Memory Part II Exam 3
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
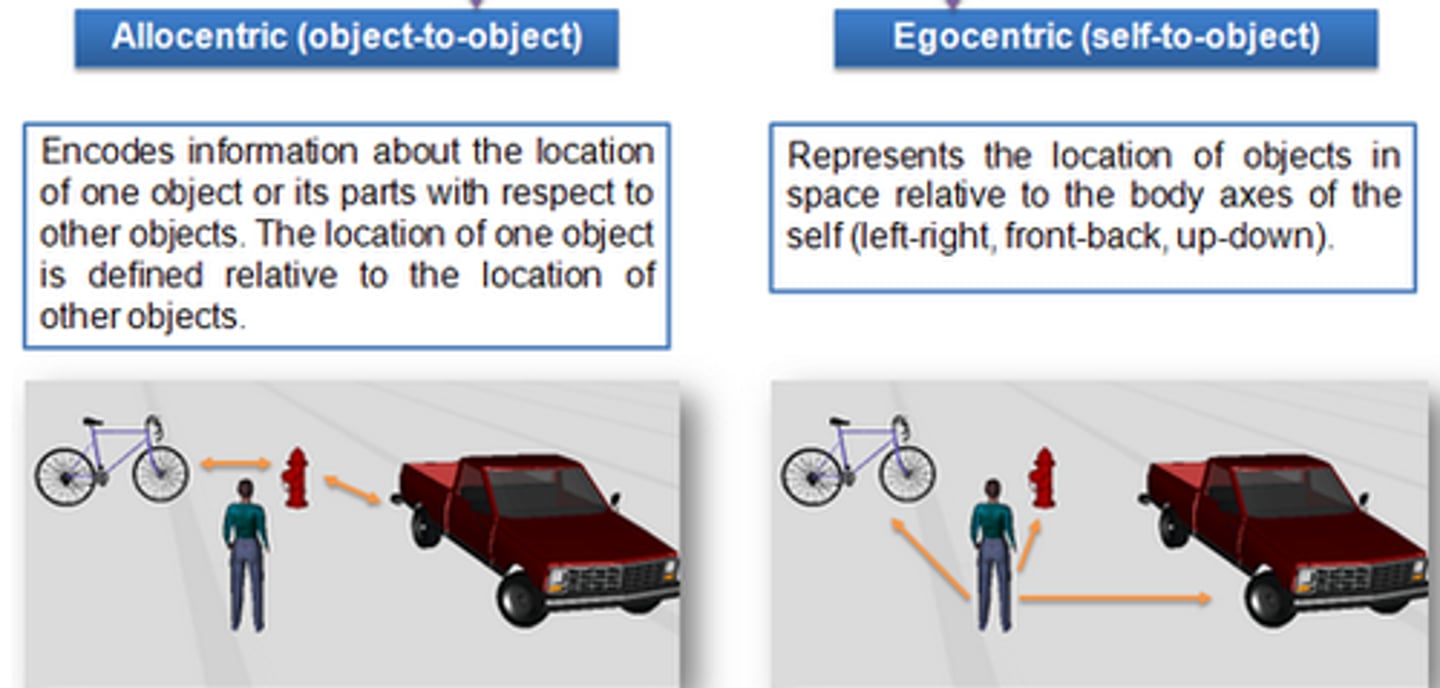
Allocentric
Making navigation choices based on the relative position of features of the environment rather than learning about actions/objects relative to their perspective.
Salient
Most noticeable or important features.

Semantic/Episodic/Explicit Memories
Processed through a network that includes your frontal lobes and hippocampus.

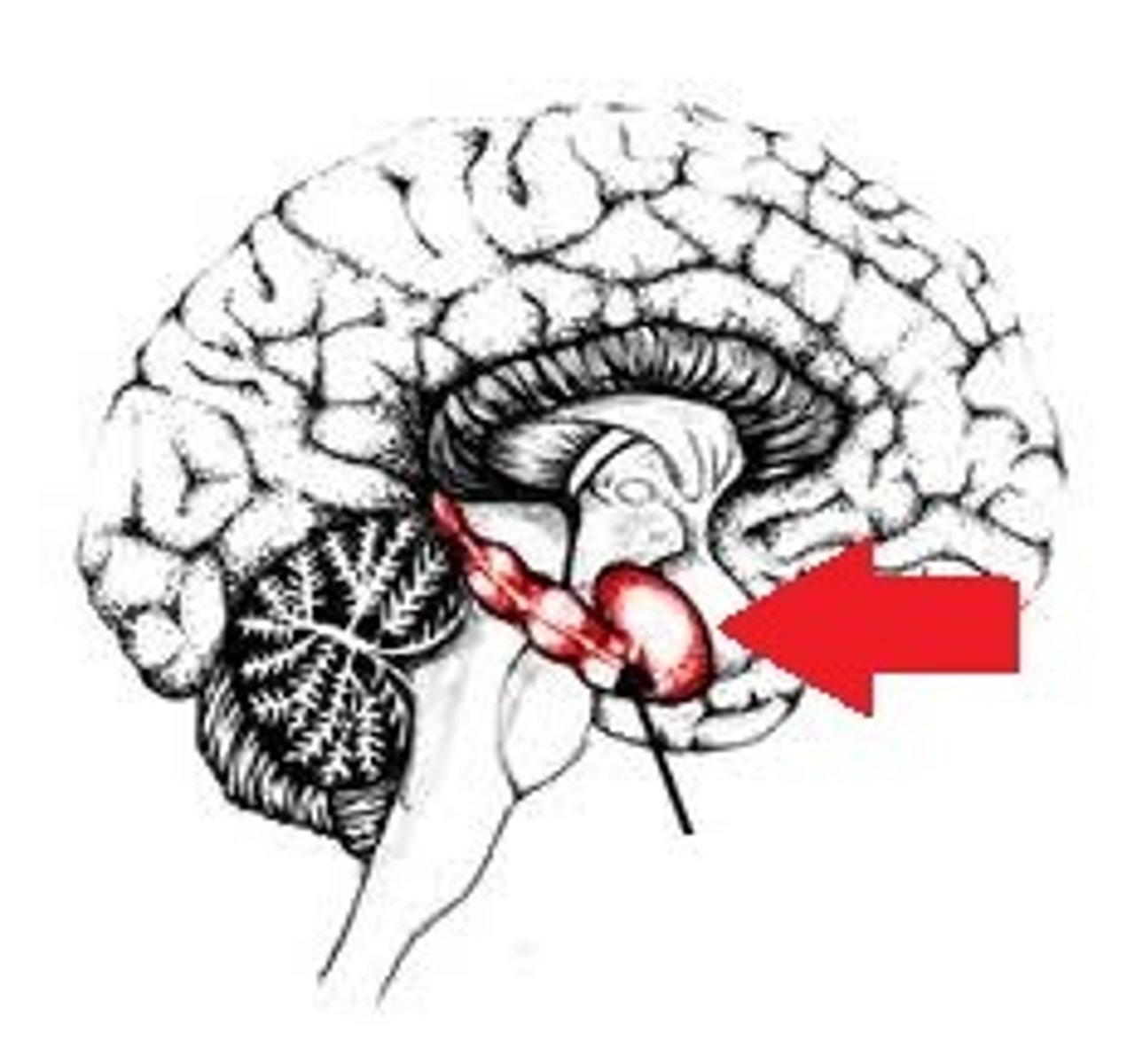
Hippocampus
One of the last brain structures to mature; Active as the brain forms explicit memories, holds elements of a memory that allow it to be recalled.
Memory Consolidation
Process of storing memories; Memories migrate to the cortex for storage; Supported by sleep.

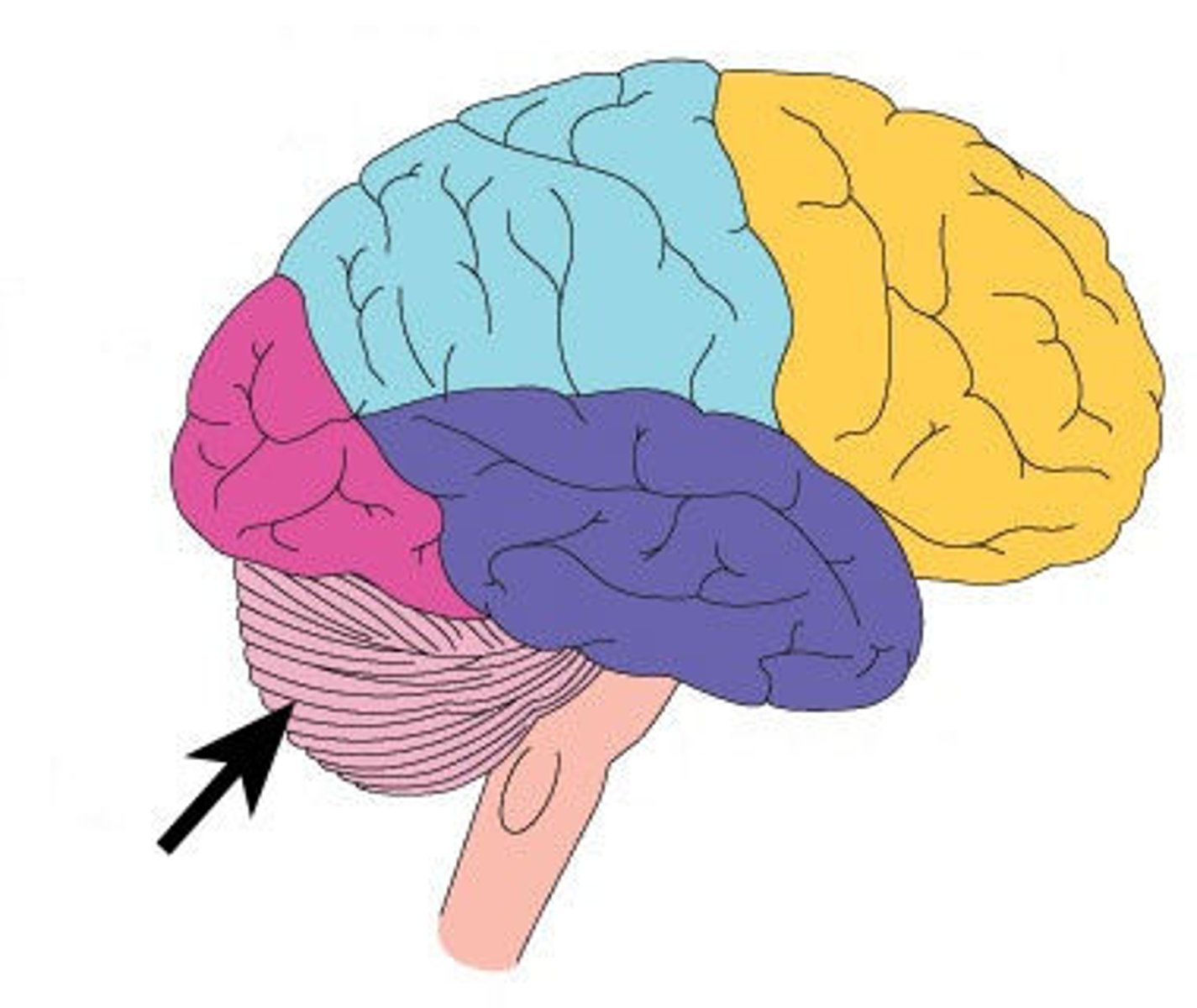
Cerebellum
Important for forming and storing implicit memories created by classical conditioning.
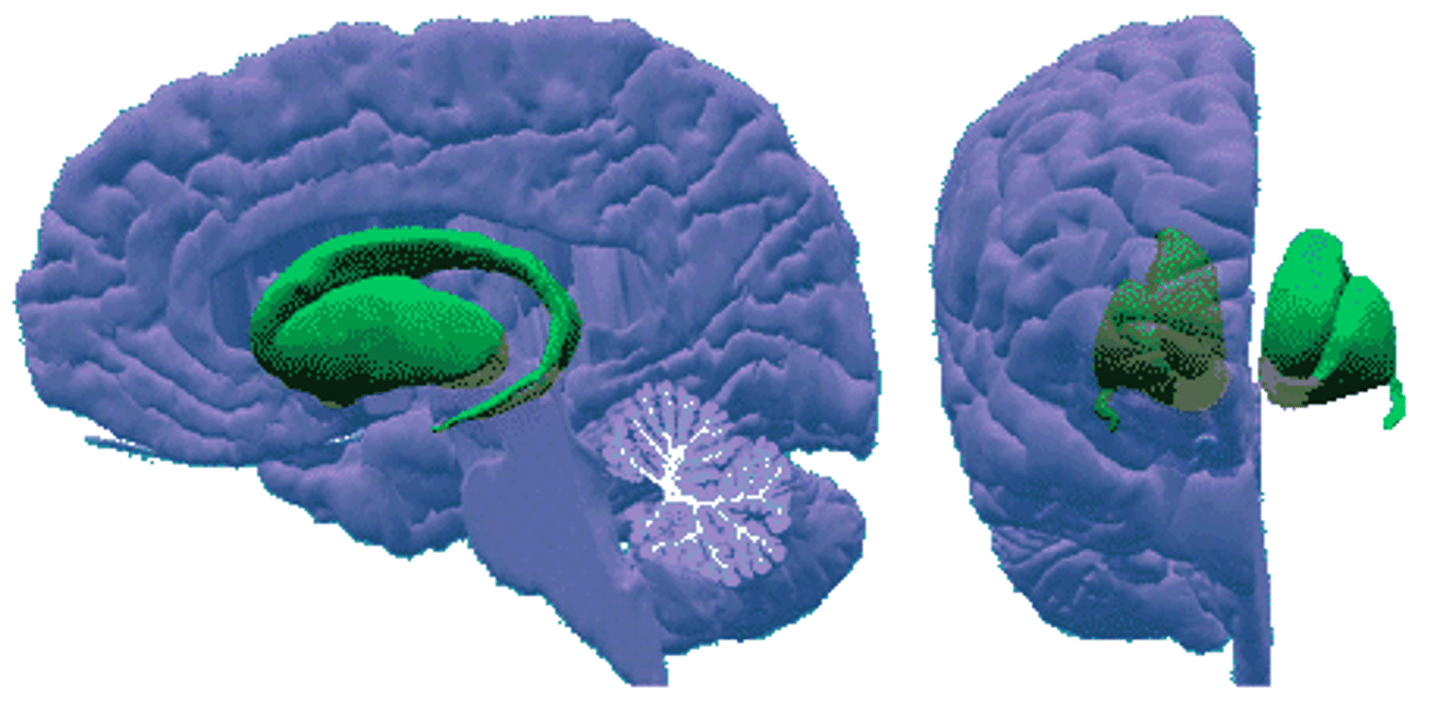
Basal Ganglia
Involved in motor movement and help form procedural memories for skills.
Forgetting
Fail to encode memory, fail to retrieve it, misremember memory, remember false things.

Hyperthymesia
Highly superior autobiographical memory can interfere with life; Enlarged brain areas and increased brain activity to memory centers.

Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new memories.

Retrograde Amnesia
Inability to remember information from one's past.

Storage Decay
Physical changes in the brain that cause the gradual loss of memory.

Proactive
Older memories make it more difficult to remember new information.
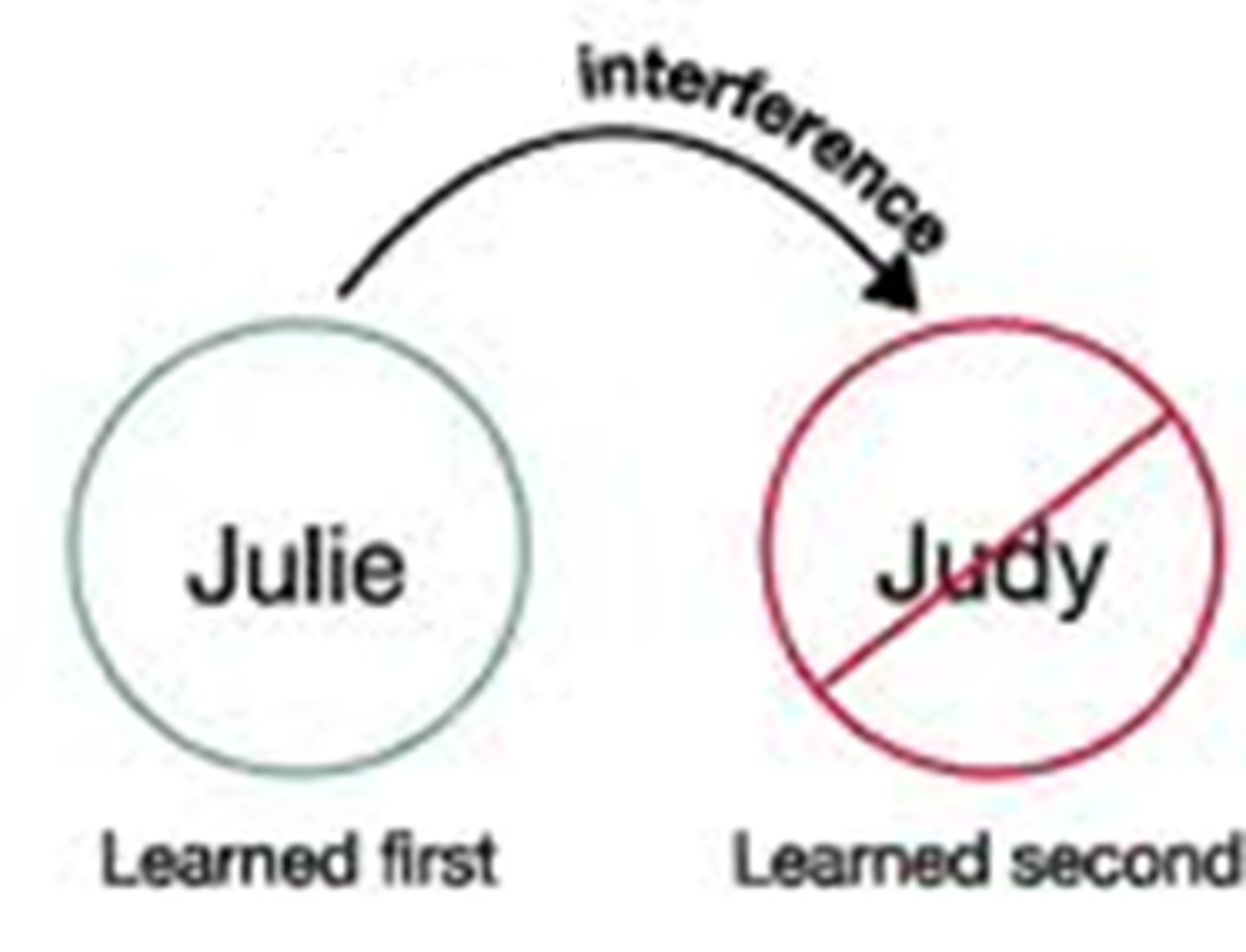
Retroactive
New learning disrupts memory for older information.
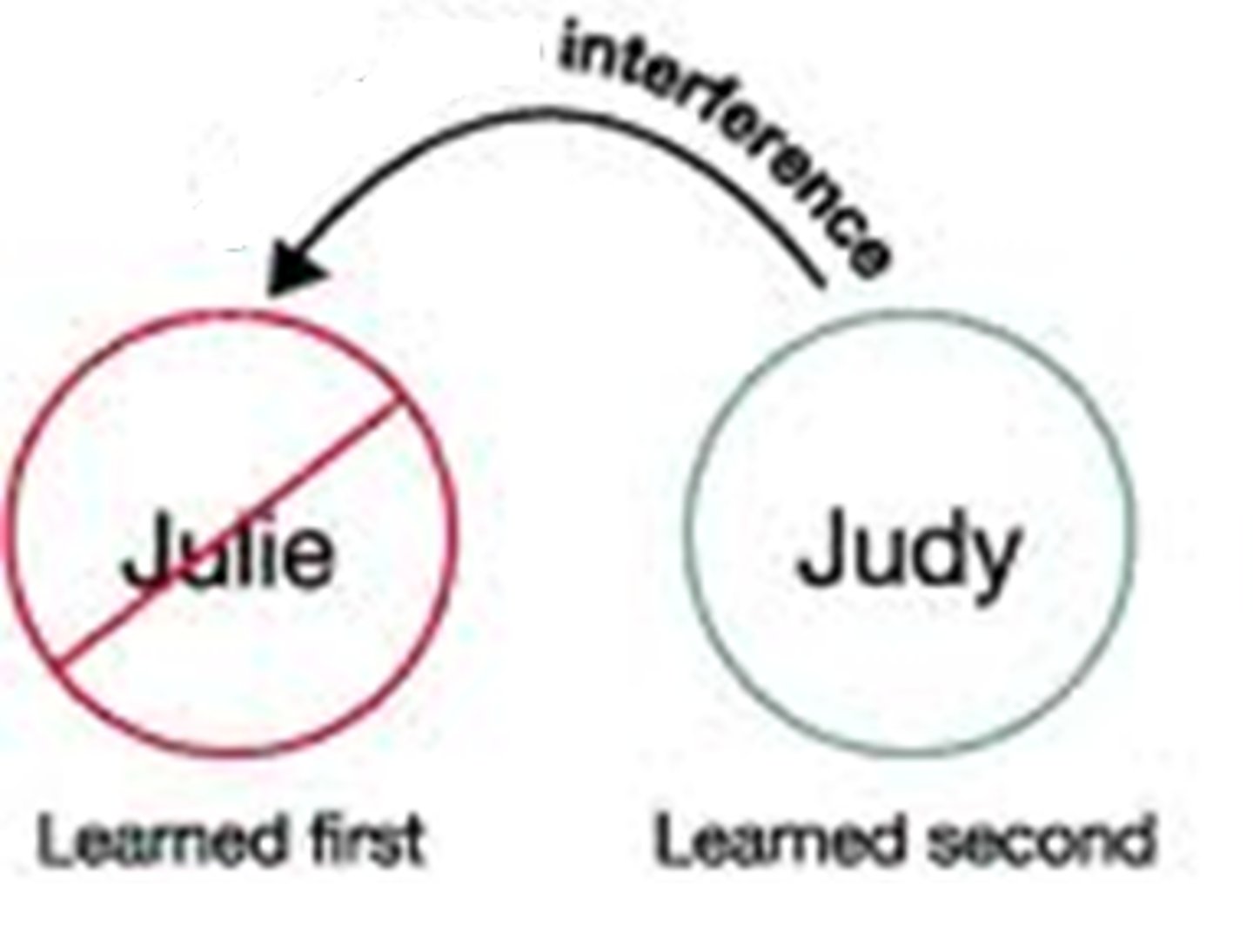
Positive Transfer
Previously learned information facilitates learning of new information.

Freud
Repressed memories protect a person's self concept and minimize anxiety; can still be retrieved later.

Reconsolidation
Stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again.

Source Amnesia
Faulty memory for how, when, or where information was learned or imagined.

Stephen Ceci and Maggie Bruck
Studied effect of suggestive interviewing techniques, showing that preschoolers produced false stories when asked leading questions.
