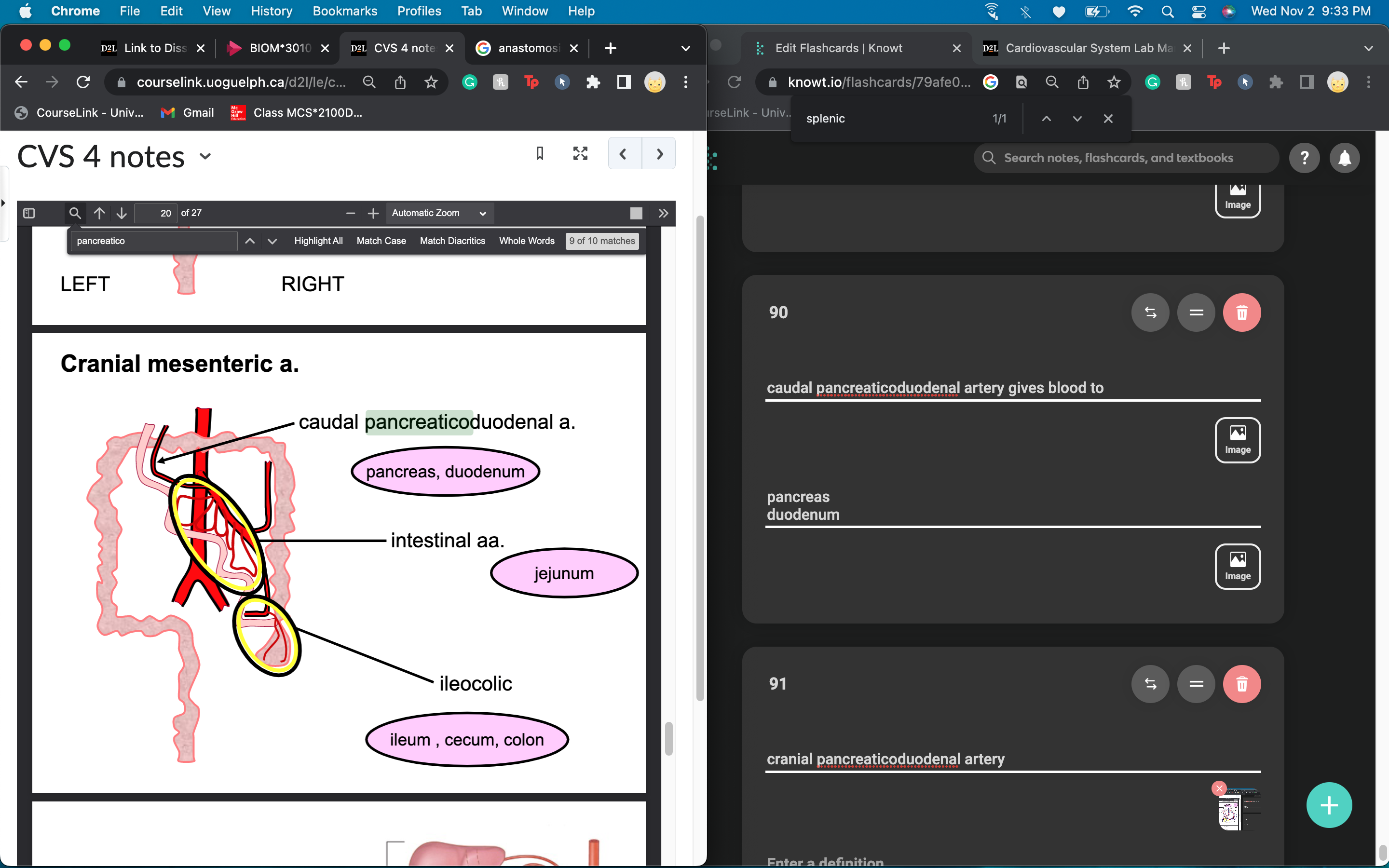
intestinal artery supplies blood to
jejunum
also a bit of ilium
also a bit of ilium
91
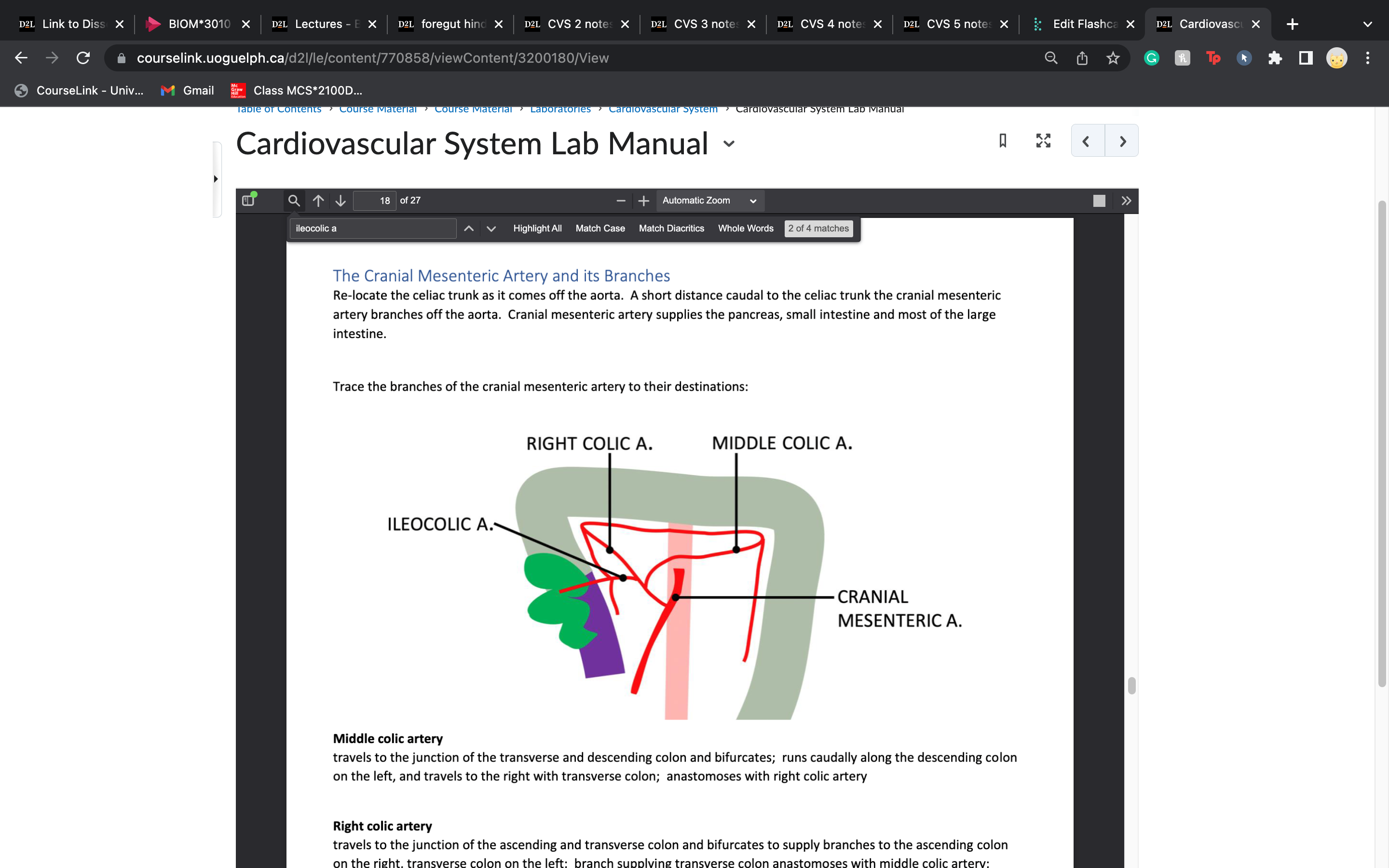
New cards
ileocolic artery supplies blood to
ileum, cecum, and colon
92
New cards
cranial rectal artery gives blood to
desceding colon and rectum
93
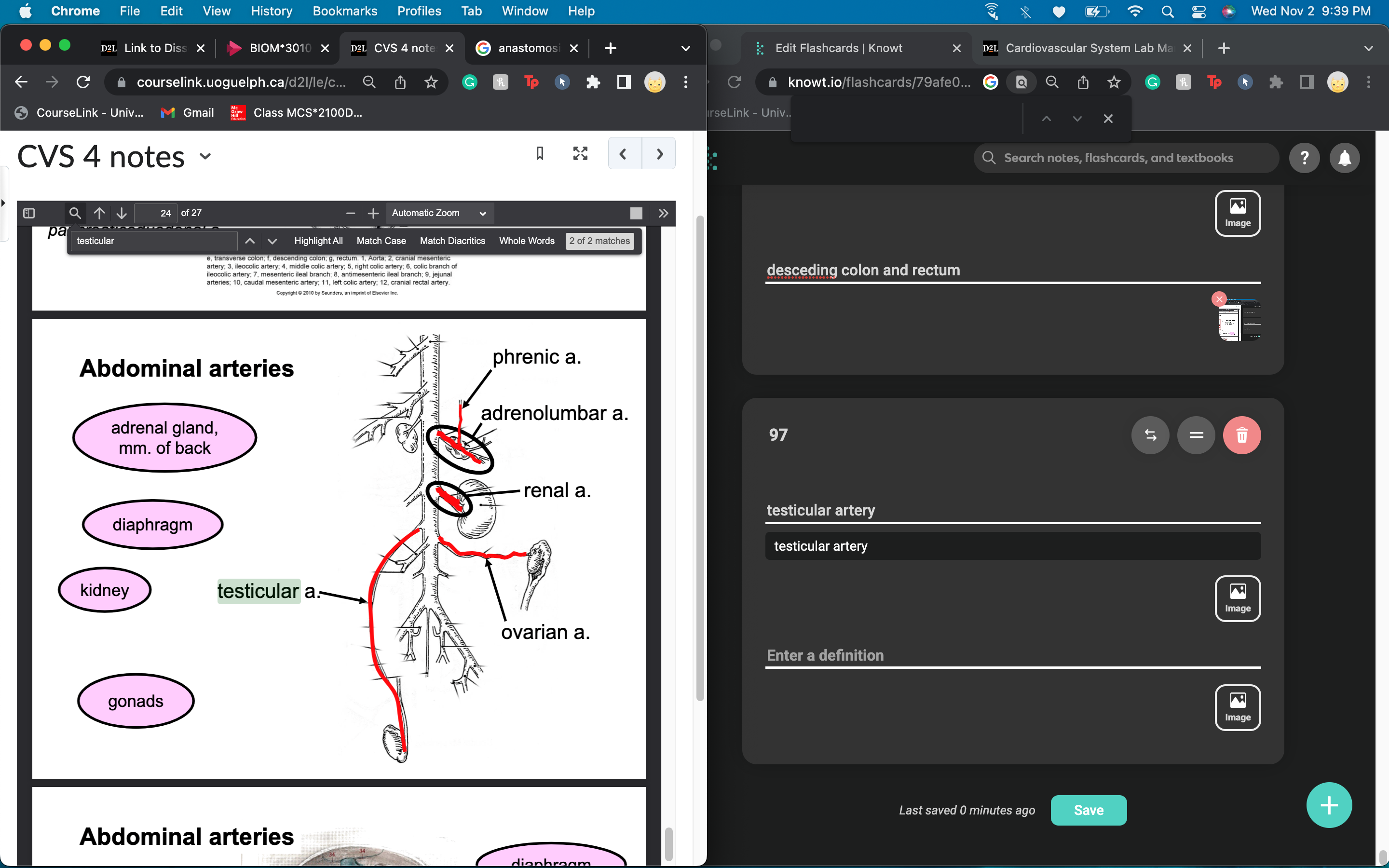
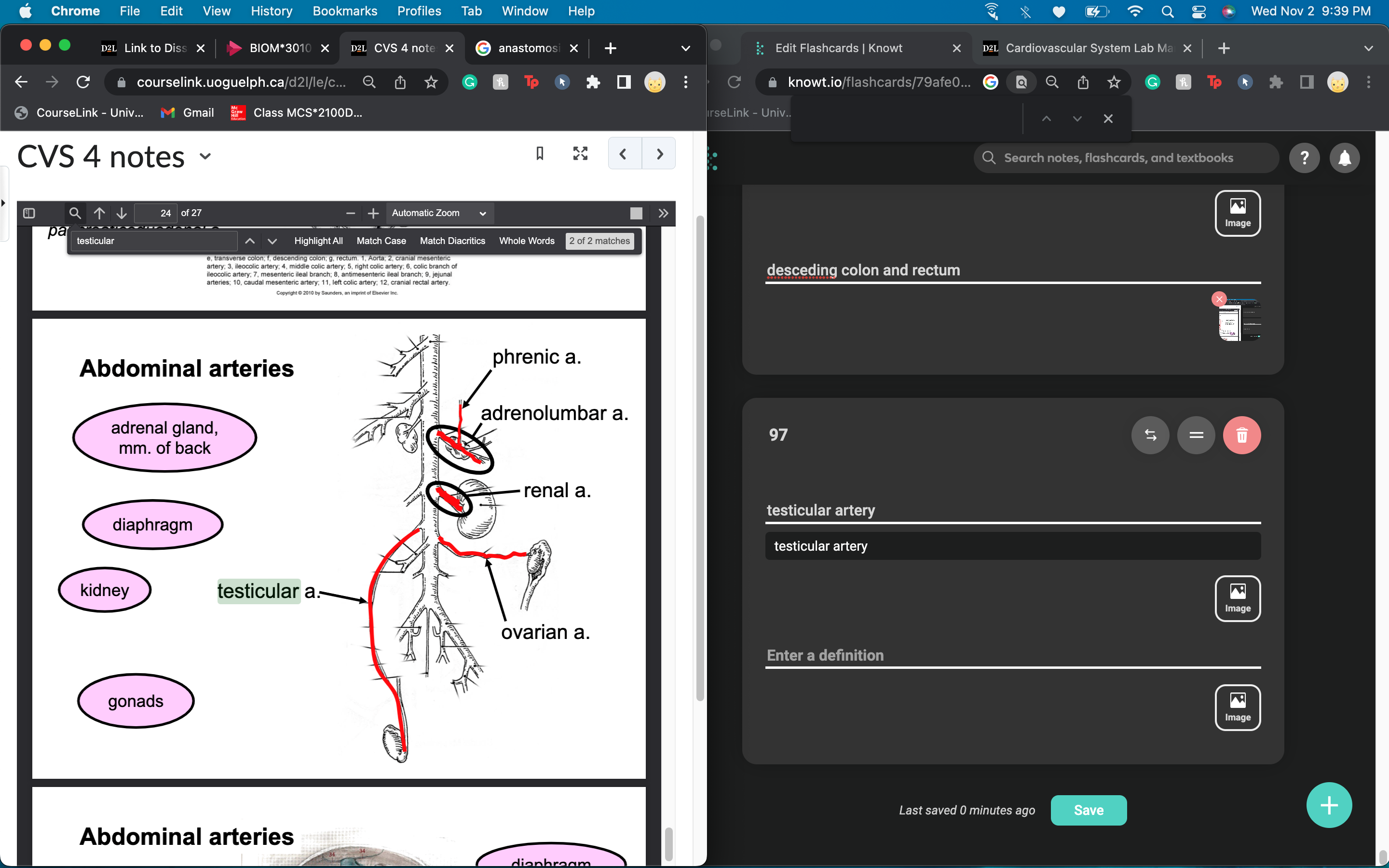
New cards
testicular and ovarian artery
94
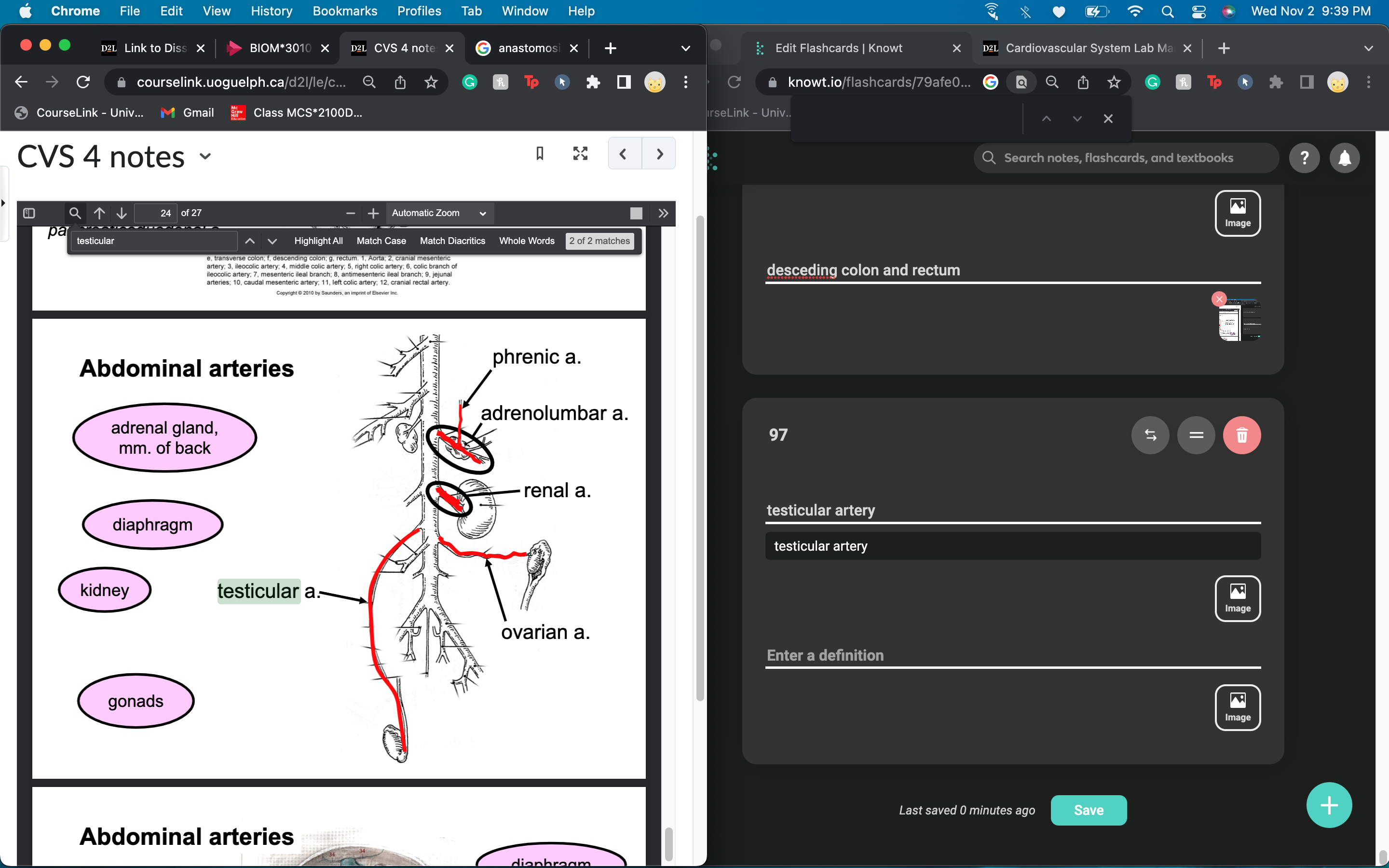
New cards
phrenic artery provides blood to__________ and branches off the _____________
diaphragm
adrenolumbar artery
adrenolumbar artery
95
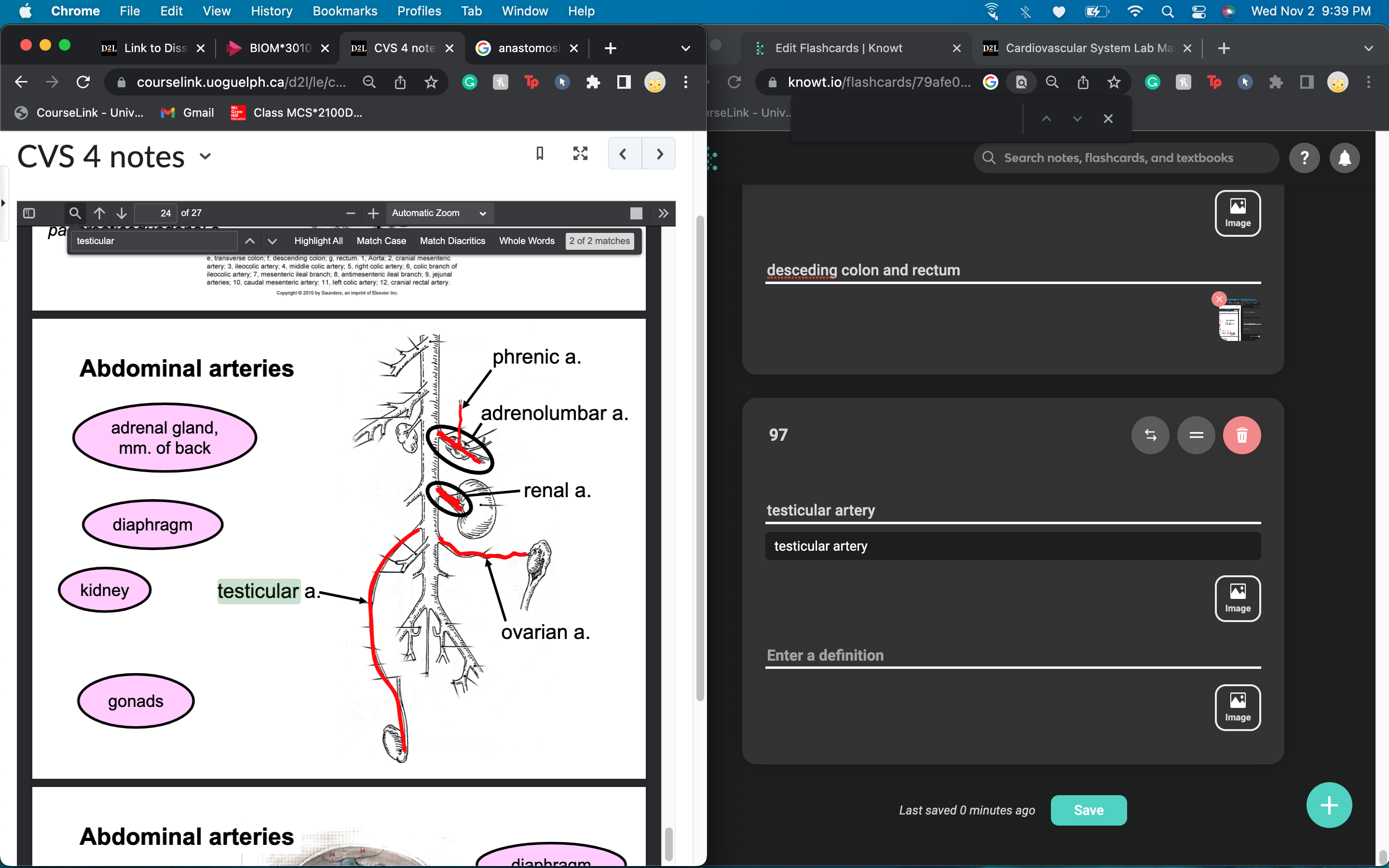
New cards
adrenolumbar artery provides blood to ____________ and _____________
adrenal gland
muscles of the back
muscles of the back
96
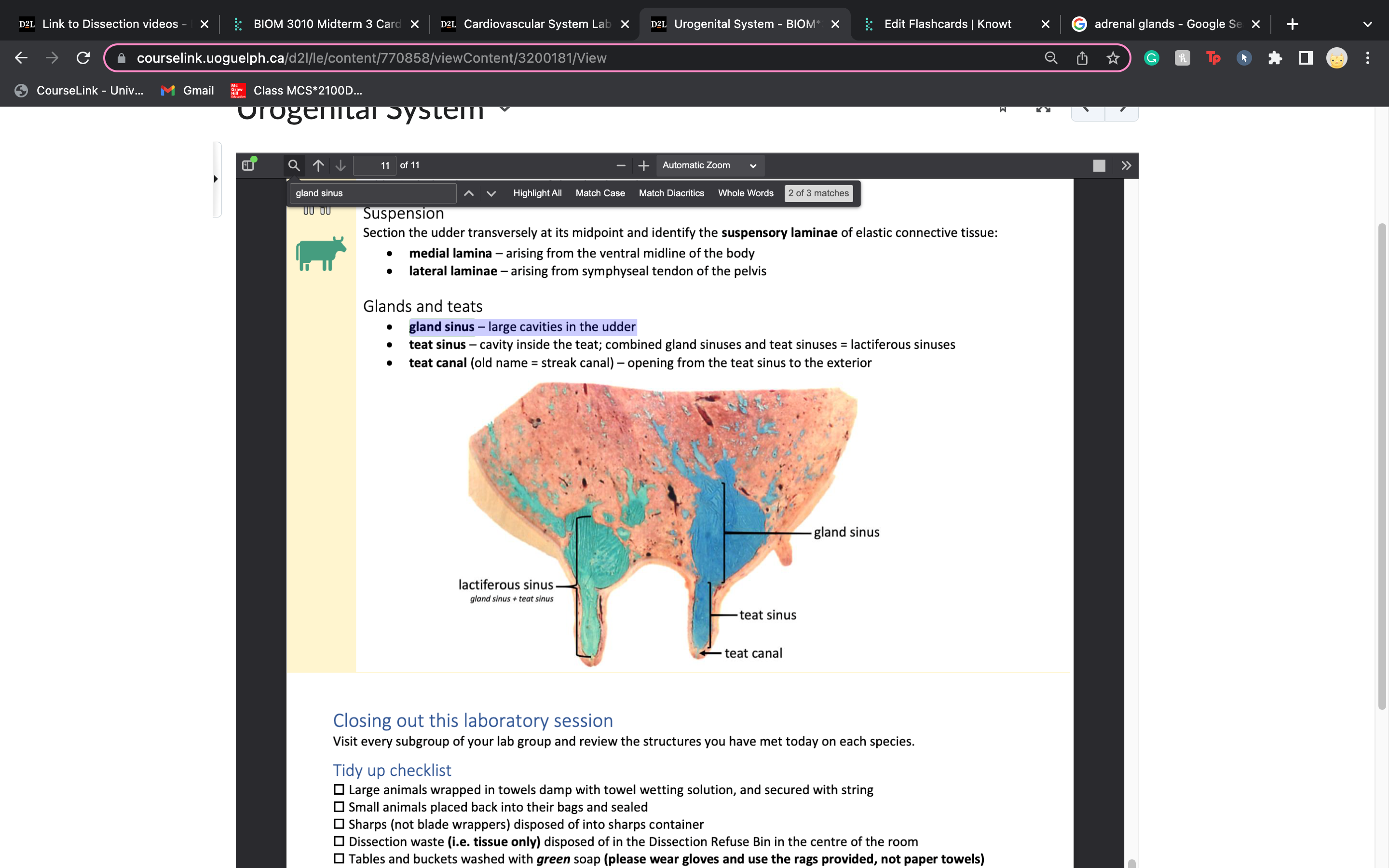
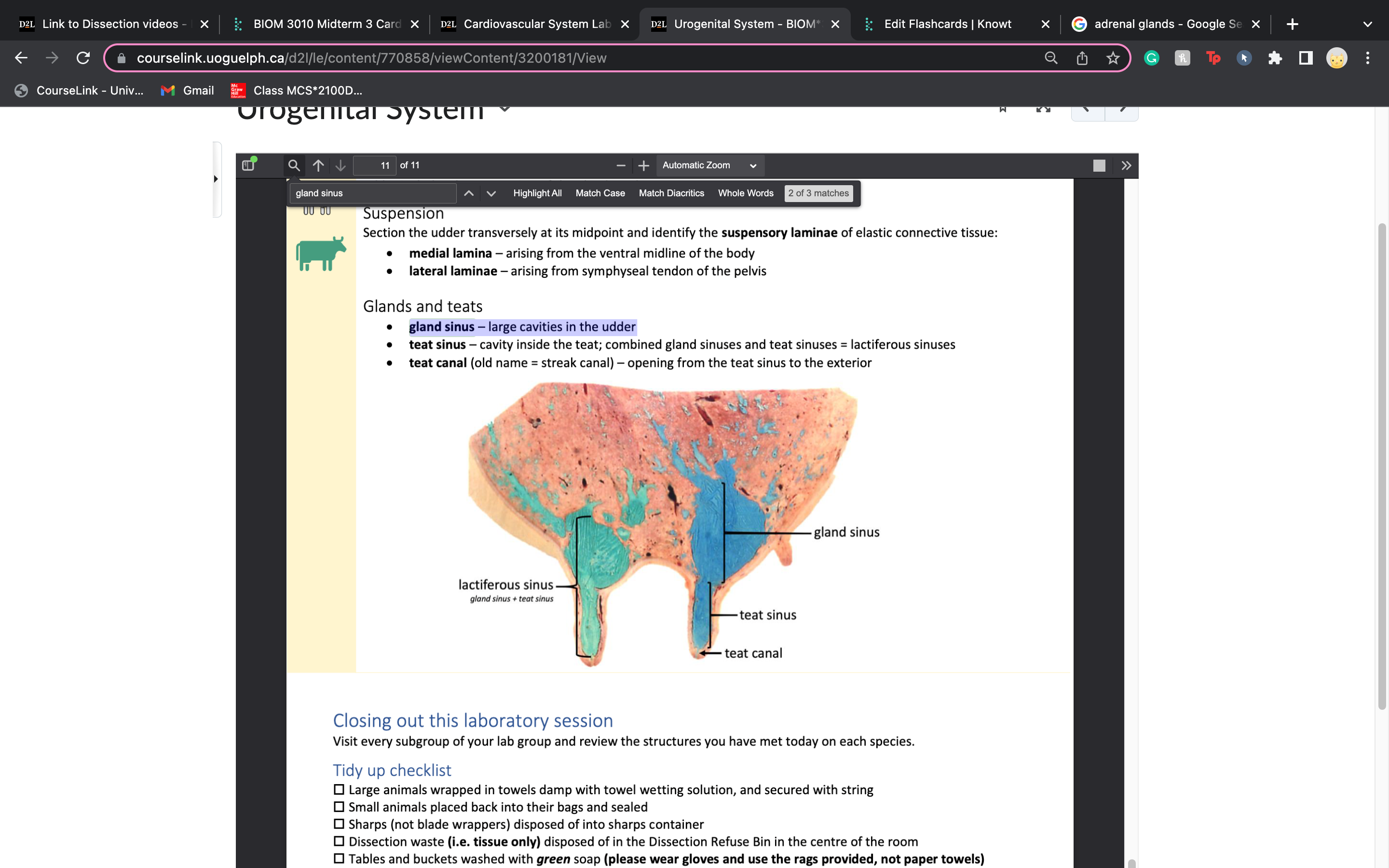
New cards
gland sinus
large cavities in the udder
97
New cards
teat sinus vs teat canal
teat sinus – cavity inside the teat; combined gland sinuses and teat sinuses = lactiferous sinuses
• teat canal (old name = streak canal) – opening from the teat sinus to the exterio
• teat canal (old name = streak canal) – opening from the teat sinus to the exterio
98
New cards
renal artery and vein
99
New cards
external and internal iliac artery
100
New cards
what does the aorta do?
brings oxygenated blood away from the heart,
arching craniodorsally and passing towards the abdomen
arching craniodorsally and passing towards the abdomen