C3.1 Integration of Body Systems
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
kms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
system hierarchy of organisms (5)
specialized cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
variety of cells in tissues (2)
may contain only 1 type of spec. cells or multiple spec. cells
eg. AT1 and AT2 cells in lung epithelium
human body systems (11)
digestive
integumentary
nervous
reproductive
skeletal
lymphatic
muscular
circulatory
endocrine
gas exchange
urinary
diffs btwn hormonal and nervous signalling (5 counting both types)
hormonal | nervous | |
type of signal | chemical | electrical |
transmission | bloodstream | neurons |
response speed/length | slow, long lasting | VERY fast, short term |
destination of signal | widespread | focused |
effectors | target cells (tissues) | muscles/glands |
types of hormone responses (5)
growth + dvlpmt
reproduction
metabolic rate
homeostasis (glucose reg)
mood, stress, thirst, sleep, horny, etc
types of nervous responses
muscle contraction (striated, smooth, cardiac)
gland responses
exocrine (eg. sweat)
endocrine (eg. adrenaline)
role of brain as an organ
central integrating organ connecting all life processes
receives info from sensory organs
sends signals to muscles or glands to carry out responses
anatomy of spinal cord (5)
white matter myelinated
grey matter not myelinated
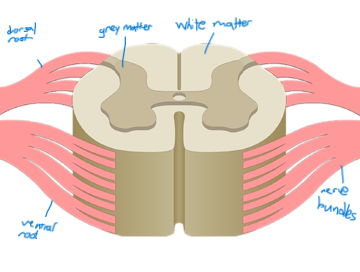
purpose of each part of spinal column (4)
white matter: carry impulses to/from brain
grey matter: unconscious processes and reflexes (faster than going up to brain first)
dorsal root: contains axons of sensory neurons
ventral root: contains axons of motor neurons
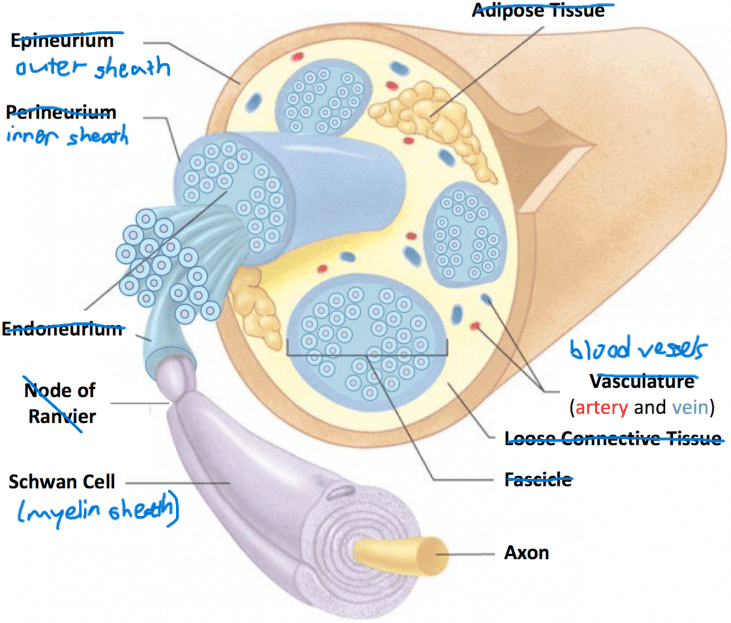
nerve anatomy (5+1)
most nerves contain nerve fibres of both sensory and motor neurons but some only contain 1 or the other
pathway of signals in grey matter (3)
neurons bring info to grey matter from brain and sense organs
motor neurons convey signals from grey matter to muscles and glands
interneurons pass impulses via synapses btwn neurons in grey matter
unconscious vs conscious processes
unconscious | conscious |
can happen when asleep | only happen when awake |
involuntary | voluntary |
controlled by brain and spinal cord | controlled by cerebral hemispheres of brain |
glands and smooth muscle controlled involuntarily | striated muscle controlled voluntarily |
eg. peristalsis in intestine | eg. chewing |
types of neurons relating to sense (5)
receptor cells: detect changes in phsyical envr
stretch receptors: sense state of contraction in muscle
chemoreceptor: monitors chemicals in blood
sensory neurons: transfers impulses from receptors to central nervous system
interneurons: connectors btwn sensory and motor neurons
pathway of sensory neurons (3)
sensory neuron axons enter either spinal cord or brain
brain receives signals from main sense organs in the head (eyes, ears, nose, tongue)
sensory inputs to brain received by specialized areas in cerebral hemispheres eg. visual cortex receiving info from rod and cone cells in eyes
pathway of control of muscles (3+1)
motor cortex sends nerve impulses to any striated muscle
striated muscle attached to bone can move
equals ctrl of posture + locomotion
(extra) grey matter in cerebral hemispheres contains many motor neurons
reflex arc (2)
rapid involuntary response to a specific stimulus
signals pass thru the smallest # of neurons = fast and advantageous
where do reflex arcs go
spinal cord or brain synapses (bc fast)
pain reflex arc (6)
pain stimulus
sensory receptors detect sitmulus and generate impulse
sensory neuron conducts signal to CNS
impulse is sent thru interneurons that send it to the brain
brain sends impulse to motor neurons, which conduct it to the effector
effector muscle produces a response (flinch away)
parts of cerebrum (6)
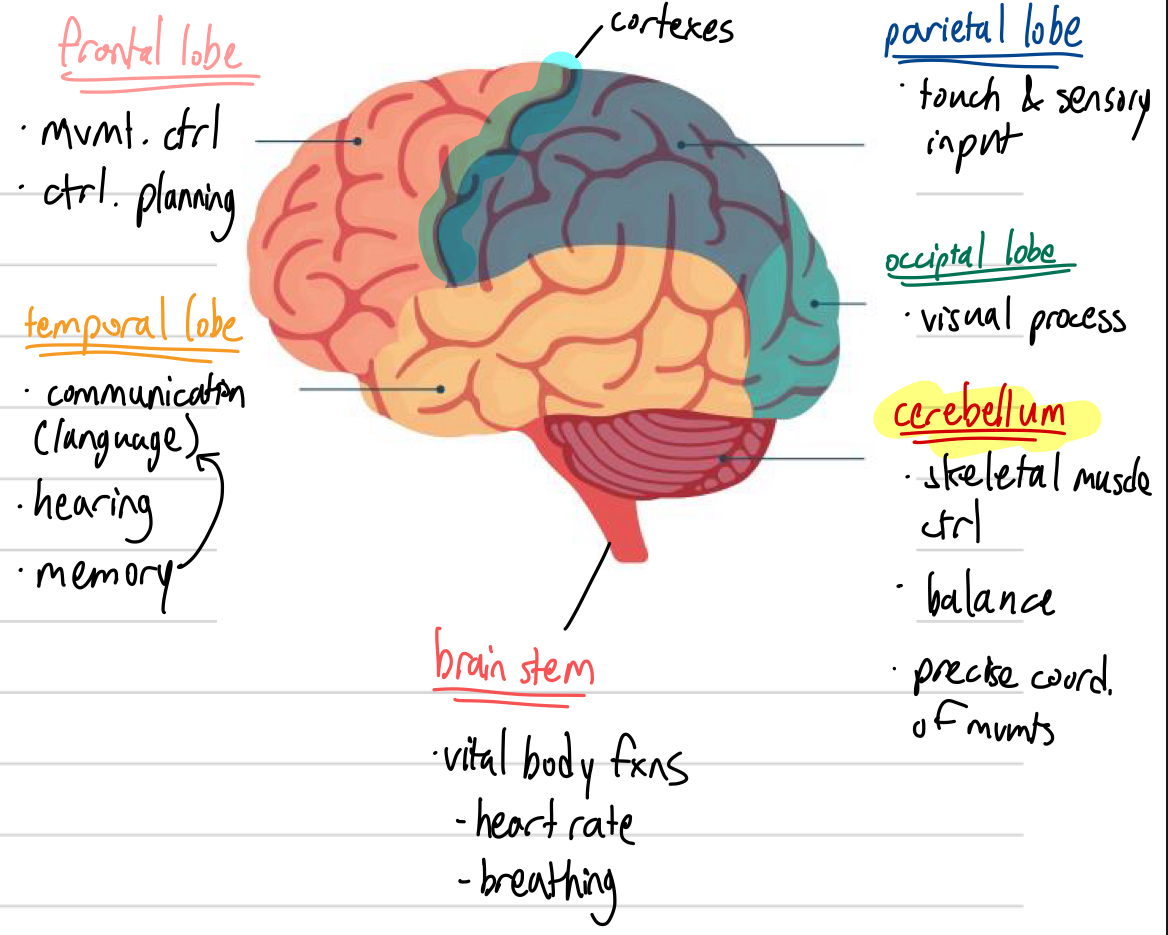
roles of each cerebrum part (6)
frontal lobe: mvmt and control
temporal lobe: communication, hearing, memory
parietal lobe: touch and sensory input
occipital lobe: visual processing
cerebellum: skeletal muscle ctrl, balance, precise ctrl of mvmts
brain stem: vital body fxns (eg. breathing and heart rate)
parts of inside brain??? (5)
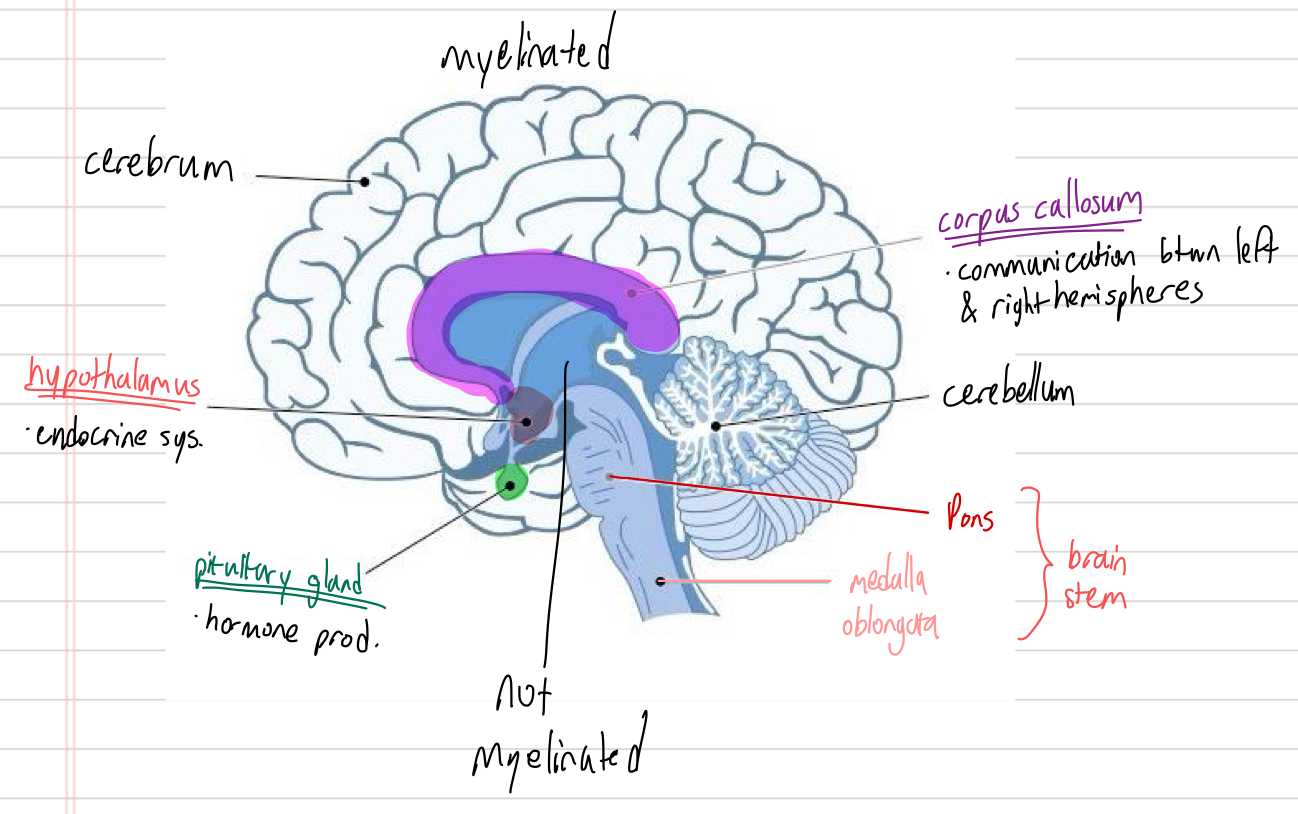
function of inside brain things idk (3)
hypothalamus: endocrine system
pituitary gland: hormone production
corpus callosum: communication btwn left and right hemispheres
circadian rhythm process (6)
light detected by retina which sends impulses to suprachiasmatic nucleus
SCN of hypothalamus signals to pineal gland
pineal gland reduces secretion of melatonin
lack of light detected by retina
SCN signals to pineal gland
pineal gland increases secretion of melatonin
times of day for melatonin stuff (2)
7:30am: melatonin secretion stops thru liver removing it from blood
9:00pm: melatonin secretion starts
effects of low melatonin (6)
++ body temp
++ blood pressure
++ alertness
++ muscle control
++ strength
++ rxn time
efects of high melatonin
-- body temp
-- BP
++ sleepiness
-- urine production
hypothalamus
links nervous system to endocrine system via pituitary gland
nuclei (biology) (2)
specialized areas in hypothalamus
uses info from a variety of sources (eg. sensors for blood temp, glucose conc. etc)
pituitary gland (3)
responsible for hypothalamus system integration (eg. puberty, osmoregulation
does this by secreting hormones to blood caps
ctrled by hypothalamus
things secreted by the pituitary gland
anterior lobe | posterior lobe |
|
|
adrenaline response (4)
stimulus triggers fight/flight response (preparing body for vigorous physical activity)
signal triggers adrenal glands
pituitary gland releases adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) which also triggers the adrenal glands
medulla of adrenal glands secrete adrenaline into bloodstream
location of adrenal glands
on the kidneys like hats
what places are affected by adrenaline response (6)
striated muscle fibres
SA node
liver
arterioles
lungs
non-essential functions eg. digestive system and urination
effetcs of adrenaline on striated muscle fibres
converts glycogen into glucose for cell resp
effects of adrenaline on SA node
incr. bpm = incr blood flow, O2, energy (from resp)
effects of adrenaline on liver
converts glycogen on glucose (ie. increases glucagen)
effects of adrenaline on non-essential functions
slows digestion, urination so that blood goes to the heart and lungs
effects of adrenaline on arterioles (2)
blood going to muscles and liver vasodilate (WIDEN) to incr. blood flow
blood gonig to gut, kidneys, skin vasoconstrict (shrink) = red. blood flow
effects of adrenaline on lungs (2)
bronchioles dilate to make vent. easier
intercostal and diaphragm muscles contract at a faster rate and more force = incr. vent rate, O2
cumulative result of adrenaline (2)
striated muscles get a greater volume of blood per min
results in incr. resp = incr ATP = incr. frequency and/or power of muscle contractions
baroreceptor
responds to blood volume and pressure in arteries
chemoreceptor (2)
responds to blood pH, which indirectly monitors blood O2
CO2 → HCO3 = -- pH = -- O2
control of heart rate by brain (4+1)
BR and CR monitor for changes in blood
(A) cardiovascular centre (CVC) in medulal oblongata ctrls freq. of impulses in parasympathetic nervous system along the vagus nerve = --- bpm
(B) CVC ctrls freq. of impulses in sympathetic nervous system = +++ bpm
causes the sinoatrial node to set the heart rate by initiating each beat
extra: signals from hypothalamus can also signal adrenal glands to secrete epinephrine (+++ bpm)
locations of BR and CR (2)
BR: carotid artery and aorta
CR: carotid artery
control of ventilation by brain (3)
CR monitor blood pH
CR in carotid monitor [O2] of blood flowing to brain
respiratory centre in brainstem sends signals to diaphragm and external intercostal muscles to contract = inhale
RC sends signals to abdomen wall muscles and internal intercostal muscles to contract = exhale
role of nervous systems in ventilation (2)
PNS: -- vent rate
SNS: ++ vent rate
peristalsis
waves of contraction and relaxation in wall of gut that moves food from mouth to stomach to intestines to anus
control of peristalsis in brain (5)
stimulus of bolus (chunk of food)
stimulation of enteric nervous system (which is the autonomous NS)
contraction of circular muscles BEHIND bolus; longitudinal muscles relaxed
contraction of longitudinal muscles AHEAD of bolus; circular muscles relaxed
repeat CM, LM contraction in a cycle to push bolus along tract
digestive things that CNS voluntarily controls
swallowing
defectation
how swallowing happens (3)
striated muscle in tongue that pushes food to bacck of mouth
food stimulates touch receptors in pharynx that are passed to brainstem
stimulates muscle contr. to push food into esophagus
how defecation happens (3)
anus contains a ring of smooth muscle (sphincter)
wall of rectum contains layers of CM and LM
during defecation, anus widens and wall of rectum contracts to push feces out
tropism and types (3)
turning all or part of an organism in a particular direction in response to stimuli
phototropism: growth in response to light
gravitropism: growth in response to gravity
phototropism in root vs shoot (2)
root | shoot |
negative tropism: auxin accumulates on dark side = root grows down (away from light) | positive tropism: auxin accum. on dark side = shoot grows up (towards light) |
gravitropism in root and shoot (2)
root | shoot |
positive tropism: auxin accum. on lower side = root grows down (towards gravity) | negative tropism: auxin accum. on lower side = shoot grows up (away from gravity) |
types of phytohormones and uses
gibberellins: ctrl. cell elongation for stem growth, seed germination, flowering, plant dormancy
ethylene: ctrl. fruit ripening
cytokinins: incr. rate of cell division
auxin: ctrl. cell elongation
jasmonic acid: secretion of enzymes to digest prey in Venus flytrap
auxin efflux response (4+1)
auxin enters cells by passive diffusion ONLY if its carboxyl is uncharged
cytoplasm of plant is alkaline so auxin loses H+ from carboxyl group, making it a negatively charged COO-; this traps it in the cell
auxin efflux carriers can pump -ve auxin molecules across PM into the surrounding cell wall
cell wall is acidic so auxin regains H+ to turn into uncharged state
auxin is pumped in the same direction by all cells, resulting in a conc gradient being generated
cellulose structure (3)
cellulose microfibrils are the main structural component of plant cell walls
inelastic so they cant stretch/extend; instead they move further apart or slide past e/o
crosslinked in cell walls by carbohydrates; the strength of these crosslinks is determiend by pH (-- pH = -- link str)
how auxin causes cell growth (4)
auxin binds to receptors on H+ pump
H+ pumped into cell wall
decreased pH reduces links of cellulose structure, causing expansion
H2O enters cell allowing it to elongate
where are auxin and cytokinin generated and go (2)
auxin: produced in shoot, goes to root in phloem
cytokinin: produced in root, goes to shoot in xylem
interactions of auxin and cytokinin (4 including both)
cell division | cell enlargement | dvlpmt of roots | dvlpmt of lateral buds | |
auxin | stimulates (if CK present) | stimulates | inhibit | stimulate |
cytokinin | stimulate | stimulates (if auxin present) | stimulate | inhibit |
interaction | synergistic | synergistic | antagonistic | antagonistic |
elongation of roots (5)
incr [A] = inhibit growth
decr. [A] = incr growth
whatever side auxin ISNT on will grow and elongate
therefore, if root grows straight down, auxin is evenly distr. = growth straight down
if root is angled, auxin accum. on lower side so the lower side is inhibited and the top side grows = downwards growth
elongation of shoots (6)
incr [A] = incr. growth
decr [A] = decr. growth
light directly above = equal auxin distr = grows straight up
angled = auxin goes to dark side = incr. growth to angle towards light
auxin also inhibits growth of axillary buds to allow main to grow big (no competition)
if main shoot is gone auxin is decreased, causing bud growth to replace the lost shoot
what happens to a fruit during ripening (4)
flesh softer
acids and starch turn to sugar
skin colour changes
nice scents to entice animals
positive feedback loop of fruit ripening (4)
ethylene produced by ripe fruit
ethylene diffuses into air and goes to other fruit
nearby fruit begin ripening too and release ethylene
more fruit ripens
repeat