forex
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Foreign exchange rate (forex) definition
Refers to the price of one currency in terms of another currency
Foreign exchange market
Market where foreign currencies are bought and sold
Types of exchange rate systems
Floating
Managed float
Fixed
Floating exchange rate system Definition
The exchange rate of a currency is determined by the market forces (demand and supply of the currency)
The equilibrium market price of one national currency in terms of other currency forms the exchange rate
Reasons for demand in a country (eg. USD) / why people buy USD
Consumers in foreign countries import(bring in) goods and services produced in USA (need USD to buy these)
US owned MNC send their profits back to US
Foreign investors who invest in USA
Foreigners save money with US bank due to attractive exchange rates (convert money to USD)
Currency speculators hold USD as they are optimistic that the USD will rise in value against other currencies
Reasons for why USD is supplied ( sold)
US consumers import (bring in) foreign foods and services from foreign countries (to do so must sell their USD to the other currency)
Foreign owned MNCs in the US send their profits back to their home countries (sell USD)
US investors invest in foreign countries (sell USD )
US resident save money with banks abroad due to more attractive interest rates
Currency speculators sell their USD as they believe it will fall in value against other currencies
What causes the exchange rate to fluctuate
Any changes in demand and supply of domestic currency
The value of floating exchange can either
Appreciate ( domestic currency can exchange for more units of foreign currency )
Depreciate ( domestic currency can exchange for less units of foreign currency)
Appreciation and due to what
A rise in the value of a currency against another currency
Due to : fall in supply of currency and increase in demand for currency
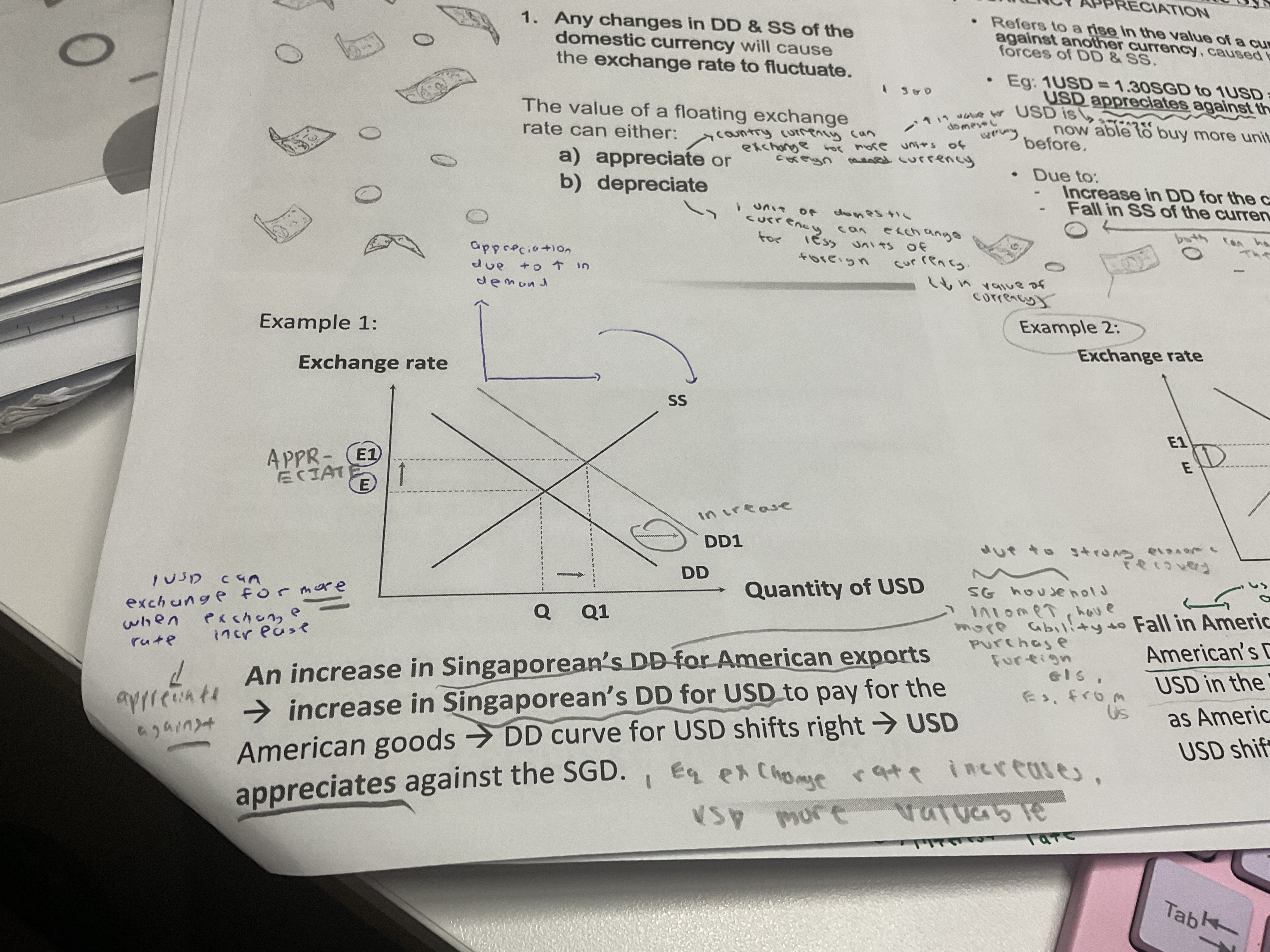
Draw the graph for an increase in demand for USD exports by Singaporeans
An increase in demand for USD causes the demand curve to shift right from D1 to D2 due to an increase in Singaporeans income . Hence, making them more able to purchase goods and services from America. To purchase these goods, they will need to buy USD. This, the exchange rate equilibrium increases from E1 to E2, causing the USD to appreciate against SGD.

Fall in Americans demand for imports from SG
A fall in Americans demand for imports from Singapore (dont want to buy sg goods so they dont sell USD) causes a fall in Americans demand for SGD. this could be due to a fall in income for Americans , making them unable to purchase goods from Singapore . Hence, there is no need to sell their USD for SGD , causing the supply of USD to shift left from S1 to S2. Thus, the exchange rate equilibrium increases from E1 to E2 , causing the USD to appreciate against SGD
Currency depreciation + due to what
Fall in the value of a currency against another currency . Due to fall in demand or increase in supply
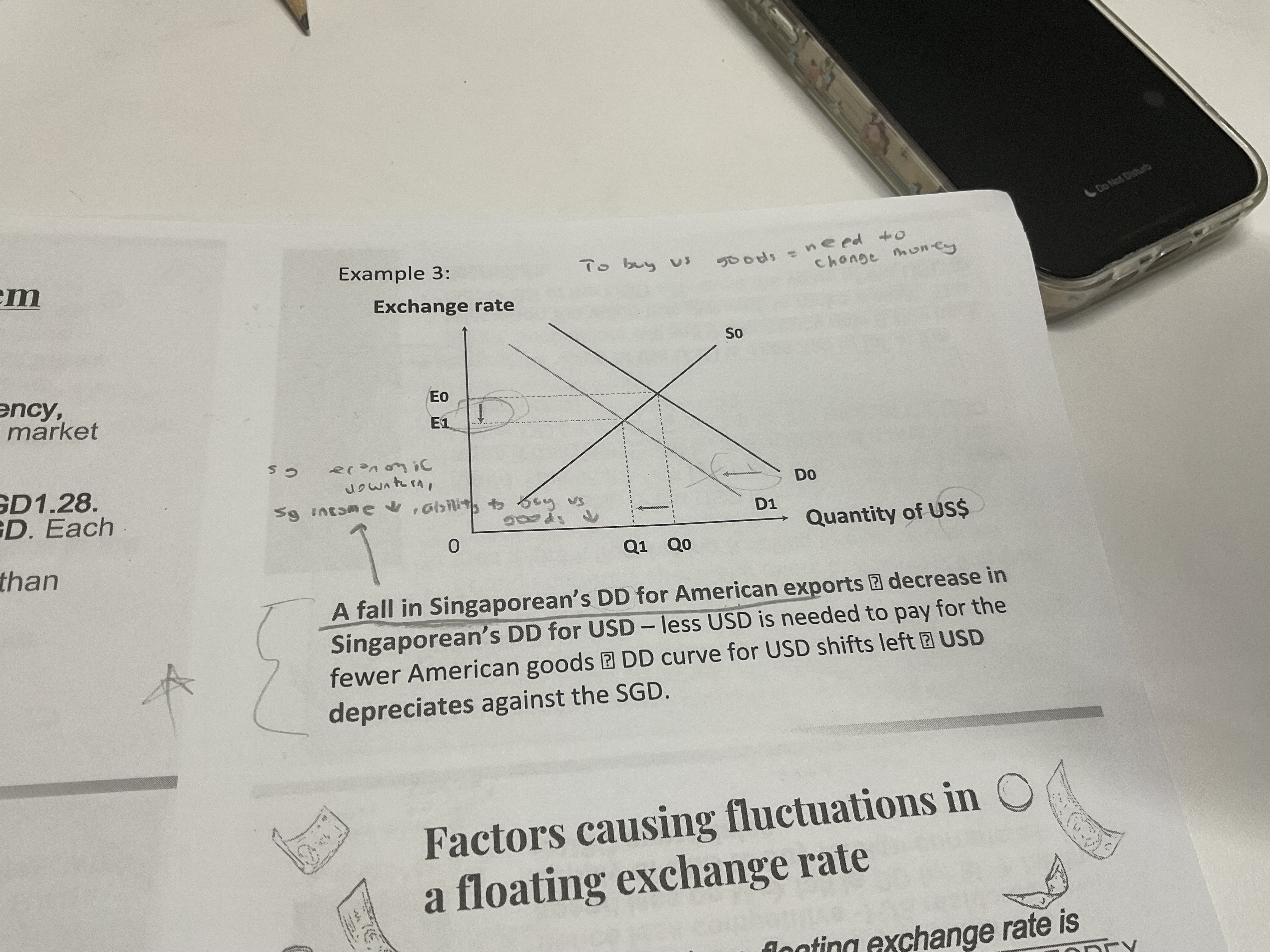
What happens when there is a fall in singaporean’s demand for American exports
A fall in Americans demand for imports from Singapore (dont want to buy sg goods so they dont sell USD) causes a fall in Americans demand for SGD. this could be due to a fall in income for Americans , making them unable to purchase goods from Singapore . Hence, there is no need to sell their USD for SGD , causing the supply of USD to shift left from S1 to S2. Thus, the exchange rate equilibrium increases from E1 to E2 , causing the USD to appreciate against SGD

What happens when there is an increase in American demand for imports from SGD
A rise in America’s demand for imports from SG (want moreSG goods , must exchange money for it), causes an increase in supply of USD from S1 to S2 and making the supply curve shift left. This could be due to (). Hence, more USD is being sold for SGD to purchase more Singapore imports. Thus, the equilibrium exchange rate decreases from E1 to E2 causing USD to depreciate against SGD
Factors causing fluctuations in foreign exchange rate
Change in demand for exports and imports
Inflation
Changes in interest rate
Speculation
Entry or denture of MNCs
when USA raises demand for imports from France what happens
USA sells/supplies more USD to be converted to euros . Euro appreciate , USD depreciate
US decrease demand for imports from France
US sell/ supply less USD to be converted to euros ,USD apppreciate , euro depreciates
French raise demand for US exports
Increase in demand for US goods, USD appreciate , euro depreciate
French reduce demand for US imports
France reduce its demand for USD , USD depreciates , Euro appreciates
Rates of inflation
Inflation means general prices of goods in that economy increases. Hence, countries with lower inflation rates than its trading partners will have exports that are more international competitive , raising demand for its national currency and casing an appreciation In the values of its currency
When inflation in US is relatively lower than other counties what happen
US exports become more competitive , increase in demand for USD to purchase US exports , USD appreciates
Other countries imports are more expensive and hence less competitive , US residents spend less on other countries imports thus supply of USD decreases ( dont sell USD for other currency) , USD appreciates
Changes in interest rate
Higher interest rate = higher rate of return. Country with most attractive interest rate attract more foreign capital, causing its currency to appreciate. Eg, US interest rate is attractive . SG people will sell more SGD for USD to invest in US bank . SGD depreciates against USD. (For short term investments )*
Foreign currency speculator
Refers to a person / firm that tries to profit from buying and selling foreign currency’s
Speculation example (If USd is expected to rise in future)
If USD value is expected to rise in the future, speculators will buy more USD now when it’s cheaper and sell it later when it has risen in value to earn profit. Causing the demand for USD to increase and USD to appreciate
Speculation exmaple (if USD is expected to fall in the future)
Speculators will sell the currency now and buy back later when the value has reduced, making a profit. Higher supply of the USD will cause the value of USD yo depreciate
Entry or departure of MNC
An economy that attracts foreign investments will see an increase in the demand for its currency and an appreciation in the value of its currency ( eg . The economy is USD , Singaporean’s must convert to USD to send money back to their company / family in US)
Effects of currency depreciation
Rise in international competitiveness and improve economic growth (cheaper export = higher demand= rise in export revenue =economic growth)
Rise in international competitiveness may improve balance of trade ( cheaper exports = higher demand = rise in export revenue = fall in import expenditure )
Inflation affects consumers (low income cannot purchase domestic goods must purchase foreign goods )
Inflation affects producers ( increase COP)
Managed floating rate system
‘Dirty float’ . Where a nations central bank may intervene in the FOREX market to help maintain a steady exchange rate
How does the central bank intervene in the forex market
By buying or sellling its own national currency using foreign currency reserves
To prevent its currency value from rising too much , central bank may
To stop appreciation → sell domestic currency and buy foreign currency → causes depreciation.
To prevent the value of its currency from falling too much , central bank may
sell foreign currency reserves to buy their domestic currency to increase demand for it so that domestic currency will appreciate